Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Reaksi Organik - Kimia Organik 4
Загружено:
akbar_rozaaqАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Reaksi Organik - Kimia Organik 4
Загружено:
akbar_rozaaqАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Oleh : Alvan Febrian Shalas, S. Farm.
, Apt
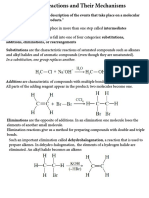
JENIS REAKSI ORGANIK
Occur when two reactants add together to form a
single product with no atoms left over.
Occur when a single reactant splits into two products,
often with formation of a small molecule
JENIS REAKSI ORGANIK
Occur when two reactants exchange parts to give
two new products
JENIS REAKSI ORGANIK
Occur when a single reactant undergoes a
reorganization of bonds and atoms to yield an isomeric
product
JENIS REAKSI ORGANIK
Classify each of the following reactions as an
addition, elimination, substitution, or
rearrangement:
EXERCISES
SUBSTITUSI
ELIMINASI
ADISI
MEKANISME REAKSI
7
Reaction mechanism describes bond-breaking
and bond-making :
1. Which bonds are broken and in what order
2. Which bonds are formed and in what order
3. What the relative rates of the steps are
4. Account for all reactants used and all products
formed
8
MEKANISME REAKSI
1. HOMOLYTIC CLEAVAGE
Symmetrical bond-breaking : One bonding
electron stays with each product
9
Unsymmetrical bond-breaking (polar): Two
bonding electrons stay with one product.
MEKANISME REAKSI
2. HETEROLYTIC CLEAVAGE
10
1. Symmetrical bond-forming : One bonding
electron is donated by each reactant
MEKANISME REAKSI
11
2. Unsymmetrical bond-forming : two bonding
electrons are donated by one reactant
MEKANISME REAKSI
REAKSI POLAR
The fundamental characteristic of all polar
organic reactions :
Electron-rich sites react with electron-poor sites
Bonds are made when an electron-rich atom
donates a pair of electrons to an electron poor
atom
Bonds are broken when one atom leaves with
both electrons from the former bond
REAKSI POLAR
REAKSI POLAR
Larger atoms with more loosely held electrons are more
polarizable
Smaller atoms with fewer, tightly held electrons are less
polarizable
Ex : Sulfur is more polarizable than oxygen, and iodine is
more polarizable than chlorine.
The measure of the response
to an external electrical
influence
The effect of this higher polarizability for sulfur
and iodine is that carbonsulfur and carbon
iodine bonds, although nonpolar according to
electronegativity values, nevertheless usually
react as if they were polar
REAKSI POLAR
REAKSI POLAR
Electron rich
site
Electron poor site
REAKSI POLAR
Electrophile is electron-loving.
An electrophile has a positively polarized, electron poor atom
and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a
nucleophile.
Electrophiles can be either neutral or positively charged.
Nucleophile is a nucleus-loving.
A nucleophile has a negatively polarized, electron-rich atom
and can form a bond by donating a pair of electrons to a
positively polarized, electronpoor atom.
