Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Diabetes Mellitus - Kuliah2013
Загружено:
Tia AriantiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Diabetes Mellitus - Kuliah2013
Загружено:
Tia AriantiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
DIABETES MELLITUS
EPIDEMIOLOGI DAN
PERMASALAHANNYA
Dr. SUHAEMI, SpPD, FINASIM
Diabetes Mellitus
Suatu Sindroma kelainan metabolik,
ditandai adanya hiperglikemia, akibat
defek sekresi insulin, defek kerja
insulin, atau kombinasi keduanya.
Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications. Department of Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance,
World Health Organization, Geneva 1999.
Definition of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is characterised by:
chronic hyperglycaemia with disturbances of
carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism
defects in insulin secretion (-cell dysfunction)
and insulin action (insulin resistance)
Type 1 diabetes
-cell destruction
Type 2 diabetes
Progressive insulin secretory defect
Other specific types of diabetes
Genetic defects in -cell function, insulin action
Diseases of the exocrine pancreas
Drug- or chemical-induced
Gestational diabetes mellitus
Classification of Diabetes
ADA. I. Classification and Diagnosis. Diabetes Care 2011;34(suppl 1):S12.
Diabetes Mellitus :
a group of diseases characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from
defects in insulin production, insulin action, or both
20.8 million in US ( 7% of population)
estimated 14.6 million diagnosed (only 2/3)
Consists of 3 types:
1) Type 1 diabetes
2) Type 2 diabetes
3) Gestational diabetes
Complications :
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Kidney disease
- Eye Disease
- Nerve Damage
Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 Diabetes
- cells that produce insulin are
destroyed
- results in insulin dependence
- commonly detected before 30
Type 2 Diabetes
- blood glucose levels rise due
to
1) Lack of insulin
production
2) Insufficient insulin
action (resistant cells)
- commonly detected after 40
- effects > 90%
- eventually leads to -cell
failure
(resulting in insulin dependence)
Gestational Diabetes
3-5% of pregnant women in the US
develop gestational diabetes
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1
Results from inability of
islet cells to produce
insulin
Also known as insulin-
dependent or juvenile-
onset diabetes
Cause is unknown, but
likely to have genetic,
autoimmune component
molcules HLA de
classe II (DR3-DR4)
virus
insuline
lymphocyte
CD 4
Ag viraux
et de cell.
CD 8
IFNg
IL-2
NK
lymphocyteB
cytokines
anticorps
cell.
activa-
tion
facteurs
d environnement?
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Results from decreased
insulin sensitivity and
decreased pancreatic
beta-cell function
Adapted from International Diabetes Center (IDC). Minneapolis, Minnesota
Natural History of Type 2 Diabetes
0 10 20 30
Years of Diabetes
-cell
function
Plasma
glucose
Insulin resistance
Insulin secretion
Fasting glucose
Post-prandial
glucose
Insulin Rx
OADs
TLC
OAD
ACEI
AIIA
Gestational Diabetes
Diabetes that first
presents during pregnancy
Occurs in 2-10% of
pregnancies
30-60% chance of
developing T2DM
RISKESDAS 2008
Diagnosed patients
Undiagnosed patients
Indonesian Basic Health
Research (RISKESDAS)
Total DM = 5,7%
Diagnosed DM = 1,5%
Undiagnosed DM = 4,2%
IGT = 10,2 %
DM patients estimated (WHO)
2000
2030
8 million >21
million
Epidemiology of Diabetes
Diabetes in the World
Viva la Vida con Salud!
millions
India
31.7
China
20.8
USA
17.7
Indonesia
8.4
Japan
6.8
Year
2000
Reference: Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27(5): 1047-1053.
Diabetes in the World
Viva la Vida con Salud!
millions
India
79.4
China
42.3
USA
30.3
Indonesia
21.3
Japan
8.9
Year
2030
Reference: Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27(5): 1047-1053.
Why is Diabetes on the
Increase?
