Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Lecture 9
Загружено:
Nurshuhada NordinОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Lecture 9
Загружено:
Nurshuhada NordinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
ELECTROCHEMISTRY
Electrode
Half cell
Types of Electrode
Electrodes potential
Types of Electrochemical cell
Cell Potential
2
Electrodes and Half Cell
When a metal is immersed in metal
ion solution it formed half cell.
M
(p)
M
n+
M
electrode
Ions
solution of
M
n+
Half cell
3
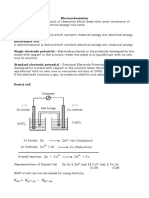
Electrodes and Half Cell
Combination of two half cell form a
electrochemical cell
V
Metal
Y
Ion Y
n+
Ion X
m+
Metal X
Salt
bridge
e
-
Anode cathode
4
Electrodes and Half Cell
Anode oxidation
Cathode reduction
Reaction in anode:
X (p) X
m+
(aq) + me
-
Cathode :
Y
n+
(aq) + ne
-
Y (p)
5
Electrodes and Half Cell
Overall cell reaction :
X
(p)
+ Y
n+
(aq)
X
m+
(aq)
+ Y
(p)
me
-
= ne
-
6
Types of electrode
Refference electrode
Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)
H
2
, 1 atm
H
+
, 1 M
Pt
298 K
7
Types of electrode
Reaction :
2H
+
(aq) + 2e
-
H
2
(g)
Symbol :H
+
|H
2
|Pt
Nernst equation:
2
2
| |
ln
2
2 2
+
+ +
=
H
H H H H
a
fH
F
RT
E E
8
Types of electrode
Silver-silver chloride electrode
A silver chloride is in contact with
solid silver chloride, which is highly
insoluble salt.
The whole is immersed in potassium
chloride solution which the chloride
ion concentration is 1 M
9
Types of electrode
Reaction:
AgCl
(s)
+ e
-
Ag
(s)
+ Cl
-
(aq)
Symbol :Cl
-
|AgCl|Ag
Nernst equation:
= aCl
zF
RT
E E
Cl Ag AgCl Cl Ag AgCl
ln
| | | |
10
Types of electrode
Combination with SHE
Pt|H
2
(1 atm)|H
+
(1M)||Cl
-
(1M)|AgCl|Ag
Anode
H
2
H
+
+ e
-
Cathode
e
-
+ AgCl Ag + Cl
-
11
Types of electrode
Overall reaction:
H
2
(g)
+ AgCl
(s)
H
+
(aq)
+ Cl
-
(aq)
+ Ag
(s)
E.m.f = 0.2224V
12
Types of electrode
Calomel electrode
mercury is in contact with mercurous
chloride (Hg
2
Cl
2
, calomel) which is
immersed in 1 M of potassium
chloride or in saturated solution of
potassium chloride
Reaction :
Hg
2
Cl
2
(s)
+ e
-
Hg
(s)
+ Cl
-
(aq)
13
Types of electrode
Symbol :Cl
-
|Hg
2
Cl
2
|Hg
Combination with SHE
Pt|H
2
|H
+
(1M)||Cl
-
(1M)|Hg
2
Cl
2
|Hg
Anode
H
2
(g) H
+
(aq) + e
-
Cathode
Hg
2
Cl
2
(s)
+ e
-
Hg
(s)
+ Cl
-
(aq)
14
Types of electrode
Overall reaction
H
2
(g)
+ Hg
2
Cl
2
(s)
H
+
(aq)
+ Hg
(s)
+ Cl
-
(aq)
E.m.f = 0.3338 V (KCl = 1 M)
E.m.f = 0.2415 V (saturated KCl)
15
Types of electrode
Redoxs electrodes
Symbol :Fe
3+
|Fe
2+
|Pt
Reaction :
Fe
3+
(aq)
+ e Fe
2+
(aq)
16
Electrode Potential
Comparison with SHE (0 V)
Reduction potential of half cell
known as standard reduction
potential, E
0
17
E
0
(+ve)
E
0
(-ve)
2H
+
(aq) + 2e
-
H
2
(g),E =0V
Reduction agent
anode
Oxidation agent
cathode
18
Types of electrochemical cell
Concentration cell
Different in electrolytes cocentration
E.g :
Pt|H
2
|HCl (m
1
)|HCl (m
2
)|H
2
|Pt
Left reaction :
H
2
H
+
(m
1
) + e
-
19
Types of electrochemical cell
right reaction:
H
+
(m
2
) + e
-
H
2
Overall reaction:
H
+
(m
2
) H
+
(m
1
)
m
2
> m
1
.
