Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fund Arch 1.4, Function
Загружено:
Tadi Fresco RoyceИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fund Arch 1.4, Function
Загружено:
Tadi Fresco RoyceАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
4.
Function in Architecture
Architecture is the art and science of designing buildings
Every building is designed to give services
Hospital where patients will be treated Court House where you find justice Theater where you see a play Hotel- where you recreate Church ( Mosque) where you practice your religion School where you learn
House where you live
The serviceability & usability of any building and its designFUNCTION
Function in Architecture (cont)
What do you feel, when you see this building?
Function in Architecture (cont)
In addition to giving services, a building affects our feelings
When you enter in some buildings, you will be excited When you are in some building, you will be depressed When you see some buildings, you will be amused When you look some buildings, you will say what a piece of art When you are in some buildings, you may be sober When you enter in some buildings, you feel relaxed
The emotional and the feeling aspect of a BUILDING or
its ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN - AESTHETICS
Function in Architecture (cont)
A building is designed to be erected or constructed, hence
It should house its occupants and furniture LIVE LOAD
It should support its own weight- DEAD LOAD
It should resist wind load- WIND FORCE It should withstand against EARCH QUICK FORCE
It should be strong enough against FLOODS
It should resist other NATURAL and ARTIFICIAL FORCES
The erectibility and constructability of a BUILDING or its ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN - STRENGTH
Function in Architecture (cont)
Hence Architecture or Building Design is all about
FUNCTION - serviceability of
AESTHETICS - emotional aspect of
STRENGTH erectibility of
B U I L D I N G
Function in Architecture (cont) Form vs Space
A building will be designed to give services To give this services, it should accommodate
People Furniture and Fixtures
Equipments
To do so, it should be void The difference b/n building and sculptor
Building is void and accessible by people
Sculptor is solid
Function in Architecture (cont)
The void part of a building - SPACE
Through which we enter, circulate, wonder and undertake different activities
The envelop or outer part of a building - FORM
Which we see, look, observe and admire
FORM is the envelop of SPACE
FORM is exterior, where as SPACE is interior of the building FORM differentiate out side and inside
SPACE is volume of hollow solid
Both SPACE and FORM have Function & Aesthetics
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Form
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Form (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Form
(cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Form (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Form (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Space
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Space (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Space (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Space (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Space (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Example of Space (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Functional Aspects or Parameters of a space of a Building
1. Enclosure
2.
3. 4.
Approach & Entry
Circulation Light
5.
6. 7. 8.
Comfort
Size Shape Adjacency & Sequence
Function in Architecture (cont)
1. Enclosure
A building houses different activities
Some activities need differentiation
Sleeping and Living activities
Spaces for these activities should
be divided by
walls, floors and ceilings
Building Components to divide spaces
are called Space Defining Elements
FORM is enclosure of interior space FORM protects the interior of a building from weather
Function in Architecture (cont)
2. Approach and Entry
To undertake different activities in a FRONTAL
building we should approach and access it
The process of being near a building is APPROACH DIAGONAL
Types of Approach
Frontal: emphasis
front view ROUND
Diagonal: shows effects of perspective Round: emphasis form of building
Function in Architecture (cont)
Approach and Entry (cont)
Frontal Approach
Function in Architecture (cont)
Approach and Entry (cont)
Diagonal Approach
Function in Architecture (cont)
Approach and Entry (cont)
The gate that allows you to enter in to a building or rooms of a building is called Entry (Entrance) Entry to a building should be emphasized and easy to identify Types of Entry
Flush:
on the wall
Projected: coming out from the wall Recessed: coming into the interior
Function in Architecture (cont)
Approach and Entry (cont)
Projected Entry
Function in Architecture (cont)
Approach and Entry (cont)
Recessed Entry
Function in Architecture (cont)
Approach and Entry (cont)
Flush Entry
Function in Architecture (cont)
3. Circulation
We need to be able to reach furniture, equipment and other facilities to perform some tasks.