Ethnicity and family history are implicated
Closely associated with overweight or obese
people
Increased switch to Western diet and lifestyle
T Y P E 2 D I A B E T E S
Obesity
International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes Atlas, 2nd Edition, 2003
Western lifestyle Genetic component
Fast Food and Obesity
200% fast-food visits 1977-1995
30% of US children (4-19 yrs) consume fast
food daily
Fast Food and Obesity
Fast-foods fat and energy
Big Mac + medium fries = 83% daily fat intake
Adversely affects dietary quality
Less fiber, fruits, vegetables and milk
Mega-meals
Mega Meals
Super Size
Each 12 oz soda has 10
tsp sugar (150 cal)
One can of soda/day
childs risk obesity 60%
Most popular Canadian
drink
> 110 L/ person/yr
1942-1998:
US production increased
9X
Diabetes
Presentation title in footer | 00 Month 0000
28
Children > 10 years
Metformin dose < 2000mg
Metformin Approved Use
Combined with Insulin
Single Therapy
POM Indonesia ; monotherapi or combination with insulin ;
- Glucophage 1000 mg film-coated tablet can be used in children from 10 years of age and adolescents.
- The maximum recommended dose of metformin hydrochloride is 2 g daily, taken as 2 or 3 divided doses.
Diabetes Today: An
Epidemic
Impact of DM
25.8 million Americans have diabetes (8.3%
of population)
The number of Americans treated for
diabetes doubled from 1996 to 2007.
1 in 3 Americans born in 2000 will have
diabetes in their lifetime
Annual costs -- $132 billion
Leading cause of blindness, ESRD,
amputations, MI, strokes
Resistensi
Insulin
Diabetes
Tipe 2
DeFronzo et al. Diabetes Care 1992;15:318-68
Diabetes Melitus
Definisi :
- gangguan metabolisme
- kenaikan kadar glukosa darah kronis
- disebabkan oleh adanya gangguan produksi insulin akibat kerusakan
sel beta pankreas dan atau kerja insulin.
Kerusakan sel
Beta pankreas
The Pathophysiology of Type 2
Diabetes Includes Three Main
Defects
32
Adapted from Buse JB et al. In Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 10th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2003:14271483; Buchanan TA Clin
Ther 2003;25(suppl B):B32B46; Powers AC. In: Harrisons Principles of Internal Medicine. 16th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2005:21522180;
Rhodes CJ Science 2005;307:380384.
Hyperglycemia
Liver
Insulin deficiency
Excess glucose output
Insulin resistance (decreased
glucose uptake)
Pancreas
Muscle and fat
Excess
glucagon
Islet
Diminished
insulin
Diminished
insulin
Alpha cell
produces
excess
glucagon
Beta cell
produces
less insulin
Copyright 2008 Dr. Salme Taagepera, All rights reserved.
http://www.fda.gov/fdac/graphics/2002graphics/insulin.jpg
Insulin activates a cell signaling pathway that results
in glucose transporters moving to the cell surface
How does insulin decrease blood sugar levels?
Types of diabetes
Copyright 2008 Dr. Salme Taagepera, All rights reserved.
1. Type 1 = autoimmune disease resulting in loss
of insulin production
2. Type 2 = associated with obesity, lack of
cellular response to insulin
Type 1
Type 2
Physiology: Role of Insulin
Normal
Patho: DM Type 1
No Insulin
Patho-Cont.:DM Type 2
History of DM
Diabetes
Greek for
passing water
like a siphon
Mellitus
Latin for
sweetened
with honey
Ebers Papyrus
(Egyptian, 1500 B.C.)
first depiction of diabetes mellitus
- urination of excess amounts
- manipulation of diet therapy
Sudah dikenal sejak zaman Ebers Papyrus 1550
SM
Willis : mencatat ada rasa manis pada urine
IBNU SINA : Gangren Diabetic
Matthew Dobson : Rasa manis karena gula
1815 : Chevreul (ahli Kimia) membuktikan bahwa
gula dalam urine adalah glukosa
1921 : Frederic Grant Banting, Charles Best
berhasil mengekstraksi insulin pertama kali dari
pankreas anjing
11 Jan 1922 : Leonardo Thompson, remaja
merupakan pasien pertama yang mendapat insulin
di RS Toronto Kanada
1979 : Goedde menghasilkan human insulin
dengan rekayasa genetik
Faktor Resiko untuk Terjadinya DM
Kelompok Usia > 45 tahun
Gemuk : BB > 120% BBI (IMT > 27 kg/m2)
Hypertensi
Riwayat Keluarga DM
Riwayat melahirkan bayi > 4 kg.
