Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Classified - Internal Use
Загружено:
Nandha Kumar0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
78 просмотров18 страницThe document discusses water treatment processes for a soft drink industry. It states that water is obtained from municipal supplies or borewells, with municipal water undergoing softening, coagulation, filtration, chlorination and pH adjustment. However, municipal water is only meant to be potable, not suitable for soft drink production. The document then provides details about various water treatment steps including coagulation, filtration using processes like pressure sand filtration and activated carbon filtration, as well as disinfection using UV and chlorine. It also lists specifications for treated water and soft water.
Исходное описание:
wt
Оригинальное название
WTP[1]
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document discusses water treatment processes for a soft drink industry. It states that water is obtained from municipal supplies or borewells, with municipal water undergoing softening, coagulation, filtration, chlorination and pH adjustment. However, municipal water is only meant to be potable, not suitable for soft drink production. The document then provides details about various water treatment steps including coagulation, filtration using processes like pressure sand filtration and activated carbon filtration, as well as disinfection using UV and chlorine. It also lists specifications for treated water and soft water.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
78 просмотров18 страницClassified - Internal Use
Загружено:
Nandha KumarThe document discusses water treatment processes for a soft drink industry. It states that water is obtained from municipal supplies or borewells, with municipal water undergoing softening, coagulation, filtration, chlorination and pH adjustment. However, municipal water is only meant to be potable, not suitable for soft drink production. The document then provides details about various water treatment steps including coagulation, filtration using processes like pressure sand filtration and activated carbon filtration, as well as disinfection using UV and chlorine. It also lists specifications for treated water and soft water.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 18
Classified - Internal use
Water constitutes of about 90% of our beverage. The Source of water
to soft drink industry is usually derived either from a municipal
supply or from a borewell. Water obtained from a municipal supply
will generally have undergone some form of treatment, such as
softening, coagulation, filtration, chlorination, and/or pH
adjustment. However, the main objective of the municipality is to
provide potable water that is safe for drinking. Potable water is
not necessarily suitable for the production of soft drinks.
Classified - Internal use
Resources
Our main sources are
1) KIADB
2) BOREWELL
3) RAIN WATER
Classified - Internal use
Basic Functions Involved
Water Storage
Coagulation
P S F
ACF
LLACF
UV
Micron Filters
Classified - Internal use
Coagulation
Tank
Raw Water
Water Treatment :Treated Water Line
Max Drawing Limit:
2500 KL/Day.
Capacity:
160m3/ hr
3-5 ppm of
Cl2 Content
Clear Water
Tank(75 kl)
Pressurized
Sand Filter
(50M
3
/Hr)
Dosing of Lime,
Ca-Hypochlorite
and Ferrous Sulfate
Process Water
Storage Tank
335 kl Capacity
ACF
80M
3
/hr
CO
2
Lead
ACF
Lag
ACF
5
Micron
Filter
3
UV
Storage
tank
UV
SYS
U.F
1
Micron
Filter
Line and
syrup
system
Classified - Internal use
Water Treatment :Soft Water Line
Chlorinated
Soft Water
75 KL
UnChlorinated
Soft Water
20 KL
2-3 ppm
Cl
2
Dosing
Raw Water Tank
3-5 ppm Cl
2
Pressurized
Sand Filter
ACF
Softner
Classified - Internal use
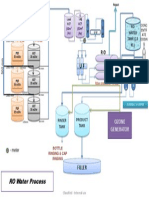
RO Water Line
Raw Water
Tank
PSF
ACF
LEAD
ACF
LAG
ACF
5
Micron
Filter
U.V
Chamber
Ultra-
Filter
R.O
Ro
Water
Storage
Kinley Water Line
Classified - Internal use
Definitions & Abbreviations:
Raw Water:
Source water obtained from Borewells or External supply (KIADB)
Treated water:
Water that subjected is to multiple barrier treatment processed and meets
all the specifications of the company.
Treated water must meet the physical, chemical and microbiological
requirements of Treated Water Specifications and Monitoring or local regulations,
whichever is more stringent.
