Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Diode and Transistor: Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu
Загружено:
Abdur Rehman0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
62 просмотров27 страницThis document discusses diodes and transistors as presented by Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu of the University of Gujrat's Physics Department. It covers doping of semiconductors to create N-type and P-type materials, the formation of a PN junction, forward and reverse biasing of diodes, rectification using half-wave and full-wave rectifiers, and the I-V characteristics of diodes. Diode breakdown and avalanche multiplication are also explained. The key concepts of depletion regions, barrier potentials, minority carrier currents, and knee voltages are introduced.
Исходное описание:
Lecture Covers the diodes & their charachteristics
Оригинальное название
Lecture 4 (Diodes)
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document discusses diodes and transistors as presented by Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu of the University of Gujrat's Physics Department. It covers doping of semiconductors to create N-type and P-type materials, the formation of a PN junction, forward and reverse biasing of diodes, rectification using half-wave and full-wave rectifiers, and the I-V characteristics of diodes. Diode breakdown and avalanche multiplication are also explained. The key concepts of depletion regions, barrier potentials, minority carrier currents, and knee voltages are introduced.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
62 просмотров27 страницDiode and Transistor: Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu
Загружено:
Abdur RehmanThis document discusses diodes and transistors as presented by Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu of the University of Gujrat's Physics Department. It covers doping of semiconductors to create N-type and P-type materials, the formation of a PN junction, forward and reverse biasing of diodes, rectification using half-wave and full-wave rectifiers, and the I-V characteristics of diodes. Diode breakdown and avalanche multiplication are also explained. The key concepts of depletion regions, barrier potentials, minority carrier currents, and knee voltages are introduced.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 27
Diode and Transistor
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
Lecture 4
Diode
Diode curves
Rectification
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
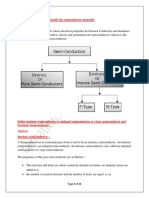
Doping (N- and P-type semiconductors)
Extrinsic semiconductors
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
Elemental semiconductors consists of group-IV of periodic table.
Doping with group-V elements make them N-type.
Doping with group-III elements make them P-type.
N-type material
P
Si Si
Si
P
Si Si Si
Si Si
P
Si Si
Si
P
Si Si Si
Si Si
P
Si
P
Si Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
Phosphorus, a pentavalent atom,
is donating an electron to the
Crystal so it is called donor
impurity. There will be as many
such electrons as the number of
P dopant atoms. These electrons
are free to move and available for
conduction.
P-type material
Al
Si Si
Si
Al
Si Si Si
Si Si
Al
Si Si
Si
Al
Si Si Si
Si Si
Al Si
Al
Si Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
Aluminum, a trivalent atom,
produces hole and ready to accept
and electron, so it is called an
acceptor impurity. There will be
as many such holes as the number
of Al dopant atoms. These holes
are free to move and available for
conduction.
PN-Junction
Si
Si Si
Si Al
Si Si
Si
Al Si Al Si
Si Si Si Si
Al Si Al Si
P
Si Si
Si P
Si Si
Si
P
Si Si
Si P
Si Si
Si
P Si P Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
A junction is formed when on side of semiconductor is doped by n-type and other side by p-
type impurity.
Diodes (The PN Junction)
Diodes (The PN Junction)
The free electrons in
the n region are
randomly drifting in
all directions. At the
instant of the pn
junction formation, the
free electrons near the
junction in the n
region begin to diffuse
across the junction
into the p region
where they combine
with holes near the
junction. The same is
true for the p-type
material.
Diodes (The Depletion
Region)
When the pn junction
is formed, the n region
loses free electrons as
they diffuse across the
junction. This creates
a layer of positive
charges (ions) near the
junction. As the
electrons move across
the junction, the p
region loses holes as
the electrons and holes
combine. This creates
a layer of negative
charges (ions) near the
junction. These two
layers of positive and
negative charges form
the depletion region.
