Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
AE 1350 Lecture Notes #8
Загружено:
psycho_zahranОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AE 1350 Lecture Notes #8
Загружено:
psycho_zahranАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AE 1350
Lecture Notes #8
We have looked at..
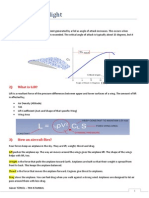
Airfoil Nomenclature
Lift and Drag forces
Lift, Drag and Pressure Coefficients
The Three Sources of Drag:
skin friction drag in laminar and turbulent flow
form drag
wave drag
Airfoil Drag Polar
C
d
vs. C
l
Rough airfoils
have turbulent flow
over them, high drag.
Smooth airfoils have
laminar flow over
at least a portion
of the surface.
Low Drag.
Form Drag
Source: http://www.allstar.fiu.edu/aerojava/flight46.htm
Form drag may be reduced
by proper design, and
streamlining the shape.
Supersonic wave Drag
For a given airfoil or wing or aircraft, as the Mach number
is increased, the drag begins to increase above a
freestream Mach number of 0.8 or so due to shock waves that
form around the configuration.
Shock waves
How can shock waves be
minimized?
Use wing sweep.
Use supercritical airfoils, which keep the
flow velocity over the airfoil and the local
Mach number from exceeding Mach 1.1 or
so.
Use area rule- the practice of making the
aircraft cross section area (from nose to tail,
including the wing) vary as smoothly as
possible.
How can shock waves be
minimized?
Use sweep.
M= 0.8
30 sweep
In your design...
The Maximum Mach number is 0.85
Wings for supersonic fighters are designed to
reduce wave drag up to 80% of the
Maximum speed.
In our case, 80% of 0.85 is 0.68.
If we use a wing leading edge sweep angle of
30 degrees or so, the Mach number normal to
the leading edge is 0.68 cos 30 ~ 0.6
Effect of Thickness and Sweep
on Wave Drag
Source:
http://www.hq.nasa.gov/office/pao/History/SP-468/ch10-4.htm
Supercritical Airfoils
Their shape is modified to keep the Mach number on the airfoils
from exceeding 1.1 or so, under cruise conditions.
Conventional vs. Supercritical
Airfoils
Wing Drag
Since a wing is made up of airfoils, it has
skin friction drag
profile drag
wave drag at high speeds,
and
Induced drag due to tip vortices
TIP VORTICES
Effect of Tip Vortices
Downwash
Induced Drag
Induced drag is caused by the downward rotation of the
freestream velocity, which causes a clockwise rotation of the lift
force.
From AE 2020 theory,
e
2
,
AR
C
C
L
i D
e= Oswald efficiency
factor
Variation of Drag with Speed
Induced drag decreases as V
increases, because we need less
values of C
L
at high speeds.
Other drag forces (form,
skin friction , interference)
increase.
Result: Drag first drops, then rises.
At High Values of a Wings Stall
We need high C
L
to take-off and land at low speeds.
http://www.zenithair.com/stolch801/design/design.html
Achieving High Lift
One form of flaps, called Fowler
flaps increase the chord length as
the flap is deployed.
High energy air from the bottom side of the airfoil
flows through the gap to the upper side, energizes slow speed
molecules, and keeps the flow from stalling.
How do slats and flaps help?
1. They increase the camber as and when needed- during
take-off and landing.