Chlorinated Soft water:
Water having a low concentration of Calcium and Magnesium ions
(Total Hardness < 100 mg/l as CaCO3) is called Soft Water and water which
contains 1 to 3
ppm of free chlorine is called chlorinated soft water.
Classified - Internal use
Classified - Internal use
Unchlorinated soft water:
Water having a low concentration of
calcium and Magnesium ions (Total Hardness < 100
mg/l as CaCO3) is called Soft Water and Water that
contains no free chlorine is called Unchlorinated
Soft Water.
Water Filtration:
Water filtration is defined as the separation
of suspended matter from water by passage through
porous media.
Coagulation /Flocculatuon:Coagulation is the
process of forming small, sticky particles through the
addition of a coagulant to the water. There are
certain soluble chemical compounds (e.g., aluminum
sulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric sulfate, and ferric
chloride) which are soluble when in concentrated
solution, but which form precipitates of insoluble
gelatinous particles when diluted with a large volume
of water.
Classified - Internal use
Coagulation /Flocculatuon:Coagulation is the
process of forming small, sticky particles through the
addition of a coagulant to the water. There are
certain soluble chemical compounds (e.g., aluminum
sulfate, ferrous sulfate, ferric sulfate, and ferric
chloride) which are soluble when in concentrated
solution, but which form precipitates of insoluble
gelatinous particles when diluted with a large volume
of water.
Chemicals used in Coagulation
The Chemicals used in Coagulation are ,
Lime, Ca Hypochlorite, and Ferrous Sulphate.
The main function of lime is reduce total alkalinity to
less than 85 mg/lt by converting Bi-Carbonates to
insoluble Carbontes.
Ca Hypochlorite is used as a disinfectant and oxidise
organic matter.
Ferrous Sulfate is used as a Coagulant which forms
floc Fe(OH)
3
which entraps all insoluble carbonates and
settles down to bottom.
Classified - Internal use
Process Of Water Treatment
Raw water flows into the coagulation tank along with
chemicals lime, Ca hypochlorite and Ferrous Sulfate . The
design of the coagulation tank is such that water has a
total time of two and half hours reaction & contact time.
The water then flows into the clear water tank. The water
then passes through PSF and after dosing of CO
2
(To
reduce pH of treated water) passes to Process water tank.
From process water tank water passes through series of
activated carbon filters such as DACF, Lead ACF, Lag
ACF
.
Then water passes through, 5 Polisher , UV
chamber, 3 before going to respective lines.
Classified - Internal use
Classified - Internal use
PSF: Pressurized Sand Filter:
Water filtration is defined as the separation
of suspended matter from water by passage through
porous media. Pressurized Sand Filters designed to
operate under pressure and using Silica sand as the porous
media are usually termed as pressure sand filters.
ACF: Activated Carbon Filter:
Water is purified in Activated Carbon Filter by
a mechanism called Adsorption to remove
Off Taste causing compounds
Odor Causing compounds
Undesirable Organic Compounds such as THMs and
certain pesticides
Chlorine in final Treated Water
.
Classified - Internal use
LLACF: Lead & Lag Activated carbon filter:
It is another series of filter next to the
Carbon filter; LLACF contains finely Granular Activated
carbon of Coal-based Carbon with 12 x 40 grade; is
filled, this carbon has better Kinetics and Isotherms
adsorption. In this filter water coming from top to
bottom.
