Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
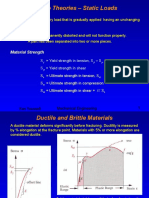
Mohr Coulomb Model
Загружено:
Mohamed A. El-Badawi0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
99 просмотров19 страницShort Course on Computational Geotechnics + Dynamics
Boulder, Colorado
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документShort Course on Computational Geotechnics + Dynamics
Boulder, Colorado
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
99 просмотров19 страницMohr Coulomb Model
Загружено:
Mohamed A. El-BadawiShort Course on Computational Geotechnics + Dynamics
Boulder, Colorado
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 19
Mohr-Coulomb Model
Short Course on Computational Geotechnics + Dynamics
Boulder, Colorado
January 5-8, 2004
Stein Sture
Professor of Civil Engineering
University of Colorado at Boulder
Contents
Idealized and Real Stress-Strain Behavior of Soils
Basic Concepts of Mohr-Coulomb Model
Mohr-Coulomb Model Modeling
Friction Angle
Influence of Intermediate Principal Stress on
Friction Angle
Drained Simple Shear Test
How to Understand
Drained Triaxial Test
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Idealized and Real Stress-Strain
Behavior of Soils
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Basic Concepts of Mohr-
Coulomb Model
Bilinear approximation of triaxial test
Basic law:
for
reversible elastic strain
irreversible plastic strain
f = yield function
c
i
=c
i
e
+c
i
p
i = x, y,etc.
c
i
e
=
c
i
p
=
c
i
p
-
= 0
f < 0
f = f (o
x
,o
y
,o
z
,o
xy
,o
yz
,o
zx
)
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Mohr-Coulomb Soil Modeling
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Mohr-Coulomb Soil Modeling
Flow rule for plastic strain:
This means: , , etc.
c
i
p
-
=
cg
co
i
c
x
p
-
=
cg
co
x
c
y
p
-
=
cg
co
y
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Mohr-Coulomb Soil Modeling
a multiplier that determines the
magnitude of plastic strains
determines the direction of plastic
strains
Classical associated plasticity: g = f
General non-associated plasticity: g = f
M-C model: f r s sin| c cos| : yield function
g r s sin c cos : plastic potential function
=
cg
co
i
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Mohr-Coulomb Soil Modeling
Nonlinear Failure Envelope Representation
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Mohr-Coulomb Soil Modeling
Friction Angle Definitions
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Mohr-Coulomb Soil Modeling
Strength Envelopes for a Range of Soil Types
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Mohr-Coulomb Soil Modeling
Versus Relative Density and Unit Weight
|
tc
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Friction Angle
Dilatancy Angle Relationships
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
A|
1
= Correction for particle shape
A|
1
= -6
o
For high sphericity and subrounded shape
A|
1
= +2
o
For low sphericity and angular shape
A|
2
= Correction for particle size (effective size, d
10
)
A|
2
= -11
o
For d
10
> 2.0 mm (gravel)
A|
2
= -9
o
For 2.0 > d
10
>0.6 mm (coarse sand)
A|
2
= -4
o
For 0.6 > d
10
>0.2 mm (medium sand)
A|
2
= 0 For 0.2 > d
10
>0.06 mm (fine sand)
A|
3
= Correction for graduation (uniformity coefficient, C
u
)
A|
3
= -2
o
For C
u
> 2.0 (well-graded)
A|
3
= -1
o
For C
u
= 2.0 (medium graded)
A|
3
= 0 For C
u
< 2.0 (poorly graded)
A|
4
= Correction for relative density (D
r
)
A|
4
= -1