Nucleophiles can be either neutral or negatively charged
REAKSI POLAR
REAKSI POLAR
EXERCISES
REAKSI POLAR
EXERCISES
a)
TUGAS
Designed by TheTemplateMart.com
1. Jelaskan yang dimaksud dengan :
a. Reaksi Eksergonis dan Endergonis
b. Reaksi Eksotermis dan Endotermis
c. Energi Disosiasi Ikatan
2. Analisalah diagram reaksi di bawah ini, dan
berikan penjelasannya
b)
Вам также может понравиться
- Apexi Powerfc Instruction ManualДокумент15 страницApexi Powerfc Instruction ManualEminence Imports0% (2)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureДокумент13 страницChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding - Study NotesДокумент15 страницChemical Bonding - Study NotesTamoghna DeyОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureДокумент14 страницChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRoshita G PillaiОценок пока нет
- Q2W2 - 1 - Chemical Bonding and Lewis StructureДокумент25 страницQ2W2 - 1 - Chemical Bonding and Lewis StructureEl Jie Ancheta Estela100% (1)
- Skills Checklist - Gastrostomy Tube FeedingДокумент2 страницыSkills Checklist - Gastrostomy Tube Feedingpunam todkar100% (1)
- Triaxial Shear TestДокумент10 страницTriaxial Shear TestAfiqah Nu'aimiОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Science 9 Week 3Документ77 страницScience 9 Week 3Eliseo MuyaОценок пока нет
- Sources of Hindu LawДокумент9 страницSources of Hindu LawKrishnaKousikiОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its StructureДокумент48 страницLesson 4 - The Polarity of Molecule Based On Its Structuretheresa balaticoОценок пока нет
- Dermatology Skin in Systemic DiseaseДокумент47 страницDermatology Skin in Systemic DiseaseNariska CooperОценок пока нет
- Richard B. Herbert (Auth.) - The Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites-Springer Netherlands (1981) PDFДокумент186 страницRichard B. Herbert (Auth.) - The Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites-Springer Netherlands (1981) PDFSiti Mamluatus Sa'adahОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Ionic and Covelant Bonds Lab ReportДокумент10 страниц2.1 Ionic and Covelant Bonds Lab Reportchai monsaleОценок пока нет
- IMCI Chart BookletДокумент43 страницыIMCI Chart Bookletmysticeyes_17100% (1)
- Methods for Analysis of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Photosynthetic Organisms: Plants, Green Algae and CyanobacteriaОт EverandMethods for Analysis of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Photosynthetic Organisms: Plants, Green Algae and CyanobacteriaОценок пока нет
- Reaksi OrganikДокумент24 страницыReaksi OrganikItamahYulaikhaОценок пока нет
- DENT1002-Lecture6-Overview of Organic Reactions-BDoganДокумент34 страницыDENT1002-Lecture6-Overview of Organic Reactions-BDoganzlarsson127Оценок пока нет
- Topic 1 - Introduction Learning Objectives:: Module 1 - Organic ChemistryДокумент8 страницTopic 1 - Introduction Learning Objectives:: Module 1 - Organic ChemistryTwinkle ToesОценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry 19-20Документ20 страницElectrochemistry 19-20system worksОценок пока нет
- Group 6 - Lab 5 - Organic Reaction MechanismsДокумент5 страницGroup 6 - Lab 5 - Organic Reaction MechanismsCloudetteMendozaОценок пока нет
- Ionic BondДокумент3 страницыIonic Bondayatolla ayatollaTMОценок пока нет
- Physical Science Polarity of MoleculesДокумент56 страницPhysical Science Polarity of MoleculeskharentaponОценок пока нет
- Polar MoleculesДокумент18 страницPolar MoleculesAly ReyesОценок пока нет
- 1.7. Types of ReactionsДокумент10 страниц1.7. Types of ReactionsRXNOFCHMОценок пока нет
- AcknowledgementДокумент14 страницAcknowledgementRohaan Mohammad100% (2)
- Module 3: Chemical Bonding and NomenclatureДокумент11 страницModule 3: Chemical Bonding and NomenclatureJay Mark CapanangОценок пока нет