1
2
ln
m
m
zF
RT
E =
20
Concentration cell
H
2
H
2
H
+
(m
1
)
H
+
(m
2
)
Cl
-
Cl
-
V
Porous plug
Anode
oxidation
Cathode
reduction
21
Redox cell
Pt|H
2
|H
+
(1M)|Fe
2+
|Fe
3+
|Pt
Left reaction
H
2
H
+
+ e
-
Right reaction
e
-
+ Fe
3+
Fe
2+
22
Overall reaction
Fe
3+
+ H
2
Fe
2+
+ H
+
23
Standard cell potential(e.m.f),
Standard condition 298K, 1 atm
and/or 1 M
sel
E
=
anode cathode
E E =
sel
E
Ox d
E E + =
Re
sel
E
24
E.g:: Sel Danielle
E.g:
In
+
In
3+
+ 2e
Br
2
+ 2e 2Br
-
=1.46V. find
V E
Zn Zn
763 . 0
|
2
=
+
V E
Cu Cu
337 . 0
|
2
+ =
+
sel
E
Ox
E
25
Nernst Equation
R = gas constant, 8.314 Jmol-1K-1
T = Absolute temperature (K)
z = numbers of mole electron involved in
overall reaction.
F = 96500 C mole
-1
Q = reaction quotient
Q < K then the reaction is proceeding in the forward direction.
Q > K then the reaction is proceeding in the reverse direction.
Q ln
zF
RT
E E
sel sel
=
sel
E
sel
E
= Standard cell potential
= Cell potential
26
Nernst Equation
Equilibrium :
E
sel
=0 and Q = K
K
nF
RT
E
sel
ln 0 =
sel
E
K
nF
RT
ln =
27
] [
] [
ln
reduction
oxidation
a
a
nF
RT
E E
sel sel
=
28
The liquid junction potential,E
J
Potential difference across the
interface of two electrolytes or
between difference concentration of
electrolytes
Slower the diffusion of faster ions
After the brief period of times, the
ions diffuse at the same rate.
29
E
j
= E
w/t
- E
w/o
) (
) (
ln ) 2 1 (
1
2
m a
m a
zF
RT
t E
j
+
=
30
Electrochemical thermodynamic
Standard
sel
nFE G = A
=
sel sel
E E
A = A G G
= A
sel
nFE G
31
Entropy change
P P
T
E
nF
T
G
S
|
.
|
\
|
c
c
=
|
.
|
\
|
c
A c
= A
S T G H A + A = A
P
T
E
nFT nFE H
|
.
|
\
|
c
c
+ = A
Gibbs-helmholtz.
32
vant Hoff isotherm
] reactant a [
] product a [
ln
nF
RT
E E
sel sel
=
sel
nFE G = A
= A
sel
nFE G
] reactant [
] product [
ln
a
a
nF
RT
nF
G
nF
G
A
=
A
33
) reactant (
) product (
ln
a
a
RT G G + A = A
vant Hoff isotherm
Вам также может понравиться
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideОт EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Chemistry Cheat SheetДокумент5 страницChemistry Cheat Sheetdadadabababa100% (8)
- IB Chemistry HL - ANSWERS - Pearson - Second Edition PDFДокумент100 страницIB Chemistry HL - ANSWERS - Pearson - Second Edition PDFAna Aguilar Garcia67% (49)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1От EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Оценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент2 страницыElectrochemistryotrebolОценок пока нет
- Reaction KineticsДокумент37 страницReaction KineticsNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Nephelometry TurbidimetryДокумент28 страницNephelometry TurbidimetrySandeep Kumar Thatikonda80% (5)
- SC21 PDFДокумент29 страницSC21 PDFA Mahmood100% (2)
- Energy Balance PDFДокумент82 страницыEnergy Balance PDFjravisrinivas100% (1)
- Cheat SheetДокумент5 страницCheat Sheetkittenface92% (13)
- Design Co2 EvaporatorsДокумент7 страницDesign Co2 EvaporatorsYutt Watt100% (1)
- Protein and Peptide Drug Delivery SystemsДокумент55 страницProtein and Peptide Drug Delivery SystemsFree Escort ServiceОценок пока нет
- Principles of Electrochemistry: Potential & ThermodynamicsДокумент13 страницPrinciples of Electrochemistry: Potential & ThermodynamicsGonzalo AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент40 страницElectrochemistryJithesh Parambath0% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- 19 - Electrochemistry - BДокумент83 страницы19 - Electrochemistry - BLissa HannahОценок пока нет
- Electrochemical EquilibriumДокумент54 страницыElectrochemical EquilibriumChelsea MartinezОценок пока нет
- How To Design and Evaluate Research in Education, 8e: Student Mastery Activities BookДокумент5 страницHow To Design and Evaluate Research in Education, 8e: Student Mastery Activities BookNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент80 страницElectrochemistryNitin NishantОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 ElectrochemistryДокумент76 страницChapter 10 ElectrochemistryPatrickОценок пока нет