o
For 0 < D
r
<0.5 (loose)
A|
4
= 0 For 0.5 < D
r
< 0.75 (intermediate)
A|
4
= +4
o
For 0.75 < D
r
< 1.00 (dense)
A|
5
= Correction for type of mineral
A|
5
= 0 For quartz
A|
5
= +4
o
For feldspar, calcite, chlorite
A|
5
= +6
o
For muscovite mica
|
tc
= 36
o
+ A|
1
+ A|
2
+ A|
3
+ A|
4
+ A|
5
in which:
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
|
cv
|
max
=|
cv
+0.8
for NC Clays vs. PI
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Influence of Intermediate Principal Stress on
Friction Angle
Introduction:
Models and soil
mechanics
Special conditions Name of test Diagram
c b a
o o o = =
True triaxial
r c b
o o o = =
Cylindrical compression
The triaxial test
0 =
b
c
Plane strain or biaxial
0 =
b
o
Plane stress
0 = = =
r c b
c c c
One-dimensional compression
The oedometer test
0 = = =
r c b
o o o
Uniaxial compression or
Unconfined compression
0 = = =
c b a
o o o
Isotropic compression
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Influence of Intermediate Principal Stress on
Friction Angle
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Drained Simple Shear Test
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
How to Understand
| = + |
i
or = | - |
i
|
i
= inter particle angle of friction
quartz sand: ~ | 30
o
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Drained Triaxial Test
c
v
=c
x
+c
y
+c
z
= 2c
x
+c
y
tano =
2sin
1sin
(identical to biaxial test)
Computational Geotechnics Mohr-Coulomb Model
Вам также может понравиться
- Soil Parameters for Drained and Undrained AnalysisДокумент48 страницSoil Parameters for Drained and Undrained AnalysisBralekОценок пока нет
- Design of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsОт EverandDesign of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsAlain PuechОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1: Modelling The Stress-Strain Behavior of Soils: Part A (5 Marks)Документ4 страницыAssignment 1: Modelling The Stress-Strain Behavior of Soils: Part A (5 Marks)Jasper FridamanОценок пока нет
- Student's Guide To Structural DesignДокумент57 страницStudent's Guide To Structural Designtony fung100% (1)
- Direct Shear TestДокумент32 страницыDirect Shear TestVinay YadavОценок пока нет
- Review of P-Y Relationships in Cohesionless SoilДокумент32 страницыReview of P-Y Relationships in Cohesionless Soiljosif100% (1)
- For Finite Element AnalysisДокумент32 страницыFor Finite Element AnalysisZhenhe SongОценок пока нет
- Lecture 9 Modified Cam Clay Model PDFДокумент43 страницыLecture 9 Modified Cam Clay Model PDFshivaОценок пока нет
- Rak-50 3149 L. l12 - Hardening Soil Model PDFДокумент111 страницRak-50 3149 L. l12 - Hardening Soil Model PDFMinhLêОценок пока нет
- Design of Monopile Foundations for Offshore Wind Energy ConvertersДокумент9 страницDesign of Monopile Foundations for Offshore Wind Energy ConvertersSachin Sithik100% (1)
- Shear Strength of SoilДокумент84 страницыShear Strength of SoilAnonymous dxsNnL6S8h100% (1)
- Cam Clay For Sand and ClayДокумент6 страницCam Clay For Sand and ClayNelsonPadrónSánchezОценок пока нет
- Strength of MaterialsДокумент15 страницStrength of Materialsjohn benedict orbeОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4+5 Mohr-Coulomb Based Models ShortДокумент109 страницLecture 4+5 Mohr-Coulomb Based Models ShortRecep AkanОценок пока нет
- Plaxis - 2DДокумент417 страницPlaxis - 2DPeteris Skels33% (3)
