Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
An Introduction To Limits
Загружено:
Miy ChanОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
An Introduction To Limits
Загружено:
Miy ChanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
An Introduction to Limits
Objective:
To understand the concept of a limit
and
To determine the limit from a graph
Calculus centers around 2 fundamental problems
1) The tangent line- differential calculus
P
Q
x
) x ( f ) x x ( f
lim m
0 x tan
A
A +
= =
A
Instantaneous rate of change
(Slope at a point)
x
) x ( f ) x x ( f
slope m change of rate . Avg
sec
A
A +
= = =
(Slope between 2 points)
2) The area problem- integral calculus
Uses rectangles to approximate the area
under a curve.
Limits: Yes finally some calculus!
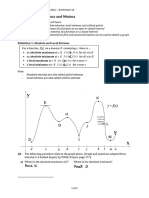
Objective: To understand the definition of a limit and to graphically determine the left and
right limits and to algebraically determine the value of a limit.
If the function f(x) becomes arbitrarily close to
a single number L (a y-value) as x approaches
c from either side, then lim
xc
f(x) = L.
*A limit is looking for the height of a curve at some x = c.
*L must be a fixed, finite number.
One-Sided Limits:
lim
xc+
f(x) =L
1
Height of the curve approach x = c
from the right
lim
xc-
f(x) =L
2
Height of the curve approach x = c
from the left
Definition of Limit:
If lim
xc+
f(x) = lim
xc-
f(x) = L then,
lim
xc
f(x)=L (Again, L must be a fixed, finite number.)
f(2) =
f(2) =
lim ( )
x
f x
+
=
2
lim ( )
x
f x
+
=
4
lim ( )
x
f x
=
2
lim ( )
x
f x
=
2
lim ( )
x
f x
+
=
lim ( )
x
f x
=
4
lim ( )
x
f x
=
4
f(4) =
lim ( )
x
f x
=
Examples:
=
+
) x ( f lim
0 x
lim ( )
x
f x
+
=
4
=
) x ( f lim
0 x
=
) x ( f lim
0 x
lim ( )
x
f x
+
=
lim ( )
x
f x
=
4
lim ( )
x
f x
=
4
f(4) =
lim ( )
x
f x
=
f(0) =
=
+
) x ( f lim
3 x
=
+
) x ( f lim
6 x
=
) x ( f lim
3 x
=
) x ( f lim
3 x
lim ( )
x
f x
+
=
=
) x ( f lim
6 x
=
) x ( f lim
6 x
f(6) =
lim ( )
x
f x
=
f(3) =
Basic Limits (for the book part)
lim
x4
2x 5 =
lim
x-3
x
2
=
lim
xt
cos x =
lim
x1
sin =
( )
2
x
Important things to note:
The limit of a function at x = c does not depend on the
value of f(c).
The limit only exists when the limit from the right equals
the limit from the left and the value is a FIXED, FINITE #!
A common limit you need to memorize:
(see proof page 63 )
Limits fail to exist: (ask for pictures)
1. Unbounded behavior not finite
2. Oscillating behavior not fixed
3. - fails def of limit
=
x
x sin
lim
0 x
) x ( f lim ) x ( f lim
c x c x +
=
Do you understand how to graphically find a limit?