UV lights:
The UV light treatment unit is a unit
installed after LLACF kept in a horizontal position
sheltered with ample ventilation, ambient temperatures
surrounding i.e., the unit should be in between 350F
(20C) and 1100F (430C). The UV treatment chamber is
comprised of multi-lamp cylinders
Raw Water Analysis
Classified - Internal use
1 Total alkalinity (M)
2 Alkalinity at the phenolphthalein end point (P)
3 Total hardness (TH)
4 Calcium hardness (CaH)
5 pH
6 Chlorine demand (to break-point)
7 Chlorides
8 Sulfates
9 Total dissolved solids (TDS)
Classified - Internal use
Following are the Specifications of the
Treated water
Must be considered as potable by the local health
authorities
Turbidity (N T U) <0.5 NTU
Ph 6.5 to 8.5
Alkalinity (M as CaCO3) <85mg/L
Total chlorine 0.0mg/L
Chlorides (as NaCl) < 250 mg/L
Sulfates (as SO4 ion ) < 250 mg/L
Total dissolved solids (TDS) < 500 mg/L
Total hardness (as CaCO3) < 100 mg/L
Iron <0.1mg/L
Taste No off taste
Odor/Appearance None
Trihalomethanes (THM) Below 100 ppb
Microbiological:
Coliform count 0/100 mL
Total Count <25 /mL
Classified - Internal use
Soft water Specifications:
Total Hardness (as CaCO3) <100 mg/L
Calcium Hardness (as CaCO3) <100 mg/L
Taste No off taste (NOT)
Odor / Appearance
No-off-odor/ Clear
(NOO)
Turbidity (N T U) <0.5 NTU
pH 6.5 to 8.5
Alkalinity (M as CaCO3) <85 mg/L
Rsiduel chlorine 1-3 mg/L
Chlorides (as NaCl) < 250 mg/L
Sulfates (as SO4 ion ) < 250 mg/L
Total dissolved solids (TDS) < 500 mg/L
Iron <0.1mg/L
Classified - Internal use
Вам также может понравиться
- Chapter 1 Sem 2021Документ136 страницChapter 1 Sem 2021ascasОценок пока нет
- Nptel Lecture On WaterДокумент32 страницыNptel Lecture On WaterNani TirumalasettiОценок пока нет
- SEV455 Assignment 1A-BusikuДокумент7 страницSEV455 Assignment 1A-BusikuBusiku SilengaОценок пока нет
- Ground B Sec Group 1Документ23 страницыGround B Sec Group 1FraolОценок пока нет
- CE6315 - Water Quality Parameters - Significance - StandardsДокумент28 страницCE6315 - Water Quality Parameters - Significance - StandardsFabliha AnberОценок пока нет
- Environmental Engineering Solutions GuideДокумент16 страницEnvironmental Engineering Solutions GuideSheila Isadru0% (1)
- CHAPTER 4 - Result and AnalysisДокумент4 страницыCHAPTER 4 - Result and AnalysisNur Hadirah Afiqah Binti Abdul RazakОценок пока нет
- 1.85 Water and Wastewater Treatment Engineering Homework 3Документ1 страница1.85 Water and Wastewater Treatment Engineering Homework 3MuhammadUsmanОценок пока нет
- Final BFC 32403 Sem 1 2013 14 - SCHEMEДокумент16 страницFinal BFC 32403 Sem 1 2013 14 - SCHEMEtashadzureenОценок пока нет
- Ecw331 Chapter 10 FinalДокумент34 страницыEcw331 Chapter 10 FinalNaqib KamarozamanОценок пока нет
- Exp 3 Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand CODДокумент29 страницExp 3 Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand CODMohamad Ridhwan Bin ZahriОценок пока нет
- HANNA General Catalog v28 Chapter12 TurbidityДокумент20 страницHANNA General Catalog v28 Chapter12 TurbidityOrtomet_SAОценок пока нет
- Final Exam - BTE 3620 Sem I 0910Документ7 страницFinal Exam - BTE 3620 Sem I 0910areeb_hussainОценок пока нет
- ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING-1Документ22 страницыENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING-1KhanОценок пока нет
- Cive3223 5 2014 2Документ4 страницыCive3223 5 2014 2Yannick HowОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 - Water and Its Treatment PDFДокумент7 страницLecture 1 - Water and Its Treatment PDFcIBIM29Оценок пока нет
- CE408 2019 Students Handout PDFДокумент92 страницыCE408 2019 Students Handout PDFClive N HoveОценок пока нет