Leading Edge Slats
Help avoid stall near the leading
edge
High Lift also Causes High Drag
Вам также может понравиться
- A330 Normal Law: Putting Fly-by-Wire Into PerspectiveОт EverandA330 Normal Law: Putting Fly-by-Wire Into PerspectiveРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- 5 WingsДокумент26 страниц5 WingsJacob_Glanzman6933Оценок пока нет
- Tech Sem 3Документ4 страницыTech Sem 3Tushar MantriОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Design: Airfoil and Geometry SelectionДокумент94 страницыAircraft Design: Airfoil and Geometry SelectionYak100% (10)
- Supersonic Flight - Design Features Lesson 7Документ61 страницаSupersonic Flight - Design Features Lesson 7MarvinОценок пока нет
- What Are Disadvantages of Wing SweepДокумент57 страницWhat Are Disadvantages of Wing SweepElton CacefoОценок пока нет
- Lesson 7 - Winglets, Raked Wingtips, Vortices, DragДокумент38 страницLesson 7 - Winglets, Raked Wingtips, Vortices, Dragaahsan345Оценок пока нет
- External Flow-Drag Lift - SU Lift ForceДокумент5 страницExternal Flow-Drag Lift - SU Lift ForceSaad SalahuddinОценок пока нет
- AircraftDesign 8 HighLiftДокумент21 страницаAircraftDesign 8 HighLiftSonu SamalaОценок пока нет
- Critical Mach Number, Transonic Area RuleДокумент11 страницCritical Mach Number, Transonic Area RuleGurunath Aero100% (2)
- High Lift DevicesДокумент33 страницыHigh Lift DevicesNitsugaОценок пока нет
- High Speed Flight Lesson 3 Design and Calculations-1Документ21 страницаHigh Speed Flight Lesson 3 Design and Calculations-1MarvinОценок пока нет
- (Class 19) Introduction To Aeronautical EngineeringДокумент48 страниц(Class 19) Introduction To Aeronautical EngineeringFabian Torres100% (2)
- Technical Topics: Understanding MY Conversion Rules Go-MindedДокумент39 страницTechnical Topics: Understanding MY Conversion Rules Go-MindedGábor KapuyОценок пока нет
- Day 1 - Complete Tech Quiz Questions - Finalised and PrintedДокумент16 страницDay 1 - Complete Tech Quiz Questions - Finalised and PrintedShabbir Bhojani89% (18)
- GD LabReportДокумент36 страницGD LabReportMuhammad Aamir HayatОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Ad2Документ23 страницыUnit 5 Ad2chrislenardraghu92Оценок пока нет
- Aircraft Design - Aerofoil and Geometry SelectionДокумент55 страницAircraft Design - Aerofoil and Geometry SelectionKrishanth Sivanathan100% (1)
- Study Project (Ayyub Achilev)Документ18 страницStudy Project (Ayyub Achilev)Ayyub AchilevОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 PT 1 N 2-Theory of FLightДокумент23 страницыChapter 3 PT 1 N 2-Theory of FLightzuliana_ismail8564100% (1)
- Aerodynamics Unit 3Документ10 страницAerodynamics Unit 3Rajni VermaОценок пока нет
- Flow Analysis of Vortex Generators On Wing Sections by Stereoscopic Particle Image Velocimetry MeasurementsДокумент12 страницFlow Analysis of Vortex Generators On Wing Sections by Stereoscopic Particle Image Velocimetry MeasurementsNITESH JHAОценок пока нет
- Advanced Aircraft Design 2 SummaryДокумент14 страницAdvanced Aircraft Design 2 SummaryJack AzadОценок пока нет
- Reducing Wave DragДокумент43 страницыReducing Wave DragJaredSagagaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Parasite and Induced DragДокумент16 страницIntroduction To Parasite and Induced DragKettlecorn KarlisОценок пока нет
- Review of Aircraft AerodynamicsДокумент13 страницReview of Aircraft AerodynamicsIaNickОценок пока нет
- 12222major ComponentsДокумент41 страница12222major ComponentsPokemon GoОценок пока нет
- Mini Ace: İçindekilerДокумент20 страницMini Ace: İçindekilerTayfun TUNAERОценок пока нет
- Project SynopsisДокумент9 страницProject SynopsisKrishna DasОценок пока нет
- Aero Lab 5Документ10 страницAero Lab 5Inigo ArpudasamyОценок пока нет
- Technical Questions With Answers 1Документ15 страницTechnical Questions With Answers 1GnitropsОценок пока нет
