Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 12 Cognitive Disorders Morales
Загружено:
John Russell MoralesАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 12 Cognitive Disorders Morales
Загружено:
John Russell MoralesАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Richard P.
Halgin
Susan Krauss Whitbourne
University of Massachusetts at Amherst
slides by Travis Langley
Henderson State University
Abnormal
Psychology
Clinical Perspectives on Psychological Disorders 5e
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Aging-Related
and Cognitive
Disorders
Processing of thoughts
Capacity to store memory
The ability to be attentive
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Cognitive Function
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
NATURE OF COGNITIVE
DISORDERS
DSM-IV diagnoses include:
Impairment of thought, memory, attention
(cognitive impairment) arising from brain
trauma, disease, or exposure to toxic
substances.
Delirium
Dementia
Amnesia
Can cause a set of presumably
psychological symptoms.
Various physically based syndromes
mimic schizophrenia, mood disorders
and personality disorders.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Attributes of Physical
Abnormalities
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating symptoms associated with a
psychological disorder from those arising
in response to a physical disorder can be
difficult.
Example:
EPILEPSY, especially the form called
TEMPORAL LOBE EPILEPSY, can be
mistaken for a psychological disorder.
Assessment of Cognitive
Disorders
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Neuropsychological Testing
Neuroimaging Techniques
Delirium
A temporary state in which individuals
experience a clouding of consciousness, they
are unaware of what is happening around
them and are unable to focus or pay attention.
In a state of delirium, people
experience cognitive changes in which
their memory is foggy and they are
disoriented.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
delirium
Caused by a change in brain
metabolism due to factors such as:
substance intoxication
substance withdrawal
head injury
high fever
vitamin deficiency
Delirium
Amnestic Disorder
Cognitive disorders involving inability to
(a)recall previously learned information or
(b)register new memories.
This inability can be very disturbing,
because the individual loses a sense of
personal identity.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Amnestic
disorders due
to medical
conditions.
chronic
transient
Substance-
induced
persisting
amnestic
disorders.
Categories of
Amnestic Disorder
Amnestic Disorders due to
Medical condition
Resulting in wide variety of medical
problems including the ff.
- Head Trauma
- Loss of Oxygen
-Herpes Complex
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Substances That Induce
Amnestic Disorder
Medications
Illicit drugs
Industrial solvents
Mercury
Lead
Insecticides
The most common
cause:
Chronic alcohol
use
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Damage to the brain caused by
exposure to trauma.
Increasingly being recognized as an
important cause of mental and physical
dysfunction.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Our brain tissue is highly sensitive to damage
caused by intense pressure to the head.
Automobile accident
A fall
An injury sustained in contact to sports or
combat.
Causes of TBI
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Headaches
Sleep disturbances
Sensitivity to light and noise
Diminished cognitive
performance(L,M,A,RA)
Depression, anxiety and emotional
outbursts.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Post-concussion Syndrome
A disorder in which a constellation of
physical, cognitive, emotional symptoms
persists from weeks to years.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Concussions are milder
forms of TBI that is caused by a blow
to the head.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Dementia
Generalized progressive deficits in
memory, learning, communication,
judgment, and motor coordination.
The first sign of dementia is memory
loss.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Dementia: Other Prominent
Symptoms
Aphasia
Wernickes
Brocas
Apraxia
Agnosia
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Dementia: Other Prominent
Symptoms
Disturbance in Executive Functioning
Executive functioning: Cognitive
abilities such as abstract thinking,
planning, organizing, and carrying out of
behaviors.
Relatively simple everyday tasks may be
forgotten or confused.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Damage to the brain
caused by exposure
to trauma is
increasingly
recognized as an
important cause of
mental and physical
dysfunction.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
ALZHEIMERS DEMENTIA
Multiple cognitive deficits associated
with dementia, probably caused by
biological abnormalities involving the
nervous system.
Subtypes
With delirium
With delusions
With depressed mood
Uncomplicated
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
ALZHEIMERS DEMENTIA
Stages
Forgetfulness
Early confusional
Late confusional
Early dementia
Middle dementia
Late dementia
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
BIOLOGICAL FEATURES
Neurofibrillary tangles
Amyloid plaques
Deficits in neurotransmitter acetylcholine
40 to 50 percent twin concordance rate
ALZHEIMERS DEMENTIA
ENVIRONMENTAL factors must play a role;
otherwise, concordance would be higher, but
specific factors are not yet confirmed.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
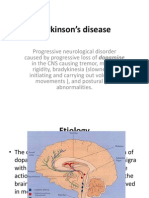
Parkinsons Disease
Involves neuronal degeneration of
subcortical structures controlling
movements.