A process of wondering through a space of a building - Circulation
Types of Circulation
Circulation within
a room: interior space
Horizontal circulation from one room to another: corridor Vertical Circulation from one floor to another: Stair, Elevator, Ramp Circulation should be
easy
to identify
comfortable to move through sizable enough to allow people and furniture to pass
Function in Architecture (cont)
Circulation (cont)
Forms of Circulation Enclosed Open one side Open on both sides
Function in Architecture (cont)
Circulation (cont)
Enclosed circulation No spatial & visual flow
Function in Architecture (cont)
Circulation (cont )
Open one side circulation spatial and visual flow on one side
Function in Architecture (cont)
Circulation (cont
Open two side circulation Visual & spatial flow on two sides Eg- ECSC
Function in Architecture (cont)
4. Light
To undertake different activities in rooms, we need light Light also affects the feeling that we feel in a room
Sources of Light
Artificial Light:
costly, unfriendly and controlled
Natural Light: no cost, friendly and reliable
Combined: good distribution of light
Natural Light Sources in Building
- Window
- Sky Light -Glass Curtain Wall -Open Down
Function in Architecture (cont)
Light Source
1. Artificial Light Source controlled different color
Function in Architecture (cont)
Light Source
Artificial Light Source (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Light Source
Artificial Light Source (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Light Source(cont)
2. Natural Light Source
Natural Light: illuminate with good intensity up to 6m
uncontrolled uni color psychologically good provide view enlarge room
Function in Architecture (cont)
Light Source(cont)
Natural Light Source (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Light Source(cont)
Natural Light Source (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Light Source(cont)
3. Combined Light Source
controlled
colorful & evenly distributed
psychologically good provide view enlarge room
Function in Architecture (cont)
Light Source(cont)
Combined Light Source (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Light Source(cont)
Combined Light Source (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source 1.Windows
light
provide view
enlarge room
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source
Windows (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source
Windows (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source
Windows (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source
Windows (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
light
2. Sky Light
good distribution of light no view increase height
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
Sky Light (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
Sky Light (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
Sky Light (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
3. Open Down
light no view Ventilation
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
Open Down (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
4. Glass Curtain Wall
light provide view enlarge room spatial continuity
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
Glass Curtain Wall (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
Glass Curtain Wall (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Natural Light Source(cont)
Glass Curtain Wall (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
5. Comfort
Ventilation
A room should have the appropriate temperature & air to feel the occupants comfort This can be done by replacing existing hot air by fresh air This process is called ventilation
Two kinds of Ventilation
Artificial Ventilation Natural Ventilation
Function in Architecture (cont)
Comfort
Purpose of Ventilation
At normal condition an adult inhale b/n 0.10 to 0.12 liters air/second exhale CO2 of 0.003 to 0.005 liters / second generate heat of 100 Watts sensible and 40 watts latent produce vapour of 59g of water vapour per hour Main Objective of Ventilation (Three)
1. 2.
to supply oxygen to create air movement
Function in Architecture (cont)
Comfort
Main Objective of Ventilation ( cont)
3. To remove unnecessary air components
carbon water
dioxide
vapor and moister
heat and smell gas and vapor from industry products out door pollutants like dust and smoke
Indoor pollutants like dust from carpet
Function in Architecture (cont)
Comfort (cont)
Artificial Ventilation
By fans using electricity It is costly Common USA & Europe
Function in Architecture (cont)
Comfort (cont)
Natural Ventilation
By using natural flow of air It is less costly Common in Africa, Asia and Latin America habitable room requires one or more ventilation openings,
the total area not be less than 1/20 of the floor area of the room
the opening must be more than 0.9 metres above floor level
Natural Ventilation design should consider
To supply fresh air for the occupants
To change the air in the room sufficiently
Function in Architecture (cont)
Comfort (cont)
A. Cross Ventilation
By using natural flow of air It is less costly
Function in Architecture (cont)
Comfort (cont)
B. Stack Effect Ventilation
Air moves when temperature and density difference exists Hot air is less dense and it rises Cold air is dense and replace the position of hot air
Function in Architecture (cont)
6. Size
Diff. activities take place in spaces
In addition to the activities, the space should be big enough to house
Users Furniture & Fixtures Equipment Vehicles Internal Circulation
Spatial Functionality Criteria related with size
Proportion Users, Furniture, Fixture and Equipment Accommodation Circulation Provision
Function in Architecture (cont)
Size (cont)
Eg.
