Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
4 Stroke Engine
Загружено:
Tasya IzaziАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
4 Stroke Engine
Загружено:
Tasya IzaziАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Norhayat B Marzuki
The
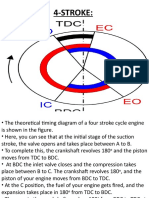
four stroke engine was first demonstrated by Nikolaus Otto in 18761, hence it is also known as the Otto cycle. The technically correct term is actually four stroke cycle. The four stroke engine is probably the most common engine type nowadays. It powers almost all cars and trucks.
The
four strokes of the cycle are
intake, compression, power, and
exhaust.
Each
corresponds to one full stroke of the piston; therefore, the complete cycle requires two revolutions of the crankshaft to complete.
During the intake stroke, the piston moves downward, drawing a fresh charge of vaporized fuel/air mixture. The illustrated engine features a poppet intake valve which is drawn open by the vacuum produced by the intake stroke. Some early engines worked this way; however, most modern engines incorporate an extra cam/lifter arrangement as seen on the exhaust valve. The exhaust valve is held shut by a spring (not illustrated here). 0-180 Cycle
As
the piston rises, the poppet valve is forced shut by the increased cylinder pressure. Flywheel momentum drives the piston upward, compressing the fuel/air mixture. Cycle
180-360
At
the top of the compression stroke, the spark plug fires, igniting the compressed fuel. As the fuel burns it expands, driving the piston downward. Cycle
360-540
At
the bottom of the power stroke, the exhaust valve is opened by the cam/lifter mechanism. The upward stroke of the piston drives the exhausted fuel out of the cylinder.
540-720
Cycle
The four strokes of the cycle are 1. intake, 2. compression, 3. power, and 4. exhaust.
The
two stroke engine employs both the crankcase and the cylinder to achieve all the elements of the Otto cycle in only two strokes of the piston.
The fuel/air mixture is first drawn into the crankcase by the vacuum that is created during the upward stroke of the piston. The illustrated engine features a poppet intake valve; however, many engines use a rotary value incorporated into the crankshaft. 0-180 Cycle
During
the downward stroke, the poppet valve is forced closed by the increased crankcase pressure. The fuel mixture is then compressed in the crankcase during the remainder of the stroke. Cycle
180-360
Brons two-stroke V8 Diesel engine driving a Heemafgenerator.
A two-stroke engine, in this case with a tuned expansion pipe illustrates the effect of a reflected pressure wave on the fuel charge. This feature is essential for maximum charge pressure (volumetric efficiency) and fuel efficiency. It is used on most high-performance engine designs.
http://www.animatedengines.com/otto.shtm
l. 14 Nov 2010 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourstroke_engine. 14 Nov 2010
Вам также может понравиться
- Engine 4 StrokeДокумент16 страницEngine 4 Strokeelsoukkary100% (2)
- Ing 64 (CV) Carburetor Part 3 (Idle Circuit)Документ4 страницыIng 64 (CV) Carburetor Part 3 (Idle Circuit)Moto CrewОценок пока нет
- Two Stroke Hydrogen Engine 1Документ4 страницыTwo Stroke Hydrogen Engine 1mrhat1234Оценок пока нет
- Ignition SystemДокумент21 страницаIgnition SystemrajeshОценок пока нет
- Mbeya Institute of Science and Technology: Power Plants Lecture No 6 Diesel Engine Power PlantsДокумент68 страницMbeya Institute of Science and Technology: Power Plants Lecture No 6 Diesel Engine Power PlantsNyandaMadili MalashiОценок пока нет