- Application of Water Quality Index To Assess The Potability of Some Domestic Water Supply Sources in Mubi North Nigeria IJERTV9IS080335 PDFДокумент13 страницApplication of Water Quality Index To Assess The Potability of Some Domestic Water Supply Sources in Mubi North Nigeria IJERTV9IS080335 PDFHyellamada DanielОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Sem 2020Документ136 страницChapter 1 Sem 2020Zahirah SaffriОценок пока нет
- Closed Conduit Water SupplyДокумент12 страницClosed Conduit Water Supplyanil_ajinkya100% (4)
- CE-15-A Civil Engineering Question PaperДокумент16 страницCE-15-A Civil Engineering Question PapersanuОценок пока нет
- Cive3223 5 2015 2Документ4 страницыCive3223 5 2015 2Yannick HowОценок пока нет
- Introduction To WSSДокумент31 страницаIntroduction To WSSAbdulRahmanshaheenОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Structure Handout (Complete)Документ137 страницHydraulic Structure Handout (Complete)Abdanur JihadОценок пока нет
- Water TreatmentДокумент29 страницWater TreatmentSubhamay BarmanОценок пока нет
- 02 Overview of Drinking Water TreatmentДокумент36 страниц02 Overview of Drinking Water TreatmentCharlie CB PortnerОценок пока нет
- Water Treatment Process: Malla Reddy Institute of Technology & ScienceДокумент12 страницWater Treatment Process: Malla Reddy Institute of Technology & ScienceGopi KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Water Supply EngineeringДокумент2 страницыWater Supply EngineeringsushilОценок пока нет
- Unit II 2 Environmental Engineering IДокумент47 страницUnit II 2 Environmental Engineering ISushmita ShrutiОценок пока нет
- Water Treatment Processes: Disinfection and Removal of SolidsДокумент24 страницыWater Treatment Processes: Disinfection and Removal of SolidsDhana BhargavОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan: How Do We Clean Polluted Water?Документ15 страницLesson Plan: How Do We Clean Polluted Water?Tarun MattaparthyОценок пока нет
- D399DДокумент5 страницD399DHilarie Jonathan100% (1)
- Stages Water Treatment ProcessДокумент2 страницыStages Water Treatment Processglo lipaodОценок пока нет
- LECTURE 11 - Conventional Water Treatment Facility2014Документ51 страницаLECTURE 11 - Conventional Water Treatment Facility2014Kaaviyan thirunyanamОценок пока нет
- Water Technology FinalДокумент74 страницыWater Technology FinalRishabhОценок пока нет
- Theory of Practice WaterДокумент5 страницTheory of Practice WaterTemimi Feras0% (1)
- 16B - Water and Waste ManagementДокумент37 страниц16B - Water and Waste ManagementHossein HejaziОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Dab 30102Документ75 страницChapter 3 Dab 30102Muhammad Fazlan AliffОценок пока нет
- Conventional Wastewater TreatmentДокумент33 страницыConventional Wastewater Treatmentsishu21Оценок пока нет
- Final Exam SMJC 3333Документ6 страницFinal Exam SMJC 3333azhani95Оценок пока нет
- CE405 Environmental Engineering - IДокумент2 страницыCE405 Environmental Engineering - IChithraОценок пока нет
- 9004.1202EEII Chapter1 3Документ76 страниц9004.1202EEII Chapter1 3पाँशुल जम्वाल राजपूतОценок пока нет
- Assignement SolutionДокумент30 страницAssignement Solutionjebril yusufОценок пока нет
- Geometric Method Presentation Final 1.Pptx LatestДокумент23 страницыGeometric Method Presentation Final 1.Pptx LatestDanner PerkinsОценок пока нет
- Treatment of Grey Water Using Technique of PhytoremediationДокумент8 страницTreatment of Grey Water Using Technique of PhytoremediationAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rОценок пока нет