- Aerofoil - Explanation, Types, Aerofoil Terminologies, Lift Coefficient 07032021Документ13 страницAerofoil - Explanation, Types, Aerofoil Terminologies, Lift Coefficient 07032021Aditya APОценок пока нет
- Aerodynamic: Prepared by Aji Hudallil MTQДокумент26 страницAerodynamic: Prepared by Aji Hudallil MTQCHAREL MAXMILLIAN LEWISОценок пока нет
- Effect of Blunted Aero-Disc On Aero-Spiked Blunt Cone-Nose at High SpeedsДокумент10 страницEffect of Blunted Aero-Disc On Aero-Spiked Blunt Cone-Nose at High SpeedsAstro BadhushaОценок пока нет
- Pof GilberthДокумент37 страницPof GilberthDarmawan Jaladri SaputraОценок пока нет
- Aerodynamics 2 Notes For All UnitДокумент44 страницыAerodynamics 2 Notes For All UnitSejal JoshiОценок пока нет
- Aerodynamics SeminarДокумент58 страницAerodynamics SeminarAntonio VilladaОценок пока нет
- DesignReport2 Grup5Документ18 страницDesignReport2 Grup5Emine YıldızОценок пока нет
- Flaps: Design and PurposeДокумент12 страницFlaps: Design and PurposedexОценок пока нет
- Drag Reduction in An AirplaneДокумент14 страницDrag Reduction in An AirplaneDhruvОценок пока нет
- Homebuilt Aircraft Drag ReductionДокумент15 страницHomebuilt Aircraft Drag ReductionYvess100% (2)
- CFD AssignmentДокумент19 страницCFD Assignmentapi-231747194Оценок пока нет
- AerodynamicsДокумент16 страницAerodynamicsSuman PalОценок пока нет
- Flow Over Delta WingДокумент6 страницFlow Over Delta WingAkash RoyОценок пока нет
- Drag DivergenceДокумент1 страницаDrag DivergenceBijin ChadayanОценок пока нет
- Aircraft General & Performance: Aerodynamic Force Created by The AerofoilДокумент49 страницAircraft General & Performance: Aerodynamic Force Created by The Aerofoilpeter stanoОценок пока нет
- Design of An Airfoil by Mathematical Modelling Using DatabaseДокумент8 страницDesign of An Airfoil by Mathematical Modelling Using DatabaseNetherlands PressОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Brake SystemДокумент3 страницыAircraft Brake SystemYadana1Оценок пока нет
- Paperwing: Name of School: National High School of Computer Science "TudorДокумент14 страницPaperwing: Name of School: National High School of Computer Science "TudorAmit SinghОценок пока нет
- Aerodynamics PDFДокумент53 страницыAerodynamics PDFRomar Aduan Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Interview For AirlineДокумент42 страницыInterview For Airlinekerem96% (27)
- Projek Sem Aku..mrsm..Документ15 страницProjek Sem Aku..mrsm..Dayang Siti Khalidah0% (1)
- Crazy Engineer Kid January 25, 2007 Science Fair Project Paper 7 Grade Sylvania Franciscan AcademyДокумент16 страницCrazy Engineer Kid January 25, 2007 Science Fair Project Paper 7 Grade Sylvania Franciscan Academydebashisneogi0% (1)
- Induced DragДокумент15 страницInduced DragPushkar KolharОценок пока нет
- B. Split FlapДокумент6 страницB. Split FlapIpsita DasОценок пока нет
- Boundary Layer, Parasitic and Induced Drag: Fundamentals of Flight NDAE-Feb06 Khaled N. Al MasriДокумент67 страницBoundary Layer, Parasitic and Induced Drag: Fundamentals of Flight NDAE-Feb06 Khaled N. Al MasriAhmed MohieddeenОценок пока нет
- Aerodynamics of Wind Turbines: Part - 3Документ37 страницAerodynamics of Wind Turbines: Part - 3John TauloОценок пока нет
- Lecture #12 Ehsan Roohi Sharif University of Technology Aerospace Engineering DepartmentДокумент21 страницаLecture #12 Ehsan Roohi Sharif University of Technology Aerospace Engineering Departmentpsycho_zahranОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4Документ21 страницаLecture 4psycho_zahranОценок пока нет
- AE 1350 Lecture Notes #6Документ16 страницAE 1350 Lecture Notes #6psycho_zahranОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ35 страницLecture 2psycho_zahranОценок пока нет
