Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Functions of HRM
Загружено:
pashariyanИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Functions of HRM
Загружено:
pashariyanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
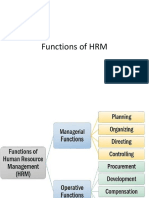
FUNCTIONS OF HRM
The functions of HRM can be broadly classified into two categories, viz., (i) Managerial functions and (ii) Operative functions. I. Managerial Functions Managerial functions of human resources management involve planning, organising, directing, and controlling. All these functions influence the operative functions. (i) Planning: It is a pre-determined course of
of action. Planning of HR programs and changes in advance that will contribute to the organizational goals. In other words involves planning of human resources , requirements, recruitment, selection, training, etc. It also involves forecasting personnel needs, changing values, attitudes and behaviour of employees and their impact on organization. (ii) Organizing: An organization is a means to an end. It is essential to carry out the determined course of action. Organization establishes relationships among the employees so that they can collectively
collectively contribute to the attainment of company goals. (iii) Directing: The willing and effective cooperation of employees for attainment of organizational goals, is possible through proper direction. Tapping the maximum potentials of the people is possible through motivation and command. (iv) Controlling: Controlling involves checking , verifying and comparing of actuals with the plans, identification of deviations, if any, and correcting of identified deviations. Auditing
training programs, analysing labour turnover records, directing morale surveys, conducting exit interviews are some of the means for the human resource management function. II. Operative Functions 1. Employment : It is the operative function of HRM. Employment is concerned with securing and employing the people possessing required kind and level of human resources necessary to achieve the organizational objectives. It covers the functions such as job analysis, human
resource planning, recruitment, selection, placement, induction and internal mobility. (i) Job Analysis: It is the process of study and collection of information relating to the operations and responsibilities of a specific job. (ii) Human Resource Planning: It is a process of determination and assuring that the organization will have an adequate number of qualified persons, available at proper times, performing jobs which meet the needs of the organization and which would provide satisfaction for the individuals involved.
(iii) Recruitment: It is the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in an organization. (iv) Selection: It is the process of ascertaining the qualifications, qualifications, experience, skill, knowledge, etc., of an applicant with a view to appraising his/her suitability to a job. (v) Placement: It is the process of assigning the selected candidate with the most suitable job in terms of job requirements. It is matching of employee specifications with job requirements.
(vi) Induction and Orientation: Induction and orientation are the techniques by which new employees are rehabilitated in the changed surrounding and introduced to the practices, policies, purposes and people, etc., of the organization. 2. Human Resource Development It is the process of improving , moulding and changing the skills, knowledge, creative ability, attitude, aptitude, values, commitment, etc., based on present and future job and organizational requirements.
(i) Performance Appraisal: It is the systematic evaluation of individuals with respect to their performance on the job and their potential for development. (ii) Training: It is the process of imparting the employees the technical and operating skills and knowledge. (iii) Management Development: It is the process of designing and conducting suitable executive development so as to develop the managerial and human relations skill of employees.
(iv) Career Planning and Development: It is the planning of ones career and implementation of career plans by means of education , training, job search and acquisition of work experiences. (v) Organization Development: It is a planned process designed to improve organizational effectiveness and health through modifications in individual and group behaviour, culture and systems of the organization using knowledge and technology of applied behavioural science.
3. Compensation: It is the process of providing adequate , equitable, and fair remuneration to the employees. It includes job evaluation, wage and salary administration, incentives, bonus, fringe benefits, social security measures. (i) Job Evaluation: It is the process of determining relative worth of jobs. (ii) Wage and Salary Administration: This is the process of developing and operating a suitable wage and salary program.
(iii) Incentives: It is the process of formulating , administering and reviewing the schemes of financial incentives in addition to regular payment of wages and salary. (iv) Bonus: It includes payment of statutory bonus according to the Payment of Bonus Act, 1965, and its latest amendments. (v) Fringe Benefits: These are the various benefits at the fringe of the wage. Management provides these benefits to motivate employees and to meet their lifes contingencies.
