Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
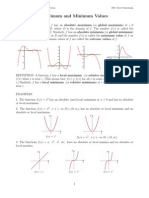
Do Now:: Aim: How Do We Find The Maximum and Minimum Values Over An Interval of A Function Using Derivatives?
Загружено:
Miy ChanИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Do Now:: Aim: How Do We Find The Maximum and Minimum Values Over An Interval of A Function Using Derivatives?
Загружено:
Miy ChanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
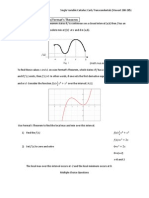
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Do Now:
Aim: How do we find the maximum and
minimum values over an interval of a
function using derivatives?
A rectangle has a length x and perimeter of 36.
a. Express the area A as a function of x and
determine the domain of the function.
b. Graph the area function
c. Find the length and width of the rectangle of
maximum area
x
36 2x
2
P = 2l + 2w
A = lw
a.
A(x) = x
36 2x
2
|
\
|
.
| 0 < x < 18
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Do Now
b. Graph the area
function
c. Find the length
and width of the
rectangle of
maximum area
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
-40 -20 20
f x ( ) =
x 36-2 x ( )
2
A(x)
(9, 81)
Max. - (x, A(x))
Max. - (9, 81)
A = lw
81 = 9w
9 = w
where on graph?
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Maximums and Minimums
Finding maximum and minimum values for
various functions and relationships is very
important and has many real-life
applications associated with the finding of
these critical values.
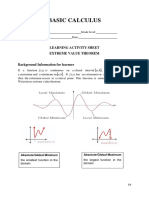
Definition of Extrema
Let f be defined on an interval I containing c.
1. f(c) is the minimum of f on I if f(c) < f(x) for all x
in I .
2. f(c) is the maximum of f on I if f(c) > f(x) for all x
in I .
3. The minimum and maximum of a function on an
interval are the extreme values, or extrema of the
function on the interval.
Note: A function does not
necessarily have a maximum or
minimum.
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Maximums and Minimums
The y value at a critical point can be called a
local/relative maximum or a local/relative
minimum.
Local/relative indicates that f(c) is when x is
in the neighborhood of c.
Global/absolute maximum and
global/absolute minimum are the largest and
smallest of the local maximua and minima.
A critical point is a point in crisis it stops
and can then go in a different direction.
A plateau point is a critical point with a zero
derivative but no max or min.
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Where Extrema Occur
Max
Min
a b
endpoints
Max
Min
stationery points
Max
Min
singular points
f levels off; tangent
line is horizontal
f fails to exist
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Extrema of a Function
6
4
2
f x
( )
= x
2
+1
6
4
2
f x
( )
= x
2
+1
f is continuous,
[-1, 2]
f is continuous,
(-1, 2)
g is not
continuous,
[-1, 2]
6
4
2
2
1, 0
( )
2, 0
x x
g x
x
+ =
=
=
minimum
(0,1)
no
maximum
[ ]
minimum
(0,1)
( )
maximum maximum
(2,5)
[ ]
no
minimum
If f is continuous on a closed interval [a, b], then
f has both a min. and a max. on the interval.
Extreme Value Theorem
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
2
-2
-4
f(x) = x
3
2x
2
relative maximum
hill
2
-2
-4
5
2
3
9( 3)
( )
x
f x
x
=
6
4
2
( ) f x x =
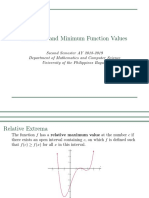
Relative Extrema
(3, 2)
(0, 0)
relative minimum
valley
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Value of Derivative at Relative Extrema
Find the derivative:
2
3
9( 3)
( )
x
f x
x
=
3 2 2
3 2
(18 ) (9)( 3)(3 )
'( )
( )
x x x x
f x
x
=
2
4
9(9 )
'( )
x
f x
x
=
Evaluate the derivative
for the relative maximum
point (3, 2).
2
4
9(9 (3) )
'(3) 0
3
f
= =
2
-2
-4
5
2
3
9( 3)
( )
x
f x
x
=
(3, 2)
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Value of Derivative at Relative Extrema
Derivative at relative minimum?