- Lecture 9 Modified Cam Clay Model PDFДокумент43 страницыLecture 9 Modified Cam Clay Model PDFshivaОценок пока нет
- Soil StiffnessДокумент24 страницыSoil StiffnessMuhamad HassanОценок пока нет
- Hardening SoilДокумент24 страницыHardening SoildiegofernandodiazsepОценок пока нет
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringОт EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringОценок пока нет
- C1 Shear StrengthДокумент62 страницыC1 Shear StrengthSara LaiОценок пока нет
- Application of Polymer Rheology for Processing ControlДокумент6 страницApplication of Polymer Rheology for Processing ControlEhteshamul IslamОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 - Drained and Undrained BehaviorДокумент19 страницLecture 3 - Drained and Undrained BehaviorAmr Elshanawany100% (1)
- 1 - Hardening Soil ModelДокумент18 страниц1 - Hardening Soil ModelAlexandra EneОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Shear Modulus Measurements of Residual SoilsДокумент14 страницDynamic Shear Modulus Measurements of Residual SoilsMohamed A. El-BadawiОценок пока нет
- Mohr-Coulomb Model and Soil StiffnessДокумент17 страницMohr-Coulomb Model and Soil StiffnessLuis Lemus MondacaОценок пока нет
- Mohr Coulomb ModelДокумент19 страницMohr Coulomb ModelSupachai JaingamОценок пока нет
- Mohr Coulomb ModelДокумент19 страницMohr Coulomb ModelkingmajorОценок пока нет
- Mohr-Coulomb Modeling and ParametersДокумент19 страницMohr-Coulomb Modeling and ParametershsetiyajiОценок пока нет
- Numerical Simulation For Slope Stability Under Infiltration Conditions Using Different Constitutive ModelsДокумент24 страницыNumerical Simulation For Slope Stability Under Infiltration Conditions Using Different Constitutive ModelsRaghu GuptaОценок пока нет
- Soil Stiffness CalcДокумент24 страницыSoil Stiffness Calchary9100Оценок пока нет
- Geology 229 Engineering and Environmental Geology: Engineering Properties of Rocks (West, Ch. 6)Документ27 страницGeology 229 Engineering and Environmental Geology: Engineering Properties of Rocks (West, Ch. 6)Mahatab HasanОценок пока нет
- Geotechnics: Marcin Cudny, Lech BałachowskiДокумент52 страницыGeotechnics: Marcin Cudny, Lech Bałachowskisharath1199Оценок пока нет
- Shear Strength of Soils ExplainedДокумент135 страницShear Strength of Soils ExplainedM Sohail AshrafОценок пока нет
- Course Notes On Nonlinear Hyperbolic Model and Parameter SelectionДокумент23 страницыCourse Notes On Nonlinear Hyperbolic Model and Parameter SelectionWei Hong TehОценок пока нет
- Azami-Yacoub-Curran Model SANDДокумент8 страницAzami-Yacoub-Curran Model SANDsonic8981Оценок пока нет
- Shear Strength in SoilsДокумент27 страницShear Strength in SoilsPranav GairolaОценок пока нет
- Ladd Finale12 FigureДокумент37 страницLadd Finale12 FigureRuwan Sampath WickramathilakaОценок пока нет
- Triaxial Tests On SandДокумент28 страницTriaxial Tests On SandKrusovice15Оценок пока нет
- Determination of Soil Stiffness ParametersДокумент24 страницыDetermination of Soil Stiffness ParametersVenkataLakshmiKorrapatiОценок пока нет
- Determination of Soil Stiffness ParametersДокумент24 страницыDetermination of Soil Stiffness ParametersmoomeejeeОценок пока нет
- Shear Strength ParametersДокумент12 страницShear Strength ParametersKalsoma CarlsОценок пока нет
- 5 Mohr Coulomb - ModelДокумент5 страниц5 Mohr Coulomb - ModelEmmanuel LizamaОценок пока нет
- Plastic Analysis of BeamsДокумент6 страницPlastic Analysis of BeamsYacoub CheikhОценок пока нет