(vi) Social Security Measures: Managements provide social security to their employees in addition to the fringe benefits. 4. Human Relations: Practising various human resources policies and programs like employment, development and compensation and interaction among employees create a sense of relationship between the individual worker and management, among workers and trade unions and management. Human Relations is the process of interaction among human beings. Human relations is an area of management in
integrating people into work situation in a way that motivates them to work together productively, co-operatively and with economic , psychological and social satisfaction.
Вам также может понравиться
- Functions of HRMДокумент18 страницFunctions of HRMsupratam50% (8)
- Job Analysis, Job Description & Job SpecificationДокумент14 страницJob Analysis, Job Description & Job SpecificationPankaj2cОценок пока нет
- Importance of Human Resource Planning NOTESДокумент9 страницImportance of Human Resource Planning NOTESMhild GandawaliОценок пока нет
- Synopsis Hris, Human Resource Information System, Mba Project Report, Features, Advantages, DisadvantagesДокумент6 страницSynopsis Hris, Human Resource Information System, Mba Project Report, Features, Advantages, Disadvantagesmalhotrasourabh0% (1)
- Compensation ManagementДокумент24 страницыCompensation ManagementAmit Sharma100% (1)
- Functions of HRMДокумент6 страницFunctions of HRMmehtamehul290475% (12)
- The Role of An HR ManagerДокумент6 страницThe Role of An HR Managernfkrec100% (1)
- On Introduction To Human Resource ManagementДокумент10 страницOn Introduction To Human Resource Managementbhautikbschoolstudy100% (3)
- Difference Between IHRM and Domestic HRMДокумент11 страницDifference Between IHRM and Domestic HRMvarun50% (2)
- Case Study - Career PlanningДокумент5 страницCase Study - Career PlanningSailesh ToppoОценок пока нет
- MIS Application in AirlineДокумент20 страницMIS Application in Airlineamardeepjassal85100% (1)
- Human Resource Information SystemДокумент17 страницHuman Resource Information Systemnithildaspalathingal0% (1)
- Introduction of HRM HDFC BankДокумент25 страницIntroduction of HRM HDFC BankAnonymous ty7mAZ50% (2)
- Study of Employee Relationship and It's Impact On Employee PerformanceДокумент61 страницаStudy of Employee Relationship and It's Impact On Employee PerformanceDeepak Singh50% (4)
- HR Project On HR PracticesДокумент64 страницыHR Project On HR Practicesaqas_khan100% (4)
- Sss Case Study (Final)Документ48 страницSss Case Study (Final)Cutie Cat100% (1)
- HRM Computer ApplicationДокумент16 страницHRM Computer ApplicationmalusenthilОценок пока нет
- Features of SHRMДокумент1 страницаFeatures of SHRMTitus ClementОценок пока нет
- Full Project ReportДокумент123 страницыFull Project Reportbabudsklr100% (1)
- E-HRM and HRISДокумент10 страницE-HRM and HRISdua khanОценок пока нет
- Recent Trends of HRD in IndiaДокумент3 страницыRecent Trends of HRD in Indiadollygupta100% (5)
- Principles in Designing HRD SystemДокумент3 страницыPrinciples in Designing HRD SystemPrabhanjana TonseОценок пока нет
- Role of HR ManagerДокумент8 страницRole of HR ManagerRajesh BastiaОценок пока нет
- A Project Report On Organization Culture at Jinabakul Forge PVT LimitedДокумент76 страницA Project Report On Organization Culture at Jinabakul Forge PVT LimitedBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (1)
