Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fretdrich Froebel Final
Загружено:
anujmeh100%(1)100% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
132 просмотров17 страницWork on Fretdrich Froebel
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документWork on Fretdrich Froebel
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(1)100% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
132 просмотров17 страницFretdrich Froebel Final
Загружено:
anujmehWork on Fretdrich Froebel
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 17
Teachings Of Educational
Philosopher Friedrich Froebel
By: Mani Mehndroo, ACERT, 2012-13.
Educational
Thought
Kindergarten
Froebels
Philosophy
of life
Understanding Froebel's
Evolution of Educational Thought
PHASE 1 Birth ,
Childhood, Early
work life & General
interests
PHASE 2
Teaching &
Educational
thought
PHASE 3 -
Kindergarten,
legacy
1782-1804
1805-1836 1837-1852
Phase 1 Growing Up
Birth
Childhood
Early
working life
Born on 21
st
April 1782 in Germany. He was brought up by his father
and stepmother, who showed little affection.
Spent much time in garden playing & exploring his surroundings,
leading to deep love & respect for nature .
At the age of 10 went to live with his maternal uncle, who was kinder
and sent him to school
At 15 learnt forestry and geometry and later worked as a forester.
At 17 enrolled at the university at Jena but despite switching
courses, found little satisfaction..
In 1804, studies architecture at Frankfurt University
Later studied mineralogy and gemmology.
Froebels Philosophy of Life
Deeply spiritual man seeing Gods hand at work everywhere in
universe
Saw patterns in nature and believed that it was possible for human
beings to experience, emulate and build on these designs.
Children could experience these patterns in kindergarten..
If man is to attain his destiny, so far as earthly development will
permit this, if he is to become truly an unbroken living unit, he must
feel and know himself to be one, not only with God and humanity but
also with nature.
Phase 2 Finding His Calling
Beginning to
teach
Developing
&
Publishing
Ideas
In 1805 joined a school in Frankfurt, based on Pestalozzis teaching,
as an educator.
In 1808 studied for 2 years at a training institute run by
Pestalozzi. Though he found the approach inspiring but thought the
concept of, Spiritual Mechanism, was missing.
Vowed to create his own type of school.
1811 -14 pursued other activities, such as studies and serving for the
Prussian army against Napoleon but he kept returning to his dream.
In 1816 founded Universal German Education Institute , for training
teachers.
In 1821, publication of "Principles, Aims and Inner Life of the
Universal German Educational Institute"
In 1826 he published his first book, The Education of Man, a
philosophical work reflecting his ideas about God, man and nature.
In 1831, was invited to Switzerland to open schools and stays for five
years
Every child possessed, at birth, his
full educational potential, and that an
appropriate educational environment
was necessary to encourage the child
to grow and develop in an optimal
manner.
Learning begins when
consciousness erupts, education
must also.
He believed that women should take
a leading role in educating small
children and therefore opened an
institute for training them for ECE.
Cultural Imposition Theory Children
should be trained to become
productive members of the larger
society so that the cultural heritage
can be preserved from generation to
generation.
Children under 7 did not attend school
Women were not expected (or often
allowed) to work professionally
His Beliefs Prevalent norms
Froebel's philosophy of education rested on four basic ideas: free self-activity,
creativity, social participation, and motor expression
Froebels Philosophy of Education
Froebels Philosophy of Education
Pillars of ECE Definition Objective Tools
Environment
Free Self-Activity Development of
qualities and skills
that make it possible
to take an invisible
idea and make it a
reality
Externalizing child's
inner nature
Play
Kindergarten
Creativity Being creative Internalizing various
concept & for
externalizing the
concept existing
within their creative
minds
Gifts &
Occupation
Kindergarten
Social Participation Harmonious social
interaction skills
Provide children with
opportunities for
interacting socially
within familiar
territory in a non-
threatening manner
Providing a
family setting
within school
environment.
Kindergarten
Motor Expression Learning by doing as
opposed to following
rote instructions.