6
4
2
( ) f x x =
(0, 0)
At x = 0, the derivative of f(x) = |x| does
not exist.
At the relative extrema, the derivative
is either zero or undefined
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Criticial Number
Let f be defined at c. If f(c) = 0 or
if f is undefined at c,
then c is a critical number of f.
4
2
-2
-5
6
4
2
5
c
c
f(c) is undefined f(c) = 0
If f has a relative minimum or relative
maximum at x = c, then c is a critical
number of f.
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Guidelines
Guidelines for Finding Extrema on a Closed
Interval
To find the extrema of a continuous function f
on a closed interval [a, b], use the following
steps.
1. Find the critical numbers of f on (a, b).
2. Evaluate f at each critical number in (a, b).
3. Evaluate f at each endpoint of [a, b].
4. The least of these values is the minimum.
The greatest is the maximum.
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Finding Extrema on a Closed Interval
Find the extrema of
on the interval [-1, 2].
4 3
( ) 3 4 f x x x =
Find the derivative:
3 2
'( ) 12 12 f x x x =
Find the values of x
for which f(x) = 0
3 2
'( ) 12 12 0 f x x x = =
2
12 ( 1) 0
0,1
x x
x
=
=
Left
Endpt.
Critical
Number
Critical
Number
Right
Endpt.
f(-1) = 7 f(0) = 0 f(1) = -1 f(2) = 16
15
10
5
-1 1 2
*
*
MIN MAX
plateau
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Model Problem
Find the extrema of
on the interval [-1, 3].
2 3
( ) 2 3 f x x x =
Find f
1 3
1 3 1 3
2 1
'( ) 2 2
x
f x
x x
| |
= =
|
\ .
Find the values of x
for which f(x) = 0
Left
Endpt.
Critical
Number
Critical
Number
Right
Endpt.
f(-1) = -5 f(0) = 0 f(1) = -1 f(2) ~
-.24
MIN MAX
4
2
-2
-4
1 3
1 3
1
'( ) 2 0
'(0) is undef. & '(1) 0
x
f x
x
f f
| |
= =
|
\ .
=
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Model Problem
Find the extrema of
on the interval [0, 2].
( ) 2sin cos2 f x x x =
Find f
'( ) 2cos 2sin2 f x x x = +
Find the values of x
for which f(x) = 0
'( ) 2cos 4cos sin 0
2 cos 1 2sin 0
f x x x x
x x
= + =
+ =
sin 2x = 2 cosx sinx
3
cos 0 when ,
2 2
x x
t t
= =
7 11
1 2sin 0 when ,
6 6
x x
t t
+ = =
4
2
-2
5
Aim: Extrema of a Function Course: Calculus
Model Problem
Find the extrema of
on the interval [0, 2].
( ) 2sin cos2 f x x x =
3
cos 0 when ,
2 2
x x
t t
= =
7 11
1 2sin 0 when ,
6 6
x x
t t
+ = =
Left
Endpt.