Dementia occurs in up to 60% of
Parkinsons patients.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms
Hands, ankles, or head may shake involuntarily.
Bradykinesia: General slowing of motor activity.
Akinesia: Muscular rigidity, difficulty initiating
movement.
Loss of fine motor coordination.
Slowed, shuffling gait.
Difficulty starting or stopping movement like
walking.
Expressionless appearance.
Loss of normal rhythmic speech quality.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
VARIOUS DEMENTIAS
Substance-Induced
Persisting Dementia
Picks Disease
Lewy Body Dementia
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
VARIOUS DEMENTIAS
Frontotemporal
Dementias
Huntingtons Disease
Creutzfeldt-Jakob
Disease
Vascular Dementia
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Pseudodementia:
False dementia, symptoms
caused by depression that
mimic those apparent in early
stages of Alzheimer's.
Pseudodementia
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
ALZHEIMERS TREATMENT
BEHAVIORAL MANAGEMENT
Target both patient and caregiver to:
Increase patient independence.
Eliminate wandering and aggression.
Provide social support for caregivers.
MEDICATION
Slow breakdown of acetylcholine.
Antioxidants target free radicals that may
damage neurons.
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
http:/www.mhhe.com/halgin6e
For more information on material covered
in this chapter, visit our Web site:
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- 1q Gsa Morales2223Документ5 страниц1q Gsa Morales2223John Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- 1st Quarter 2023Документ44 страницы1st Quarter 2023John Russell Morales0% (1)
- Sabbath School Handbook PDFДокумент121 страницаSabbath School Handbook PDFJohn Russell Morales50% (2)
- Summative TestДокумент1 страницаSummative TestJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- 5 Part Lesson Plan TraditionalДокумент2 страницы5 Part Lesson Plan TraditionalJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- December 10Документ1 страницаDecember 10John Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Subject SchedДокумент16 страницSubject SchedJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- GYLC 18 Registration Application Revised 1Документ5 страницGYLC 18 Registration Application Revised 1John Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Explaining and Predicting Filipino Industrial WorkersДокумент1 страницаExplaining and Predicting Filipino Industrial WorkersJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Sample Fn:catog/classsched/jrm/hcp: All Documents' File Name Should Be in This FormatДокумент1 страницаSample Fn:catog/classsched/jrm/hcp: All Documents' File Name Should Be in This FormatJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Summative TestДокумент1 страницаSummative TestJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- John Russell V. Morales: January 13, 2016Документ1 страницаJohn Russell V. Morales: January 13, 2016John Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Doccumentation: in Mrs. Jocelyn Benituasan's Class - Grade IIДокумент1 страницаDoccumentation: in Mrs. Jocelyn Benituasan's Class - Grade IIJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- George Frideric HandelHandelДокумент7 страницGeorge Frideric HandelHandelJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 10 Classroom Rules: Activity 1 Origin of My NameДокумент2 страницы10 Classroom Rules: Activity 1 Origin of My NameJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- The Four Basic Elements of NegligenceДокумент2 страницыThe Four Basic Elements of NegligenceJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Control Loop CharacteristicsДокумент10 страницControl Loop CharacteristicsJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Recruitment and SelectionДокумент15 страницRecruitment and SelectionJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Application FormДокумент2 страницыApplication Formjohn100% (1)
- Ay Program Template 2016Документ3 страницыAy Program Template 2016John Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Tecarro College FoundationДокумент8 страницTecarro College FoundationJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Food Menu: April 27, 2015 April 28, 2015Документ2 страницыFood Menu: April 27, 2015 April 28, 2015John Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Necrological Service: Maria Adtoon BalateroДокумент6 страницNecrological Service: Maria Adtoon BalateroJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Application FormДокумент2 страницыApplication Formjohn100% (1)