- 10 ElectrochemistryДокумент77 страниц10 ElectrochemistrySyamil Adzman100% (1)
- ElectrodeДокумент32 страницыElectrodeAaron Phillip50% (2)
- 29eec5 Chapter 20-2Документ78 страниц29eec5 Chapter 20-2Phani Raj MОценок пока нет
- 5 - Electrochemistry PDFДокумент15 страниц5 - Electrochemistry PDFthinkiit100% (1)
- Electrochemistry FinalДокумент58 страницElectrochemistry Finalrp7workОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ36 страницChapter 2Faiq AqillahОценок пока нет
- Electrochemical Cells: Dr. B. FarrellДокумент0 страницElectrochemical Cells: Dr. B. FarrellborgiamatriceОценок пока нет
- Half-Cell Notation SolnДокумент3 страницыHalf-Cell Notation SolnAngates1Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 18 ElectrochemistryДокумент19 страницChapter 18 ElectrochemistryNagarajan MaradaiyeeОценок пока нет
- Electro Analytical ChemistryДокумент10 страницElectro Analytical ChemistryStephany Solis GuerraОценок пока нет
- Review: Balancing Redox ReactionsДокумент16 страницReview: Balancing Redox Reactionsjanda bodongОценок пока нет
- CHAP 6 SEM 1 2020-2021 TERKINI Part 2 NewДокумент46 страницCHAP 6 SEM 1 2020-2021 TERKINI Part 2 NewNUR KHALISAH AZMANОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry and Redox Titration: Dr. Cherrie Pascual Institute of Chemistry UP DilimanДокумент57 страницElectrochemistry and Redox Titration: Dr. Cherrie Pascual Institute of Chemistry UP DilimanAcadGucciManeОценок пока нет
- Elektrokimia KuliahДокумент68 страницElektrokimia KuliahrofiqaasriОценок пока нет
- Important Relations - 1Документ6 страницImportant Relations - 1Bharath GowdaОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 2 2023 ElectrochemistryДокумент46 страницCHAPTER 2 2023 Electrochemistrym.yassinmansor19Оценок пока нет
- Basics of Electrochemistry and It's Application in ProblemДокумент41 страницаBasics of Electrochemistry and It's Application in ProblemMehul Khimani100% (1)
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry: I. Redox Reactions II. Galavanic or Voltaic CellsДокумент48 страницRedox Reactions and Electrochemistry: I. Redox Reactions II. Galavanic or Voltaic CellsAdzimahОценок пока нет
- Electrode ChemДокумент17 страницElectrode Chemapi-372366467% (3)
- Oxidation and Reduction (Redox)Документ56 страницOxidation and Reduction (Redox)Abdur RashidОценок пока нет
- Hsslive Xii CH 2 Electro Chemistry AnilДокумент10 страницHsslive Xii CH 2 Electro Chemistry AnilFathima NithinshaОценок пока нет
- Electrochemical Cells: (Review Electrochemistry in CHM 102)Документ43 страницыElectrochemical Cells: (Review Electrochemistry in CHM 102)Najmul Puda PappadamОценок пока нет
- Physical Chemistry Chapter 4 - ElectrochemistryДокумент36 страницPhysical Chemistry Chapter 4 - Electrochemistryjatropos6810Оценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry 110811014016 Phpapp01Документ38 страницElectrochemistry 110811014016 Phpapp01Jerung FixОценок пока нет
- PAK 6-Redox and Potentiometric TitrationДокумент50 страницPAK 6-Redox and Potentiometric TitrationSiskaWahyuniОценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент80 страницElectrochemistryAshish KumarОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry Topic 9Документ30 страницElectrochemistry Topic 9sharmieranasaОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry 20222023 (REVIEWED)Документ101 страницаElectrochemistry 20222023 (REVIEWED)alyaainsyirah04Оценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент80 страницElectrochemistrykunalwahОценок пока нет
- Nernst EqnДокумент17 страницNernst EqnDella Fajar PОценок пока нет
- ElectrolysisДокумент24 страницыElectrolysisSMELLY CATОценок пока нет
- Spontaneity of Redox ReactionsДокумент21 страницаSpontaneity of Redox Reactionssaeikip0% (1)
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Che Target-1 Level-1 Chapter-3Документ26 страницCLS JEEAD-19-20 XII Che Target-1 Level-1 Chapter-3Archita Ray0% (1)
