Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Menu Planning - ppt.2010-11
Загружено:
ninayniОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Menu Planning - ppt.2010-11
Загружено:
ninayniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
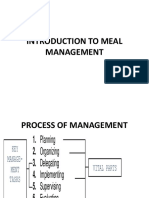
Meal Planning
Menu Planning
scheduling intake of meals for a general or specific individual requirements.
- the process of planning and
Principles of Meal Planning 1. Fulfill the nutritional needs of the family members. (Family size and composition)
2. Plan meals within the family income. Maximum use of the money available, in the best possible way.
Principles of Meal Planning 3. Aid in the proper purchase, preparation and service of food. 4. Economize on time, labor and fuel. 5. Provide variety in the diet, by making proper selection of foods from within each of the three food groups.
Principles of Meal Planning
6. Make meals appealing and palatable by proper selection of food in terms of color, texture and flavor.
7. Provide nutrition meals taking into account individual preferences.
Principles of Meal Planning
8. Plan meals in advance, so that any pre-preparation required can be made and also the leftovers from the previous meals can be economically utilized.
9. Create balance & appropriate diet for various age groups & conditions.
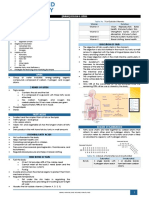
1. Get the DBW using Tannhausers Method. 2. Know the caloric reqt / the Total Energy Allowance (TEA) of the patient. 3. Know the nutrient or diet distribution of the patient. 4. Calculate the diet Rx in grams. 5. Make a table for the computation of exchanges. 6. Make a meal plan distribution of exchanges for a day. 7. Convert meal plan distribution to household measurements.
Note:
1) Vegetable A dont change nutrient value if served cup cooked or 1 cup raw.
e.g. cup cooked no value; with value only if doubled (e.g. 1 cup, 2 cups,3 cups..) 1 cup raw no value; with value if doubled (e.g. 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 cups. )
Nutrients
Regular Diet 60% 15% 25%
Modified Diet
DM Renal CVA/ Stroke Postop GIT prob.
2) Normal consumption of sugar of healthy persons is 5-7 exchanges; maximum of 9 unless C/I. 3) 2-3 exchanges of vegetable are allowed per day. 4)3-4 exchanges of fruits are allowed unless restricted. 5) Condiments have no value (e.g.pepper, salt, soy sauce); with value only if consumed in large amounts (e.g.catsup, gravy). Standard Tolerance: +/-5 grams - in each nutrient +/-50 grams - in total calories
CHO CHON
50% 20% 30%
70% 10% 20%
60% 25% 15%
60% 20% 20%
60% 15% 25%
Fats
Computation of Rice, Meat & Fat Exchange
Rice exchange Add the value of carbo Subtract the amt. of Rx carbo Divide it by 23 (1exc. of rice=23) Meat exchange Add the value of CHON Subtract the amount of Rx CHON Divide it by 8 (1exc. of meat=8) Fat exchange
Add the value of fats Subtract the Rx amt.of fats Divide it by 5 (1exc. of fat=5)
Breakfast 1 piece apple, 65 gms. 1 cup fresh carabaos milk 1 cup rice cooked 1 pc. sardines in tomato sauce
pm Snack 4 tsp. cocojam 3 pcs. pandesal (5x5 cm)
am Snack 4 tsp. strawberry jam 4 slices wheat Lunch Ginisang Gulay 1/8 tomato, 1/8 onion (cup/cooked) baguio beans (cup/cooked) togue (cup/cooked) carrot (cup/cooked) 2 pcs. tokwa (cup/cooked) 1 matchbox size pork (cup/cooked) 1 cup rice cooked 1 pc. latundan banana 1 tsp. oil as panggisa
Dinner Nilagang Okra with Galunggong cup cooked nilagang okra fried galunggong (w/ 2 tsp oil) 1 cup cooked rice cup pure mango juice w/ 1 tsp. sugar
Вам также может понравиться
- Food Selection and Preparation: A Laboratory ManualОт EverandFood Selection and Preparation: A Laboratory ManualРейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (2)