Bath Room Size Determination & Design for Fixtures
Space
Function in Architecture (cont)
Size (cont)
Bath Room (cont)
Space
for Activities
Function in Architecture (cont)
Size (cont)
Bath Room (cont)
Area
Determination
Function in Architecture (cont)
Size (cont)
Bath Room (cont)
Final Design
Function in Architecture (cont)
6. Shape
A room or space needs to have the appropriate shape to
provide the
required function
accommodate the necessary furniture avoid wastage of space house enough and clear circulation
Function in Architecture (cont)
Shape ( cont)
A. Rectangular Spaces
Easy
to accommodate furniture
Less wastage of space Flexible
Function in Architecture (cont)
Shape ( cont)
Rectangular Spaces (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Shape ( cont)
B. Triangular & Angular Spaces
Difficult to
accommodate furniture
High wastage of space Less Flexible Difficult to circulate
Function in Architecture (cont)
Shape ( cont)
Triangular & Angular Spaces (cont)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Shape ( cont)
C. Curved Spaces
Difficult to
accommodate furniture
Need Special Furniture Less Flexible
Function in Architecture (cont)
Shape (cont)
St
Function in Architecture (cont)
7. Adjacency and Sequence (cont)
Spaces which have related functions should be side by side
Spaces which have incompatible functions should be far to each others Public spaces should be at front Private spaces should be at back Spaces, that need view, should be oriented to view Spaces, that dont need noise, should be far from noises Spaces should be also orient based on solar orientation
Entrances should be clear and visible (emphasis)
Function in Architecture (cont)
Adjacency and Sequence(cont)
Private Spaces should be away from Frontage & Noise Every room should be Accessible from corridor Stair case should be visible from lobby Entrance should be at front Public Spaces should be near entrance Service Spaces should be at back
Function in Architecture (cont)
Adjacency and Sequence(cont)
Kitchens & Dining Room are Related
Maid Room & Kitchen are Related
Entranced & Garage are Related
Entrance, Living Rm & Stair are Related
Function in Architecture (cont)
Adjacency and Sequence(cont)
Bath Rm & Bed Rm are Related
Bed Rm & Dressing Rm are related
Function in Architecture (cont)
Adjacency and Sequence(cont)
Function Ends
Space Follows
Next Classes
Bubble & Zone Diagram Consultation
Вам также может понравиться
- FUNCTIONДокумент92 страницыFUNCTIONephremОценок пока нет
- BASIC ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN PRINCIPLESДокумент47 страницBASIC ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN PRINCIPLESAbebe ToraОценок пока нет
- Architectural StylesДокумент66 страницArchitectural StylesBasheer Al-KhuzaeiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 - Evolution and Components of ArchitectureДокумент16 страницLecture 3 - Evolution and Components of ArchitectureAshru SigdelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 06 - The Design ProcessДокумент60 страницChapter 06 - The Design ProcessSaurav ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Architectural Expressions of Auditorium DesignДокумент5 страницArchitectural Expressions of Auditorium DesignPratik LondheОценок пока нет
- Achyut Kanvinde PPT HoaДокумент26 страницAchyut Kanvinde PPT Hoarajesh350Оценок пока нет
- LECTURE NOTES - Week 4 8 TOA1Документ26 страницLECTURE NOTES - Week 4 8 TOA1Ayan GerminoОценок пока нет
- ID423 - Precedent AnalysisДокумент31 страницаID423 - Precedent Analysisraheen99riazОценок пока нет
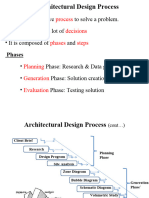
- Fund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessДокумент18 страницFund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessTadi Fresco Royce100% (2)