- Lecture 3 Kinetics PDFДокумент69 страницLecture 3 Kinetics PDFmanishtubОценок пока нет
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XII Che Study-Package-5 SET-1 Chapter-3 PDFДокумент18 страницCLS Aipmt-18-19 XII Che Study-Package-5 SET-1 Chapter-3 PDFJayant KumarОценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент7 страницElectrochemistrythinkiitОценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент13 страницElectrochemistryanieshОценок пока нет
- ElectrochemistryДокумент48 страницElectrochemistryZainalAbidinОценок пока нет
- Chap.1 ElectrochemistryДокумент93 страницыChap.1 ElectrochemistryAnushkaSinhaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18: Electrochemistry: Key TopicsДокумент25 страницChapter 18: Electrochemistry: Key TopicsMoises Tapia BaezОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry: Applications of RedoxДокумент40 страницElectrochemistry: Applications of Redoxcatsathish1Оценок пока нет
- Chem321chapter14 15Документ91 страницаChem321chapter14 15Xiaosong QuОценок пока нет
- Electrochemirstry ConceptsДокумент48 страницElectrochemirstry ConceptsgyirgaОценок пока нет
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsОт EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckОценок пока нет
- Tetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 3.21-30От EverandTetrahedron Reports on Organic Chemistry: Volume 3.21-30Derek BartonОценок пока нет
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenОт EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenR. BrillОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6Документ17 страницLecture 6Nurshuhada Nordin0% (1)
- Order Inventory: Customer HP No Date Item Unit PT MYRДокумент1 страницаOrder Inventory: Customer HP No Date Item Unit PT MYRNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- The Third Law of ThermodynamicДокумент7 страницThe Third Law of ThermodynamicNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Dash Diet PamphletДокумент64 страницыDash Diet PamphletbohnjucurОценок пока нет
- Prof. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarДокумент24 страницыProf. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Reaction MechanismДокумент37 страницReaction MechanismNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Exercise CH 10Документ17 страницExercise CH 10Nurshuhada Nordin0% (2)
- Exercise CH 13Документ6 страницExercise CH 13Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Transition State TheoryДокумент10 страницTransition State TheoryNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Exercise CH 11Документ10 страницExercise CH 11Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Exercise CH 22Документ5 страницExercise CH 22Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Exercise CH 01Документ9 страницExercise CH 01Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Exercise CH 07Документ11 страницExercise CH 07Nurshuhada Nordin0% (1)
- Exercise CH 08Документ10 страницExercise CH 08Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Exercise CH 06Документ13 страницExercise CH 06Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Locating and Reviewing The LiteratureДокумент5 страницChapter 3: Locating and Reviewing The LiteratureNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Exercise CH 04Документ9 страницExercise CH 04Nurshuhada Nordin0% (1)
- Exercise CH 02Документ8 страницExercise CH 02Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 25: Preparing Research Proposals and Reports: Activity 25.1: Put Them in OrderДокумент2 страницыChapter 25: Preparing Research Proposals and Reports: Activity 25.1: Put Them in OrderNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 24: Action Research: Activity 24.1: Action Research Questions Activity 24.2: True or False?Документ3 страницыChapter 24: Action Research: Activity 24.1: Action Research Questions Activity 24.2: True or False?Nurshuhada Nordin50% (2)