PN-Junction
Si
Si Si
Si Al
Si Si
Si
Al Si Al Si
Si Si Si Si
Al Si Al Si
P
Si Si
Si P
Si Si
Si
P
Si Si
Si P
Si Si
Si
P Si P Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
Electrons and holes present near the junction recombine. Electrons diffuse to the left leaving
behind pentavalent atom as positive ion in N-type and trivalent atom as a negative ion in P-
type. Hole disappears and electrons becomes a valance electron. A pair of ions form a dipole.
Electron hole diffusion
Al
Si Si
Si
Si Si
Si
Al Si Si
Si Si Si Si
Al Si Si
Si Si
Si P
Si Si
Si
Si Si
Si P
Si Si
Si
Si P Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
Si
Depletion Region and Barrier potential
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
Electrons diffuse to the left forming dipoles, positive ions are formed in N-type side and
negative ions in P-type side. As dipoles build up, region near the junction is emptied of
carriers. This region is charged region (having +ve and ve ions) but have no charge carrier
(electrons and holes), and is called depletion region. Since dipole has an electric field
between +ve and ve ions, when fresh electrons try to enter the depletion region, electric field
try to push them back. Strength of field increase with each crossing electron until equilibrium
is reached and stops further diffusion of electrons. This is barrier potential whose value is
0.7V for silicon.
Formation of depletion region in pn-junction:
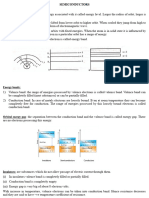
Diodes (Forward Bias )
To bias a pn junction, apply an external dc voltage across it. Forward bias
is the condition that allows current through a pn junction. The picture
shows a dc voltage source connected by conductive material (contacts and
wire) across a pn junction in the direction to produce forward bias.
This external bias voltage is designated as V
BIAS
. Notice that the negative
side of V
BIAS
is connected to the n region of the pn junction and the
positive side is connected to the p region. This is one requirement for
forward bias. A second requirement is that the bias voltage, V
BIAS
, must be
greater than the barrier potential (0.7V in silicon and 0.3 in germanium).
Diodes (Forward Bias )
Because like charges repel, the negative side of the bias-voltage
source "pushes" the free electrons, which are the majority carriers
in the n region, toward the pn junction. This flow of free electrons
is called electron current. The negative side of the source also
provides a continuous flow of electrons through the external
connection (conductor) and into the n region as shown.
Forward biased pn-junction
Depletion region and potential barrier reduced
Reverse biased diode
Depletion region becomes wider,
barrier potential higher
Biasing of diode
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
Biasing is to apply voltage for current flow in a diode. It is of two types
Forward biasing
Reverse biasing
Forward biasing
In forward biasing, P-side is connected to +ve and N-side to ve terminal of battery. Battery pushes
electrons and holes towards the junction. If battery voltage is less than barrier potential (0.7V for
Silicon), free electrons do not have enough energy to get through depletion region. Otherwise, free
electrons have enough energy to pass through depletion region and combine with holes which
produces a continuous current. Therefore current easily flows when diode is forward biased and
width of depletion region becomes smaller.
Diode act as a complete circuit and conducts during such forward biasing.
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
In reverse biasing, P-side is connected to ve and N-side to +ve terminal of battery. Negative
terminal of battery attracts holes and positive terminal of battery attracts electrons away from the
junction. Therefore depletion region widens and opposes the flow of current across junction. The
wider the depletion layer, greater the junction potential. Depletion region stop growing when
junction potential equals the applied reverse voltage. Therefore electrons and holes stop moving
away from junction then.
Diode act as an open circuit and does not conduct during such reverse biasing.
Reverse biasing
Reverse minority saturation current
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
In reverse biasing a small current exists which is due to flow of minority charge carriers. Such
minority charge carriers are electrons in P-side and holes in N-side produce due to bonds broken by
thermal energy. Most of these minority carriers recombine with majority carriers but those present
inside depletion region may cross the junction produces small current called reverse current. This
is also called minority saturation current, since it does not depend upon battery but temperature.