Assign: WS and bookwork for 1.2
Вам также может понравиться
- Introduction To LimitsДокумент24 страницыIntroduction To LimitsJessa Mae100% (1)
- An Introduction To LimitsДокумент10 страницAn Introduction To LimitsPrabath Suranaga MorawakageОценок пока нет
- BASCALC Lesson 1.1 - Limit of A FuncitonДокумент82 страницыBASCALC Lesson 1.1 - Limit of A FuncitonRaymond James OconerОценок пока нет
- 1.3-Theorems On LimitsДокумент22 страницы1.3-Theorems On LimitsFaith TabanОценок пока нет
- Calculus - Class 1 (Introduction To Limits)Документ8 страницCalculus - Class 1 (Introduction To Limits)Mike GraczykОценок пока нет
- 1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning GoalsДокумент58 страниц1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning GoalsMiy ChanОценок пока нет
- Syllabus of MAT 1001 For First LectuureДокумент11 страницSyllabus of MAT 1001 For First LectuureADITYA PRATAP SINGH 19BCY10053Оценок пока нет
- Calculus - Class 1 (Introduction To Limits)Документ7 страницCalculus - Class 1 (Introduction To Limits)Mike GraczykОценок пока нет
- Ch11 Limits ApreviewtocalculusДокумент76 страницCh11 Limits ApreviewtocalculusmoshetalkarОценок пока нет
- Limits IntroductionДокумент25 страницLimits IntroductionJuan LappayОценок пока нет
- Calculus Cheat Sheet LimitsДокумент2 страницыCalculus Cheat Sheet LimitsArn Stefhan JimenezОценок пока нет
- Jignesh Shah Dhiren Prajapati Kaustubh Parkar Akash Jadhav Deepali Jain Rahul GavaliДокумент43 страницыJignesh Shah Dhiren Prajapati Kaustubh Parkar Akash Jadhav Deepali Jain Rahul GavaliDhiren Praj100% (1)
- Limits and Continuity Worksheet - Spring 2020Документ5 страницLimits and Continuity Worksheet - Spring 2020Haji KhalilОценок пока нет
- MATH 221 Final Exam Statistics For DecisionДокумент8 страницMATH 221 Final Exam Statistics For DecisiongeorgettashipleyОценок пока нет
- 1.1.1. An Introduction To Thinkwell's CalculusДокумент1 страница1.1.1. An Introduction To Thinkwell's Calculuschunkymonkey323Оценок пока нет
- Ch01-Calculus 9E LimitsДокумент34 страницыCh01-Calculus 9E Limitsrofi modiОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 Limit LawsДокумент9 страницLecture 4 Limit LawsgontseОценок пока нет
- Binomial ExpansionДокумент32 страницыBinomial ExpansionAmber CoffeyОценок пока нет
- G11 Q3 LAS Week2 L1.4.2 Basic CalculusДокумент8 страницG11 Q3 LAS Week2 L1.4.2 Basic CalculusFranzhean Balais CuachonОценок пока нет
- Packet 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusДокумент3 страницыPacket 0 A - Are You Ready For CalculusteachopensourceОценок пока нет
- Limit of A FunctionДокумент41 страницаLimit of A FunctionHanzMarianoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - DifferentiationДокумент56 страницChapter 4 - DifferentiationTOBY RANОценок пока нет
- 6-3 Projectile Motion - JHДокумент73 страницы6-3 Projectile Motion - JHJanalynn CoutoОценок пока нет
- RulesDifferentiation PDFДокумент3 страницыRulesDifferentiation PDFsheelasalu100% (1)
- 201-103-RE - Calculus 1 Worksheet: LimitsДокумент60 страниц201-103-RE - Calculus 1 Worksheet: LimitsArwaa AlmaghrabiОценок пока нет
- 3c3-TrigonometSubstitu Stu PDFДокумент12 страниц3c3-TrigonometSubstitu Stu PDFMahmoud Abdel-SalamОценок пока нет
- Relations and Functions Notes and WorksheetsДокумент27 страницRelations and Functions Notes and WorksheetsTitser Laarni33% (3)
- Practice Questions For Quizzes and Midterms - SolutionДокумент38 страницPractice Questions For Quizzes and Midterms - SolutionBrandon KimОценок пока нет
- 5.2 Ellipse and HyperbolaДокумент18 страниц5.2 Ellipse and HyperbolaJessy OeungОценок пока нет
- InequalityДокумент43 страницыInequalityAndrew AndrewОценок пока нет
- Rational Function IntroductionДокумент23 страницыRational Function IntroductionUddin NimatОценок пока нет