- Presentation2 Modefied 140406104819 Phpapp01Документ278 страницPresentation2 Modefied 140406104819 Phpapp01sonchemen100% (1)
- Nutrient & Pathogen Removal in Wastewater TreatmentДокумент27 страницNutrient & Pathogen Removal in Wastewater TreatmentMohammed BarniОценок пока нет
- Septic Tank and Soak Well SizingДокумент4 страницыSeptic Tank and Soak Well Sizingadera1Оценок пока нет
- Wastewater Engineering Lab Manual Revised (Submission)Документ39 страницWastewater Engineering Lab Manual Revised (Submission)Nora ZuraОценок пока нет
- ENG341 - Exam Study PDFДокумент18 страницENG341 - Exam Study PDFBlake MarxsenОценок пока нет
- Wastewater Treatment Methods Physical Unit Operations Chemical Unit Operations Biological Unit OperationsДокумент34 страницыWastewater Treatment Methods Physical Unit Operations Chemical Unit Operations Biological Unit OperationsNumanОценок пока нет
- ENE130: Water Quality ParametersДокумент18 страницENE130: Water Quality ParametersErica Nicole LabialОценок пока нет
- Report TreatmentPond PDFДокумент10 страницReport TreatmentPond PDFSérgio Dos SantosОценок пока нет
- Raw Water Treatment (Group 1)Документ34 страницыRaw Water Treatment (Group 1)AMIRAH AFIQAH BINTI ABDUL RAHIM MKK211007Оценок пока нет
- Water Softening ProcessДокумент29 страницWater Softening ProcessAbo-Khaled MohammedОценок пока нет
- WATER TREATMENT TECHNOLOGY (TAS 3010) LECTURE NOTES 9e - DisinfectionДокумент17 страницWATER TREATMENT TECHNOLOGY (TAS 3010) LECTURE NOTES 9e - Disinfectionmamat88Оценок пока нет
- Disinfection Methods for Water TreatmentДокумент6 страницDisinfection Methods for Water TreatmentAriff JasniОценок пока нет
- Municipal Wastewater Treatment: Evaluating Improvements in National Water QualityОт EverandMunicipal Wastewater Treatment: Evaluating Improvements in National Water QualityОценок пока нет
- WTP RO Flow Chart1Документ1 страницаWTP RO Flow Chart1Nandha KumarОценок пока нет
- CH 100: Fundamentals For Chemistry: Chapter 1: Introduction Lecture NotesДокумент132 страницыCH 100: Fundamentals For Chemistry: Chapter 1: Introduction Lecture NotesNandha KumarОценок пока нет
- 2007 Ch158 A3 Basicsorg Update For 2010Документ40 страниц2007 Ch158 A3 Basicsorg Update For 2010Nandha KumarОценок пока нет
- Basic ChemistryДокумент14 страницBasic ChemistryAtul DwivediОценок пока нет
- Lect 1 Fundamentals of ChemistryДокумент23 страницыLect 1 Fundamentals of ChemistryNandha KumarОценок пока нет
- Chemistry: An Introduction: CHY 105: Fundamentals of ChemistryДокумент31 страницаChemistry: An Introduction: CHY 105: Fundamentals of ChemistryNandha KumarОценок пока нет
- Waste Heat Recovery: Industrial Waste Heat Recovery SystemsДокумент9 страницWaste Heat Recovery: Industrial Waste Heat Recovery SystemsNandha KumarОценок пока нет
- CNC Machines GuideДокумент36 страницCNC Machines GuideAhmad ElsheemyОценок пока нет
- Baja Saeasia2101 Rulebook Ver.1Документ73 страницыBaja Saeasia2101 Rulebook Ver.1bikramjeet_17Оценок пока нет
- 4-JL Structural ReportДокумент48 страниц4-JL Structural ReportJeet BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- 03-04 Mini Baja - Frame, Roll Cage, and CockpitДокумент1 страница03-04 Mini Baja - Frame, Roll Cage, and Cockpitsalman526Оценок пока нет
- GATE Syllabus 2012 For Mechanical EngineeringДокумент4 страницыGATE Syllabus 2012 For Mechanical EngineeringVatsal KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- Air QualityДокумент21 страницаAir QualityNandha KumarОценок пока нет
- Fluid Power ApplicationsДокумент2 страницыFluid Power ApplicationsNandha KumarОценок пока нет
- Water PDFДокумент40 страницWater PDFAnjney100% (1)
- Ozone Treatment of Small Water Systems Paper8 - Ioapag98Документ23 страницыOzone Treatment of Small Water Systems Paper8 - Ioapag98Steve DennisОценок пока нет