Besides this thermally produced minority carrier current, a small current flows on the surface of
crystal (due to surface impurities) called surface leakage current.
Diode breakdown
(Process of avalanche)
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
Diodes have maximum voltage ratings. There is a
limit to how much reverse voltage a diode can
withstand before it destroyed. If reverse voltage is
continuously increases, there will be breakdown
voltage. For most of diodes it is nearly 50 V. After
increases applied voltage more than breakdown
voltage a large number of minority charge carriers
appear and diode conducts heavily. These large
number of carriers are produced by avalanche
effect.
When reverse voltage is increased it forces
minority carriers more quickly which collide with
atoms of crystals and knock valence electrons
producing free electrons. The process is geometric
producing 1,2,4,8. Electrons.
Exceeding breakdown voltage does not
necessary mean the destroy of diode.
Diode curves
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
Forward Region
When diode is forward biased. Voltage at which current rapidly Increases is called
Knee voltage. It is equal to barrier potential. For Silicon it is 0.7V, for Germanium It is 0.3V.
Reverse Region
When diode is forward biased, current is very small.
Forward (closed) and Reveres (open)
biasing of diode.
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
Half wave rectifier
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
Rectification is process of conversion of AC to DC.
Input A.C Output D.C
Full wave rectifier
Full wave rectifier (Bridge rectifier)
Dr. Abdul Majid Sandhu, Department of
Physics, University of Gujrat.
Вам также может понравиться
- UOG Chemistry Syllabus DocumentДокумент111 страницUOG Chemistry Syllabus DocumentAbdur Rehman80% (5)
- Math IA HLДокумент13 страницMath IA HLDev Shah100% (6)
- 091 Vijaya Prasaadam 01 05Документ41 страница091 Vijaya Prasaadam 01 05aruna11668% (72)
- Cost and Benefit Analysis of Solar Panels at HomeДокумент8 страницCost and Benefit Analysis of Solar Panels at HomePoonam KilaniyaОценок пока нет
- What Is A Diode?: Current ResistanceДокумент8 страницWhat Is A Diode?: Current ResistanceadeelОценок пока нет
- Diode: What Is A Diode?Документ8 страницDiode: What Is A Diode?shayma ahmedОценок пока нет
- Diode - Definition, Symbol, and Types of Diodes - Electrical4UДокумент11 страницDiode - Definition, Symbol, and Types of Diodes - Electrical4UEr Suraj Kumar100% (1)
- Diode:: Unbiased Diode and Depletion LayerДокумент10 страницDiode:: Unbiased Diode and Depletion LayerAnonymous ovAm3yJXОценок пока нет
- Physics ProjectДокумент11 страницPhysics ProjectDimpySurya44% (25)
- Diodes: Principles and ApplicationsДокумент9 страницDiodes: Principles and ApplicationsEnitsuj Eam EugarbalОценок пока нет
- Physics ProjectДокумент11 страницPhysics ProjectJayesh PandyaОценок пока нет
- Eee 204 NoteДокумент37 страницEee 204 Noteleslie woodsОценок пока нет
- ED and CA Unit 1Документ25 страницED and CA Unit 1rsnagakumarОценок пока нет
- Diode, Zener Diode, Transistor NotesДокумент20 страницDiode, Zener Diode, Transistor Notesgetata2599Оценок пока нет
- 201806014043+HASAN MD TANVIR + Homework of Chapter 2Документ10 страниц201806014043+HASAN MD TANVIR + Homework of Chapter 2nahar elaОценок пока нет
- UNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEEДокумент12 страницUNIT 4 PN Junction Diode Complete Notes BEESomesh Singh RathoreОценок пока нет
- Analogue Electronic Design Module E - Diode V-I CharacteristicsДокумент50 страницAnalogue Electronic Design Module E - Diode V-I CharacteristicsArvish RamseebaluckОценок пока нет