- Functions of Several VariablesДокумент4 страницыFunctions of Several VariablesKonal ShahОценок пока нет
- Math 38 UPLB Taylor Series ExpansionДокумент8 страницMath 38 UPLB Taylor Series ExpansionKennypherneliaОценок пока нет
- Definition of de Morgan's LawДокумент4 страницыDefinition of de Morgan's LawSaad ullahОценок пока нет
- Calculus 2 - Increments and DifferentialsДокумент6 страницCalculus 2 - Increments and DifferentialsAyie KhairieОценок пока нет
- Maths InequalitiesДокумент10 страницMaths InequalitiesJonah Mae MonevaОценок пока нет
- Chapter Test FunctionsДокумент8 страницChapter Test FunctionsRanns Meldrik SantosОценок пока нет
- Number Systems and Conversion: This Chapter in The Book IncludesДокумент34 страницыNumber Systems and Conversion: This Chapter in The Book Includes최재원Оценок пока нет
- Applications of DerivativesДокумент10 страницApplications of DerivativesRana JahanzaibОценок пока нет
- AP Calculus ReviewДокумент75 страницAP Calculus ReviewJuliaОценок пока нет
- ExercisesДокумент6 страницExercisesMazter Cho100% (1)
- College Algebra, Final ExamДокумент8 страницCollege Algebra, Final ExamErza_AmmyОценок пока нет
- A2 Reference Sheet 01Документ5 страницA2 Reference Sheet 01rajbmohanОценок пока нет
- Solving Rational EquationsДокумент16 страницSolving Rational EquationsCy Borg KumaОценок пока нет
- Problem SolvingДокумент106 страницProblem SolvingSathis KumarОценок пока нет
- 11 - Trigonometric IdentitiesДокумент6 страниц11 - Trigonometric IdentitiesQwert RОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 - LIMITS OF FUNCTIONSДокумент59 страницLesson 1 - LIMITS OF FUNCTIONSJohn Roi AlanoОценок пока нет
- Math 30-1: Polynomial, Radical, and Rational Functions: Practice ExamДокумент14 страницMath 30-1: Polynomial, Radical, and Rational Functions: Practice ExamJayri-an Go DemegilloОценок пока нет
- Boolean Algebra and Logic GatesДокумент57 страницBoolean Algebra and Logic GatesABDULLAH AAMIRОценок пока нет
- Matrices and Basic Calculus For Non Majors-MT161Документ11 страницMatrices and Basic Calculus For Non Majors-MT161Hamisi Mzari100% (1)
- 7.8 Implicit Differentiation 5 PDFДокумент7 страниц7.8 Implicit Differentiation 5 PDFHin Wa LeungОценок пока нет
- CSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Differential CalculusДокумент8 страницCSU-Cabadbaran Advance Review For EE: Topic: Differential CalculusCinderella WhiteОценок пока нет
- Multiplying Monomials and BinomialsДокумент30 страницMultiplying Monomials and BinomialsKenny Ann Grace BatiancilaОценок пока нет
- Pascal's and Binomial TheoremДокумент4 страницыPascal's and Binomial TheoremPaul JayLord BagunuОценок пока нет
- ExtrapolationДокумент3 страницыExtrapolationmakarandwathОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2-01 Probability STATДокумент13 страницLesson 2-01 Probability STATallan.manaloto23100% (1)
- Ma1103 4THWДокумент13 страницMa1103 4THWDanur WendaОценок пока нет
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 2 Number Unit Limits of Function Continuity of Function Unit SubjectДокумент35 страницFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 2 Number Unit Limits of Function Continuity of Function Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Оценок пока нет
- RPP Update Report 2013Документ15 страницRPP Update Report 2013Miy ChanОценок пока нет
- Do Now:: Aim: How Do We Find The Maximum and Minimum Values Over An Interval of A Function Using Derivatives?Документ15 страницDo Now:: Aim: How Do We Find The Maximum and Minimum Values Over An Interval of A Function Using Derivatives?Miy ChanОценок пока нет
- Calculus 5e: Limits and DerivativesДокумент5 страницCalculus 5e: Limits and DerivativesMiy ChanОценок пока нет