- Relevance of Values in ManagementДокумент19 страницRelevance of Values in ManagementPrashant Nair83% (6)
- A Project Report ON "HR Policies and Its Implementation" AT "Deepak Nitrite Limited"Документ72 страницыA Project Report ON "HR Policies and Its Implementation" AT "Deepak Nitrite Limited"abhishek150286% (29)
- Functions of HRMДокумент10 страницFunctions of HRMkerthsОценок пока нет
- Expatriate and Repatriate Support and Development: ExpatriatesДокумент5 страницExpatriate and Repatriate Support and Development: ExpatriatesrishiganeshОценок пока нет
- Talent Managament Project ReportДокумент76 страницTalent Managament Project Reportaurorashiva1Оценок пока нет
- Project On Employee RelationsДокумент23 страницыProject On Employee Relationskhushbuamar57% (7)
- Lecture 7, Acquiring Human ResourcesДокумент35 страницLecture 7, Acquiring Human ResourcesSrabon Ahmed100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Strategic Human Resource PlanningДокумент4 страницыChapter 1 Strategic Human Resource PlanningJayson Ryan LinoОценок пока нет
- Approaches of International CompensationДокумент16 страницApproaches of International Compensationvedant100% (2)
- BIBLIOGRAPHYДокумент4 страницыBIBLIOGRAPHYgorishsharmaОценок пока нет
- Recruitment and SelectionДокумент64 страницыRecruitment and SelectionPuja Kumari50% (2)
- Production Management - BBA NotesДокумент6 страницProduction Management - BBA Notesmadhuphd131650% (2)
- Impact of Globalisation in HRMДокумент12 страницImpact of Globalisation in HRMSai Ragini RamachandranОценок пока нет
- Changes in Recruitment and Company Expectations From Newly Hired Candidates During Covid SituationДокумент50 страницChanges in Recruitment and Company Expectations From Newly Hired Candidates During Covid SituationSuyog Rane100% (1)
- Role of Diagramming in Systems InvestigationДокумент25 страницRole of Diagramming in Systems InvestigationAnkita Shetty100% (1)
- A Study On Impact of Intra Organizational Relationship On Organizational Effectiveness of VKC Compan1Документ92 страницыA Study On Impact of Intra Organizational Relationship On Organizational Effectiveness of VKC Compan1eshu83% (12)
- Human Resource Management BBA (MDU) StudentsДокумент133 страницыHuman Resource Management BBA (MDU) StudentsRishabh Gupta100% (14)
- Project Report On Compensation Management Case Study Have Tobe IncludedДокумент33 страницыProject Report On Compensation Management Case Study Have Tobe IncludedmohitОценок пока нет
- List of Authors HR PolicyДокумент7 страницList of Authors HR PolicySanthu SaravananОценок пока нет
- Project Report On Training and DevelopmentДокумент85 страницProject Report On Training and DevelopmentSubrat PatnaikОценок пока нет
- Job Analysis and Job EvaluationДокумент35 страницJob Analysis and Job Evaluationsupriyas1338100% (3)
- Approaches To HRPДокумент16 страницApproaches To HRPAltaf Kondakamarala100% (1)
- Indian Experience of Od in Public and PrivateДокумент13 страницIndian Experience of Od in Public and PrivateDinoop Rajan100% (1)
- HRD 4Документ17 страницHRD 4Dr-Shefali GargОценок пока нет
- Project Report Role of Emotional Inntelligence in Employee Performance (COLLEGE)Документ46 страницProject Report Role of Emotional Inntelligence in Employee Performance (COLLEGE)Sankalp GahlotОценок пока нет
- Presentation On Stock Taking & Work Force FlowДокумент11 страницPresentation On Stock Taking & Work Force Flowmanpreet jassal83% (12)