To make sense out of
both his subjective &
objective world
Trained
educator
Kindergarten
Phase 3 The Kindergarten Movement
Kindergarte
n set up
Gifts
&
Occupation
Death ,
Legacy &
Influence
In 1837 the 1
st
Play and Activity Institute was founded by him.
In 1840 he officially coined the term Kindergarten.
In 1843 published Mutter and Koselieder, series of songs for mothers
In 1847 seven Kindergartens established in Germany.
In 1948 further forty four Kindergartens opened throughout Germany.
In 1849 begins training of kindergarten teachers.
In1851 Kindergartens were banned in Prussia for political reasons.
On 21
st
June,1852 Friedrich Froebel died, dispirited by the ban.
Spread of his philosophy & its impact on ECE at large.
Influence on role of women in education & the toys market.
Froebel designed a series of instructional materials that he called
"gifts and occupations.
Froebels Kindergarten
MeantGarden of children- The layout was not limited to class rooms but
essentially also included a strip of land, interactive gardens.
A transitional stage from home to school (Age group 3-7 years)
Knowledgeable and appropriately qualified early childhood professionals.
Parents and educator working in harmony and partnership.
Involved skilled and informed observation of children, to support effective
development, learning and teaching.
A holistic view on each childs development by laying emphasis on free
self-activity, creativity, social interaction & motor expression through play,
educational material (gifts/occupation), games, dance, songs, stories,
crafts and interaction with nature, peers, community .
Children are like tiny flowers; they are varied and need care, but each is
beautiful alone and glorious when seen in the community of peers."
The Basic Construct
Froebels Kindergarten Tools
Froebel's significant contributions to early childhood education was his
theory of introducing Play as a means of engaging children in free self-
activity for the purpose of externalizing their inner natures.
Play enlists all of child's imaginative powers, thoughts, and physical
movements and includes activities such as songs, stories, games, group
activities and use of educational material.
Starts at each stage starting from simplest activity progressing towards the
most diverse and complex form.
Supreme goal is realization of childs budding powers and continually
carries him from one plane of educational growth to another.
Play is the highest expression of human development of childhood for it
alone is the free expression of what is in the childs soul .
Theory of Play
He designed a series of educational materials, to provide children with
many stimulating activities to enhance their creativity.
A gift was an object provided for a child to play with--such as a sphere,
cube, or cylinder- which helped the child to understand and internalize the
concepts of shape, dimension, size, and their relationships. He developed
20 set of gifts.
The occupations were items such as paints and clay which the children
could use to make what they wished; through the occupations, children
externalized the concepts existing within their creative minds.
Gifts and occupations enable the child in understanding inner and outer
properties of things as he moves through the developmental stages of the
educational process.
I wish to find the right forms for awakening the higher senses of the child:
what symbol does my ball offer to him? That of unity. The ball connects
the child with nature as much as the universe connects man with God.
Gifts and Occupations
Froebels Kindergarten Tools
Froebel believed that parents provided the first as well as the most
consistent educational influence in a childs life.
Since a childs first educational experiences occur within the family unit, he
is already familiar with the home environment as well as with the
occupations carried on within this setting and tries to imitate them.
Froebel believed that providing a family setting within the school
environment would promote social interaction within familiar territory in a
non-threatening manner.
Focusing on the home environment occupations as the foundation for
beginning subject-matter content allowed the child to develop social
interaction skills that would prepare him for higher level subject-matter
content in later educational developmental stages.
The union of Family and School life is the indispensable requisite of
education .
Family Setting
Froebels Kindergarten Tools
Froebel believed that the child should learn by doing as opposed to following
rote instructions (motor expression) and allowed to grow at his own pace.
Responsible educators should strive to recognize each child's individual
level of development so that essential materials and activities, to stimulate
appropriate educational growth, can be provided.
Required skilled and informed observation of children, to support effective
development, learning and teaching.
The destiny of nations lie far more in the hands of women, the mothers than
in the possessors of power or those of innovators who for the most part do
not understand themselves. We must cultivate women, who are the
educators of the human race, else the new generation cannot accomplish its
tasks.