Riwayat DM pada waktu hamil (DM Gestasi)
Dislipidemia : HDL < 35 mg/dl, Trigliserida > 250
mg/dl
Pernah mengalami gangguan toleransi glukosa
Etiologi
Herediter, diperlukan faktor lain yang disebut
faktor risiko atau faktor pencetus
Virus
Pada DM tipe 1 dijumpai HLA gen yang rentan
terhadap infeksi virus tertentu.
Virus yang selalu menimbulkan insulitis adalah :
Coxackie, Mumps, Rubella, Cytomegalovirus,
Herpes, dll.
Obesitas
Kadar Insulin cukup tetapi tidak efektif (Resistensi
Insulin )
Memakai obat-obatan yang menyebabkan
Kadar Gula Darah meningkat
Not specified
Others
Tuberculosis
Accident / suicide
Gangrene
Renal insufficiency
Diabetic coma
Infections
Tumors
Stroke
Myocardial infarction
0 10 20 30 40
% deaths in diabetics 3.4
11.4
0.9
2.1
2.7
2.9
3.1
6.7
10
22
34.7
Panzram G. Diabetologia 1987; 30: 120-31
Causes of Mortality in Diabetic
Patients
Pankreas
Terletak dibelakang lambung
Berat : 200 250 gram
Bentuk : Kerucut terbaring
Bagian yang lebar : Kepala (Caput)
Bagian yang kecil : Ekor (Cauda)
Terdapat kumpulan sel disebut pulau-pulau Langerhans
yang berisi sel Beta dan mengeluarkan hormon Insulin.
Disamping sel Beta terdapat sel Alfa yang mengeluarkan
Glukagon yang bekerja berlawanan dengan insulin yaitu
meningkatkan kadar gula darah. Juga ada sel Delta yang
mengeluarkan Somatostatin
INSULIN
Definisi :
Insulin adalah hormon yang
dikeluarkan oleh sel beta
pankreas yang berperanan
dalam mengatur kadar glukosa
darah
Insulin diibaratkan sbg anak
kunci yang membuka pintu
masuknya glukosa ke dalam sel
KERJA FISIOLOGIS INSULIN
& PENGLEPASAN INSULIN
Insulin dibentuk dari pro insulin distimulasi dg pe
glukosa darah menghasilkan insulin & C-peptide yg
akan masuk ke dlm aliran darah & akan me kan kadar
glukosa darah
Insulin membantu meningkatkan sintesa protein,
meningkatkan penyimpanan lemak, menstimulasi
mesuknya glukosa ke dlm sel utk sumber energi dan
membantu penyimpanan glikogen dlm lemak dan hati
Insulin : endogen & eksogen
Insulin
Tenaga
Glukosa darah
Pintu masuk sel
Insulin
Insulin Insulin
Glukosa dibakar
pembawa glukosa
NORMAL
Insulin
Insulin
Pintu
terbuka
Insulin
Tenaga
Glukosa darah
Pintu masuk sel
Tak ada yang dibakar
Pembawa glukosa
DIABETES
Pintu
tertutup
Glukosa darah
F A S E 1 F A S E - 2
F A S E - 1
F A S E - 2
Individu normal
Penderita DM tipe-2
Insulin
plasma
waktu
Insulin
plasma
(Tumpul)
(Lebih tinggi dan lama)
(Delayed Insulin secretion)
Waktu
3-5 mnt
50-60 menit
60 ng/ml
100
80
60
40
20
0
Years from Diagnosis
B
e
t
a
-
C
e
l
l
F
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
(
%
)
Beta-Cell Function in the UKPDS
-12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6
Diagnosis
KERJA FISIOLOGIK INSULIN
MEMASUKKAN GLUKOSA DARI DALAM DARAH KE:
Hati:
Glukosa di robah jadi glikogen (Glikogenesis)
Glikogen hati menjadi cadangan gula dalam tubuh
Otot:
Glukosa di robah jadi Glikogen (Glikogenesis)
Glikogen otot dibakar menjadi sumber kalori.
