Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DDE2063 BY En. Khairulnizam Bin Othman
Загружено:
Suhayl AzminОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DDE2063 BY En. Khairulnizam Bin Othman
Загружено:
Suhayl AzminАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DDE2063 BY En. Khairulnizam Bin Othman
Objective
To introduce the concepts of position, displacement, velocity, and acceleration. To study particle motion along a straight line. The motion equation application, concept and calculation.
Rectilinear Kinematics Section 12.2
Rectilinear : Straight line motion Kinematics : Study the geometry of the motion dealing with s, v, a. Rectilinear Kinematics : To identify at any given instant, the particles position, velocity, and acceleration.
(All objects such as rockets, projectiles, or vehicles will be considered as particles has negligible size and shape
particles : has mass but negligible size and shape
Position
Position : Location of a particle at any given instant with respect to the origin
r : Displacement ( Vector ) s : Distance ( Scalar )
Distance & Displacement
Displacement : defined as the change in position. r : Displacement ( 3 km ) s : Distance ( 8 km ) Total length
For straight-line Distance = Displacement s = r Ds = Dr
River
City QUT
3km
My Place X
8 km
Vector is direction oriented Dr positive (left ) Dr negative (right)
Velocity & Speed
Velocity : Displacement per unit time Average velocity : V = Dr / Dt Speed : Distance per unit time Average speed : usp = sT / Dt (Always positive scalar )
Speed refers to the magnitude of velocity Average velocity : uavg = Dr / Dt
Rectilinear Kinematics: Erratic Motion
ds v= dt
v =slope of s t graph
Graph S-t
45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 0 5 15 t(s) 22 27
Figure show Graph s - t for a body moving in a straight line. Assuming that the sudden change in velocity at time t = 5, 15, 22 s can be carried out. Draw the graph of v-t ?.
s(m)
Rectilinear Kinematics: Erratic Motion
Answer
v=
ds dt
20 0 = 4ms 1 5 36 20 t = 5 15s _ v = = 1.6ms 1 15 5 40 36 t = 15 22 s _ v = = 0.6ms 1 22 15 0 40 t = 22 27 s _ v = = 8ms 1 27 22 t = 0 5s _ v =
Rectilinear Kinematics: Erratic Motion
dv a= dt
a =slope of v t graph
Graph v-t
15 10 5
t(s)
0 -5 0 -10 -15 v(m /s) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
Figure show Graph v - t for a body moving in a straight line. Assuming that the sudden change in velocity at time t = 2, 6, 10 s can be carried out. Draw the graph of a - t ?.
Rectilinear Kinematics: Erratic Motion
Answer
a= dv dt
10 0 = 5ms 2 20 t = 2 6 s _ a = 0ms 2 t = 0 2s _ a = (10) (10) = 5ms 2 10 6 0 (10) t = 10 16 s _ a = = 1.7 ms 2 16 10 t = 6 10 s _ a =
Rectilinear Kinematics: Erratic Motion
Dv = adt
Change in = Area Under Velocity A t Graph
Dv = adt
Rectilinear Kinematics: Erratic Motion
Ds = vdt
Change in = Area Under Displacement v t Graph
Ds = vdt
Velocity as a Function of Time
dv ac = dt
dv = ac dt
dv = a
vo 0
dt
v = v0 act
Position as a Function of Time
ds v= = v0 ac t dt
ds = (v
so 0
ac t ) dt
1 2 s = s0 v0t ac t 2
velocity as a Function of Position
v dv = ac ds
v dv = a
v0 s0
ds
1 2 1 2 v v0 = ac ( s s0 ) 2 2
v = v0 2ac ( s s0 )
2 2
Free Fall
Ali and Omar are standing at the top of a cliff of height H. Both throw a ball with initial speed v0, Ali straight down and Omar straight up. The speed of the balls when they hit the ground are vA and vO respectively. Which of the following is true: (b) vA = vO (c) vA > vO
(a) vA < vO
Ali v0 vA
v0
Omar H
vO
Free fall
Since the motion up and back down is symmetric, intuition should tell you that v = v0 We can prove that your intuition is correct:
Equation:
2 v 2 v0 = 2( g )H H = 0
Omar v0
v = v0
H
This looks just like Omar threw the ball down with speed v0, so the speed at the bottom should be the same as Alis ball. y=0
Free fall
We can also just use the equation directly:
Ali
2 2 : v v 0 = 2( g )0 H
Omar: v
2 v0 = 2( g )0 H
same !!