- Ay Programme 2016 Schedule ProposalДокумент2 страницыAy Programme 2016 Schedule ProposalJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Many Years Later Ahab Became The King of The Kingdom of IsraelДокумент9 страницMany Years Later Ahab Became The King of The Kingdom of IsraelJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Julyan Straight LinesДокумент1 страницаJulyan Straight LinesJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Registration Without NameДокумент1 страницаRegistration Without NameJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- Learning Outcomes: Maria Teresa Cruz Padilla Member, Ched-TcmidedДокумент2 страницыLearning Outcomes: Maria Teresa Cruz Padilla Member, Ched-TcmidedJohn Russell MoralesОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Manajemen Terapi Intensif PresДокумент60 страницManajemen Terapi Intensif PresFebry HartantoОценок пока нет
- Angliski SeminarskaДокумент13 страницAngliski SeminarskaMarija AleksovaОценок пока нет
- Parkinson's DiseaseДокумент65 страницParkinson's DiseaseGerald Resubal OriñaОценок пока нет
- BSC Nursing: Medical Surgical Nursing - I Unit V - Disorders of The Cardio Vascular SystemДокумент36 страницBSC Nursing: Medical Surgical Nursing - I Unit V - Disorders of The Cardio Vascular SystemPoova RagavanОценок пока нет
- Pregnancy skin conditionsДокумент8 страницPregnancy skin conditionsrizqi_cepiОценок пока нет
- Clinical Review October 20 2017 - SHINGRIXДокумент158 страницClinical Review October 20 2017 - SHINGRIXPayneMaxОценок пока нет
- Fast Scan 2022Документ9 страницFast Scan 2022rosieОценок пока нет
- Prostate Cancer PDFДокумент2 страницыProstate Cancer PDFkapczukОценок пока нет
- Dara Yastrzemski-Assignment 2 WeeeblyДокумент5 страницDara Yastrzemski-Assignment 2 Weeeblyapi-323159742Оценок пока нет
- Perf. PeritonitisДокумент5 страницPerf. PeritonitisChiriţoiu AnamariaОценок пока нет
- CV SAMEEP - PathologistДокумент7 страницCV SAMEEP - PathologistMumtaj AnsariОценок пока нет
- International Travelers Medical Center PrescriptionДокумент1 страницаInternational Travelers Medical Center PrescriptionDeo Warren SilangОценок пока нет
- Patho Physiology: Pathophysiology of Myelomeningocele and HydrocephalusДокумент3 страницыPatho Physiology: Pathophysiology of Myelomeningocele and Hydrocephalusjettski_10Оценок пока нет
- RESEARCH 1 Fi 2Документ20 страницRESEARCH 1 Fi 2Alondra SagarioОценок пока нет
- The Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You byДокумент6 страницThe Complete Weight Loss Guide: Brought To You bySam YoussefОценок пока нет
- Nasal Obstruction: Nitha K 2nd Year MSC NursingДокумент65 страницNasal Obstruction: Nitha K 2nd Year MSC NursingNITHA KОценок пока нет
- Torticolis OdtДокумент25 страницTorticolis OdtAndreea CimpoiОценок пока нет
- Prostate Cancer Symptoms, Screening, Stages and Treatment OptionsДокумент45 страницProstate Cancer Symptoms, Screening, Stages and Treatment OptionsNeethiselvam Devadoss100% (2)
- Clinical Approach To Respiratory Distress in NewbornДокумент29 страницClinical Approach To Respiratory Distress in Newbornabhivnair100% (1)
- Sansure Biotech: Six Respiratory Pathogens Nucleic Acid Diagnostic Kit (PCR-Fluorescence Probing)Документ4 страницыSansure Biotech: Six Respiratory Pathogens Nucleic Acid Diagnostic Kit (PCR-Fluorescence Probing)paulaОценок пока нет
- AJCC Cancer Staging Form Supplement PDFДокумент514 страницAJCC Cancer Staging Form Supplement PDFSaint Germain Valencia RondónОценок пока нет
- Choose The Most Accurate Single Answer: (1 Mark Each)Документ9 страницChoose The Most Accurate Single Answer: (1 Mark Each)Salmonella TyphiОценок пока нет
- Vitamin B12 InfographicДокумент2 страницыVitamin B12 InfographicIan WynneОценок пока нет
- Frequently Asked Questions About Laser TherapyДокумент5 страницFrequently Asked Questions About Laser TherapyShahRizal Che JamelОценок пока нет
- 131 - Acute Vs Chronic InflammationДокумент7 страниц131 - Acute Vs Chronic InflammationAqib KhalidОценок пока нет
- Untitled Presentation 4Документ18 страницUntitled Presentation 4sumegh sagareОценок пока нет
- 2010 Guideline AFДокумент61 страница2010 Guideline AFyamtotlОценок пока нет
- Atls Trauma ThermalДокумент36 страницAtls Trauma ThermalsheisamarinkaОценок пока нет
- Coronary Artery Disease-Cad OR Ischaemic Heart Disease - IhdДокумент99 страницCoronary Artery Disease-Cad OR Ischaemic Heart Disease - IhdMwanja MosesОценок пока нет
- Multiple MyelomaДокумент8 страницMultiple MyelomaFelipeОценок пока нет