- Shimano SLX HG81 Cassette Service ManualДокумент1 страницаShimano SLX HG81 Cassette Service ManualJose Luis GutierrezОценок пока нет
- SI ENGINE and BASIC IGNITION SYSTEMДокумент41 страницаSI ENGINE and BASIC IGNITION SYSTEMShrvan HirdeОценок пока нет
- Turbochargerd SnowmobileДокумент28 страницTurbochargerd SnowmobileAhmed El-wenchОценок пока нет
- PistonДокумент7 страницPistongauravarora93100% (1)
- Homelite String Trimmer Parts Manual Trim N' Edge String Trimmer UT 20772Документ12 страницHomelite String Trimmer Parts Manual Trim N' Edge String Trimmer UT 20772Jerry HОценок пока нет
- Design ConsiderationДокумент17 страницDesign ConsiderationPranav Rawat100% (3)
- Engine Component 1Документ6 страницEngine Component 1anuradhaОценок пока нет
- DKD1801 Oil GuideДокумент56 страницDKD1801 Oil Guidennacy2702100% (1)
- Engine: An Engine Is Motor Which Converts Chemical Energy of A Fuel Into The Mechanical EnergyДокумент61 страницаEngine: An Engine Is Motor Which Converts Chemical Energy of A Fuel Into The Mechanical EnergyZain Ul AbideenОценок пока нет
- Two Stroke IC EngineДокумент72 страницыTwo Stroke IC EngineTomesh SahuОценок пока нет
- Piston-To-Wall Clearance Myths, Mysteries, and Misconceptions ExplainedДокумент20 страницPiston-To-Wall Clearance Myths, Mysteries, and Misconceptions ExplainedAnonymous SYwPALTОценок пока нет
- Four-Stroke Diesel EngineДокумент18 страницFour-Stroke Diesel Enginebs esliye me aap ka fan ho gya100% (2)
- Diesel MechanicДокумент23 страницыDiesel MechanicAtif MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Common Specifications For Briggs & Stratton Vanguard Ohv V-Twin Cylinder Engine ModelsДокумент2 страницыCommon Specifications For Briggs & Stratton Vanguard Ohv V-Twin Cylinder Engine Modelsvulpinor50% (2)
- 13 - Valve Systems and Engine TimingДокумент6 страниц13 - Valve Systems and Engine TimingMenard SoniОценок пока нет
- 06C1 GHH PDFДокумент3 страницы06C1 GHH PDFm.b.homsyОценок пока нет
- Basic Introduction To TurbochargingДокумент6 страницBasic Introduction To TurbochargingAngelino Martini de LeonОценок пока нет
- 2-Four and Two Stroke EnginesДокумент27 страниц2-Four and Two Stroke EnginesAHMADОценок пока нет
- Turbocharging of Ic EnginesДокумент5 страницTurbocharging of Ic EnginesKrishna MurthyОценок пока нет
- Engine BreathingДокумент18 страницEngine BreathingNimalanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Engine Components and ClassificationДокумент42 страницыChapter 1 - Engine Components and ClassificationAdib MaharunОценок пока нет
- Eliminator Torsion Axles: Shock Cord Cross SectionДокумент23 страницыEliminator Torsion Axles: Shock Cord Cross SectionRaju ManjuОценок пока нет
- 2017 Catalog Compressed PDFДокумент140 страниц2017 Catalog Compressed PDFDaniel DonosoОценок пока нет
- Vehicles Maintenance Workshops Layout and Its Management To Reduce Noise Pollution and Improve Maintenance QualityДокумент5 страницVehicles Maintenance Workshops Layout and Its Management To Reduce Noise Pollution and Improve Maintenance QualityStephen DuamorОценок пока нет
- Carburetor Definition PDFДокумент12 страницCarburetor Definition PDFAhtisham Amjad100% (2)
- Power Steering System PresentationДокумент15 страницPower Steering System PresentationDeepak Kango100% (1)
- Zama KarburatorДокумент3 страницыZama KarburatorZoran KovacevicОценок пока нет
- Holley EFI Idle Tuning NotesДокумент7 страницHolley EFI Idle Tuning NotesJam Bab100% (1)
- Camshaft and Valvetrain BasicsДокумент10 страницCamshaft and Valvetrain BasicsRamesh RamasamyОценок пока нет
- Wankel EngineДокумент15 страницWankel EngineMuhammad Bin RiazОценок пока нет
- Cylinder Head DesignДокумент9 страницCylinder Head Designjmanuel_225Оценок пока нет