Ali v0
v0
Omar
y=H
y=0
Summary
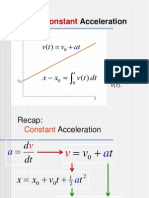
Time dependent acceleration
Constant acceleration
s (t )
ds v= dt 2 dv d s a= = 2 dt dt
v = v0 act
v = v 2ac ( s s0 )
2 2 0
This applies to a freely falling object:
1 2 s = s0 v0t ac t 2
a ds = v dv
a = g = 9.81 m / s 2
Question 1
Initially, the car travels along a straight road with a speed of 35 m/s. If the brakes are applied and the speed of the car is reduced to 10 m/s in 15 s, determine the constant deceleration of the car.
v = v0 act
v = u at
Quiz 1
Initially, the car travels along a straight road with a speed of 60 m/s. If the brakes are applied and the speed of the car is reduced to 25 m/s in 20 s, determine the constant deceleration of the car.
Question 2
A truck traveling along a straight road at speed v1 (20km/h), increases its speed to v2 (120km/h) in 15 s. If its acceleration is constant, determine the distance traveled.
u = 20 km km v = 120 t = 15s hr hr solution v v a = 2 1 = 1.852m / s 2 t 1 2 s = ut at s = 291.67 m 2
Quiz 1
A truck traveling along a straight road at speed v1 (40km/h), increases its speed to v2 (100km/h) in 3000m. If its acceleration is constant, determine the time traveled.
Вам также может понравиться
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsДокумент22 страницыKing Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsAnonymous CmgstGQCIgОценок пока нет
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsДокумент22 страницыKing Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsTommyVercettiОценок пока нет
- S S A A: Kinematics of Linear MotionДокумент28 страницS S A A: Kinematics of Linear MotionTakiYa SaruMaruОценок пока нет
- Chapter2.1-Equationofmotion DynamicДокумент27 страницChapter2.1-Equationofmotion Dynamicshakirr aimannОценок пока нет
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn MalaysiaДокумент24 страницыUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn MalaysiafikreyrОценок пока нет
- Chapter-2 - Kinematics of Linear MotionДокумент27 страницChapter-2 - Kinematics of Linear MotionSherena Peter GovindОценок пока нет
- Rectilinear Kinematics Erratic Motion PDFДокумент28 страницRectilinear Kinematics Erratic Motion PDFThibankumar Arumugam0% (1)
- Lecture 12Документ37 страницLecture 12Sarah Rachel100% (1)
- MECHANICS Kinematics: Chapter 2 - Motion Along A Straight LineДокумент11 страницMECHANICS Kinematics: Chapter 2 - Motion Along A Straight LineDan AltmanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - KinematicsДокумент8 страницChapter 1 - KinematicsREXTERYXОценок пока нет
- Motion in Two or Three DimensionsДокумент58 страницMotion in Two or Three DimensionsMarc Howard Detera PanganibanОценок пока нет
- Dynamics Lecture2 General Curvilinear Motion - Rectangular Components and Projectile MotionДокумент41 страницаDynamics Lecture2 General Curvilinear Motion - Rectangular Components and Projectile MotionJJ Enzon100% (1)
- Week 9 KinematicsДокумент64 страницыWeek 9 Kinematicsiwhy_Оценок пока нет
- Ie IRODOV SOLUTION PART 1Документ95 страницIe IRODOV SOLUTION PART 1alienx60582% (22)
- Dynamics Chapter 12Документ26 страницDynamics Chapter 12Sudarshan KambleОценок пока нет
- Chap12 (3) 3Документ65 страницChap12 (3) 3Vince HarrisОценок пока нет
- MMB222 - KinematicsParticles-01-OneDimension Lecture 1Документ27 страницMMB222 - KinematicsParticles-01-OneDimension Lecture 1Olefile Mark MolokoОценок пока нет
- Mech 2Документ71 страницаMech 2Gino Mandado0% (1)
- Ch12 Kinematics - of - A - ParticleДокумент46 страницCh12 Kinematics - of - A - ParticletarntodОценок пока нет
- 1-Kinematics of Particles 0Документ46 страниц1-Kinematics of Particles 0Rabiatul AdawiahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Part1Документ116 страницChapter 1 Part1G00GLRОценок пока нет
- Kinematic of Linear Motion Matriculation STPMДокумент79 страницKinematic of Linear Motion Matriculation STPMJue Saadiah100% (9)
- Chapter 2: Force and Motion 2.1 Linear Motion: Vector QuantityДокумент13 страницChapter 2: Force and Motion 2.1 Linear Motion: Vector QuantityAbby TanОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 1 SolutionsДокумент10 страницTutorial 1 SolutionsNicholas Bonn SingОценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент11 страницPhysicsEthylОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ7 страницChapter 2the_truth_94Оценок пока нет
