Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Enzymes Explained: How They Work and Their Importance
Загружено:
Thana Segar0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров27 страницbiology
Оригинальное название
Enzymes What Are They 2
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документbiology
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров27 страницEnzymes Explained: How They Work and Their Importance
Загружено:
Thana Segarbiology
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 27
Enzymes
Learning objective: to examine what enzymes are and
describe how they work.
16
th
October
Enzymes
What are they?
Why do we need them?
Name some examples ?
Enzymes
Globular proteins that catalyse chemical reactions in living organisms
Properties
Enzymes
Globular proteins that catalyse chemical reactions in living organisms
Properties
Specific
Enzymes
Globular proteins that catalyse chemical reactions in living organisms
Properties
Specific
Increase rate of the reaction
Enzymes
Globular proteins that catalyse chemical reactions in living organisms
Properties
Specific
Increase rate of the reaction
Unchanged at the end of the reaction
Enzymes
Globular proteins that catalyse chemical reactions in living organisms
Properties
Specific
Increase rate of the reaction
Unchanged at the end of the reaction
Need them
Enzymes
Globular proteins that catalyse chemical reactions in living organisms
Properties
Specific
Increase rate of the reaction
Unchanged at the end of the reaction
Need them
Reactions too slow to maintain life
Cant increase temperatures/pressure in cells (fatal)
Enzymes Are Proteins
The enzyme binds to the substrates by its active site
The active site is a pocket formed by the folding of the protein
where the substrates bind.
Enzymes Are Proteins
The enzyme binds to the substrates by its active site
The active site is a pocket formed by the folding of the protein
where the substrates bind.
Active site
The active site involves a small number of key residues that actually bind the
substrates
The rest of the protein structure is needed to maintain these residues in position
How do enzymes work?
An Example
An Example
Sucrose + H
2
O
Glucose + Fructose
An Example
Sucrose + H
2
O
Glucose + Fructose
Substrates
Products
For a reaction to occur the sucrose
and water would have to collide with
enough energy to break and form bonds
For a reaction to occur the sucrose
and water would have to collide with
enough energy to break and form bonds
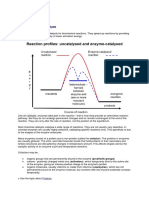
This is the activation energy
Sucrose + H
2
O Glucose + Fructose
+
+
Substrates Products
Energy
Progress of reaction
Energy
Progress of reaction
Substrates
Energy
Progress of reaction
Substrates
Products
Energy
Progress of reaction
Substrates
Products
High energy
intermediate
Energy
Progress of reaction
Substrates
Products
High energy
intermediate
Activation energy
The minimum amount of energy needed to start
the reaction, leading to the formation of a high
energy intermediate
= The Activation energy
Energy
Progress of reaction
Substrates
Products
High energy
intermediate
Activation energy
Enzymes reduce the
height of the energy
barrier
Questions
1. Write a definition for the following: Active Site
Substrate
Products
2. Explain how the structure of the protein is linked to its ability to act
as an enzyme?
3. How does heating a mixture increase the chance that a chemical reaction
Will occur? Why cant this approach be used in cells?
4. Write a paragraph in your own words describing how enzymes act as
catalysts by lowering activation energy.
Read page 57-60
This powerpoint was kindly donated to
www.worldofteaching.com
http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a
thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a
completely free site and requires no registration. Please
visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.