The Purpose of teaching is to bring more out of a man than to put more in
him.
Role of an Educator
Froebels Kindergarten Tools
An Environment which...
Is physically safe but intellectually challenging, promoting curiosity, enquiry,
sensory stimulation and aesthetic awareness.
Demonstrates the unity of indoors and outdoors, of the cultural and the
natural. Allows free access to a rich range of materials that promote open-
ended opportunities for play, representation and creativity.
Entails the setting being an integral part of the community it serves, working
in close partnership with parents and other skilled adults.
Is educative rather than merely amusing or occupying. Promotes
interdependence as well as independence, community as well as
individuality and responsibility as well as freedom
"Let us educate the senses, train the faculty of speech, the art of receiving,
storing, and expressing impressions, which is the natural gift of infants, and
we shall not need books to fill up the emptiness of our teaching until the
child is at least seven years old."
Froebels Kindergarten
Froebels Death, Legacy, Influence
Kindergarten were banned in Prussia
in 1851. They were very radical in
their time and the Prussian Govt.
linked them to the more fiery socialist
views of his cousin.
Froebel died in 1852, probably heart-
broken by the apparent failure of his
lifes work.
However his ideas had travelled far
and wide and his philosophies spread
to Europe, USA and Britain and to
the entire world where they have
survived to this day.
Influence of Froebels Philosophy on:
- ECE at large.
- Role of women in education &
- Toy market.
If three hundred years after my death my method of education shall be completely
established according to its idea, I shall rejoice in heaven."
Thanks
Вам также может понравиться
- Froebel: by Neema K I ST Year M.Ed. School of Pedagogical Science, Dharamsala, Kannur UniversityДокумент39 страницFroebel: by Neema K I ST Year M.Ed. School of Pedagogical Science, Dharamsala, Kannur Universityneema100% (2)
- Froebel ContributionДокумент11 страницFroebel ContributionCoffee's MochaОценок пока нет
- The Philosophy Behind Froebel's Kindergarten ApproachДокумент2 страницыThe Philosophy Behind Froebel's Kindergarten Approachmohanraj2purushothamОценок пока нет
- The Path To Early Math: What Preschool Teachers Need to KnowОт EverandThe Path To Early Math: What Preschool Teachers Need to KnowОценок пока нет
- Access to Life Science: Investigation Starters for Preschool, Kindergarten and the Primary GradesОт EverandAccess to Life Science: Investigation Starters for Preschool, Kindergarten and the Primary GradesОценок пока нет
- From Crisis To Tranquility: A Guide to Classroom: Management Organization and DisciplineОт EverandFrom Crisis To Tranquility: A Guide to Classroom: Management Organization and DisciplineОценок пока нет
- CMPДокумент26 страницCMPapi-404206727Оценок пока нет
- Freedom and Discipline Ruxandra GutuДокумент15 страницFreedom and Discipline Ruxandra GutuRuksichkaОценок пока нет
- Classroom PDFДокумент30 страницClassroom PDFNorhayati Yusof100% (1)
- Professional StatementДокумент7 страницProfessional Statementapi-623697645Оценок пока нет
- Urie Bronfenbrenner: Moscow Russia Ithaca New York Human EcologyДокумент2 страницыUrie Bronfenbrenner: Moscow Russia Ithaca New York Human EcologyCristyl Banaag100% (1)
- Articles MontessoriДокумент14 страницArticles MontessoriAhsan AliОценок пока нет
