Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Antibody Production: Policlonal Derived Biotherapeutis
Загружено:
Fitrah Nur RabbanyИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Antibody Production: Policlonal Derived Biotherapeutis
Загружено:
Fitrah Nur RabbanyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Antibody production: Polyclonalderived biotherapeutics
Abstract
Antibody based therapies using monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies are emerging as an important therapeutic approach for the treatment of a number of diseases. With increasing emphasis on new technologies associated with monoclonal antibody expression and purication, the clinical need of polyclonal therapeutics for treatment of a variety of specic illnesses and infections is often overlooked. Despite being largely abandoned in the early twentieth century due to the development of antibiotics, polyclonal antibody therapeutics are today widely used in medicine for viral and toxin neutralization and for replacement therapy in patients with immunoglobulin deciencies. Over the past 20 years, intravenous immunoglobulins have shown benecial immunomodulatory and anti-inammatory effects in many illnesses. Hyperimmune antibody preparations have been used over the past century for the treatment of a variety of infectious agents and medical emergencies, including digoxin toxicity, snake envenomation and spider bites. Here, we examine the contemporary techniques and applications, and assess the future therapeutic potential, for polyclonal-derived antibody therapeutics.
Antibodies play an important role in the defense against pathogens. They specically recognize and bind to foreign antigens, resulting in the activation of a number of immune effector functions capable of selectively eliminating foreign micro-organisms, viruses and molecules.
ANTIGEN-SPESIFIC RECOMBINANT POLYCLONAL ANTIBODIES
TECHNOLOGY TO DEVELOP NEXT G E N E R AT I O N P O LY C L O N A L A N T I B O D I E S . SYMPHOGEN(DENMARK) SYMPRESS SYMPRESS C U LT U R E USING MAMMALIAN CELL
TRANSGENIC POLYCLONAL THERAPEUTICS
LARGE-SCALE PRODUCTION OF P O LY C L O N A L ANTIBODIES USING ARTIFICIAL CHROMOSOME (HAC) TRANSGENIC PROCESS.
H A C C O N TA I N C H R O M O S O M E WITH ANTIBODY EXPRESSION.
HUMAN HUMAN WITH
22
NUMBER
H E M AT E C H L C C ( C O N N E C T I C U T, U S A ) C A LV E S ; T H E R A U P E T I C H U M A N P O LY C L O N A L S I N C . (CALIFORNIA, USA)RABBIT; O R I G E N T H E R A P E U T I C I N C ( U S A ) AV I A N EMBRYONIC
CELL.
POLYCLONAL ANTIBODIES FOR BIODEFENSE APPLICATIONS
C O M B AT B I O L O G I C A L W A R FA R E A G E N T S B Y M I M I C K I N G T H E PA S S I V E I M M U N I Z AT I O N . W I L L B E A D VA N TA G E O U S , B U T T H E R E R E S O M E FA C TO R S N E E D TO B E C O N S I D E R E D :
Immune response to a pathogen doesnt always correlate to protective immunity; Role of memory B cells in long term immunity often depends on the incubation period of pathogen.
OFFERING CLINICAL PROTECTION I M M E D I AT E LY A F T E R E X P O S U R E T O PAT H O G E N I C B A C T E R I A S O R V I R U S E S .
THE FUTURE OF POLYCLONAL ANTIBODY THERAPEUTICS
M O N O C L O N A L A N D P O LY C L O N A L ANTIBODIES.
N E O VA C S S A ( F R A N C E ) A N T I - C Y T O K I N E T H E R A P E U T I C S , T R E AT M E N T O F H I V. A D V A N T A G E S O F P O L Y C L O N A L A N T I B O D Y.