Adiposa:
Glucosa dirobah (?) jadi trigliserida
Mencegah pemecahan lemak (Antilipolisis)
Mengaktifkan Lipoprotein Lipase di sel sel endotel P.darah
Jaringan lain: Meningkatkan sintesa protein dari A.Amino
INSULIN MENURUNKAN KADAR GLUKOSA DARAH
SlametS 53
100
75
50
25
0
UKPDS :
Natural Deterioration of -Cell Function
Years from Diagnosis
Lebovitz H. Diabetes Review 1999;7:139-53
B
e
t
a
C
e
l
l
F
u
n
c
t
i
o
n
(
%
)
-12 10 -6 -2 0 2 6 10 14
Th/Expectation
Facts
Strategy to Prevent the Deterioration
of Type 2 Diabetes
Years from Diagnosis
Lebovitz H. Diabetes Review 1999;7:139-53
T2DM phase III
Beta Cell
Function
(%)
IGT Postprandial
Hyperglycemia
T2 DM
phase I
T2DM
phase II
-12 10 -6 -2 0 2 6 10 14
Monotherapy
Life Style
Oral Hypo(s)
Combination
Insulin with
or without
Oral Hypo
Glycemic agent
SlametS 55
Hyperglycemia
Glucose autoxidation Sorbitol pathwayr
AGE formation
Oxidative Sress
Antoxidants
Lipid peroxidation
Leukocyte adhesion
Foam cell formation
TNF a
Endothelial dysfunction
NO Endothelin
Prostacyclin
TXA
2
Hypercoagulability
Fibrinolysis
Coagulability
Platelet reactivity
Vascular complications
Retinopathy Nephropathy
Neuropathy
Stehouwer CDA et al. 2004
Oxidative stress
Sorbitol
pathway
DAG-PKC
pathway
Hexosamine
pathway
AGE
pathway
Increase of :
Extracellular
matrix
Collagen
Fibronectin
Increase of pro-
coagulant proteins
von Willebrandt
factor
tissue factor
Decrease of
proliferation,
migration,
and fibrinolytic
potential
Increase of
apoptosis
Vascular complications
INSULIN DALAM JUMLAH YANG NOR
MAL TIDAK DAPAT BEKERJA SECARA
OPTIMAL DI JARINGAN SASARAN NYA
SEPERTI DI OTOT, HATI DAN ADIPOSA.
Sel sel pancreas mengkompensasi keadaan ini
dengan meningkatkan produksi insulin dan me
nyebabkan HIPERINSULINEMIA
Insulin Resistance
Hyperglycemia (Type 2 DM)
Increase Lipolysis
Decrease Lipogenesis
Adipose tissue
(Obesity)
Elevated
Plasma
FFA
Elevated
TNF-a
Insulin secretion
Insulin resistance
Hyperinsulinemia
Amyloid deposit
Islet -cell degranulation;
Reduced insulin content
Reduced plasma
insulin
Increased hepatic
glucose output
+
-
Gluconeo
genesis
decreased
glucose uptake
Glucose
toxicity
Lipotoxicity
Glucose Transporters
GLUT 1 : Endothelium
GLUT 2 : Liver, B-cells of Pancreas
GLUT 3 : Neurons
GLUT 4 : Muscle, Adipose Tissue
GLUT 5 : Intestine
Copyright 2008 Dr. Salme Taagepera, All rights reserved.
Insulin functions to promote transmembrane
transport of glucose into the cell
1. Binding of insulin to the cells insulin
receptor causes the receptor to become
activated (autophosphorylation)
2. The activated receptor, in turn, activates
a signaling pathway
(IRS-1 PI3-kinase PDK Akt)
3. The activated signaling pathway causes
the translocation of the intracellular
GLUT4 transporter to the cell surface
4. NET RESULT: GLUT4 (insulin-
responsive) glucose transporters import
glucose across the membrane into the
cell
1
2
3
4
promoter
Coding reg
transcription
mRNA
Modified from Howard L. Foyt et al. Thiazolidinediones. Diabetes Mellitus: a Fundamental and Clinical Text, 2
nd
Ed.
Synthesis GLUT 4
PPARg
PPRE
Insulin
receptor
Insulin
RXR
Glucose
Insulin Action
PPARg
promoter
Coding reg
+RXR
Modified from Howard L. Foyt et al. Thiazolidinediones. Diabetes Mellitus: a Fundamental and Clinical Text, 2
nd
Ed.