- Lecture #13 Ehsan Roohi Sharif University of Technology Aerospace Engineering DepartmentДокумент2 страницыLecture #13 Ehsan Roohi Sharif University of Technology Aerospace Engineering Departmentpsycho_zahranОценок пока нет
- 6CH07 01 Que 20130508Документ12 страниц6CH07 01 Que 20130508psycho_zahranОценок пока нет
- Biology: Edexcel GCEДокумент16 страницBiology: Edexcel GCEmuhajireenОценок пока нет
- B.SC Physics-Sllaybus 270618Документ67 страницB.SC Physics-Sllaybus 270618AryanОценок пока нет
- G8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureДокумент49 страницG8 - Light& Heat and TemperatureJhen BonОценок пока нет
- 4PH0 1PR Que 20140515Документ32 страницы4PH0 1PR Que 20140515ramexistsОценок пока нет
- Casting DefectsДокумент16 страницCasting DefectsAshok PradhanОценок пока нет
- Waves and Sound Waves PDFДокумент11 страницWaves and Sound Waves PDFSanatan KumarОценок пока нет
- Ekadhikena Purvena - Mltiplication - Vedic MathsДокумент3 страницыEkadhikena Purvena - Mltiplication - Vedic MathsSowmya Srinivasan100% (1)
- Section 1.1: Motion and Motion GraphsДокумент15 страницSection 1.1: Motion and Motion GraphsMiranda M. Y. LeungОценок пока нет
- S-Domain Circuit Analysis: Operate Directly in The S-Domain With Capacitors, Inductors and ResistorsДокумент25 страницS-Domain Circuit Analysis: Operate Directly in The S-Domain With Capacitors, Inductors and Resistorsjaspreet964Оценок пока нет
- My SVPWMprojectДокумент68 страницMy SVPWMprojectHari Reddy100% (1)
- Determination of Iron With 1,10-PhenanthrolineДокумент5 страницDetermination of Iron With 1,10-PhenanthrolineOmSilence26510% (1)
- Suggestedproblem ch12 PDFДокумент4 страницыSuggestedproblem ch12 PDFJorgeHernándezОценок пока нет
- متحدد من foxi5Документ26 страницمتحدد من foxi5Nader AlaaОценок пока нет
- An Electro Vibrocone For EvaluationДокумент10 страницAn Electro Vibrocone For EvaluationImmanuel LumbantobingОценок пока нет
- Jee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Solutions Ionic EquilibriumДокумент3 страницыJee 2014 Booklet3 HWT Solutions Ionic EquilibriumvarunkohliinОценок пока нет
- Lathe DesignДокумент11 страницLathe DesignShiyas Basheer0% (1)
- Total Length Calcs For Pipes Valves and Fittings RevAДокумент9 страницTotal Length Calcs For Pipes Valves and Fittings RevAlutfi awnОценок пока нет
- A Is Shear Stress Momentum FluxДокумент21 страницаA Is Shear Stress Momentum FluxPamela MendozaОценок пока нет
- Edexcel GCE: Chemistry (Nuffield)Документ16 страницEdexcel GCE: Chemistry (Nuffield)Danny AdonisОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Unit 1Документ7 страницChemistry Unit 1Natasha Liliane LootОценок пока нет
- Organometallic CompoundsДокумент40 страницOrganometallic CompoundsDezta Fandity' VantycaОценок пока нет
- Formation of Differential EquationДокумент5 страницFormation of Differential EquationSadek Ahmed100% (1)
- Edexcel Physics Experiment SheetsДокумент27 страницEdexcel Physics Experiment SheetsMuhammad Shafnoon Kabir100% (1)
- Dynamic Light ScatteringДокумент53 страницыDynamic Light ScatteringsonorousgОценок пока нет
- Physical Chemistry FormulasДокумент10 страницPhysical Chemistry Formulasunlucky678Оценок пока нет
- Reduction With Rieke ZincReduction With Rieke ZincДокумент3 страницыReduction With Rieke ZincReduction With Rieke ZinciramshaguftaОценок пока нет
- Lapse Rates and Stability PDFДокумент26 страницLapse Rates and Stability PDFVerra Myza AratОценок пока нет
- Bending Moment and Shear ForceДокумент13 страницBending Moment and Shear ForceYixiang TanОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Systems - Booster CoilДокумент2 страницыAircraft Systems - Booster CoilzcrackОценок пока нет
- Physics ExperimentДокумент11 страницPhysics ExperimentrashbasheerОценок пока нет
- Remote Turbine Vibration Diagnostics Service (Technical Data)Документ22 страницыRemote Turbine Vibration Diagnostics Service (Technical Data)Candra Yanuar SalehОценок пока нет