- Post-Lab Report: de Luna Doronila Mendoza Villarosa Group 6Документ27 страницPost-Lab Report: de Luna Doronila Mendoza Villarosa Group 6CloudetteMendozaОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureДокумент14 страницChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRoshita G PillaiОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms of Elec TrophilesДокумент10 страницMechanisms of Elec TrophilesjoeОценок пока нет
- An Overview of Organic ReactionsДокумент80 страницAn Overview of Organic Reactions110003551 110AОценок пока нет
- AttachmentДокумент69 страницAttachmentAbi ManОценок пока нет
- CH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionДокумент33 страницыCH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionHARPACAОценок пока нет
- Science Curriculum by Aaron KellerДокумент7 страницScience Curriculum by Aaron KellerResta THawОценок пока нет
- Guía Quimica 3Документ3 страницыGuía Quimica 3599d2vrgxtОценок пока нет
- Klein Chapter 1Документ84 страницыKlein Chapter 1alyssa_marie_keОценок пока нет
- Kim3201 Chapter 1 Part 2 23032021Документ69 страницKim3201 Chapter 1 Part 2 23032021Business MatterОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Basic ChemistryДокумент3 страницыChapter 2 Basic ChemistryClarisse Anne QuinonesОценок пока нет
- Ionic and Covalent BondsДокумент5 страницIonic and Covalent BondsFern HofileñaОценок пока нет
- The Lewis Electron Dot StructureДокумент10 страницThe Lewis Electron Dot StructureMaribel Membrado GreciaОценок пока нет
- Chem 101 Lec: Pt.1 Chemical BondingДокумент36 страницChem 101 Lec: Pt.1 Chemical BondingSarip RymahОценок пока нет
- Lect 4-6 (Physical Chemistry III) Chem 340Документ14 страницLect 4-6 (Physical Chemistry III) Chem 340eva982205Оценок пока нет
- 11 ChemistryДокумент20 страниц11 ChemistrykabhiОценок пока нет
- Chem 3 - Organic Reactions PDFДокумент35 страницChem 3 - Organic Reactions PDFFeaid Aina OrnedoОценок пока нет
- What Are Redox Reactions?Документ18 страницWhat Are Redox Reactions?Mr. Zee KhanОценок пока нет
- Basic Chemistry ReviewДокумент5 страницBasic Chemistry ReviewArman Neil J. BudogОценок пока нет
- Alkanes: Alkenes:: Atom EconomyДокумент9 страницAlkanes: Alkenes:: Atom EconomyHyder OmarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic ReactionsДокумент10 страницChapter 6 An Overview of Organic ReactionsRen Liew Jia QingОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding: John Hope Tabamo BCHE 111/L The University of Mindanao-TagumДокумент48 страницChemical Bonding: John Hope Tabamo BCHE 111/L The University of Mindanao-Tagumranny beganОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding 1Документ81 страницаChemical Bonding 1RIMMY AUGUSTINE 2138110Оценок пока нет
- Polarity of Molecules 2Документ37 страницPolarity of Molecules 2eryelОценок пока нет
- Matter - Bonding, Naming, and Counting Its ParticlesДокумент7 страницMatter - Bonding, Naming, and Counting Its Particlestlga.amberdominiquebediaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Part 1Документ17 страницChapter 1 Part 1morireОценок пока нет
- Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 2 Revision NotesДокумент2 страницыClass 10 Chemistry Chapter 2 Revision NotesMd TaaseenОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 Review of General Chemistry ConceptsДокумент32 страницыLesson 1 Review of General Chemistry Conceptsnorlene narita macedaОценок пока нет
- Unit-3Electrochemistry 88896Документ37 страницUnit-3Electrochemistry 88896Dhatri SriramОценок пока нет
- Organic ChemistryДокумент38 страницOrganic ChemistryPhú BìnhОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeДокумент35 страницChapter 2: The Chemical Context of LifeJustin RobenyОценок пока нет
- Class 11 Chemistry Lesson PlanДокумент19 страницClass 11 Chemistry Lesson PlanJaya KaushikОценок пока нет
- Bscpe Sci1 SLM 5Документ25 страницBscpe Sci1 SLM 5April Joy GonzalesОценок пока нет
- GCFGCGCFGFDGДокумент15 страницGCFGCGCFGFDGZabrinaRuizОценок пока нет
- Gen Chem RebyuwerДокумент11 страницGen Chem Rebyuweryousef shalabyОценок пока нет
- 5 2024 245 CH 5 ReactionsAlkenesAlkynes Lecture V3 STUDENTДокумент38 страниц5 2024 245 CH 5 ReactionsAlkenesAlkynes Lecture V3 STUDENTdingdong19690Оценок пока нет