Critical
Number
Critical
Number
Critical
Number
Critical
Number
Right
Endpt
f(0) = -1
f(/2) =
3
f(7/6)
= -3/2
f(3/2)
= -1
f(11/6)
= -3/2
f(2) =
-1
MIN MAX
4
2
-2
5
Вам также может понравиться
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsОт EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Test2 en MaterialДокумент16 страницTest2 en MaterialAlejandro Ca MaОценок пока нет
- Las Basic Calculus Wk6 For StudДокумент12 страницLas Basic Calculus Wk6 For StudJohn Michael EcaranОценок пока нет
- Maximum and Minimum ValuesДокумент8 страницMaximum and Minimum ValuesChetan B ArkasaliОценок пока нет
- Fin118 Unit 3Документ27 страницFin118 Unit 3ayadi_ezer6795Оценок пока нет
- Applicatios of DerivativesДокумент19 страницApplicatios of Derivativessohail66794154Оценок пока нет
- Extreme Value Theorem ReviewДокумент10 страницExtreme Value Theorem Reviewktcheersocca93Оценок пока нет
- Applications of DerivativesДокумент10 страницApplications of DerivativesRana JahanzaibОценок пока нет
- WEEK5Документ34 страницыWEEK5Crius DiomedesОценок пока нет
- Extreme Value Theorem V2Документ14 страницExtreme Value Theorem V2Axel Gayondato0% (1)
- Worksheet On Stationary PointsДокумент2 страницыWorksheet On Stationary PointsMalcolmCoОценок пока нет
- Calculus Chapter 4Документ97 страницCalculus Chapter 4nestorОценок пока нет
- Cal42 Optimization Global Maxima and MinimaДокумент3 страницыCal42 Optimization Global Maxima and Minimamarchelo_cheloОценок пока нет
- (3-1) Max and Min ValuesДокумент10 страниц(3-1) Max and Min ValuesAndrea DeteraОценок пока нет
- Maxima and Minima Gate Study Material in PDF 0f9b7b0aДокумент7 страницMaxima and Minima Gate Study Material in PDF 0f9b7b0aOm GawandeОценок пока нет
- Solution To Practice Exercise For Lecture 23Документ3 страницыSolution To Practice Exercise For Lecture 23Raja Tausif AhmedОценок пока нет
- DerivativesДокумент8 страницDerivativesTrung BảoОценок пока нет
- Derivatives: Its ApplicationsДокумент77 страницDerivatives: Its ApplicationsJerome Paul Edullantes Diokno-AlfonsoОценок пока нет
- 151 Exam 1 Review AU10Документ3 страницы151 Exam 1 Review AU10Nathan W. SerafiniОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 8 Solutions PDFДокумент21 страницаProblem Set 8 Solutions PDFfrancis_tsk1Оценок пока нет
- Applicaton of DerivativesДокумент14 страницApplicaton of DerivativesAli HamzaОценок пока нет
- Maxima and MinimaДокумент13 страницMaxima and MinimaSharafat KarimОценок пока нет
- Math 53 LE 3 Reviewer ProblemsДокумент14 страницMath 53 LE 3 Reviewer ProblemsJc QuintosОценок пока нет
- Absolute Maxima and MinimaДокумент7 страницAbsolute Maxima and MinimaDaiszyBarakaОценок пока нет
- Increasing and Decreasing Functions: Relative Extrema First Derivative TestДокумент18 страницIncreasing and Decreasing Functions: Relative Extrema First Derivative TestizumiОценок пока нет
- College Algebra4Документ25 страницCollege Algebra4AbchoОценок пока нет
- MathsДокумент10 страницMathsSudarshan NeupaneОценок пока нет
- Chapter2 - Problems of Chapter 2Документ48 страницChapter2 - Problems of Chapter 2Vuthy Chey100% (1)
- 4 - 1a With 4 - 4Документ4 страницы4 - 1a With 4 - 4nickОценок пока нет
- CalculusДокумент15 страницCalculusrpdemaladeОценок пока нет
- Maximum and Minimum Function ValuesДокумент18 страницMaximum and Minimum Function ValuesCarlo CaniedoОценок пока нет
- Extreme Value TheoremДокумент2 страницыExtreme Value TheoremGuyrandy 'Gee' Jean-GillesОценок пока нет
- Maxima and Minima - GATE Study Material in PDFДокумент7 страницMaxima and Minima - GATE Study Material in PDFSupriya SantreОценок пока нет
- Calculus I FinalДокумент7 страницCalculus I FinalRodrigo RomeroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: Quadratic Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs General Form of Quadratic FunctionДокумент4 страницыChapter 3: Quadratic Functions 3.1 Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs General Form of Quadratic FunctionShafiqah SamsuriОценок пока нет