- Ec8252 Electronicdevices 997787639 Ec8252 NotesДокумент96 страницEc8252 Electronicdevices 997787639 Ec8252 NoteschandanpgowdachandanpОценок пока нет
- SemiconductorДокумент23 страницыSemiconductormillinagi95Оценок пока нет
- Assignment - EEE 103Документ4 страницыAssignment - EEE 103Abu BasharОценок пока нет
- Charge Carriers Crossing The JunctionДокумент5 страницCharge Carriers Crossing The Junctionhoangloc NgoОценок пока нет
- ' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityДокумент8 страниц' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityVam ArmodiaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Diode CircuitsДокумент29 страницUnit 1 Diode Circuitseee3 semОценок пока нет
- SemiconductorДокумент3 страницыSemiconductorzubairwahidОценок пока нет
- Presentation ON Semiconduct ORSДокумент14 страницPresentation ON Semiconduct ORSParagОценок пока нет
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12Документ7 страницPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12vidushiinksОценок пока нет
- Unit-I Pn-Junction DiodeДокумент48 страницUnit-I Pn-Junction DiodeBabu GundlapallyОценок пока нет
- SemiconductorsДокумент16 страницSemiconductorsDefny FernandesОценок пока нет
- SemiconductorsДокумент38 страницSemiconductorssomarshidubeyОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ14 страницModule 1Bhakti 2913Оценок пока нет
- First Year Notes MGUДокумент139 страницFirst Year Notes MGUVIPIN VОценок пока нет
- BEEER23 PartBДокумент130 страницBEEER23 PartBK S Ravi Kumar (MVGR EEE)Оценок пока нет
- 21EES101T-EEE-Unit-2 NotesДокумент35 страниц21EES101T-EEE-Unit-2 Notessr1343Оценок пока нет
- PN Junction Diode Working & Biases ExplainedДокумент2 страницыPN Junction Diode Working & Biases ExplainedRaghuramОценок пока нет
- Analog and Digital Electronics: S. M. Jahadun-NobiДокумент39 страницAnalog and Digital Electronics: S. M. Jahadun-NobiJune C. OsunaОценок пока нет
- Sem 2Документ78 страницSem 2Tech TeamОценок пока нет
- Electronics XIIДокумент17 страницElectronics XIIMonjurul LaskarОценок пока нет
- PN Junction Diode: Fundamentals and CharacteristicsДокумент9 страницPN Junction Diode: Fundamentals and CharacteristicsVaishnevОценок пока нет
- PN JunctionДокумент10 страницPN Junctionasdxws feОценок пока нет
- AjphysicsДокумент17 страницAjphysicsAadi JainОценок пока нет
- Rectem EletronicsДокумент4 страницыRectem Eletronicsseun DosunmuОценок пока нет
- What Is A Diode?Документ48 страницWhat Is A Diode?B SaiОценок пока нет
- Module - 1 18ELN14Документ38 страницModule - 1 18ELN14DaisyQueen100% (1)
- PN Junction Lecture NotesДокумент10 страницPN Junction Lecture NotessuperbangadakОценок пока нет
- P-N Junction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент8 страницP-N Junction - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaphaninderОценок пока нет
- Solids and Semi ConductorДокумент11 страницSolids and Semi ConductorGayatriОценок пока нет
- Final Project of Rectifier (Riya)Документ20 страницFinal Project of Rectifier (Riya)RaviОценок пока нет
- SEMICONDUCTORSДокумент7 страницSEMICONDUCTORSPaul KagunyaОценок пока нет
- MODULE-I - PN Junction DiodeДокумент17 страницMODULE-I - PN Junction DiodeAnurag HodgeОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Theory Theory SupportДокумент17 страницSemiconductor Theory Theory SupportathomeОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Materials and TypesДокумент33 страницыSemiconductor Materials and TypesSaidur Rahman SidОценок пока нет
- Chapter-2 Semiconductor Diodes and Their Applications: DiodeДокумент35 страницChapter-2 Semiconductor Diodes and Their Applications: DiodeYaregal ChalachewОценок пока нет