- Water Treatment Engineering: A Concise GuideДокумент21 страницаWater Treatment Engineering: A Concise Guidethomas yapОценок пока нет
- Feka Pepsi GonderДокумент62 страницыFeka Pepsi GonderZemariyam Bizuayehu100% (2)
- WATER TREATMENT TECHNOLOGY (TAS 3010) LECTURE NOTES 9a - Water Intake, Screening, Aeration, CoagulationДокумент46 страницWATER TREATMENT TECHNOLOGY (TAS 3010) LECTURE NOTES 9a - Water Intake, Screening, Aeration, Coagulationmamat8894% (16)
- Siting Criteria and Consent Conditions Notification PDFДокумент20 страницSiting Criteria and Consent Conditions Notification PDFPrince JoseОценок пока нет
- Water Treatment Plant OP&MДокумент53 страницыWater Treatment Plant OP&MNguyen Phuc Pham100% (1)
- ProjectДокумент38 страницProjectShubhamUpadhyayОценок пока нет
- Report On Site Visit DamДокумент3 страницыReport On Site Visit Dambayuberduri100% (2)
- Lecture 3 (Water Treatment)Документ59 страницLecture 3 (Water Treatment)NomanОценок пока нет
- Modelling coagulant dosage in a water treatment plantДокумент4 страницыModelling coagulant dosage in a water treatment plantDini AryantiОценок пока нет
- Environmental Engineering Laboratory Open-Ended Lab Report: 2 Marks CommentsДокумент10 страницEnvironmental Engineering Laboratory Open-Ended Lab Report: 2 Marks CommentsMOHAMAD NOOR AZIZI ZAINUDINОценок пока нет
- Final Paper - Edit 1130pmДокумент103 страницыFinal Paper - Edit 1130pmMark Macky BabaoОценок пока нет
- Clean Water Supply SystemДокумент29 страницClean Water Supply SystemMuh GafurОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 3Документ38 страницChapter 1 3Edita O PanuncioОценок пока нет
- Refinery Wastewater Treatment TrainingДокумент27 страницRefinery Wastewater Treatment TrainingHariajahОценок пока нет
- Good Practice Guide Operation Drinking Water Research PRJ 1074Документ52 страницыGood Practice Guide Operation Drinking Water Research PRJ 1074Michael FredericoОценок пока нет
- Liquid Analytics Standard Configurations 2 1Документ71 страницаLiquid Analytics Standard Configurations 2 1knchnОценок пока нет
- Proforma For Hygienic Conditions Periodic InspectionДокумент2 страницыProforma For Hygienic Conditions Periodic InspectionJagannath Majhi50% (2)
- Water QAS10 379 - 27072010Документ23 страницыWater QAS10 379 - 27072010Surendar KesavanОценок пока нет
- Ep-160016 ManualДокумент342 страницыEp-160016 ManualJohn PonceОценок пока нет
- PSD CEU 201july13Документ26 страницPSD CEU 201july13nermeen ahmedОценок пока нет
- Grundfosliterature 5247253Документ64 страницыGrundfosliterature 5247253Dio Mi100% (1)
- Hi-Flo 6 Hi-Flo 9 Twin Hi-Flo 6 Twin Hi-Flo 9 and Triple Media Filters 2000 LineДокумент37 страницHi-Flo 6 Hi-Flo 9 Twin Hi-Flo 6 Twin Hi-Flo 9 and Triple Media Filters 2000 LineДмитрий Черных100% (4)
- Clean Water For A Healthy WorldДокумент33 страницыClean Water For A Healthy WorldMuhammed NazardeenОценок пока нет
- Defluoridation Using The Nalgonda Technique in Tanzania - Dahi 1996Документ3 страницыDefluoridation Using The Nalgonda Technique in Tanzania - Dahi 1996GeeleegoatОценок пока нет
- T FoskettДокумент18 страницT FoskettkuaОценок пока нет
- 10 State StandardДокумент166 страниц10 State StandardAdnan Ghaffar LodhiОценок пока нет
- Foaming in The Cooling Tower - FlatДокумент1 страницаFoaming in The Cooling Tower - FlatJavier GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Design of A Combined Bread Factory and Water Treatment Plant Layout-3 - 081752Документ18 страницDesign of A Combined Bread Factory and Water Treatment Plant Layout-3 - 081752Austine OdhiamboОценок пока нет