- Sing Levar OptДокумент29 страницSing Levar OptDiego Isla-LópezОценок пока нет
- Oldexam Ws0708 SolutionДокумент14 страницOldexam Ws0708 SolutionhisuinОценок пока нет
- Week 8 - Calc 2Документ61 страницаWeek 8 - Calc 2liljae149Оценок пока нет
- MATH1009 Test 4 SolutionsДокумент3 страницыMATH1009 Test 4 SolutionsfatdogeОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 113 (A1) Final Examination Fall 2010: InstructionsДокумент4 страницыMathematics 113 (A1) Final Examination Fall 2010: InstructionsexamkillerОценок пока нет
- Roots of Equations: Numerical Methods For Civil EngineersДокумент21 страницаRoots of Equations: Numerical Methods For Civil EngineersRibesha MushОценок пока нет
- Computational Lab in Physics: Finding Roots of Nonlinear FunctionsДокумент12 страницComputational Lab in Physics: Finding Roots of Nonlinear Functionsbenefit187Оценок пока нет
- Topics: Critical Points, Identification of Relative Maxima and Minima, 1st and SecondДокумент7 страницTopics: Critical Points, Identification of Relative Maxima and Minima, 1st and SecondLuCiFeR GamingОценок пока нет
- PC Exam ReviewДокумент4 страницыPC Exam Reviewklb925Оценок пока нет
- Debark University College of Natural and Computational Science Mathematics Department Applied Mathematics I YearДокумент3 страницыDebark University College of Natural and Computational Science Mathematics Department Applied Mathematics I YearyacobОценок пока нет
- 3.2 Max MinДокумент2 страницы3.2 Max MinBradley SinghОценок пока нет
- U1 Limit and Continuity HW AnswersДокумент17 страницU1 Limit and Continuity HW AnswersnevinОценок пока нет
- Basic Calculus Quarter 3 Week 6: Extreme Value Theorem and OptimizationДокумент9 страницBasic Calculus Quarter 3 Week 6: Extreme Value Theorem and OptimizationMarjohn MolinaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Functions and Graphs 4.1) Basics of Functions Definition 1: RelationsДокумент32 страницыChapter 4: Functions and Graphs 4.1) Basics of Functions Definition 1: Relationssf1dОценок пока нет
- Final Exam: April 29, 2003 (150 Minutes)Документ8 страницFinal Exam: April 29, 2003 (150 Minutes)ABC CheckОценок пока нет
- Name: MATH-2211 - Calculus-I - CRN 808 Test-3Документ2 страницыName: MATH-2211 - Calculus-I - CRN 808 Test-3Ghislain DjedjeroОценок пока нет
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 2 Number Unit Limits of Function Continuity of Function Unit SubjectДокумент35 страницFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 2 Number Unit Limits of Function Continuity of Function Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Оценок пока нет
- 1asn SLNДокумент2 страницы1asn SLNDaniel OhОценок пока нет
- Global (Absolute) Extrema Point: Report TitleДокумент14 страницGlobal (Absolute) Extrema Point: Report TitleDaneal SofiОценок пока нет
- Math013 Calculus I Final Exam Solution, Fall 08Документ13 страницMath013 Calculus I Final Exam Solution, Fall 08JessicaОценок пока нет
- Part 1 Review CalculusДокумент54 страницыPart 1 Review CalculusNat NaОценок пока нет
- Y MX B: Linearization and Newton's MethodДокумент7 страницY MX B: Linearization and Newton's MethodTony CaoОценок пока нет
- Numerical Computing Assignment - IV: Instructor: Soumyashant NayakДокумент8 страницNumerical Computing Assignment - IV: Instructor: Soumyashant NayakTreanungkur MalОценок пока нет
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"От EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Рейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (2)
- Two Sides of Effective Oral CommunicationДокумент17 страницTwo Sides of Effective Oral CommunicationSharath KumarОценок пока нет
- 07 Eugenia Tan - Singapore PDFДокумент11 страниц07 Eugenia Tan - Singapore PDFkelton_chee5234Оценок пока нет