Вам также может понравиться
- Enzymes: Learning Objective: To Examine What Enzymes Are andДокумент27 страницEnzymes: Learning Objective: To Examine What Enzymes Are andCarl Agape DavisОценок пока нет
- Biology Coursework Enzymes PHДокумент5 страницBiology Coursework Enzymes PHkllnmfajd100% (2)
- Gen BioДокумент35 страницGen Biomikechristian073Оценок пока нет
- Enzymes PDFДокумент4 страницыEnzymes PDFrasha nada100% (1)
- General Biology: Peralta III Edwin C. STEM-GalileoДокумент10 страницGeneral Biology: Peralta III Edwin C. STEM-GalileoSavage CabbageОценок пока нет
- EnzymesДокумент14 страницEnzymesshivani.shahОценок пока нет
- Bio Sem 1Документ123 страницыBio Sem 1HALFAH BT HASSANОценок пока нет
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade 9 5. Enzymes NotesДокумент43 страницыAlwadi International School Biology Grade 9 5. Enzymes NotesMohammed HelmyОценок пока нет
- Notes #5 - EnzymesKey CleanДокумент10 страницNotes #5 - EnzymesKey CleanLanz MoenОценок пока нет
- Biology CH 6Документ8 страницBiology CH 6jalalОценок пока нет
- 5.2 EnzymesДокумент22 страницы5.2 EnzymesShehbaaz SinghОценок пока нет
- AP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersДокумент12 страницAP BIO Febraury Break With AnswersMehak BectorОценок пока нет
- Enzyme ChemistryДокумент9 страницEnzyme ChemistryVictor OmoloОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Speed Up Reactions (StudentДокумент5 страницEnzymes Speed Up Reactions (StudentsushantОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Документ26 страницEnzyme Kinetics and Applications (Part 1a: Kinetics of Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions)Nur AishaОценок пока нет
- Enzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting ActivityДокумент5 страницEnzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting Activitytiyf mojaleedОценок пока нет
- Week 7 GenBio 1Документ4 страницыWeek 7 GenBio 1.....Оценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesДокумент10 страницBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadОценок пока нет
- Study Guide Key 2.4Документ6 страницStudy Guide Key 2.4Andrea HernandezОценок пока нет
- AP Biology Lab-11Документ22 страницыAP Biology Lab-11ldlewisОценок пока нет
- Enzymes and The Active SiteДокумент23 страницыEnzymes and The Active SiteLaura GambaОценок пока нет
- 1. Enzyme2. Active site 3. Enzyme-substrate complex4. CatalystДокумент10 страниц1. Enzyme2. Active site 3. Enzyme-substrate complex4. CatalystNushrat KaziОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Chapter: Key Concepts and MechanismsДокумент11 страницEnzymes Chapter: Key Concepts and MechanismsChong HyenОценок пока нет
- Describing the Components of EnzymesДокумент4 страницыDescribing the Components of EnzymesEZRA THERESE DE JESUSОценок пока нет
- EnzymesДокумент5 страницEnzymeseyosiyas tekleweyinОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Lab: Investigating Factors that Impact Reaction RateДокумент15 страницEnzyme Lab: Investigating Factors that Impact Reaction RateAshalee JonesОценок пока нет
- Enzymes (Bio Chem) : Mariano Marcos State University College of Teacher Education Laoag CityДокумент34 страницыEnzymes (Bio Chem) : Mariano Marcos State University College of Teacher Education Laoag CityJared TabangcuraОценок пока нет
- Flashcards - Topic 5 Enzymes - CAIE Biology IGCSEДокумент25 страницFlashcards - Topic 5 Enzymes - CAIE Biology IGCSEJane LeaОценок пока нет
- Enzymes: by Nura Malahayati THP-FP UnsriДокумент71 страницаEnzymes: by Nura Malahayati THP-FP UnsriIkhsan muttaqinОценок пока нет
- S.5 EnzymesДокумент16 страницS.5 Enzymesmusokelukia6Оценок пока нет
- GCSE EnzymesДокумент32 страницыGCSE EnzymesFrankie BarnesОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Chapter SummaryДокумент8 страницEnzyme Chapter Summarythanks btОценок пока нет
- BIO 11 Lab 02 2004 Enz. Copy - DoДокумент10 страницBIO 11 Lab 02 2004 Enz. Copy - DoKizzy Anne Boatswain CarbonОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Are Proteins A Definitive Guide of 4000+ Words (Updated)Документ15 страницEnzymes Are Proteins A Definitive Guide of 4000+ Words (Updated)mammmmОценок пока нет
- Enzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanДокумент11 страницEnzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanRabia KhalilОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Functions ModelsДокумент43 страницыEnzymes Functions ModelsMaryAnn LasacaОценок пока нет
- Cell Bio Chapter 6Документ32 страницыCell Bio Chapter 6GuteОценок пока нет