- Fund Arch 1.1, Intr0. To ArchДокумент68 страницFund Arch 1.1, Intr0. To Arch9rq5cj4w25Оценок пока нет
- ART05 - Form and Space in Architecture - Student NotesДокумент16 страницART05 - Form and Space in Architecture - Student NotesAlex PandyanОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Architecture FundamentalsДокумент110 страницIntroduction to Architecture FundamentalsEesha NairОценок пока нет
- SBS5312 Indoor Lighting DesignДокумент54 страницыSBS5312 Indoor Lighting DesignKhaled BellegdyОценок пока нет
- Three components of architecture: Commodity, Delight, FirmnessДокумент43 страницыThree components of architecture: Commodity, Delight, FirmnessRigo SantachazОценок пока нет
- AI Theories and Principles of Architectural InteriorsДокумент26 страницAI Theories and Principles of Architectural InteriorsWINONA DASHA ESPIÑAОценок пока нет
- Conceptual Design of StructuresДокумент21 страницаConceptual Design of StructuresmakkusaОценок пока нет
- LECTURE - 5 - Architecture, Architects and TheoristsДокумент23 страницыLECTURE - 5 - Architecture, Architects and TheoristsYeshiwas MelkamuОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Architecture Lecture Slide For Civil Engineering Students by Architect/ Planner Ujjwal Ghimire, Kathmandu, Nepal.Документ182 страницыFundamentals of Architecture Lecture Slide For Civil Engineering Students by Architect/ Planner Ujjwal Ghimire, Kathmandu, Nepal.Ujjwal GhimireОценок пока нет
- Developing Architectural ConceptsДокумент46 страницDeveloping Architectural ConceptsAnas QaderОценок пока нет
- 2018-10-22 - Week 09 - Considerations SAPPK & FSRD - EnglishДокумент53 страницы2018-10-22 - Week 09 - Considerations SAPPK & FSRD - Englishraissa damiriОценок пока нет
- Theory of ArchitectureДокумент127 страницTheory of ArchitectureArki TinОценок пока нет
- Commercial LightingДокумент18 страницCommercial LightingRaja A. AlnasrullahОценок пока нет
- Hitech Richard Rogers and Renzo PianoДокумент46 страницHitech Richard Rogers and Renzo Pianoharini100% (1)
- 106 FTP PDFДокумент8 страниц106 FTP PDFvolodeaTisОценок пока нет
- Design ProcessДокумент18 страницDesign ProcessNejib MohОценок пока нет
- Architectural Basics Design Studio I & IIhahuethiopiaДокумент25 страницArchitectural Basics Design Studio I & IIhahuethiopiathe hungrypanda101 pandaОценок пока нет
- Ar. Achyut Prakash Kanvinde BiographyДокумент7 страницAr. Achyut Prakash Kanvinde BiographyKrupa NidhiОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Definitions, Theories, Concepts PDFДокумент101 страница1.1 Definitions, Theories, Concepts PDFMaia Bea CleofeОценок пока нет
- INTR372 - Lecture 1Документ55 страницINTR372 - Lecture 1Rahma TarekОценок пока нет
- Debre Markos University: College of TechnologyДокумент39 страницDebre Markos University: College of TechnologyLij Davis100% (1)
- Study of With Reference To Priyadarshini Institute of Architecture and Design StudiesДокумент22 страницыStudy of With Reference To Priyadarshini Institute of Architecture and Design StudiesPratik Parakh60% (5)
- Theory of DesignДокумент38 страницTheory of DesignbadjatyagunjanОценок пока нет
- Site Approach and Building EntranceДокумент13 страницSite Approach and Building EntranceAdrienne GamaОценок пока нет
- Fund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessДокумент18 страницFund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessHabtamu Hailemariam AsfawОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4Документ38 страницLesson 4Nino IvanidzeОценок пока нет
- Transition SpacesДокумент22 страницыTransition SpacessagrikakhandkaОценок пока нет