- A Method of Approximate Tool Wear Analysis in Cold Roll FormingДокумент6 страницA Method of Approximate Tool Wear Analysis in Cold Roll FormingAly MahdyОценок пока нет
- Foundation settlements analysis methods and calculationsДокумент23 страницыFoundation settlements analysis methods and calculationsHari Amudhan IlanchezhianОценок пока нет
- Application of The Blast Fragmentation Models in A Sandstone QuarryДокумент9 страницApplication of The Blast Fragmentation Models in A Sandstone QuarryrakoОценок пока нет
- Q1: Explain The Phenomena of Cohesion Zero For Clay in CD With Proper ReferenceДокумент4 страницыQ1: Explain The Phenomena of Cohesion Zero For Clay in CD With Proper ReferenceUsman HasanОценок пока нет
- Numericalmodelingofdynamiccompactionindry Sand Using Different Constitutive ModelsДокумент8 страницNumericalmodelingofdynamiccompactionindry Sand Using Different Constitutive ModelsRafael WolfgangОценок пока нет
- Soil Shear Strength Laboratory TestsДокумент67 страницSoil Shear Strength Laboratory TestsYashika Bhathiya JayasingheОценок пока нет
- A Note On The Mohr-Coulomb and Drucker-Prager StreДокумент7 страницA Note On The Mohr-Coulomb and Drucker-Prager StreSutanuBhowmickОценок пока нет
- Applicability of Elastoplastic Modelling For Simulating Tunnel ExcavationДокумент18 страницApplicability of Elastoplastic Modelling For Simulating Tunnel ExcavationMoataz Hesham SolimanОценок пока нет
- 148 ICSFF Singapore 2004Документ12 страниц148 ICSFF Singapore 2004Abdelmoez ElgarfОценок пока нет
- Shear Strength of SoilsДокумент63 страницыShear Strength of SoilsEbrahem saeedОценок пока нет
- Hardening Soil-Model GTSNXДокумент8 страницHardening Soil-Model GTSNXAlex AntonescuОценок пока нет
- Steel-Concrete Composite Column Design StepsДокумент25 страницSteel-Concrete Composite Column Design Stepshemant_durgawaleОценок пока нет
- Seminar-2 Dec 2011 Experimental InvestigationДокумент32 страницыSeminar-2 Dec 2011 Experimental Investigationموسى الخروصيОценок пока нет
- Shear Strength of Soils: Mohr-Coulomb Failure CriterionДокумент109 страницShear Strength of Soils: Mohr-Coulomb Failure CriterionAastha SoniОценок пока нет
- Advanced Soil Mechanics HW2Документ2 страницыAdvanced Soil Mechanics HW2Zack FengОценок пока нет
- Hardening Soil model captures small strain stiffnessДокумент58 страницHardening Soil model captures small strain stiffnessgeologist84100% (2)
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationОт EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertОценок пока нет
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportОт EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportОценок пока нет
- Method of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsОт EverandMethod of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- 22 PLAXIS Bulletin DilatancyДокумент20 страниц22 PLAXIS Bulletin DilatancyMohamed A. El-BadawiОценок пока нет
- Topic15 4 GeotechnicalEarthquakeEngineeringHandouts PDFДокумент23 страницыTopic15 4 GeotechnicalEarthquakeEngineeringHandouts PDFJózsef Tóth-HorgosiОценок пока нет
- ZSoilDay2011 HSmodels-Course v3.1Документ104 страницыZSoilDay2011 HSmodels-Course v3.1Mohamed A. El-BadawiОценок пока нет
- Mohr Coulomb ModelДокумент19 страницMohr Coulomb ModelMohamed A. El-BadawiОценок пока нет
- Influence of Seismic Cyclic Loading History On Small Strain DRДокумент13 страницInfluence of Seismic Cyclic Loading History On Small Strain DRMohamed A. El-BadawiОценок пока нет