- Dynamics: Lesson OutcomesДокумент7 страницDynamics: Lesson OutcomesNaqib NordinОценок пока нет
- Phy - Motion Graph AnalysisДокумент63 страницыPhy - Motion Graph AnalysisGkid GkidОценок пока нет
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Teacher'sДокумент13 страницForm 4 Physics Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Teacher'sPavithiran100% (2)
- Introduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1 - 12.2)Документ15 страницIntroduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: CONTINUOUS MOTION (Sections 12.1 - 12.2)Mohamed DamraОценок пока нет
- PHY10 Lesson 2 Kinematics (Full)Документ35 страницPHY10 Lesson 2 Kinematics (Full)Luke CruzОценок пока нет
- Note Chapter2-Student PDFДокумент14 страницNote Chapter2-Student PDFFeby Zarratina HadiОценок пока нет
- HWK 12Документ24 страницыHWK 12subash1111@gmail.com67% (3)
- Force and Motion JPN Pahang AnsДокумент34 страницыForce and Motion JPN Pahang Anssummer0130Оценок пока нет
- Dynamics GLA-1c PDFДокумент9 страницDynamics GLA-1c PDFAhmad IrfanОценок пока нет
- Describing Motion: Kinematics in One DimensionДокумент56 страницDescribing Motion: Kinematics in One DimensionReehmaMendinaОценок пока нет
- Kinematics in One Dimension: Giancoli, PHYSICS, 6/E © 2004. ElectronicallyДокумент39 страницKinematics in One Dimension: Giancoli, PHYSICS, 6/E © 2004. ElectronicallySN JohnОценок пока нет
- Motion in A Straight Line: Initial PositionДокумент7 страницMotion in A Straight Line: Initial PositionEngelbert Bicoy AntodОценок пока нет
- Distance and DisplacementДокумент37 страницDistance and DisplacementHany ElGezawyОценок пока нет
- Uniform Circular Motion: ReviewДокумент61 страницаUniform Circular Motion: ReviewMohit SharmaОценок пока нет
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 8Документ11 страницNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 8shahulОценок пока нет
- Dynamics - CH12 NotesДокумент15 страницDynamics - CH12 NotesHaardik GargОценок пока нет
- KinematicsДокумент72 страницыKinematicsRenerio P. Gentallan Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ35 страницChapter 2younessinaОценок пока нет
- Tajuk 2Документ70 страницTajuk 2gsharkzОценок пока нет
- Document From MarziaДокумент39 страницDocument From MarziaMaarij AsifОценок пока нет
- FisicaДокумент26 страницFisicaNata WestiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 OneSlideДокумент143 страницыChapter 12 OneSlideSupper CoolОценок пока нет
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsДокумент22 страницыKing Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsTommyVercettiОценок пока нет
- KinematicsДокумент65 страницKinematicsGarlapati Srinivasa Rao100% (1)
- SM PDF Chapter2Документ28 страницSM PDF Chapter2kyara906Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Motion in 2DДокумент7 страницChapter 3 Motion in 2Dbmz00000Оценок пока нет
- Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankОт EverandApplications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankОценок пока нет
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (10)
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsОт EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Gantt ChartДокумент2 страницыGantt ChartSuhayl AzminОценок пока нет
- StatikДокумент2 страницыStatikSuhayl AzminОценок пока нет
- Objectives of WeldingДокумент8 страницObjectives of WeldingSuhayl Azmin100% (3)
- Karnival Bahasa Jerman Seksyen 2 Sesi 2013/2014Документ7 страницKarnival Bahasa Jerman Seksyen 2 Sesi 2013/2014Suhayl AzminОценок пока нет
- QuestionnaireДокумент4 страницыQuestionnaireSuhayl Azmin100% (1)
- 1 Objectives 1 2 2 3 Discussion and Result 3-4 4 Types 5 5 Types of Feeding Systems and Accessories 6Документ8 страниц1 Objectives 1 2 2 3 Discussion and Result 3-4 4 Types 5 5 Types of Feeding Systems and Accessories 6Suhayl AzminОценок пока нет
- Sample Progress ReportДокумент2 страницыSample Progress ReportSuhayl AzminОценок пока нет
- Taekwondo SparringДокумент3 страницыTaekwondo SparringSuhayl AzminОценок пока нет