- Unit-2: 2.1. Generation and Recombination of Carriers: Generation of Carriers (Free Electrons and Holes)Документ13 страницUnit-2: 2.1. Generation and Recombination of Carriers: Generation of Carriers (Free Electrons and Holes)shivaniОценок пока нет
- Diode Fundamentals Explained: Formation, Energy Bands & Junction PotentialДокумент24 страницыDiode Fundamentals Explained: Formation, Energy Bands & Junction Potentialmuvin236Оценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Physics and Devices ExplainedДокумент41 страницаSemiconductor Physics and Devices ExplainedVishal GuptaОценок пока нет
- PN Diode and Zener Diode AS PER BEEE NOTES MainДокумент17 страницPN Diode and Zener Diode AS PER BEEE NOTES MainMohd AbrarОценок пока нет
- P-N Junction DiodeДокумент32 страницыP-N Junction Diodesashi_s2Оценок пока нет
- unit-5 BEEE (semiconductor, diode & transistor) (2)Документ30 страницunit-5 BEEE (semiconductor, diode & transistor) (2)Patel SaОценок пока нет
- How a PN Junction FormsДокумент3 страницыHow a PN Junction FormsHuidrom SharatОценок пока нет
- PN Junction Diode: A Guide to Its Structure and OperationДокумент5 страницPN Junction Diode: A Guide to Its Structure and OperationVickeyОценок пока нет
- Bed Unit 1Документ29 страницBed Unit 1AravindОценок пока нет
- Linear FunctionalsДокумент19 страницLinear FunctionalsAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Muqaddama e QuranДокумент8 страницMuqaddama e QuranAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Hilbert SpacesДокумент18 страницHilbert SpacesAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Linear OperatorsДокумент16 страницLinear OperatorsAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- 10.defence Language Institute Persian Reader PDFДокумент121 страница10.defence Language Institute Persian Reader PDFEric Erik100% (1)
- Idrees Aazad - Allama Iqbal Kay Mazhabi AqaaidДокумент17 страницIdrees Aazad - Allama Iqbal Kay Mazhabi AqaaidAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Qari Hanif - Mera AkhlaqДокумент12 страницQari Hanif - Mera AkhlaqAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Banach SpacesДокумент19 страницBanach SpacesAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Banach SpacesДокумент9 страницBanach SpacesAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Noman Ali Khan - Zahanat or Takhliqi SalahiyatДокумент9 страницNoman Ali Khan - Zahanat or Takhliqi SalahiyatAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Qari Hanif - Imam ShobaДокумент14 страницQari Hanif - Imam ShobaAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- CRO Bs-3rdДокумент44 страницыCRO Bs-3rdAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Faizullah Khan - QandozДокумент5 страницFaizullah Khan - QandozAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Muhammad F Alvi - Nabi Ki NamazДокумент8 страницMuhammad F Alvi - Nabi Ki NamazAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Idrees Aazad - Allama Iqbal Kay Mazhabi AqaaidДокумент17 страницIdrees Aazad - Allama Iqbal Kay Mazhabi AqaaidAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- 04.the Routledge Introductory Persian Course SupplementДокумент21 страница04.the Routledge Introductory Persian Course SupplementKeep CalmОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Lecture on Atomic Structure, N-type and P-type MaterialsДокумент21 страницаSemiconductor Lecture on Atomic Structure, N-type and P-type MaterialsAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Letters of Iqbal To JinnahДокумент16 страницLetters of Iqbal To JinnahAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 MPEДокумент34 страницыLecture 1 MPEAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Hiat HefizДокумент163 страницыHiat HefizaverroistОценок пока нет