Вам также может понравиться
- Antibiotic in Obstetric and GynecologyДокумент36 страницAntibiotic in Obstetric and GynecologyDrAbdi YusufОценок пока нет
- Hey Friends B TBДокумент152 страницыHey Friends B TBTizianoCiro CarrizoОценок пока нет
- 3-3 No Antibiotic in Hand InfectionДокумент26 страниц3-3 No Antibiotic in Hand InfectionProfesseur Christian DumontierОценок пока нет
- Neisseria MeningitidisДокумент53 страницыNeisseria MeningitidisPratibha AgarwalОценок пока нет
- G - Ethylene Oxide Correct AnswerДокумент56 страницG - Ethylene Oxide Correct AnswerVictor FabunmiОценок пока нет
- Pharm 415b - Antibiotics For Dummies Presentation FinalДокумент40 страницPharm 415b - Antibiotics For Dummies Presentation Finalapi-204163358Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 - Topic 5Документ8 страницLesson 3 - Topic 5Ferlyn Delos Santos IslaОценок пока нет
- AntibioticsДокумент84 страницыAntibioticsNandini GulurОценок пока нет
- Immunoparasitology: Blood Parasites Tissue Parasites Intestinal ParasitesДокумент14 страницImmunoparasitology: Blood Parasites Tissue Parasites Intestinal ParasitesCLEMENTОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 VaccinesДокумент35 страницChapter 13 VaccinesJalil HaddadinОценок пока нет
- Thesis Statement On Antibiotic ResistanceДокумент8 страницThesis Statement On Antibiotic Resistancebsbbq7qp100% (3)
- Resistensi AntibiotikaДокумент55 страницResistensi AntibiotikaDavid Cahyo WibisonoОценок пока нет
- Gram Negative Bacteria of Medical Importance - PPTX, MONDAYДокумент113 страницGram Negative Bacteria of Medical Importance - PPTX, MONDAYGeorge C. KasondaОценок пока нет
- Antimicrobial AgentsДокумент244 страницыAntimicrobial AgentsN Gv FcОценок пока нет
- Trends in Antibiotic Therapy: Rt. Rev. Prof. C.S.S. BelloДокумент47 страницTrends in Antibiotic Therapy: Rt. Rev. Prof. C.S.S. BelloanneОценок пока нет
- Bacterial VaccineДокумент44 страницыBacterial VaccineShrenik LuniyaОценок пока нет
- Bailey's CH 3-Syrarah NewДокумент58 страницBailey's CH 3-Syrarah NewthtklОценок пока нет
- Role of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy in The Treatment of Infectious DiseaseДокумент5 страницRole of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy in The Treatment of Infectious Diseaseioana antonesiОценок пока нет
- Bio Target and Bio DefenseДокумент30 страницBio Target and Bio DefenseAnogenОценок пока нет
- Jurnal AntibiotikДокумент4 страницыJurnal AntibiotikYuli IndrawatiОценок пока нет
- Resistencia ClorhexidinaДокумент30 страницResistencia ClorhexidinaVlady78Оценок пока нет
- Week6 Fri LectureNotesДокумент47 страницWeek6 Fri LectureNotesEezhar JumadiОценок пока нет
- E-Book - Antibiotics For MedicineДокумент20 страницE-Book - Antibiotics For Medicineaditya kaleОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics in DentistryДокумент25 страницAntibiotics in Dentistryimmortalneo100% (1)
- Group C PresentationДокумент45 страницGroup C PresentationFELICIA KASIMUОценок пока нет
- General Xtics. Neisseria Meningitidis (Meningococcus) : Gram-Negative CocciДокумент19 страницGeneral Xtics. Neisseria Meningitidis (Meningococcus) : Gram-Negative CocciMoses Tamba MomohОценок пока нет
- Final Exam PointersДокумент53 страницыFinal Exam PointersBelleОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics in Periodental TreatmentДокумент29 страницAntibiotics in Periodental TreatmentJana AliОценок пока нет
- Principles of Antibiotic TherapyДокумент5 страницPrinciples of Antibiotic TherapyWilliam L McGillОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics in Oral and Maxillofacial SurgeryДокумент25 страницAntibiotics in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeryindian dental academyОценок пока нет