- Assignment StaticДокумент24 страницыAssignment StaticSuhayl AzminОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Technical Communication: Cydwee@uthm - Edu.myДокумент12 страницIntroduction To Technical Communication: Cydwee@uthm - Edu.mySuhayl AzminОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Technical DefinitionsДокумент20 страницChapter 2 - Technical DefinitionsSuhayl AzminОценок пока нет
- Manual Casio Era 500L PDFДокумент7 страницManual Casio Era 500L PDFDraganescu CristianОценок пока нет
- Irf3207 MOSFETДокумент12 страницIrf3207 MOSFETKennedy IruОценок пока нет
- Calculate Size of Diesel GeneratorДокумент1 страницаCalculate Size of Diesel GeneratorIonut ArdeleanОценок пока нет
- Magnetic PropertiesДокумент20 страницMagnetic Propertiespatrick saliwanОценок пока нет
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: C.F. Calvillo, A. Sánchez-Miralles, J. VillarДокумент15 страницRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: C.F. Calvillo, A. Sánchez-Miralles, J. VillarSakshiDawarОценок пока нет
- SquidsДокумент20 страницSquidsMushfique HussainОценок пока нет
- Models Used Must Be Appropriate For Transient Stability AnalysisДокумент6 страницModels Used Must Be Appropriate For Transient Stability AnalysisadauОценок пока нет
- MTS9000A Multiple Telecommunication System User Manual Russia Megafone MTS9513A-AD2002Документ65 страницMTS9000A Multiple Telecommunication System User Manual Russia Megafone MTS9513A-AD2002Влад ТолчеевОценок пока нет
- Active Harmonic FilterДокумент8 страницActive Harmonic FilterKanai BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Touch and Step PotentialsДокумент10 страницTouch and Step PotentialsMirela JakОценок пока нет
- Ee Electrical and Electronic MeasurementsДокумент33 страницыEe Electrical and Electronic MeasurementsNilamani Umashankar JenaОценок пока нет
- ACSEE Physics F5 T3 FluidDynamicsДокумент4 страницыACSEE Physics F5 T3 FluidDynamicsKennedy Oswald AikaruwaОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Activity 3 Application of Bernoullis TheoremДокумент13 страницLaboratory Activity 3 Application of Bernoullis TheoremChardel PorlaresОценок пока нет
- Capacitor MKPДокумент29 страницCapacitor MKPMartina KОценок пока нет
- Electronic Materials: Mid - ReviewДокумент20 страницElectronic Materials: Mid - Reviewchinh buiОценок пока нет
- Kinematics WSДокумент19 страницKinematics WSMadhav JainОценок пока нет
- Ybus Matrix With Regulating Transformer - Self Study TopicДокумент21 страницаYbus Matrix With Regulating Transformer - Self Study TopicSankar MuthuswamyОценок пока нет
- Electrical Lab Manual Volume OneДокумент60 страницElectrical Lab Manual Volume OneMahesh M P NairОценок пока нет
- Efficiency Testing Methods For Centrifugal PumpsДокумент16 страницEfficiency Testing Methods For Centrifugal PumpsAfnian SariОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент41 страницаUntitledSushant Kumar JhaОценок пока нет
- Bipolar Junction Transistors Talha Syed NaqviДокумент51 страницаBipolar Junction Transistors Talha Syed NaqviMuhammad AwaisОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 6-CentroidsДокумент24 страницыCHAPTER 6-CentroidsYohannes MesfinОценок пока нет
- 535 1 NLSC Sample 24 GuideДокумент6 страниц535 1 NLSC Sample 24 Guidekyeyuneyasin572100% (1)
- AOZ3015AIДокумент14 страницAOZ3015AIIcomОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 - InductanceДокумент53 страницыChapter 10 - InductanceAlejandro TV Learning ChannelОценок пока нет
- Exam021 MIdterm Gen - Phy1Документ7 страницExam021 MIdterm Gen - Phy1Jerome RacalОценок пока нет
- Lecture-III Basics of Pinch Analysis - 2Документ35 страницLecture-III Basics of Pinch Analysis - 2Chalachew NigussieОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Properties of Materials 2.6Документ6 страницMagnetic Properties of Materials 2.6reaktorenergiОценок пока нет
- Oriental Motor RK Series PDFДокумент28 страницOriental Motor RK Series PDFTinesh ShanОценок пока нет
- What Is A Demagnetization Curve?: More Than Just Your SupplierДокумент2 страницыWhat Is A Demagnetization Curve?: More Than Just Your Suppliersurabhi0706Оценок пока нет