- Exercise 9. Planning Preparation Evaluation of Energy Rich Meal FinalДокумент18 страницExercise 9. Planning Preparation Evaluation of Energy Rich Meal FinalHaroldJohnCabalgadaОценок пока нет
- Meal Planning: Adeniji A. O. NTD 226 - Institutional Food Management Bowen University Nutrition and DieteticsДокумент39 страницMeal Planning: Adeniji A. O. NTD 226 - Institutional Food Management Bowen University Nutrition and DieteticsPrincess Jane BalagtasОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts in Meal ManagementДокумент13 страницBasic Concepts in Meal ManagementPauline Grace PabulayanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8Документ6 страницChapter 8Marc ManzonОценок пока нет
- Food Selection and EvaluationДокумент14 страницFood Selection and EvaluationRizabelle TubioОценок пока нет
- Ma. Aileen C. Carating: RND MMДокумент35 страницMa. Aileen C. Carating: RND MMJaja MikaelaОценок пока нет
- Type of Vegetable Cutting.Документ5 страницType of Vegetable Cutting.Ally MaurerОценок пока нет
- Cookery Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыCookery Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanRAWDA ZAILONОценок пока нет
- Handouts CKY AppetizersДокумент16 страницHandouts CKY Appetizersaileen paz100% (1)
- Module 3 Lesson 2 (FSM 105 - Food Procesisng, Packaging and Labeling)Документ13 страницModule 3 Lesson 2 (FSM 105 - Food Procesisng, Packaging and Labeling)mary joy gomezОценок пока нет
- Menu and Product Knowledge Managemen TДокумент55 страницMenu and Product Knowledge Managemen TLaelannie Magpayo100% (1)
- The Meal Manager and The Meal Management ProcessДокумент19 страницThe Meal Manager and The Meal Management ProcessPauline Grace PabulayanОценок пока нет
- Sto (1) - Tomas Nutrition ProgramДокумент8 страницSto (1) - Tomas Nutrition ProgramMarites BautistaОценок пока нет
- Importance & Principle of Meal PlanningДокумент18 страницImportance & Principle of Meal PlanningSaher YasinОценок пока нет
- Household Resource ManagementДокумент35 страницHousehold Resource ManagementKring DonaireОценок пока нет
- FSM2 ReferenceДокумент26 страницFSM2 ReferenceJames F. LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Syllabus: College of Teacher Education Bachelor of Technology and Livelihood Education AY: 2019-2020 Curriculum: BTLEDДокумент10 страницSyllabus: College of Teacher Education Bachelor of Technology and Livelihood Education AY: 2019-2020 Curriculum: BTLEDMae CaspeОценок пока нет
- Culinary Learning OutcomesДокумент3 страницыCulinary Learning OutcomesCindy Ortiz Gaston0% (1)
- DLL All Subjects 2 q3 w10 d2Документ4 страницыDLL All Subjects 2 q3 w10 d2Genner RazОценок пока нет
- ClassificationДокумент3 страницыClassificationNguyễn Phước Bảo TânОценок пока нет
- Principles of Food Selection, Preparation and ServiceДокумент4 страницыPrinciples of Food Selection, Preparation and ServiceJohnny WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Classification of Food Service IndustryДокумент10 страницClassification of Food Service IndustryEmmanuel Deo BorgoniaОценок пока нет
- Baking Tools and EquipmentДокумент31 страницаBaking Tools and EquipmentLea Galano Manarpaac100% (2)
- Grains2190 PowerpointДокумент35 страницGrains2190 Powerpointapi-245680208100% (1)
- Cleaning and Maintain KP - Cooking ToolsДокумент21 страницаCleaning and Maintain KP - Cooking Toolsmary ann morenoОценок пока нет
- Form 5B BTLEd Home EconomicsДокумент4 страницыForm 5B BTLEd Home EconomicsJoven100% (1)
- 5SДокумент14 страниц5Sgajendra2010Оценок пока нет
- SANDWICHESДокумент72 страницыSANDWICHESVhel ZamoraОценок пока нет
- Purchasing, Receiving, and Storing FoodДокумент15 страницPurchasing, Receiving, and Storing FoodJohnson Fernandez100% (1)
- Tools Used in Food PreparationДокумент33 страницыTools Used in Food PreparationJohn Nelson A Picones100% (5)