- MMV Sample MCQ and EMQs PDFДокумент7 страницMMV Sample MCQ and EMQs PDFLian BaylosisОценок пока нет
- MMV Sample MCQ and EmqsДокумент7 страницMMV Sample MCQ and EmqsLian BaylosisОценок пока нет
- MICROQUESДокумент32 страницыMICROQUESYangyang R. AzradОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology Unit 2 Antimicrobial DrugsДокумент62 страницыPharmacology Unit 2 Antimicrobial DrugsAsif Ali LashariОценок пока нет
- Use of Antibiotics 2017Документ17 страницUse of Antibiotics 2017bernard.triciaОценок пока нет
- Multidrug-Resistant - Organisms (MDROsДокумент59 страницMultidrug-Resistant - Organisms (MDROsTariq100% (2)
- Antibiotics: Success and FailuresДокумент43 страницыAntibiotics: Success and Failurestummalapalli venkateswara raoОценок пока нет
- CALDERON Bacteriology Worksheet With AnswersДокумент3 страницыCALDERON Bacteriology Worksheet With AnswersJames Belgira TamayoОценок пока нет
- Micro ChAP 15Документ34 страницыMicro ChAP 15Farah ZahidОценок пока нет
- Microbial ResistanceДокумент16 страницMicrobial ResistanceDixa MeОценок пока нет
- Antibiotic Resistance Thesis StatementДокумент6 страницAntibiotic Resistance Thesis Statementkatelogebellevue100% (2)
- Principles of Antimicrobial TherapyДокумент12 страницPrinciples of Antimicrobial TherapyAnne Abejuela ObialОценок пока нет
- Superbugs: - Staphylococcus - VancomycinДокумент17 страницSuperbugs: - Staphylococcus - Vancomycinanon_92497062Оценок пока нет
- DR - PARTHA - 2018 Clinical Microbiology II PDFДокумент88 страницDR - PARTHA - 2018 Clinical Microbiology II PDFNuzki YofandaОценок пока нет
- A Diagnostic Dilemma: Tanis C. Dingle, PH.D, D (ABMM)Документ10 страницA Diagnostic Dilemma: Tanis C. Dingle, PH.D, D (ABMM)erdi afacanОценок пока нет
- Binder 1Документ29 страницBinder 1Narasimha MurthyОценок пока нет
- Antibiogram Perdalin FeraIbrahimДокумент62 страницыAntibiogram Perdalin FeraIbrahimTJANG RICKY CHANDRAОценок пока нет
- BD Lab OДокумент16 страницBD Lab Onydiacastillom2268Оценок пока нет
- Vaccines: Presented By: Arpita Batta EmailДокумент35 страницVaccines: Presented By: Arpita Batta EmailarpitabattaОценок пока нет
- Monoclonal AntibodiesДокумент6 страницMonoclonal AntibodiesIram AnwarОценок пока нет
- 1-крок-1-ЛС-KROK 2007-2017-English - microbiologyДокумент58 страниц1-крок-1-ЛС-KROK 2007-2017-English - microbiologyAbhani MøhitОценок пока нет
- Mrcpath Part 1 in Medical Microbiology & VirologyДокумент5 страницMrcpath Part 1 in Medical Microbiology & VirologyjedipowerОценок пока нет
- Neisseria Meningitidis - Advanced Methods and Protocols (PDFDrive)Документ442 страницыNeisseria Meningitidis - Advanced Methods and Protocols (PDFDrive)RaffaharianggaraОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics (Role and Abuse) 2016Документ35 страницAntibiotics (Role and Abuse) 2016Mohd Johari Mohd ShafuwanОценок пока нет
- Advances in The Development of Vaccines Against Neisseria MeningitidisДокумент10 страницAdvances in The Development of Vaccines Against Neisseria MeningitidisstephaniedianОценок пока нет
- Sas 9-14Документ8 страницSas 9-14Bráian Tzéims άλμπαОценок пока нет
- Case Study HIV With DiarrheaДокумент29 страницCase Study HIV With DiarrheaMatin Ahmad Khan100% (1)
- Microbiology MMV-Sample-MCQsДокумент8 страницMicrobiology MMV-Sample-MCQsMuhammad AttiqueОценок пока нет
- Advances in Immunopharmacology: Proceeding of the Fourth International Conference on Immunopharmacology, Osaka, Japan, 16-19 May 1988От EverandAdvances in Immunopharmacology: Proceeding of the Fourth International Conference on Immunopharmacology, Osaka, Japan, 16-19 May 1988Оценок пока нет