- Philosophy of LiteracyДокумент6 страницPhilosophy of Literacyapi-236897811Оценок пока нет
- Discipline PDFДокумент19 страницDiscipline PDFKarGarcia LuisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Approaches & CurriculumДокумент53 страницыChapter 3 Approaches & CurriculumNorina Mohamad Najib100% (1)
- Module 4 Birth and Development of Children PDFДокумент15 страницModule 4 Birth and Development of Children PDFKevin PajarilloОценок пока нет
- Article - Compare 3 Preschool ApproachesДокумент7 страницArticle - Compare 3 Preschool ApproachesTomas MongeОценок пока нет
- Neaum, S. (2016) Observing and Assessing Children's Learning and Development. London, Sage. - PDFДокумент15 страницNeaum, S. (2016) Observing and Assessing Children's Learning and Development. London, Sage. - PDFRuqiya zainabОценок пока нет
- Classroom Management ModelДокумент10 страницClassroom Management Modelapi-2848296240% (1)
- Abraham Maslow enДокумент19 страницAbraham Maslow enMenesteroso DesgraciadoОценок пока нет
- ASS Event 2-Documentation, Planning and Assessment 2Документ13 страницASS Event 2-Documentation, Planning and Assessment 2Liz LopezОценок пока нет
- Malaysia Folk Literature in Early Childhood EducationДокумент8 страницMalaysia Folk Literature in Early Childhood EducationNur Faizah RamliОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Observing and Assessing Young ChildrenДокумент16 страницChapter 6 Observing and Assessing Young ChildrenAdeeba AleesyaОценок пока нет
- Teaching Philosophy PaperДокумент8 страницTeaching Philosophy Paperapi-463766553Оценок пока нет
- Math in Early ChildhoodДокумент4 страницыMath in Early Childhoodapi-241706225100% (1)
- O'Brien, L. M. (2000) - Engaged Pedagogy - One Alternative To "Indoctrination" Into DAP. Childhood Education, 76 (5), 283-288.Документ6 страницO'Brien, L. M. (2000) - Engaged Pedagogy - One Alternative To "Indoctrination" Into DAP. Childhood Education, 76 (5), 283-288.Weiping WangОценок пока нет
- Emergent LiteracyДокумент4 страницыEmergent LiteracyMario David Mondragon LinaresОценок пока нет
- Emergent Curriculum Course FlyerДокумент1 страницаEmergent Curriculum Course Flyerjoanne_babalisОценок пока нет
- Teaching Practice: A Handbook For Student Teachers: January 2017Документ53 страницыTeaching Practice: A Handbook For Student Teachers: January 2017Hanan badran100% (1)
- ECE223.ASSIGNMENTS Children - Special.Needs PDFДокумент8 страницECE223.ASSIGNMENTS Children - Special.Needs PDFmichaelsim2020Оценок пока нет
- Spotlight On Young Children Exploring Language and Literacy ExcerptДокумент8 страницSpotlight On Young Children Exploring Language and Literacy Excerptapi-533726217Оценок пока нет
- Assessment Tool - For Primary Schools in Kenya PDFДокумент28 страницAssessment Tool - For Primary Schools in Kenya PDFArnoldОценок пока нет
- Practical LifeДокумент47 страницPractical LifeAndrea CanОценок пока нет
- Aas14 Ece13 ReviewerДокумент9 страницAas14 Ece13 ReviewerALMALYN ANDIHОценок пока нет
- Spotlight On Play 21-1Документ5 страницSpotlight On Play 21-1api-238210311Оценок пока нет
- Brain-Based Learning and Its Implication in TeachingДокумент8 страницBrain-Based Learning and Its Implication in TeachingAnonymous CwJeBCAXpОценок пока нет
- Theories of LearningДокумент13 страницTheories of Learningbasran87Оценок пока нет
- FETAC Childcare AssignmentДокумент7 страницFETAC Childcare AssignmentBenjamin TrevinoОценок пока нет
- Science in Early Childhood Classrooms Content and ProcessДокумент11 страницScience in Early Childhood Classrooms Content and Processapi-378051746Оценок пока нет