- HRM CapsuleДокумент61 страницаHRM CapsuleNupur Agarwal Jain100% (2)
- UNIT 1 - Perspectives in HRMДокумент16 страницUNIT 1 - Perspectives in HRMPhilip George OommenОценок пока нет
- HRMДокумент15 страницHRMMittal SahabОценок пока нет
- Ak-1 HRM - CH - 1Документ17 страницAk-1 HRM - CH - 1Kunal KostiОценок пока нет
- Functions and Role of Human Resource Manager: Submitted To: Mrs Jasleen Sehgal Submitted By: Shilpa Rani GMT 3Документ16 страницFunctions and Role of Human Resource Manager: Submitted To: Mrs Jasleen Sehgal Submitted By: Shilpa Rani GMT 3Mittal SahabОценок пока нет
- 3787.introduction To HRMДокумент21 страница3787.introduction To HRMNaveen KumarОценок пока нет
- HRM ContentДокумент27 страницHRM ContentShalini ShaliniОценок пока нет
- HR Assignment - 1Документ10 страницHR Assignment - 1Akthar HussainОценок пока нет
- 3787.introduction To HRMДокумент21 страница3787.introduction To HRMAbhienav MishraОценок пока нет
- Unit - 2 Human Resources Management: Meaning and DefinationДокумент21 страницаUnit - 2 Human Resources Management: Meaning and Definationmisba shaikhОценок пока нет
- Human Resource Management (B.com Sem 5)Документ38 страницHuman Resource Management (B.com Sem 5)Yatin GolaОценок пока нет
- Definition and Purposes of Strategic Planning Linking Performance Management To The Strategic PlanДокумент28 страницDefinition and Purposes of Strategic Planning Linking Performance Management To The Strategic PlanMaryam SaleemОценок пока нет
- Project Management: Unit-II - Project Identification & PlanningДокумент33 страницыProject Management: Unit-II - Project Identification & PlanningpashariyanОценок пока нет
- Basic Communication SkillsДокумент17 страницBasic Communication SkillsAzhar Abbas100% (40)
- Emotional Intelligence: Emotions Can Get in The Way or Get You On The Way. - Mavis MazhuraДокумент16 страницEmotional Intelligence: Emotions Can Get in The Way or Get You On The Way. - Mavis MazhurapashariyanОценок пока нет
- Managing Outflow: LayoffsДокумент21 страницаManaging Outflow: LayoffspashariyanОценок пока нет
- 4 Methods of ProductionДокумент16 страниц4 Methods of ProductionpashariyanОценок пока нет
- Consumer ProtectionДокумент9 страницConsumer ProtectionpashariyanОценок пока нет
- Consumer Protection MannДокумент22 страницыConsumer Protection MannpashariyanОценок пока нет
- QuotesДокумент10 страницQuotespashariyanОценок пока нет
- Consumer Protection MannДокумент22 страницыConsumer Protection MannpashariyanОценок пока нет
- E TailingДокумент9 страницE TailingpashariyanОценок пока нет
- Six SigmaДокумент10 страницSix SigmapashariyanОценок пока нет
- SVURESET2015 Counselling ScheduleДокумент2 страницыSVURESET2015 Counselling SchedulepashariyanОценок пока нет
- Train The TrainerДокумент23 страницыTrain The TrainerpashariyanОценок пока нет
- Personlaity and Paradigm ShiftsДокумент6 страницPersonlaity and Paradigm ShiftspashariyanОценок пока нет
- Day Wise - Information Sheet-Mba - Mba-ThuДокумент1 страницаDay Wise - Information Sheet-Mba - Mba-ThupashariyanОценок пока нет
- Six Sigma An OverviewДокумент45 страницSix Sigma An OverviewpashariyanОценок пока нет
- Proforma 2011 MBAДокумент7 страницProforma 2011 MBApashariyanОценок пока нет
- Evolution of HRMДокумент8 страницEvolution of HRMRamu NagatiОценок пока нет