- Matlab Int, DiffДокумент4 страницыMatlab Int, DiffMohamed A. El-BadawiОценок пока нет
- FLAC2 DДокумент180 страницFLAC2 DMohamed A. El-BadawiОценок пока нет
- Linear Modal Time History Analysis V1.1Документ13 страницLinear Modal Time History Analysis V1.1Ravi TejaОценок пока нет
- Ucf - Tutorial of Modal AnalysisДокумент13 страницUcf - Tutorial of Modal AnalysisemelrapchanОценок пока нет
- Lec7 Flexibility Method and Stiffness MethodДокумент34 страницыLec7 Flexibility Method and Stiffness MethodVasu Dev VkmОценок пока нет
- Calculations and Assumptions For Penetration ModelДокумент5 страницCalculations and Assumptions For Penetration Modelvksingh_188005Оценок пока нет
- Static Load Failure TheoriesДокумент15 страницStatic Load Failure TheoriesLuiz CordeiroОценок пока нет
- Physics Project On Properties of ElasticityДокумент25 страницPhysics Project On Properties of Elasticitybagiyo condroОценок пока нет
- Elastomeric Bearings - Recommended Test MethodsДокумент125 страницElastomeric Bearings - Recommended Test MethodsmashrurfatehОценок пока нет
- Rail Wheel 1Документ28 страницRail Wheel 1rajanjasuОценок пока нет
- Ten So MeterДокумент6 страницTen So MeterSohaib AhmadОценок пока нет
- Lab QuestionsДокумент5 страницLab QuestionsMohamed Salah0% (1)
- Non-Local Continuum Mechanics and Fractional Calculus: K.A. LazopoulosДокумент5 страницNon-Local Continuum Mechanics and Fractional Calculus: K.A. Lazopoulosrs0004Оценок пока нет
- Expertfea Com Catalog June 2014Документ291 страницаExpertfea Com Catalog June 2014Prakash Kancharla100% (3)
- Compressive Properties of Rigid Plastics: Standard Test Method ForДокумент8 страницCompressive Properties of Rigid Plastics: Standard Test Method ForFernando Da RosОценок пока нет
- Design requirements for structural components subjected to fatigue and repeated loadingДокумент1 страницаDesign requirements for structural components subjected to fatigue and repeated loadingAbdullah NajjarОценок пока нет
- Cavity Expansion in Rock Masses Obeying The Hoek-Brown Failure CriterionДокумент15 страницCavity Expansion in Rock Masses Obeying The Hoek-Brown Failure CriterionAlexander ArdilesОценок пока нет
- Soluciones AdvancedДокумент19 страницSoluciones AdvancedEdna Odette Melo UscangaОценок пока нет
- TEST-PENCIL VIEJO-Static 1-1-67KGДокумент12 страницTEST-PENCIL VIEJO-Static 1-1-67KGJoséMiguelSánchezGОценок пока нет
- STRESS-STRAIN DIAGRAMSДокумент20 страницSTRESS-STRAIN DIAGRAMSRamu Amara100% (1)
- Strength of Materials ExperimentsДокумент44 страницыStrength of Materials ExperimentsDeepak SahОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1-BS-ME07Документ2 страницыAssignment 1-BS-ME07Mateenullah MeoОценок пока нет
- EN1994 4 HanswilleДокумент73 страницыEN1994 4 Hanswillearamosgavilan100% (1)
- Final Material TaskДокумент7 страницFinal Material TaskMuhammad Fahmi AdjiОценок пока нет
- Optistruct CompositesДокумент36 страницOptistruct CompositesJitendra ItankarОценок пока нет
- 18ME32Документ59 страниц18ME32Pratham J TudoorОценок пока нет
- The Effects of Addendum Modification Coefficient On Tooth Stresses of Spur GearДокумент8 страницThe Effects of Addendum Modification Coefficient On Tooth Stresses of Spur GearSezgin BayrakОценок пока нет
- Desmopan KU 2-8080Документ1 страницаDesmopan KU 2-8080Shailendra KumarОценок пока нет
- Bending Lab Stresses and DeflectionsДокумент7 страницBending Lab Stresses and DeflectionsAnnemarie SummersОценок пока нет