- Lesson 5Документ24 страницыLesson 5hk_scribdОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Food and Technology - Midterm ExamДокумент4 страницыFundamentals of Food and Technology - Midterm ExamSharon May Tayuran100% (1)
- Knife SkillsДокумент15 страницKnife SkillsAbbie TantengcoОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1: Professionalism: Cookery Is Become An Art, A Noble Science Cooks Are GentlemenДокумент15 страницLesson 1: Professionalism: Cookery Is Become An Art, A Noble Science Cooks Are GentlemenKarl VillarubiaОценок пока нет
- Vegetable CutsДокумент5 страницVegetable CutsLea Galano ManarpaacОценок пока нет
- Home Economics Literacy SyllabusДокумент7 страницHome Economics Literacy SyllabusMarco BicaldoОценок пока нет
- Syllabus in Home Economics LiteracyДокумент11 страницSyllabus in Home Economics LiteracyNoriel TorreОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1: Use and Maintain Kitchen Tools and EquipmentДокумент70 страницLesson 1: Use and Maintain Kitchen Tools and EquipmentVerna Aguas Clava100% (1)
- Lesson # 3 Types of Food and Beverage Linen 2Документ34 страницыLesson # 3 Types of Food and Beverage Linen 2Emerson Cruz100% (1)
- Starch and AlimentaryДокумент25 страницStarch and AlimentaryArwin A Pitas100% (3)
- Topic 2-FUNDAMENTALS OF FOOD TECHNOLOGYДокумент31 страницаTopic 2-FUNDAMENTALS OF FOOD TECHNOLOGYRosalinda LaranОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 ResearchДокумент32 страницыChapter 1 ResearchMattОценок пока нет
- Standardize RecipeДокумент19 страницStandardize RecipeThessalonica Manguiat SinohinОценок пока нет
- History of FoodserviceДокумент6 страницHistory of FoodserviceSharina Canaria ObogОценок пока нет
- Food PreservationДокумент5 страницFood PreservationUmarani Mohanasundaram0% (1)
- Module 6 (Finals)Документ6 страницModule 6 (Finals)Mark Anthony Nieva Rafallo0% (1)
- Introduction To Meal Management 2Документ49 страницIntroduction To Meal Management 2Kipchirchir AbednegoОценок пока нет
- Marketable MealsДокумент39 страницMarketable MealsG-BOY ABANGAN100% (1)
- Meal ManagementДокумент3 страницыMeal ManagementRoviene Malcontento100% (9)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in TeachingДокумент9 страницA Detailed Lesson Plan in TeachingTetchie GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Tle DLPДокумент4 страницыTle DLPcecilynОценок пока нет
- Livelihood Productivity Skills Development Training: College of Teacher EducationДокумент4 страницыLivelihood Productivity Skills Development Training: College of Teacher EducationMa. Rochelle CabralesОценок пока нет
- Grade 12 Meal Pattern PDFДокумент17 страницGrade 12 Meal Pattern PDFJohnson Fernandez100% (1)
- Week 5.lesson-3-Introduction To Rhytmic ActivitiesДокумент2 страницыWeek 5.lesson-3-Introduction To Rhytmic ActivitiesErron Francisco NicolОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan in TVL Home Economics - COOKERY Grade 12: I. ObjectiveДокумент2 страницыLesson Plan in TVL Home Economics - COOKERY Grade 12: I. ObjectiveDarlene Daguno Cabrido100% (1)
- 233 - 8-Nutritional Care &WT ControlДокумент51 страница233 - 8-Nutritional Care &WT ControlHussain AliОценок пока нет
- Carb Counting ToolДокумент8 страницCarb Counting ToolcanicazulОценок пока нет
- Nutrition in The Life Cycle: NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy LaboratoryДокумент3 страницыNutrition in The Life Cycle: NCM 105A Nutrition and Diet Therapy LaboratoryKryzza Leizell50% (2)
- Diet TherapyДокумент2 страницыDiet TherapyR-Chian Jose GermanpОценок пока нет
- Meal Planning For The FamilyДокумент19 страницMeal Planning For The FamilyJoan Liezl LamasanОценок пока нет
- Indeks Glikemik Gula SemutДокумент9 страницIndeks Glikemik Gula Semutnovita suci wulandariОценок пока нет