- Exercise CH 17Документ7 страницExercise CH 17Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 23: Mixed-Methods ResearchДокумент5 страницChapter 23: Mixed-Methods ResearchNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 20: Content AnalysisДокумент5 страницChapter 20: Content AnalysisNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 21: Ethnographic ResearchДокумент5 страницChapter 21: Ethnographic ResearchNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Exercise CH 16Документ5 страницExercise CH 16Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18: The Nature of Qualitative ResearchДокумент4 страницыChapter 18: The Nature of Qualitative ResearchNurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- Exercise CH 19Документ6 страницExercise CH 19Nurshuhada NordinОценок пока нет
- and 68070 S2012 Final v2 No AnswersДокумент42 страницыand 68070 S2012 Final v2 No AnswersZadrin TuckerОценок пока нет
- An Experimental Study of The Orientation Effect On Fatigue Crack Propagation in Rolled AZ31B Magnesium AlloyДокумент10 страницAn Experimental Study of The Orientation Effect On Fatigue Crack Propagation in Rolled AZ31B Magnesium AlloyFrancoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Fuel Characteristics and Properties Coal 2020Документ80 страницChapter 5 Fuel Characteristics and Properties Coal 2020Bassam RiachiОценок пока нет
- Carnate Science Fair 2021 6Документ4 страницыCarnate Science Fair 2021 6api-547258647Оценок пока нет
- Kaolin Lab ReportДокумент15 страницKaolin Lab ReportEmeso OjoОценок пока нет
- Science Chapter 7: The Night Sky - 7.2 Handouts (The Constellation)Документ14 страницScience Chapter 7: The Night Sky - 7.2 Handouts (The Constellation)Kimmy LamОценок пока нет
- Grounding For CNCДокумент5 страницGrounding For CNCFreiky StuffОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper SA1 2010Документ10 страницCBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper SA1 2010honey1002Оценок пока нет
- Neutron Radiography: What Is NDT?Документ4 страницыNeutron Radiography: What Is NDT?mohamedОценок пока нет
- Active Ingredients in Pain RelieverДокумент13 страницActive Ingredients in Pain RelieverkatrinaarnaizОценок пока нет
- A-Level PhysicsДокумент160 страницA-Level PhysicsObert MupomokiОценок пока нет
- Permainan MolekulДокумент5 страницPermainan MolekulSyarifah R100% (1)
- Chem 3410 - Instrumental Methods of Analysis: Lab ManualДокумент25 страницChem 3410 - Instrumental Methods of Analysis: Lab Manualसुनिल बाबु खत्रीОценок пока нет
- Aceiteka Chem3.o 2023Документ6 страницAceiteka Chem3.o 2023EMMANUEL BIRUNGIОценок пока нет
- Suzhou Hengda Product CatalogДокумент13 страницSuzhou Hengda Product CatalogFabiola HernandezОценок пока нет
- Buffering Systems in The Human BodyДокумент2 страницыBuffering Systems in The Human Bodyjp08121972Оценок пока нет
- The Mole and Chemical Calculations: Pure ChemistryДокумент2 страницыThe Mole and Chemical Calculations: Pure Chemistryyuxiang32Оценок пока нет
- Year 10-Ict-First Term-Output DevicesДокумент3 страницыYear 10-Ict-First Term-Output DevicesToni AdelanaОценок пока нет
- Wrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Sheet and Strip For Surgical Implants (UNS S31673)Документ4 страницыWrought 18Chromium-14Nickel-2.5Molybdenum Stainless Steel Sheet and Strip For Surgical Implants (UNS S31673)Angel ChangОценок пока нет
- Can Anybody Give Me Syllabus of Allen Enthusiast Course? Do It Cover 11th Syllabus AlsoДокумент1 страницаCan Anybody Give Me Syllabus of Allen Enthusiast Course? Do It Cover 11th Syllabus AlsoG HaОценок пока нет
- Sambungan LasДокумент30 страницSambungan LasMei'o KuroОценок пока нет
- Manual MaДокумент21 страницаManual MaSergio RecabarrenОценок пока нет
- Biological Adhesives Second Edition PDFДокумент380 страницBiological Adhesives Second Edition PDFCristina Marco MartínezОценок пока нет