- Essentials of The Islamic Faith by Fethullah GulanДокумент133 страницыEssentials of The Islamic Faith by Fethullah GulanAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Heat & ThermodynamicsДокумент21 страницаHeat & ThermodynamicsAbdur RehmanОценок пока нет
- Monetary PolicyДокумент21 страницаMonetary PolicyAbdur Rehman100% (1)
- How to convert a Galvanometer into a VoltmeterДокумент5 страницHow to convert a Galvanometer into a VoltmeterAbdur Rehman100% (1)
- HVT Substation Equipment - Product List PDFДокумент2 страницыHVT Substation Equipment - Product List PDFAmol DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Double Inlet Airfoil Fans - AtzafДокумент52 страницыDouble Inlet Airfoil Fans - AtzafDaniel AlonsoОценок пока нет
- OnsemiДокумент15 страницOnsemijeos20132013Оценок пока нет
- Aircraft Electrical Systems (Pallett)Документ192 страницыAircraft Electrical Systems (Pallett)Abolfazl Mazloomi100% (2)
- Resistors, Dynamic Breaking YaskawaДокумент14 страницResistors, Dynamic Breaking YaskawaCarlitos BaezОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics titleДокумент8 страницElectrostatics titleRupinder SidhuОценок пока нет
- 1) Solid Pad Mount Switchgear - Eng - MexicoДокумент16 страниц1) Solid Pad Mount Switchgear - Eng - MexicoJims Poma VilcahuamanОценок пока нет
- Cooper ArresterДокумент8 страницCooper ArresterHongОценок пока нет
- Draw and calculate voltages in series and parallel circuitsДокумент3 страницыDraw and calculate voltages in series and parallel circuitsBen HoangОценок пока нет
- VCE Physics Solutions 2017 Sample PaperДокумент6 страницVCE Physics Solutions 2017 Sample PaperLeo JaszОценок пока нет
- DiodeДокумент6 страницDiodepetrishia7_317164251Оценок пока нет
- Technical Particular and Guarantee: Pt. Prima Indah LestariДокумент2 страницыTechnical Particular and Guarantee: Pt. Prima Indah Lestaritees220510Оценок пока нет
- Candy Cmd106 16sДокумент23 страницыCandy Cmd106 16sBranko SavicОценок пока нет
- MHT–CET – 2017: PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CODE – 44 EXAM GUIDEДокумент23 страницыMHT–CET – 2017: PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY CODE – 44 EXAM GUIDEpranav kandalkarОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Fields of High-Speed Transportation Systems: The International Maglev BoardДокумент22 страницыElectromagnetic Fields of High-Speed Transportation Systems: The International Maglev BoardMayur PuriОценок пока нет
- EMT10 NewДокумент12 страницEMT10 NewzcaptОценок пока нет
- KM M CM MM: Basic MeasurementsДокумент5 страницKM M CM MM: Basic MeasurementsMuralee VeeramalaiОценок пока нет
- Die CalculationsДокумент13 страницDie CalculationsDhinakaran R100% (1)
- Static & Kinetic FrictionДокумент15 страницStatic & Kinetic FrictionAishah DarwisyaОценок пока нет
- AbstractДокумент9 страницAbstractNathan BerheОценок пока нет
- USAHAДокумент36 страницUSAHAsamsulsman1btgОценок пока нет
- g3rv - j180 E2 02 PDFДокумент14 страницg3rv - j180 E2 02 PDFSdiri OùMaimàОценок пока нет
- 2GCS304014B0070-CLMD BrochureДокумент12 страниц2GCS304014B0070-CLMD BrochureRitaban R. BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- PaperДокумент6 страницPapermohitОценок пока нет
- BF01015003Документ7 страницBF01015003jymmyneutronnОценок пока нет
- Disjunctor BVAC ScheronДокумент4 страницыDisjunctor BVAC ScheronDobrete KatyОценок пока нет
- Shallow Foundation PDFДокумент54 страницыShallow Foundation PDFYUK LAM WONGОценок пока нет