- Piston and Connecting RodДокумент54 страницыPiston and Connecting RodWebsoft Tech-HydОценок пока нет
- O-470-U Type Certificate E-273 ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS ................................ O-470-UДокумент1 страницаO-470-U Type Certificate E-273 ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS ................................ O-470-Ueljonny01Оценок пока нет
- Two Stroke EngineДокумент13 страницTwo Stroke EngineAaron PriceОценок пока нет
- Ic Engine PPT 4 StrokeДокумент8 страницIc Engine PPT 4 StrokeAbhishek SathianОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Maintenance Manual Aircraft Maintenance Manual Aircraft Maintenance Manual Aircraft Maintenance ManualДокумент173 страницыAircraft Maintenance Manual Aircraft Maintenance Manual Aircraft Maintenance Manual Aircraft Maintenance ManualMohammad JaleelОценок пока нет
- 6.2 Twin TurboДокумент10 страниц6.2 Twin TurboDave MilnerОценок пока нет
- Block - ConrodДокумент22 страницыBlock - ConrodArnold ChafewaОценок пока нет
- LV06 - Engines - Issue 1Документ72 страницыLV06 - Engines - Issue 1Valentin Silvan Valentin SilvanОценок пока нет
- Installation and Operation Manual: Tire Changer Models: R23LT / R23ATДокумент52 страницыInstallation and Operation Manual: Tire Changer Models: R23LT / R23ATphankhoa83-1Оценок пока нет
- Two Cylinder ModelsДокумент8 страницTwo Cylinder ModelsPaul MartinОценок пока нет
- Porting and Cylinder ScavengingДокумент2 страницыPorting and Cylinder Scavenging69x4Оценок пока нет
- Engine - Blower Hardware - All 110101Документ58 страницEngine - Blower Hardware - All 110101Didier Van Der LeeОценок пока нет
- VW Aircraft Engine Conversion by Bob HooverДокумент133 страницыVW Aircraft Engine Conversion by Bob HooverJose Toronzo100% (1)
- Ignition System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент64 страницыIgnition System: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediachiku16octОценок пока нет
- Engine Blow Out DiagramДокумент2 страницыEngine Blow Out Diagramsiva99Оценок пока нет
- Homelite UT70131Документ22 страницыHomelite UT70131dsiucОценок пока нет
- 2009-2011 DS Service Manual PDFДокумент416 страниц2009-2011 DS Service Manual PDFDaemionОценок пока нет
- Octane NumberДокумент4 страницыOctane NumberMm AbdulaОценок пока нет
- How Car Engines Work PDFДокумент3 страницыHow Car Engines Work PDFMiguel Campusano RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Trouble Shooting Carb and Compression BRIGGS & STRATTONДокумент1 страницаTrouble Shooting Carb and Compression BRIGGS & STRATTONvulpinor100% (1)
- Hartzell Propeller Owner's Manual P/N 147 147-0000-AДокумент308 страницHartzell Propeller Owner's Manual P/N 147 147-0000-ACTM Bravo Aviation100% (1)
- Report of Cam ShaftДокумент85 страницReport of Cam ShaftkotoyayОценок пока нет
- Invoice To Team: SMKTP Permai Athletic SMK Tasek Permai, Jalan Permai K, 68000 Ampang, Selangor 68000, SelangorДокумент2 страницыInvoice To Team: SMKTP Permai Athletic SMK Tasek Permai, Jalan Permai K, 68000 Ampang, Selangor 68000, SelangorTasya IzaziОценок пока нет
- Jom Sertai !!! Pelbagai Hadiah Lumayan Menanti Anda : Anjuran Panitia PJPK, SMK Tasek PermaiДокумент1 страницаJom Sertai !!! Pelbagai Hadiah Lumayan Menanti Anda : Anjuran Panitia PJPK, SMK Tasek PermaiTasya IzaziОценок пока нет
- Grab Your Cake & Cupcake: Come Now!Документ1 страницаGrab Your Cake & Cupcake: Come Now!Tasya IzaziОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations: Paper 1Документ6 страницChapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations: Paper 1Tasya Izazi100% (1)