- Theory of Architecture-1Документ74 страницыTheory of Architecture-1Oira, Maica ShaneОценок пока нет
- KENZO TANGE (Final)Документ27 страницKENZO TANGE (Final)Anamika AnilОценок пока нет
- Azalia Naba Sarah Dugmush PDFДокумент17 страницAzalia Naba Sarah Dugmush PDFSudhanshu RanjanОценок пока нет
- D & E Module 1Документ52 страницыD & E Module 1Aari WalkerОценок пока нет
- Design & EngineeringДокумент54 страницыDesign & EngineeringiammanuprasadОценок пока нет
- Norman Foster Phylosophy and WorkДокумент16 страницNorman Foster Phylosophy and WorkMuhammad Barry Budi PrimaОценок пока нет
- 10578622Документ25 страниц10578622Meron GetahunОценок пока нет
- Architectural DrawingДокумент26 страницArchitectural DrawingnyamandimatthewОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ64 страницыChapter 2amiraОценок пока нет
- Hi-Tech ArchitectureДокумент19 страницHi-Tech Architecturesri100% (2)
- 12 Physical Function of ArtДокумент12 страниц12 Physical Function of ArtKenneth BillonesОценок пока нет
- 2023 - Hecu - Concept LectureДокумент220 страниц2023 - Hecu - Concept LectureFatuma SulymanОценок пока нет
- Contemporary Architecture: Lesson 4.3 Unit Iv Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsДокумент20 страницContemporary Architecture: Lesson 4.3 Unit Iv Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsAlexis John MurilloОценок пока нет
- Theory of Modern ArchitectureДокумент24 страницыTheory of Modern Architectureace dateОценок пока нет
- Architectural DesignДокумент39 страницArchitectural DesignKidus FelekeОценок пока нет
- Lighting System DesignДокумент30 страницLighting System Designsreerajgk@gmail.com100% (1)
- Sensual Sculptural Sustainable Spaces.2pdfДокумент50 страницSensual Sculptural Sustainable Spaces.2pdfJona MojaresОценок пока нет
- Fund Arch 1.2, Arch Design ProcessДокумент18 страницFund Arch 1.2, Arch Design Process9rq5cj4w25Оценок пока нет
- Structural Engineering For BeginnersДокумент36 страницStructural Engineering For Beginnerssdewss100% (1)
- Architecture and Town Planning: Unit 1Документ15 страницArchitecture and Town Planning: Unit 1GMC GamingОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1-Poa I July 2019-1Документ64 страницыLecture 1-Poa I July 2019-1neelaksh tanwarОценок пока нет
- Fund Arch 1.1, Intr0. To ArchДокумент80 страницFund Arch 1.1, Intr0. To ArchTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- CIB6832Документ503 страницыCIB6832mohamedОценок пока нет
- Wrong Locations On The Map Report FormatДокумент2 страницыWrong Locations On The Map Report FormatTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Construction Method Statement: at The Property Known As 18 Old Church Street London, Sw3 5DqДокумент14 страницConstruction Method Statement: at The Property Known As 18 Old Church Street London, Sw3 5DqRoland HarteОценок пока нет
- Site Construction Methodology Gypsum BoaДокумент75 страницSite Construction Methodology Gypsum BoaLhiee Ziur100% (2)
- Ready Mix Requistion Form: Customer InformationДокумент1 страницаReady Mix Requistion Form: Customer InformationTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Retaining Wall StepsДокумент9 страницRetaining Wall StepsTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- E Material ListДокумент9 страницE Material ListTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Drawing (18 11 2019) PDFДокумент1 страницаDrawing (18 11 2019) PDFTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Ufgs 09 23 00 PDFДокумент19 страницUfgs 09 23 00 PDFTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Site Construction Methodology Gypsum BoaДокумент75 страницSite Construction Methodology Gypsum BoaLhiee Ziur100% (2)