- Köppen Climate Classification - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент15 страницKöppen Climate Classification - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAndreea Tataru StanciОценок пока нет
- Washing Machine: Service ManualДокумент66 страницWashing Machine: Service ManualFernando AlmeidaОценок пока нет
- User Manual For Speed Control of BLDC Motor Using DspicДокумент12 страницUser Manual For Speed Control of BLDC Motor Using DspicTrung TrựcОценок пока нет
- Review1 ScheduleДокумент3 страницыReview1 Schedulejayasuryam.ae18Оценок пока нет
- Nama: Yossi Tiara Pratiwi Kelas: X Mis 1 Mata Pelajaran: Bahasa InggrisДокумент2 страницыNama: Yossi Tiara Pratiwi Kelas: X Mis 1 Mata Pelajaran: Bahasa InggrisOrionj jrОценок пока нет
- Tetralogy of FallotДокумент8 страницTetralogy of FallotHillary Faye FernandezОценок пока нет
- Fusion Implementing Offerings Using Functional Setup Manager PDFДокумент51 страницаFusion Implementing Offerings Using Functional Setup Manager PDFSrinivasa Rao Asuru0% (1)
- Application Activity Based Costing (Abc) System As An Alternative For Improving Accuracy of Production CostДокумент19 страницApplication Activity Based Costing (Abc) System As An Alternative For Improving Accuracy of Production CostM Agus SudrajatОценок пока нет
- Pe 03 - Course ModuleДокумент42 страницыPe 03 - Course ModuleMARIEL ASIОценок пока нет
- Hima OPC Server ManualДокумент36 страницHima OPC Server ManualAshkan Khajouie100% (3)
- Richardson Heidegger PDFДокумент18 страницRichardson Heidegger PDFweltfremdheitОценок пока нет
- Turning PointsДокумент2 страницыTurning Pointsapi-223780825Оценок пока нет
- Theories of International InvestmentДокумент2 страницыTheories of International InvestmentSamish DhakalОценок пока нет
- Thermally Curable Polystyrene Via Click ChemistryДокумент4 страницыThermally Curable Polystyrene Via Click ChemistryDanesh AzОценок пока нет
- Activity # 1 (DRRR)Документ2 страницыActivity # 1 (DRRR)Juliana Xyrelle FutalanОценок пока нет
- Elements of ArtДокумент1 страницаElements of Artsamson8cindy8louОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form 4 Daily Lesson Plan - CompressДокумент3 страницыChemistry Form 4 Daily Lesson Plan - Compressadila ramlonОценок пока нет
- Ob NotesДокумент8 страницOb NotesRahul RajputОценок пока нет
- The Construction of Optimal Portfolio Using Sharpe's Single Index Model - An Empirical Study On Nifty Metal IndexДокумент9 страницThe Construction of Optimal Portfolio Using Sharpe's Single Index Model - An Empirical Study On Nifty Metal IndexRevanKumarBattuОценок пока нет
- Roleplayer: The Accused Enchanted ItemsДокумент68 страницRoleplayer: The Accused Enchanted ItemsBarbie Turic100% (1)
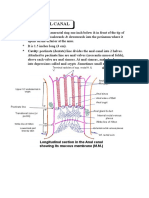
- Anatomy Anal CanalДокумент14 страницAnatomy Anal CanalBela Ronaldoe100% (1)
- The Mantel Colonized Nation Somalia 10 PDFДокумент5 страницThe Mantel Colonized Nation Somalia 10 PDFAhmad AbrahamОценок пока нет
- ISBN Safe Work Method Statements 2022 03Документ8 страницISBN Safe Work Method Statements 2022 03Tamo Kim ChowОценок пока нет
- Aleksandrov I Dis 1-50.ru - enДокумент50 страницAleksandrov I Dis 1-50.ru - enNabeel AdilОценок пока нет
- Waterstop TechnologyДокумент69 страницWaterstop TechnologygertjaniОценок пока нет
- De Thi Hoc Ki 1 Mon Tieng Anh Lop 5 Co File NgheДокумент10 страницDe Thi Hoc Ki 1 Mon Tieng Anh Lop 5 Co File Nghetuyen truongОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Data Collection InstrumentsДокумент19 страницChapter 8 Data Collection InstrumentssharmabastolaОценок пока нет
- FAMOUS PP Past TenseДокумент21 страницаFAMOUS PP Past Tenseme me kyawОценок пока нет
- Proceeding of Rasce 2015Документ245 страницProceeding of Rasce 2015Alex ChristopherОценок пока нет