- Ers Narrative RevisedДокумент7 страницErs Narrative Revisedapi-596349166Оценок пока нет
- Nebulae 0Документ3 страницыNebulae 0delia atenaОценок пока нет
- Final Assessment Advanced Historical and Philosophical Foundation of Islamic Education PDFДокумент17 страницFinal Assessment Advanced Historical and Philosophical Foundation of Islamic Education PDFsanggeethambigai vijayakumarОценок пока нет
- Tally Event SamplingДокумент7 страницTally Event Samplingapi-237394235Оценок пока нет
- Observation Sheet-PrimaryДокумент9 страницObservation Sheet-Primaryapi-295103593Оценок пока нет
- Biography of DR Maria MontessoriДокумент9 страницBiography of DR Maria MontessoriAna Carolina VarellaОценок пока нет
- Outcomes PDFДокумент36 страницOutcomes PDFdelia atena100% (1)
- Scaffolding For ReasoningДокумент5 страницScaffolding For ReasoningMichael KingОценок пока нет
- Friedrich FroebelДокумент2 страницыFriedrich FroebelREM ROBОценок пока нет
- Creating Early Learning Environments PDFДокумент25 страницCreating Early Learning Environments PDFkrisnahОценок пока нет
- HBEC1103 - Topic 4 - Programme ModelsДокумент36 страницHBEC1103 - Topic 4 - Programme ModelsIrfan Azmil100% (1)
- Theorist Theory Implication To Education: Arthur Jensen Theory of IntelligenceДокумент30 страницTheorist Theory Implication To Education: Arthur Jensen Theory of IntelligenceNORY MAE ESCABARTE100% (1)
- Children Development Thrive - OMS 2018Документ64 страницыChildren Development Thrive - OMS 2018Esteban NollaОценок пока нет
- Create A Discipline Plan-2Документ3 страницыCreate A Discipline Plan-2api-588112218Оценок пока нет
- Reggio Emilia ProgramДокумент10 страницReggio Emilia ProgramPrince BarnalОценок пока нет
- Challenges of TeachingДокумент5 страницChallenges of TeachingJFHRamirezОценок пока нет
- Dialogic Teaching: "Talk 2 Learn, Talk 2 Think"Документ16 страницDialogic Teaching: "Talk 2 Learn, Talk 2 Think"3alliumcourtОценок пока нет
- The Roadmap For Innovating Sarawak Educational LandscapeДокумент5 страницThe Roadmap For Innovating Sarawak Educational Landscapebrenda nyapusОценок пока нет
- Traits of The TeachersДокумент1 страницаTraits of The TeachersZonllam Aryl DialorОценок пока нет
- Anecdotal Record KohlmannДокумент3 страницыAnecdotal Record Kohlmannapi-247068331Оценок пока нет
- Friedrich FroebelДокумент17 страницFriedrich Froebelanujmeh67% (3)
- Planetary Influences On Human Affairs by BV RamanДокумент107 страницPlanetary Influences On Human Affairs by BV Ramanattikka88% (17)
- Hora (D-2) ChartДокумент9 страницHora (D-2) ChartVisti Larsen100% (9)
- Pitru DoshДокумент12 страницPitru DoshRahul K Mistry83% (6)
- IshtadevataДокумент17 страницIshtadevataVedskeTajne VedicSecrets100% (1)
- Amsa Lords D-60Документ2 страницыAmsa Lords D-60anujmehОценок пока нет
- American Express: HR Policies and Practices of The CompanyДокумент13 страницAmerican Express: HR Policies and Practices of The CompanySachin NakadeОценок пока нет
- Peace Corps Training For Resiliency: Staff and Volunteer Modules and ResourcesДокумент223 страницыPeace Corps Training For Resiliency: Staff and Volunteer Modules and ResourcesAccessible Journal Media: Peace Corps Documents100% (1)
- Should Students Consider Taking A Gap Year Before Starting UniversityДокумент20 страницShould Students Consider Taking A Gap Year Before Starting Universityzahra321Оценок пока нет
- Science Lesson Plan SampleДокумент13 страницScience Lesson Plan SamplePritipriyaОценок пока нет