- MotivationДокумент1 страницаMotivationTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Site Construction Methodology Gypsum BoaДокумент75 страницSite Construction Methodology Gypsum BoaLhiee Ziur100% (2)
- To: - MDM Developers Project: - Grand View Apartment Subject: - Intent To Claim Regarding Additional Pex Fittings and Request For Revised DrawingДокумент1 страницаTo: - MDM Developers Project: - Grand View Apartment Subject: - Intent To Claim Regarding Additional Pex Fittings and Request For Revised DrawingTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- To: - MDM Developers Project: - Grand View Apartment Subject: - Intent To Claim Regarding Additional Pex Fittings and Request For Revised DrawingДокумент1 страницаTo: - MDM Developers Project: - Grand View Apartment Subject: - Intent To Claim Regarding Additional Pex Fittings and Request For Revised DrawingTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Proposed Work Methodology Submitall FormДокумент1 страницаProposed Work Methodology Submitall FormTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Letter Follow UpДокумент11 страницLetter Follow UpTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Drawing (18 11 2019)Документ1 страницаDrawing (18 11 2019)Tadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Ufgs 09 23 00 PDFДокумент19 страницUfgs 09 23 00 PDFTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Draft Soils, Materials and Pavement Design Report (Sta. 0+000 - 25+000)Документ1 страницаDraft Soils, Materials and Pavement Design Report (Sta. 0+000 - 25+000)Tadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Drug Facts: Active Ingredients (In Each 30 ML) PurposeДокумент2 страницыDrug Facts: Active Ingredients (In Each 30 ML) PurposeTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Subject Page Range Homework Amharic: (For April 6 To April 12,2020)Документ1 страницаSubject Page Range Homework Amharic: (For April 6 To April 12,2020)Tadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Take A TourДокумент2 страницыTake A TourTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Section 8Документ4 страницыSection 8Tadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Thank You For Your CooperationДокумент1 страницаThank You For Your CooperationTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Schedule WorldCup2018 enДокумент1 страницаSchedule WorldCup2018 enTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Gong Wing 2 Sub Basement Col, Retaining, Shear Wall BarДокумент56 страницGong Wing 2 Sub Basement Col, Retaining, Shear Wall BarTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Personal Budget Worksheet - Tracking Weekly Expenses (Rahel-October)Документ7 страницPersonal Budget Worksheet - Tracking Weekly Expenses (Rahel-October)Tadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- HighwayDesignReport (App 4) JuneДокумент22 страницыHighwayDesignReport (App 4) JuneTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- F 3 D Runner Server Debug LogДокумент1 страницаF 3 D Runner Server Debug LogTadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Book 1Документ2 страницыBook 1Tadi Fresco RoyceОценок пока нет
- Call For IPSF-EMRO Regional Working Group Subcommittees 2018-19Документ4 страницыCall For IPSF-EMRO Regional Working Group Subcommittees 2018-19IPSF EMROОценок пока нет
- Particulate Contamination in Aviation Fuels by Laboratory FiltrationДокумент11 страницParticulate Contamination in Aviation Fuels by Laboratory FiltrationMuhammad KhairuddinОценок пока нет
- Advisory Note 11 ASFP Cell Beam RationaleДокумент2 страницыAdvisory Note 11 ASFP Cell Beam RationalePavaloaie Marian ConstantinОценок пока нет