- Service Marketing: BY:-Praveen Parmar Professor (C.M.)Документ35 страницService Marketing: BY:-Praveen Parmar Professor (C.M.)debajyotiОценок пока нет
- MKTG PP Ch08-Developing Managing ProductsДокумент48 страницMKTG PP Ch08-Developing Managing ProductspashariyanОценок пока нет
- 1UPSCPORTALMagazineCivil Services 2009 Pre Special PDFДокумент113 страниц1UPSCPORTALMagazineCivil Services 2009 Pre Special PDFManda Swamy100% (1)
- Income Tax, Tax RemДокумент23 страницыIncome Tax, Tax RemAlyanna CabralОценок пока нет
- Week 3 Case Digests Page 57Документ137 страницWeek 3 Case Digests Page 57Andrew Mercado NavarreteОценок пока нет
- Teja G SДокумент9 страницTeja G Sinspire techОценок пока нет
- Fringe Benefits 2Документ45 страницFringe Benefits 2Ajey MendiolaОценок пока нет
- Human Resource Management: TybbiДокумент262 страницыHuman Resource Management: TybbijyotiangelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 VДокумент14 страницChapter 6 VAdd AllОценок пока нет
- BIR RegulationsДокумент13 страницBIR RegulationsDaphne Dione BelderolОценок пока нет
- MCS New Hire GuideДокумент45 страницMCS New Hire GuideEsha ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Talent Acquisition.Документ13 страницTalent Acquisition.Smiti Agarwal100% (2)
- IGCSE Business Studies NotesДокумент63 страницыIGCSE Business Studies Notesjeff100% (2)
- Bernardo Vs NLRC - 122917 - July 12, 1999 - JДокумент14 страницBernardo Vs NLRC - 122917 - July 12, 1999 - JalicianatalialevisteОценок пока нет
- AHM 530 Network ManagementДокумент357 страницAHM 530 Network ManagementsundarvaradОценок пока нет
- HRM Compensiation and BenifitsДокумент37 страницHRM Compensiation and BenifitsAlex RanaОценок пока нет
- Components Under Flexible BenefitsДокумент3 страницыComponents Under Flexible BenefitsPrajay MathurОценок пока нет
- Introduction To HR AuditДокумент8 страницIntroduction To HR AuditfarazensteinОценок пока нет
- VSPD EpfДокумент115 страницVSPD EpfDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATEОценок пока нет
- LNL Iklcqd /: Employee Share Employer Share Employee Share Employer ShareДокумент2 страницыLNL Iklcqd /: Employee Share Employer Share Employee Share Employer ShareRajesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Fixed Term Employment Agreement: Page 1 of 11Документ11 страницFixed Term Employment Agreement: Page 1 of 11Nandan SarkarОценок пока нет
- MWSS vs. CAДокумент8 страницMWSS vs. CALaura MangantulaoОценок пока нет
- Word Problems TaДокумент15 страницWord Problems TaMaissyОценок пока нет
- ThesisДокумент9 страницThesisMelanie GrutaОценок пока нет
- Fringe Benefit TaxДокумент4 страницыFringe Benefit TaxJoshua Stalin SelvarajОценок пока нет
- GST & BAS Detailed HandbookДокумент60 страницGST & BAS Detailed Handbooktestnation100% (1)
- Andrew Sutton vs. Lambdastar Infrastructure Partners JUDGEMENT, Et AlДокумент41 страницаAndrew Sutton vs. Lambdastar Infrastructure Partners JUDGEMENT, Et AlJayОценок пока нет
- Assignment-KMBN FM02-III-Shaleen Suneja-2022-23Документ2 страницыAssignment-KMBN FM02-III-Shaleen Suneja-2022-23Vivek SharmaОценок пока нет
- Salary Survey 2006-Macdonald & Company Middle East Salary and Benefits SurveyДокумент56 страницSalary Survey 2006-Macdonald & Company Middle East Salary and Benefits SurveysanjeevОценок пока нет
- Policy Directive: Salary Packaging Policy and Procedure ManualДокумент94 страницыPolicy Directive: Salary Packaging Policy and Procedure ManualBlake MiltonОценок пока нет