- Beyond The Rim 1 - Free Jump ProgramДокумент216 страницBeyond The Rim 1 - Free Jump ProgramElias VaziryОценок пока нет
- Nutrition NotesДокумент5 страницNutrition Notesdrng48Оценок пока нет
- Batangas Cold Storage AssessmentДокумент3 страницыBatangas Cold Storage AssessmentJoshua M. GenoviaОценок пока нет
- 20 Foods That Are Highly Loaded With Vitamin B12Документ6 страниц20 Foods That Are Highly Loaded With Vitamin B12Imtiaz KhanОценок пока нет
- School Form 8 (SF 8)Документ2 страницыSchool Form 8 (SF 8)Queenie Alicaba BelonioОценок пока нет
- Fermenting Yogurt at Home: Brian A. Nummer, Ph.D. National Center For Home Food Preservation October 2002Документ6 страницFermenting Yogurt at Home: Brian A. Nummer, Ph.D. National Center For Home Food Preservation October 2002MohsinОценок пока нет
- Female Line Body Weight and Feeding Program: Ross 308 Grandparent StockДокумент2 страницыFemale Line Body Weight and Feeding Program: Ross 308 Grandparent StockWijianto WijiantoОценок пока нет
- "Calories In, Calories Out" and Macronutrient Intake: The Hope, Hype, and 1 Science of Calories.Документ12 страниц"Calories In, Calories Out" and Macronutrient Intake: The Hope, Hype, and 1 Science of Calories.Nanci GuestОценок пока нет
- The Beginner's Guide To Intermittent FastingДокумент10 страницThe Beginner's Guide To Intermittent FastingMaru PabloОценок пока нет
- Grand FCS A Chap 6Документ38 страницGrand FCS A Chap 6Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudОценок пока нет
- Nutrilite Body Key Traning DeckДокумент92 страницыNutrilite Body Key Traning DeckTapan Chowdhury100% (1)
- Carbohydrates WorksheetДокумент2 страницыCarbohydrates WorksheetEllaine Salcedo31% (13)
- Soal Bing Us - 13 UtamaДокумент11 страницSoal Bing Us - 13 UtamaRaffi NurhayadiОценок пока нет
- LIKHAДокумент22 страницыLIKHAAngelica SampangОценок пока нет
- Air Fryer Falafel - Elavegan - RecipesДокумент3 страницыAir Fryer Falafel - Elavegan - RecipesShailesh BalasubramanianОценок пока нет
- Mineral Content of Fruit and VegetablesДокумент1 страницаMineral Content of Fruit and VegetablesJose LuizОценок пока нет
- 3 Adime Form For Diabete Case 1Документ2 страницы3 Adime Form For Diabete Case 1api-309275032Оценок пока нет
- Lance Diet Project For Social StudiesДокумент2 страницыLance Diet Project For Social Studiestini singhОценок пока нет
- Cookery 10: Technology and Livelihood Education Learning Activity Sheet (Q4 - Week 1)Документ4 страницыCookery 10: Technology and Livelihood Education Learning Activity Sheet (Q4 - Week 1)Angeline Cortez100% (1)
- Local FruitsДокумент9 страницLocal Fruitsmanikavi_mkОценок пока нет
- SITXINV002 Student Assessment TasksДокумент28 страницSITXINV002 Student Assessment TasksÇrox Rmg PunkОценок пока нет
- Outline: Digestion of FatsДокумент3 страницыOutline: Digestion of FatsSheky GeriosaaaОценок пока нет
- Eat This Not That GuideДокумент14 страницEat This Not That Guidexdownloader50% (2)
- A Identifying Nutrition Prob & Its CausesДокумент23 страницыA Identifying Nutrition Prob & Its CausesGabriel Philippe100% (1)
- HW5e Elem Test Unit 8AДокумент3 страницыHW5e Elem Test Unit 8AEmreОценок пока нет
- Aspen Pediatric Heart Failure NutritionДокумент7 страницAspen Pediatric Heart Failure NutritionkhairachungОценок пока нет
- Chicken LasagnaДокумент2 страницыChicken LasagnaAdrianaОценок пока нет
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossОт EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Pati's Mexican Table: The Secrets of Real Mexican Home CookingОт EverandPati's Mexican Table: The Secrets of Real Mexican Home CookingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (9)