- From Self Disorders To The Schizophrenic Self: Riccardo Piero Dalle LucheДокумент31 страницаFrom Self Disorders To The Schizophrenic Self: Riccardo Piero Dalle LucheMichel de NostredameОценок пока нет
- DLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W4Документ9 страницDLL - Mathematics 5 - Q1 - W4Avelino Coballes IVОценок пока нет
- Jason Capital Screw Jobs PDFДокумент50 страницJason Capital Screw Jobs PDFДжек П100% (3)
- Holt MCD Earth Science Chapter 30Документ34 страницыHolt MCD Earth Science Chapter 30ADEDAMOPE ODUESOОценок пока нет
- American Statistical AssociationДокумент7 страницAmerican Statistical Associationmantu6kumar-17Оценок пока нет
- Brochure GM IM Roller Mill Antares MDDR MDDT en LowДокумент8 страницBrochure GM IM Roller Mill Antares MDDR MDDT en Lowahmed shomanОценок пока нет
- GA 33 KV VCB HT Panel - Siddharth Nagar Project. UPДокумент17 страницGA 33 KV VCB HT Panel - Siddharth Nagar Project. UPaayushОценок пока нет
- List of Syonoyms: Word Synonym SynonymДокумент6 страницList of Syonoyms: Word Synonym SynonymPraveen KumarОценок пока нет
- Three Theories of TruthДокумент1 страницаThree Theories of TruthDn AngelОценок пока нет
- Modelacion Fisicomatematica Del Transporte de Metales PesadosДокумент11 страницModelacion Fisicomatematica Del Transporte de Metales PesadosdiegoОценок пока нет
- Daniel Kipkirong Tarus C.VДокумент19 страницDaniel Kipkirong Tarus C.VPeter Osundwa KitekiОценок пока нет
- Engine Retrofit Guide v8Документ70 страницEngine Retrofit Guide v8Romulo AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Implementing Product ManagementДокумент156 страницImplementing Product ManagementJyoti MohantyОценок пока нет
- NASA: 2202main COL Debris Boeing 030121Документ9 страницNASA: 2202main COL Debris Boeing 030121NASAdocumentsОценок пока нет
- The Ultimate Guide to Building an Engaged CommunityДокумент24 страницыThe Ultimate Guide to Building an Engaged CommunityCarla UttermanОценок пока нет
- Children's Film in The Digital Age - Essays On Audience, Adaptation and Consumer Culture (PDFDrive)Документ211 страницChildren's Film in The Digital Age - Essays On Audience, Adaptation and Consumer Culture (PDFDrive)Basia KowalskaОценок пока нет
- 2010 Final Exam (Answers)Документ10 страниц2010 Final Exam (Answers)T FОценок пока нет
- Resil Mojares Writing About OurselvesДокумент21 страницаResil Mojares Writing About OurselvesSalimОценок пока нет
- Radiation Safety Officers Handbook A PDFДокумент100 страницRadiation Safety Officers Handbook A PDFAlejandro Zubiate100% (1)
- AN-029Wired Locker Access Control ENДокумент13 страницAN-029Wired Locker Access Control ENpetar petrovicОценок пока нет
- Maintenance Manual - Booms: S Booms Z BoomsДокумент185 страницMaintenance Manual - Booms: S Booms Z BoomsRafael Vieira De AssisОценок пока нет
- Quote: Quotation Prepared By: Sloan SellersДокумент2 страницыQuote: Quotation Prepared By: Sloan SellersRubén CastañoОценок пока нет
- LGBT Workplace Equality Policy and Customer Satisfaction: The Roles of Marketing Capability and Demand InstabilityДокумент20 страницLGBT Workplace Equality Policy and Customer Satisfaction: The Roles of Marketing Capability and Demand InstabilityFatima ZafarОценок пока нет
- Arrester Facts 004a - Externally Gapped ArresterДокумент2 страницыArrester Facts 004a - Externally Gapped ArresterCbdtxd PcbtrОценок пока нет
- 7 Robert Boyle and Experimental Methods: © 2004 Fiona KisbyДокумент8 страниц7 Robert Boyle and Experimental Methods: © 2004 Fiona Kisbydaveseram1018Оценок пока нет
- DCP-L2550DW BrochureДокумент2 страницыDCP-L2550DW BrochureKaren CariagaОценок пока нет
- Stanley I. Sandler: Equations of State For Phase Equilibrium ComputationsДокумент29 страницStanley I. Sandler: Equations of State For Phase Equilibrium ComputationscsandrasОценок пока нет