- 1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning GoalsДокумент58 страниц1.2:rates of Change & Limits Learning GoalsMiy ChanОценок пока нет
- Budget EstimationДокумент1 страницаBudget EstimationMiy ChanОценок пока нет
- Material DerivativeДокумент22 страницыMaterial DerivativeKotsiras YannisОценок пока нет
- Topic 10 - Past Year Student SM015 2022-2023Документ6 страницTopic 10 - Past Year Student SM015 2022-2023四叶草Оценок пока нет
- West Visayas State University: College of Education Lesson Plan in MathematicsДокумент5 страницWest Visayas State University: College of Education Lesson Plan in MathematicsMary John PinuelaОценок пока нет
- Manual For Instructors: TO Linear Algebra Fifth EditionДокумент10 страницManual For Instructors: TO Linear Algebra Fifth EditionMuhammad Umer ShahОценок пока нет
- f (x) = x π ≤ x ≤ π: halaman 512 exercise 11.1.c expand the following functions unsing fourier series: (a) ,Документ3 страницыf (x) = x π ≤ x ≤ π: halaman 512 exercise 11.1.c expand the following functions unsing fourier series: (a) ,Ega RahmawatiОценок пока нет
- Exercise - 6 PDFДокумент6 страницExercise - 6 PDFKritiОценок пока нет
- Control System Question BankДокумент17 страницControl System Question BankerrakeshagrawalОценок пока нет
- Inverse Hyperbolic FunctionsДокумент4 страницыInverse Hyperbolic Functionscircleteam123Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 IntegrationДокумент61 страницаChapter 5 IntegrationefiОценок пока нет
- Cayley's TheoremДокумент4 страницыCayley's TheoremNaveen GuptaОценок пока нет
- Alonso & Lamata PDFДокумент15 страницAlonso & Lamata PDFEva Natalia SiraitОценок пока нет
- 1000 Ext 2 QuestionsДокумент294 страницы1000 Ext 2 QuestionsMark DanialОценок пока нет
- Moment Diagram by Parts SolmanДокумент21 страницаMoment Diagram by Parts SolmanJosell Caipang100% (1)
- Monte Carlo MethodДокумент68 страницMonte Carlo MethodKanmani Ganesan100% (1)
- HW1 - 2016 Flight MechanicsДокумент2 страницыHW1 - 2016 Flight MechanicsSerdar BilgeОценок пока нет
- Qaacidiyinka MathsДокумент7 страницQaacidiyinka MathsMustapha MohamedОценок пока нет
- MATH F113 HandoutДокумент2 страницыMATH F113 HandoutJatinОценок пока нет
- Week 11 - D9 - Max and MinДокумент5 страницWeek 11 - D9 - Max and Mintrang.nguyen.whОценок пока нет
- MCQ Cse PutДокумент8 страницMCQ Cse PutAnurag ChauhanОценок пока нет
- An Isogeometric Analysis Approach For The Study of Structural VibrationsДокумент59 страницAn Isogeometric Analysis Approach For The Study of Structural VibrationsBharti SinghОценок пока нет
- 2020 Assessment 1 - Alternate Task Ext1 (William's Work) PDFДокумент7 страниц2020 Assessment 1 - Alternate Task Ext1 (William's Work) PDF黑剑Оценок пока нет
- Bezier Curves and B-Splines, Blossoming: New York UniversityДокумент8 страницBezier Curves and B-Splines, Blossoming: New York UniversityBalbirОценок пока нет
- Lyapunov StabilityДокумент16 страницLyapunov StabilitySukhbir DhillonОценок пока нет
- SG Quadratic TheoryДокумент3 страницыSG Quadratic Theoryzahirul007Оценок пока нет
- Research Article: A Novel Hybrid Bat Algorithm With Harmony Search For Global Numerical OptimizationДокумент22 страницыResearch Article: A Novel Hybrid Bat Algorithm With Harmony Search For Global Numerical OptimizationNithinОценок пока нет
- Act. StatДокумент10 страницAct. StatGA RICAFRENTE67% (3)
- Square RootДокумент3 страницыSquare RootAngel RamosoОценок пока нет
- LEC - 25 Buckling of Columns - Part 1Документ29 страницLEC - 25 Buckling of Columns - Part 1Asif HameedОценок пока нет
- Grade 8 Lockdown Maths 2021Документ24 страницыGrade 8 Lockdown Maths 2021general kanuОценок пока нет
- Matrices Worksheet 1Документ4 страницыMatrices Worksheet 1siany adeОценок пока нет