- Plastic To The Basket! A Community Project - 1Документ25 страницPlastic To The Basket! A Community Project - 1Rojas, Jasmine Rose LОценок пока нет
- Differences Among Dark Triad Components - A Meta-Analytic Investigation (Vize Et Al, 2018)Документ58 страницDifferences Among Dark Triad Components - A Meta-Analytic Investigation (Vize Et Al, 2018)GokushimakОценок пока нет
- PANalyticals HighScore Suite BrochureДокумент8 страницPANalyticals HighScore Suite BrochuresenthilОценок пока нет
- 01Документ12 страниц01Junaid Ahmad100% (1)
- Handbook of Scheme of Instruction and Syllabi 2018 19 PDFДокумент598 страницHandbook of Scheme of Instruction and Syllabi 2018 19 PDFNitishОценок пока нет
- Management Information System: Dr. Nilima PatilДокумент23 страницыManagement Information System: Dr. Nilima Patilsharadp007Оценок пока нет
- Brac University Brac Business School Course Outline: Spring 2015 Subject: Introduction To Business (Bus 101)Документ6 страницBrac University Brac Business School Course Outline: Spring 2015 Subject: Introduction To Business (Bus 101)Tonmoy RoyОценок пока нет
- Dr. K. ReddyДокумент14 страницDr. K. ReddyUpendra SinghОценок пока нет
- Jurnal 4Документ13 страницJurnal 4septi arum pradanaОценок пока нет
- PR2 Lesson 10 Sampling and Sampling TechniquesДокумент21 страницаPR2 Lesson 10 Sampling and Sampling TechniquesBruh MomentОценок пока нет
- Millennials ' Attitude Toward Chatbots: An Experimental Study in A Social Relationship PerspectiveДокумент21 страницаMillennials ' Attitude Toward Chatbots: An Experimental Study in A Social Relationship PerspectiveaıshdksdОценок пока нет
- ATC 115 Preliminary CoverДокумент188 страницATC 115 Preliminary Covertecanasio100% (1)
- The Challenges of Classroom ManagementДокумент72 страницыThe Challenges of Classroom ManagementJonathan AndayaОценок пока нет
- Summer Internship Report On STUDY of PERДокумент82 страницыSummer Internship Report On STUDY of PERsahilsorakhe036Оценок пока нет
- Books Held in Psychology Test Library (As at 26 July 2012)Документ13 страницBooks Held in Psychology Test Library (As at 26 July 2012)Idham AnwarОценок пока нет
- Master Thesis Proposal Electrical EngineeringДокумент7 страницMaster Thesis Proposal Electrical Engineeringannmontgomeryjackson100% (1)
- Artifact 4 Te807 - Think-Pair-Plan ProjectДокумент18 страницArtifact 4 Te807 - Think-Pair-Plan Projectapi-534347791Оценок пока нет
- Educ 109 Handout Unit 1 CompleteДокумент23 страницыEduc 109 Handout Unit 1 Completetanjikamado321Оценок пока нет
- Culture and Congruence The Fit Between Management Practices and National Culture - NEWMANДокумент27 страницCulture and Congruence The Fit Between Management Practices and National Culture - NEWMANRodrigo MenezesОценок пока нет
- Bialystok 2015Документ5 страницBialystok 2015Miza AfrizalОценок пока нет
- Answers To ExercisesДокумент19 страницAnswers To ExercisesBea ValerioОценок пока нет
- Research ProposalДокумент7 страницResearch ProposalKurva UshaОценок пока нет
- The Halo Effect Research ProposalДокумент8 страницThe Halo Effect Research ProposalOllie FairweatherОценок пока нет
- Zelazo Et Al 2024 Fostering Executive Function Skills and Promoting Far Transfer To Real World Outcomes The ImportanceДокумент7 страницZelazo Et Al 2024 Fostering Executive Function Skills and Promoting Far Transfer To Real World Outcomes The ImportanceultimatedeliciaОценок пока нет
- The Role of Positive Emotion Mediates Fashion Involvement On Impulse BuyingДокумент8 страницThe Role of Positive Emotion Mediates Fashion Involvement On Impulse BuyingSatriya Galih HandhitaОценок пока нет
- PR1 Quarter 3 Module 3Документ47 страницPR1 Quarter 3 Module 3justinejoy.acalaОценок пока нет
- Thesis Format ChecklistДокумент11 страницThesis Format ChecklistJennifer0% (1)
- FDA Guidance StandardДокумент40 страницFDA Guidance Standardajitbasrur445Оценок пока нет