- Chapter 2: The Structure of The Atom: Paper 1Документ6 страницChapter 2: The Structure of The Atom: Paper 1Tasya IzaziОценок пока нет
- Easily Confused Vocabulary ItemsДокумент10 страницEasily Confused Vocabulary ItemsTasya IzaziОценок пока нет
- Dinosaurs: Welcome To Dinosaurs WorldДокумент13 страницDinosaurs: Welcome To Dinosaurs WorldTasya IzaziОценок пока нет
- Expedition 2010Документ405 страницExpedition 2010Alejandro Luna Olmos100% (1)
- Dp6h Ufaa62 ProposalДокумент10 страницDp6h Ufaa62 ProposalFerdinan Tulus Yones TobingОценок пока нет
- Norton 750 CommandoДокумент191 страницаNorton 750 CommandoIronHorseRiders100% (2)
- Sl. Partno. Description Application 2021 MRPДокумент13 страницSl. Partno. Description Application 2021 MRPKazi UdhoyОценок пока нет
- MoTeC Catalog 1.40Документ77 страницMoTeC Catalog 1.40Alberto RuizОценок пока нет
- GM Obd1 Codes ListДокумент3 страницыGM Obd1 Codes ListBien BonjourОценок пока нет
- Chevrolet SAIL3 Parts CatalogueДокумент3 страницыChevrolet SAIL3 Parts Cataloguecifer.xiongОценок пока нет
- 08 Engine MechanicalДокумент80 страниц08 Engine MechanicalmadcostaОценок пока нет
- Motor 4m41 Mitsubishi PDFДокумент105 страницMotor 4m41 Mitsubishi PDFAntónio SilvaОценок пока нет
- KM2V80 ENGINE Maintenance ManalДокумент55 страницKM2V80 ENGINE Maintenance Manalluis gomezОценок пока нет
- 4-2.0L Gasoline EngineДокумент187 страниц4-2.0L Gasoline EngineMarco Antonio Tomaylla Huamani100% (1)
- Diesel Engine TechnologyДокумент59 страницDiesel Engine TechnologyAnonymous f2zDTm7kmОценок пока нет
- Suzuki GSX-R1000K7 '07 Service Manual Correction (#165)Документ3 страницыSuzuki GSX-R1000K7 '07 Service Manual Correction (#165)Nikolas KarrerОценок пока нет
- h50ct Manual de PeçaДокумент328 страницh50ct Manual de Peçafabio kelly SantanaОценок пока нет
- Pulsar 200 NS PDFДокумент82 страницыPulsar 200 NS PDFrgopceОценок пока нет
- Sisweb Sisweb Techdoc Techdoc Print Pag - pdf1Документ91 страницаSisweb Sisweb Techdoc Techdoc Print Pag - pdf1MatiussChesteerОценок пока нет
- John Deere Cts Parts CatalogДокумент20 страницJohn Deere Cts Parts Catalogmary100% (55)
- YC6J245-30 (J61LA) 柴油机零件图册 YC6J245-30 (J61LA) : Parts Catalogue of Diesel EngineДокумент68 страницYC6J245-30 (J61LA) 柴油机零件图册 YC6J245-30 (J61LA) : Parts Catalogue of Diesel EnginecesarОценок пока нет
- Cams Are Used To Convert Rotary Motion Into Reciprocating MotionДокумент93 страницыCams Are Used To Convert Rotary Motion Into Reciprocating MotionAhmed Sobhi l أحمد صبحيОценок пока нет
- 2010 Chevrolet Captiva Sport X2 (LE5 o LE9)Документ6 страниц2010 Chevrolet Captiva Sport X2 (LE5 o LE9)PANHA MEN100% (1)
- Parts Manual XL1000V-VA 07-09Документ160 страницParts Manual XL1000V-VA 07-09maccsyОценок пока нет
- 941 WS3Документ194 страницы941 WS3Luis Jesus100% (1)
- 015 Skoda OCTAVIA InglesДокумент88 страниц015 Skoda OCTAVIA InglesFranTSB100% (3)
- 2006 Johnson 9.9, 15 Tiller 4 StrokeДокумент56 страниц2006 Johnson 9.9, 15 Tiller 4 StrokeАлександр ПрохоренкоОценок пока нет
- SSP 508 The 1.0l 44 55 KW MPI EngineДокумент36 страницSSP 508 The 1.0l 44 55 KW MPI Enginedavorin59Оценок пока нет
- Cummins n14 Parts CatalogДокумент10 страницCummins n14 Parts Catalogjohn100% (53)
- Motor3 Suzuki VL800Документ20 страницMotor3 Suzuki VL800Crisan SorinОценок пока нет
- 53501-1-PM Rev3.6 021215 LRДокумент211 страниц53501-1-PM Rev3.6 021215 LRalderОценок пока нет
- The V10-TDI Engine: Self-Study Programme 303Документ48 страницThe V10-TDI Engine: Self-Study Programme 303Cyrus CameleonОценок пока нет
- 1.0-l 3-Cylinder TSI Engine: Design and FunctionДокумент28 страниц1.0-l 3-Cylinder TSI Engine: Design and FunctionAlin Mirea100% (1)