- ENERGYДокумент3 страницыENERGYLei Anne GacayanОценок пока нет
- Chemical BondingДокумент22 страницыChemical BondingshamsvocesОценок пока нет
- Pptx5 Chemical BondingДокумент39 страницPptx5 Chemical BondingLumbay, Jolly MaeОценок пока нет
- Abstract NKI KnoopsДокумент1 страницаAbstract NKI Knoopsakbar_rozaaqОценок пока нет
- 7.alkil Halida (SN Dan E)Документ33 страницы7.alkil Halida (SN Dan E)akbar_rozaaqОценок пока нет
- Alkohol: Oleh: Alvan Febrian Shalas, S. Farm., AptДокумент45 страницAlkohol: Oleh: Alvan Febrian Shalas, S. Farm., Aptakbar_rozaaqОценок пока нет
- Struktur Atom Dan Ikatan - Kimor 1Документ30 страницStruktur Atom Dan Ikatan - Kimor 1akbar_rozaaqОценок пока нет
- Ikatan Kovalen Polar Dan Asam Basa - Kimor 2Документ29 страницIkatan Kovalen Polar Dan Asam Basa - Kimor 2akbar_rozaaqОценок пока нет
- Sayre's Materia Medica FreeДокумент84 страницыSayre's Materia Medica Freeakbar_rozaaqОценок пока нет
- Eloy-Stock English Full PDFДокумент0 страницEloy-Stock English Full PDFR.s. WartsОценок пока нет
- Safety Procedures in Using Hand Tools and EquipmentДокумент12 страницSafety Procedures in Using Hand Tools and EquipmentJan IcejimenezОценок пока нет
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Govt4396.002.08s Taught by Gregory Thielemann (Gregt)Документ2 страницыUT Dallas Syllabus For Govt4396.002.08s Taught by Gregory Thielemann (Gregt)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupОценок пока нет
- Sociology As A Form of Consciousness - 20231206 - 013840 - 0000Документ4 страницыSociology As A Form of Consciousness - 20231206 - 013840 - 0000Gargi sharmaОценок пока нет
- Health Post - Exploring The Intersection of Work and Well-Being - A Guide To Occupational Health PsychologyДокумент3 страницыHealth Post - Exploring The Intersection of Work and Well-Being - A Guide To Occupational Health PsychologyihealthmailboxОценок пока нет
- Scholastica: Mock 1Документ14 страницScholastica: Mock 1Fatema KhatunОценок пока нет
- Case Study 2Документ5 страницCase Study 2api-247285537100% (1)
- Lecture 2 Effects of Operating Conditions in VCCДокумент9 страницLecture 2 Effects of Operating Conditions in VCCDeniell Joyce MarquezОценок пока нет
- Review On AlgebraДокумент29 страницReview On AlgebraGraziela GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Heimbach - Keeping Formingfabrics CleanДокумент4 страницыHeimbach - Keeping Formingfabrics CleanTunç TürkОценок пока нет
- MCI Approved Medical College in Uzbekistan PDFДокумент3 страницыMCI Approved Medical College in Uzbekistan PDFMBBS ABROADОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Public Health ManagementДокумент3 страницыFundamentals of Public Health ManagementHPMA globalОценок пока нет
- Lecture 14 Direct Digital ManufacturingДокумент27 страницLecture 14 Direct Digital Manufacturingshanur begulaji0% (1)
- Technology Based Project: Special Track 1)Документ14 страницTechnology Based Project: Special Track 1)Kim ChiquilloОценок пока нет
- W25509 PDF EngДокумент11 страницW25509 PDF EngNidhi SinghОценок пока нет
- 16783Документ51 страница16783uddinnadeemОценок пока нет
- Chapter 23Документ9 страницChapter 23Javier Chuchullo TitoОценок пока нет
- 8051 NotesДокумент61 страница8051 Notessubramanyam62Оценок пока нет
- Quiz 140322224412 Phpapp02Документ26 страницQuiz 140322224412 Phpapp02Muhammad Mubeen Iqbal PuriОценок пока нет
- Mosfet Irfz44Документ8 страницMosfet Irfz44huynhsang1979Оценок пока нет
- How To Block HTTP DDoS Attack With Cisco ASA FirewallДокумент4 страницыHow To Block HTTP DDoS Attack With Cisco ASA Firewallabdel taibОценок пока нет
- Micro Lab Midterm Study GuideДокумент15 страницMicro Lab Midterm Study GuideYvette Salomé NievesОценок пока нет
- Aleutia Solar Container ClassroomДокумент67 страницAleutia Solar Container ClassroomaleutiaОценок пока нет
- Lamentation of The Old Pensioner FinalДокумент17 страницLamentation of The Old Pensioner FinalRahulОценок пока нет