- Pooja Raut Resume - Java DeveloperДокумент3 страницыPooja Raut Resume - Java DeveloperVaibhav PahuneОценок пока нет
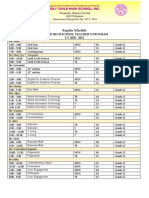
- Regular Schedule For Senior HighДокумент4 страницыRegular Schedule For Senior HighCecille IdjaoОценок пока нет
- Basketball Skills Assessment Tests (BSAT) : DribblingДокумент3 страницыBasketball Skills Assessment Tests (BSAT) : DribblingPatricia QuiloОценок пока нет
- Perrotta Et Al 2022 - Consulation For The 2023 GEM Report On Technology and EducationДокумент17 страницPerrotta Et Al 2022 - Consulation For The 2023 GEM Report On Technology and EducationT AlencastroОценок пока нет
- 2016 Tesol Convention Full Program PDFДокумент268 страниц2016 Tesol Convention Full Program PDFscribdnikolett100% (1)
- COT 1 Plate Boundaries Science 10Документ6 страницCOT 1 Plate Boundaries Science 10Christy Rose VelascoОценок пока нет
- Mercer TalentSIMДокумент3 страницыMercer TalentSIMJelenaMiloševićОценок пока нет
- Parenting A Teen Girl: A Crash Course On Conflict, Communication & Connection With Your Teenage DaughterДокумент11 страницParenting A Teen Girl: A Crash Course On Conflict, Communication & Connection With Your Teenage DaughterNew Harbinger Publications100% (6)
- Cst-Grpi Model - Group 1Документ14 страницCst-Grpi Model - Group 1gtgsscvwОценок пока нет
- 1machine Learning With PythonДокумент12 страниц1machine Learning With PythonAmbika ThakurОценок пока нет
- Project Appendix Freud's Use of The Concept of Regression, Appendix A To Project For A Scientific PsychologyДокумент2 страницыProject Appendix Freud's Use of The Concept of Regression, Appendix A To Project For A Scientific PsychologybrthstОценок пока нет
- Law Student Government: Ateneo de Naga UniversityДокумент1 страницаLaw Student Government: Ateneo de Naga UniversityFbarrsОценок пока нет
- Basic English Dialogs Valentines DayДокумент3 страницыBasic English Dialogs Valentines DaychuantillyОценок пока нет
- Nav BR LP Pre b08 1 GRДокумент2 страницыNav BR LP Pre b08 1 GRJessy FarroñayОценок пока нет
- ML0101EN Clas Decision Trees Drug Py v1Документ5 страницML0101EN Clas Decision Trees Drug Py v1Rajat SolankiОценок пока нет
- EE2001 Circuit Analysis - OBTLДокумент7 страницEE2001 Circuit Analysis - OBTLAaron TanОценок пока нет
- Behaviorally Anchored Rating ScalesДокумент6 страницBehaviorally Anchored Rating Scalesmanoj2828Оценок пока нет
- Lesson X Selecting Instructional MaterialsДокумент18 страницLesson X Selecting Instructional MaterialsLarah Joy BasitОценок пока нет
- AEJ Special Edition December 2016 TESOL Indonesia Conference Volume 5Документ218 страницAEJ Special Edition December 2016 TESOL Indonesia Conference Volume 5BimaОценок пока нет
- Rubrics For Skit or Role PlayДокумент1 страницаRubrics For Skit or Role PlayGheyDelaCueva50% (2)
- English 8: First Monthly ExaminationДокумент2 страницыEnglish 8: First Monthly ExaminationFloramie MorenoОценок пока нет
- Writing The Précis: English For Academic and Professional PurposesДокумент10 страницWriting The Précis: English For Academic and Professional PurposesDengDengОценок пока нет
- Invincible Magazine Sep 2018Документ6 страницInvincible Magazine Sep 2018Shubham MishraОценок пока нет
- FIRO Element BДокумент19 страницFIRO Element Bnitin21822Оценок пока нет
- School Geometry III IV HallДокумент140 страницSchool Geometry III IV HallKirti Chhaya50% (2)
- Social Ethical ResponsibilitiesДокумент16 страницSocial Ethical ResponsibilitiesRenz Daniel R. ElmidoОценок пока нет