- ENZYMES - AGRI 501.final2 BeshДокумент60 страницENZYMES - AGRI 501.final2 BeshIvan Jhon AnamОценок пока нет
- Bio-Ch 5-EnzymesДокумент6 страницBio-Ch 5-EnzymesHassan RiazОценок пока нет
- BIO C5 NOTESДокумент11 страницBIO C5 NOTESTHEN YUE PINGОценок пока нет
- 4.0 CHPT 4 - Enzymes and The Regulation of Biochemical PathwaysДокумент41 страница4.0 CHPT 4 - Enzymes and The Regulation of Biochemical PathwaysshinymaterialsОценок пока нет
- Enzymes ...Документ13 страницEnzymes ...Glen MangaliОценок пока нет
- Biology ProjectДокумент41 страницаBiology ProjectGanesan Siva67% (12)
- Enzymes as biological catalysts (E:BCДокумент6 страницEnzymes as biological catalysts (E:BCelena piovesanОценок пока нет
- Enzyme kinetics and applications overviewДокумент63 страницыEnzyme kinetics and applications overviewNur AishaОценок пока нет
- Cellular MetabolismДокумент65 страницCellular Metabolismjasmeen.kaur8105Оценок пока нет
- Enzymes Virtual LabДокумент4 страницыEnzymes Virtual Labapi-34000547527% (11)
- Lecture On EnzymesДокумент26 страницLecture On EnzymesDAVIE MATIASОценок пока нет
- Grade 10 Biology Sec.2.4Документ33 страницыGrade 10 Biology Sec.2.4zakaria AlshurmanОценок пока нет
- enzymesДокумент5 страницenzymeskhadija92sara32Оценок пока нет
- EnzymesДокумент5 страницEnzymesjaiОценок пока нет
- Enzymes: Anushree ChaturvediДокумент39 страницEnzymes: Anushree ChaturvediDeepal ShahОценок пока нет
- Enzyme ReviewДокумент7 страницEnzyme Reviewsmbdy tbhhhОценок пока нет
- C9e Answers Active Reading 08Документ7 страницC9e Answers Active Reading 08melissa_chow_1100% (6)
- Bio Investigatory (Study of Enzymes) - 3Документ18 страницBio Investigatory (Study of Enzymes) - 3Deepa SinghОценок пока нет
- Unit 6: Enzymes: Image Modified From " ," by Openstax College, BiologyДокумент4 страницыUnit 6: Enzymes: Image Modified From " ," by Openstax College, BiologyAbraham BanjoОценок пока нет
- Enzymes: Function, Structure, and Factors Affecting ActivityДокумент5 страницEnzymes: Function, Structure, and Factors Affecting ActivitySameer ButtОценок пока нет
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Biology Hot Spot Topics & SPM 2017 Set 1Документ1 страницаBiology Hot Spot Topics & SPM 2017 Set 1Thana Segar100% (1)
- Presentation 1Документ9 страницPresentation 1Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Introducing Science - An OverviewДокумент20 страницIntroducing Science - An OverviewwshopОценок пока нет
- Biology & ChemistryДокумент1 страницаBiology & ChemistryThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Sains Standard 6Документ16 страницSains Standard 6Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Chemi SeminarДокумент5 страницChemi SeminarThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Answering TechДокумент17 страницAnswering TechChiYenОценок пока нет
- Maths KidsДокумент14 страницMaths KidsThana SegarОценок пока нет
- CongratulationsДокумент1 страницаCongratulationsThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Maths Kids 2Документ19 страницMaths Kids 2Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Science Year 5Документ28 страницScience Year 5Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Sains Standard 6Документ16 страницSains Standard 6Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Physic Paper 1Документ16 страницPhysic Paper 1Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Blood SugarДокумент16 страницBlood SugarCarl Agape DavisОценок пока нет
- Science Year 5Документ28 страницScience Year 5Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Notes 1Документ1 страницаNotes 1Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Free FallingДокумент1 страницаFree FallingThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Enzymes Models of Action 2Документ29 страницEnzymes Models of Action 2Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- AДокумент2 страницыAThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Global WarmingДокумент1 страницаGlobal WarmingThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Seminar Biology SPMДокумент10 страницSeminar Biology SPMThana Segar100% (2)
- Enzymes and Digestion 2Документ14 страницEnzymes and Digestion 2Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Definition N Factors 2Документ27 страницDefinition N Factors 2Thana SegarОценок пока нет