- The Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyОт EverandThe Diabetes Code: Prevent and Reverse Type 2 Diabetes NaturallyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Mostly Plants: 101 Delicious Flexitarian Recipes from the Pollan FamilyОт EverandMostly Plants: 101 Delicious Flexitarian Recipes from the Pollan FamilyРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (11)
- Magnolia Table, Volume 3: A Collection of Recipes for GatheringОт EverandMagnolia Table, Volume 3: A Collection of Recipes for GatheringРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- The Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldОт EverandThe Encyclopedia of Spices & Herbs: An Essential Guide to the Flavors of the WorldРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (5)
- Love Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)От EverandLove Yourself, Heal Your Life Workbook (Insight Guide)Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (40)
- Waiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterОт EverandWaiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (487)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellОт EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (82)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarОт EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (352)
- The Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsОт EverandThe Arm: Inside the Billion-Dollar Mystery of the Most Valuable Commodity in SportsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (49)
- Sugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthОт EverandSugar Crush: How to Reduce Inflammation, Reverse Nerve Damage, and Reclaim Good HealthРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Secrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainОт EverandSecrets From the Eating Lab: The Science of Weight Loss, the Myth of Willpower, and Why You Should Never Diet AgainРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (38)
- Surprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion—with a Little Something Extra InsideОт EverandSurprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion—with a Little Something Extra InsideРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- The Blue Apron Cookbook: 165 Essential Recipes & Lessons for a Lifetime of Home CookingОт EverandThe Blue Apron Cookbook: 165 Essential Recipes & Lessons for a Lifetime of Home CookingОценок пока нет
- Mexican Today: New and Rediscovered Recipes for Contemporary KitchensОт EverandMexican Today: New and Rediscovered Recipes for Contemporary KitchensРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Instant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookОт EverandInstant Loss On a Budget: Super-Affordable Recipes for the Health-Conscious CookРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Find Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeОт EverandFind Your Path: Honor Your Body, Fuel Your Soul, and Get Strong with the Fit52 LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Glucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingОт EverandGlucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (61)
- The Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonОт EverandThe Beck Diet Solution Weight Loss Workbook: The 6-Week Plan to Train Your Brain to Think Like a Thin PersonРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (33)
- Grit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeОт EverandGrit & Grace: Train the Mind, Train the Body, Own Your LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomОт EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- The Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyОт EverandThe Body Book: The Law of Hunger, the Science of Strength, and Other Ways to Love Your Amazing BodyОценок пока нет