- Global ExpansionДокумент1 страницаGlobal ExpansionThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Const Ruct Sample Answer Proble M Statem Ent Hypot Hesis Varia Bles List of Appar Atus and Materi Als Exper Iment Al Proce DureДокумент2 страницыConst Ruct Sample Answer Proble M Statem Ent Hypot Hesis Varia Bles List of Appar Atus and Materi Als Exper Iment Al Proce DureThana SegarОценок пока нет
- ExcercisesДокумент2 страницыExcercisesThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Const Ruct Sample Answer Proble M Statem Ent Hypot Hesis Varia Bles List of Appar Atus and Materi Als Exper Iment Al Proce DureДокумент2 страницыConst Ruct Sample Answer Proble M Statem Ent Hypot Hesis Varia Bles List of Appar Atus and Materi Als Exper Iment Al Proce DureThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Notes of MicroorganismsДокумент1 страницаNotes of MicroorganismsThana SegarОценок пока нет
- Paper 2 and 3 Teknik Menjawab Biology SPMДокумент5 страницPaper 2 and 3 Teknik Menjawab Biology SPMJaafar HzОценок пока нет
- Centre of Mass ProblemsДокумент10 страницCentre of Mass ProblemsazsaОценок пока нет
- Pe Unit2Документ2 страницыPe Unit2srikaanth06Оценок пока нет
- Speed Control of Brushless DC Motor Using Conventional ControllersДокумент9 страницSpeed Control of Brushless DC Motor Using Conventional ControllersMuhdnursalam ZolkepliОценок пока нет
- Abcdef Ghijkl Mnopq Rstuv Wxyz Alphabet Backpack Book Bookcase CalculatorДокумент4 страницыAbcdef Ghijkl Mnopq Rstuv Wxyz Alphabet Backpack Book Bookcase Calculatornutka88Оценок пока нет
- E-STATEMENT Emirates Bank International/eStatements/E-STATEMENT 0215827741601 06 APR 2023 1601 MRETL 06-04-2023 PDFДокумент12 страницE-STATEMENT Emirates Bank International/eStatements/E-STATEMENT 0215827741601 06 APR 2023 1601 MRETL 06-04-2023 PDFShanish JobОценок пока нет
- Research Instruments SamplesДокумент29 страницResearch Instruments SamplesJUNRIL BUTALОценок пока нет
- Sample of Med CertДокумент1 страницаSample of Med CertRegineDagumanFuellasОценок пока нет
- Mutual FundДокумент40 страницMutual Fundn kОценок пока нет
- Archana PriyadarshiniДокумент7 страницArchana PriyadarshiniJagriti KumariОценок пока нет
- DCIT 21 & ITECH 50 (John Zedrick Iglesia)Документ3 страницыDCIT 21 & ITECH 50 (John Zedrick Iglesia)Zed Deguzman100% (1)
- SeminarДокумент30 страницSeminarRahul prajapatiОценок пока нет
- Sales & Distribution Management Presentation NewДокумент35 страницSales & Distribution Management Presentation NewVivek Sinha0% (1)
- EHV AC Transmission System Design and AnalysisДокумент104 страницыEHV AC Transmission System Design and Analysispraveenmande100% (1)
- Wi-Fi Planning and Design Questionnaire 2.0Документ12 страницWi-Fi Planning and Design Questionnaire 2.0Free Space67% (3)
- Solid Waste Management Center RevisedДокумент44 страницыSolid Waste Management Center RevisedPrimo Ernesto CanoyОценок пока нет
- Green Schools Project LAC PlanДокумент2 страницыGreen Schools Project LAC PlanJolly Mar Tabbaban Mangilaya100% (1)
- Experiment 1 Tensile Testing (Universal Tester) : RD THДокумент23 страницыExperiment 1 Tensile Testing (Universal Tester) : RD THShangkaran RadakrishnanОценок пока нет
- Biomed Part-B QuestionsДокумент4 страницыBiomed Part-B QuestionsNirmal KumarОценок пока нет
- Neotextil 8: Installation and Activation GuideДокумент21 страницаNeotextil 8: Installation and Activation GuideRamesh PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- 2022 Australian Grand Prix - Race Director's Event NotesДокумент5 страниц2022 Australian Grand Prix - Race Director's Event NotesEduard De Ribot SanchezОценок пока нет
- Magnesium Alloy Anodes For Cathodic ProtectionДокумент2 страницыMagnesium Alloy Anodes For Cathodic Protectiongautam100% (1)
- Journal Pre-Proof: Crop ProtectionДокумент34 страницыJournal Pre-Proof: Crop ProtectionKenan YılmazОценок пока нет
- Wa0000.Документ6 страницWa0000.Sanuri YasaraОценок пока нет
- Rail Section As Per IrsДокумент6 страницRail Section As Per IrskarnagaОценок пока нет
- Site Handover and Completion FormДокумент3 страницыSite Handover and Completion FormBaye SeyoumОценок пока нет
- Getting More Effective: Branch Managers As ExecutivesДокумент38 страницGetting More Effective: Branch Managers As ExecutivesLubna SiddiqiОценок пока нет
- Tanbin Chowdhury ResumeДокумент2 страницыTanbin Chowdhury ResumeTanbin RafeeОценок пока нет
- Parasitosis TCMДокумент277 страницParasitosis TCMRoberto Biglia100% (2)
- Monroes Motivated Sequence LessonДокумент3 страницыMonroes Motivated Sequence Lessonapi-257123630Оценок пока нет
- Parallel Merge Sort With MPIДокумент12 страницParallel Merge Sort With MPIIrsa kanwallОценок пока нет