PPRE
Insulin
Insulin Resistance
Glucose
mRNA
Synthesis GLUT 4
X
X
transcription
Insulin
receptor
Translocation
Muscle
Cells
4:00
25
50
8:00 12:00 16:00 20:00 24:00 4:00
Breakfast Lunch Dinner
P
l
a
s
m
a
i
n
s
u
l
i
n
(
U
/
m
l
)
Time
8:00
Physiological Serum Insulin
Secretion Profile
Diabetic
retinopathy
Leading cause
of blindness
in working-age
adults
1
Diabetic
nephropathy
Leading cause of
end-stage renal disease
2
Cardiovascular
disease
Stroke
1.2- to 1.8-fold increase
in stroke
3
Diabetic
neuropathy
Leading cause of non-
traumatic lower
extremity amputations
5
75% diabetic patients
die from CV events
4
Type 2 Diabetes is NOT a mild
disease
1
Fong DS, et al. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26 (Suppl. 1): S99S102.
2
Molitch ME, et al. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26 (Suppl. 1): S948.
3
Kannel WB, et al. Am Heart J. 1990; 120: 6726.
4
Gray RP & Yudkin JS. In Textbook of Diabetes 1997.
5
Mayfield JA, et al. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26 (Suppl. 1): S78S79.
Microvascular
Macrovascular
Testing :
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
(FPG) - (cheap, fast)
*fasting B.G.L. 100-125
mg/dl signals pre-diabetes
*>126 mg/dl signals diabetes
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
(OGTT)
*tested for 2 hrs after
glucose-
rich drink
*140-199 mg/dl signals pre-
diabetes
*>200 mg/dl signals diabetes
80 to 90 mg per 100 ml, is the normal fasting blood
glucose concentration in humans and most mammals
which is associated with very low levels of insulin
secretion.
A.K.A.: Glycated Hemoglobin tests
A1C
Chronic Complications-
Microvascular :
1. Diabetic Retinopathy
Chronic Complications-
Microvascular
2. Nephropathy
Chronic Complications-
Microvascular
3. Diabetic Neuropathy
Clinical assessment
symptoms and signs
may be obvious or subtle
- history of rest pain at night
- gangrene
colour
- white
- red (hyperaemic skin)
temperature
- cool
Pulses and ABPI
Effects on Blood Vessels
Blood Vessel
Lumen
Chronic Complications-Microvascular
Sexual problems for men
erectile dysfunction
retrograde ejaculation
Sexual problems for women
decreased vaginal lubrication
decreased sexual response
Urologic problems for men and
women
urinary tract infections
neurogenic bladder
liver
pancreas
liver
Regulation of Blood Sugar
blood sugar level
(90mg/100ml)
insulin
body
cells take
up sugar
from blood
liver stores
sugar
reduces
appetite
glucagon
pancreas
liver
releases
sugar
triggers
hunger
high
low
Feedback
Endocrine System Control
GEJALA KLASIK DM
4 P
1. POLI DIPSIA
2. POLIFAGIA
3. POLI URIA
3. PENURUNAN BERAT BADAN
Signs and Symptoms
Klinis Diabetes Melitus :
Polifagia : sel mengalami starvasi karena cadangan
KH,Lemak, Protein berkurang ( tdk ada pengisian depot yg
biasanya dilakukan oleh Insulin )
Polidipsia : glukosuria (diuresis osmotik) dehidrasi
intraselular dan stimulasi pusat haus di hipotalamus)
kompensasi: penderita banyak minum
Poliuria : glukosuria (diuresis osmotik) penderita
banyak kencing
Penurunan BB : cairan tubuh berkurang karena diuresis
osmotik, protein dan lemak berkurang karena dipecah sbg
sumber energi.
Lelah : Metabolisme tdk berjalan sebagaimana mestinya.
Kriteria Diagnosa DM
Gejala Klasik DM + Kadar Gula Darah Sewaktu
> 200 mg/dl
Gejala Klasik DM + Kadar Gula Darah Puasa >
126 mg/dl
Kadar Gula Darah 2 jam TTGO > 200 mg/dl
Puasa diartikan tidak mendapat kalori tambahan
sedikitnya 8 jam TTGO dengan standar WHO,
menggunakan beban glukosa yang setara
dengan 75 gram glukosa anhidrous yang
dilarutkan dalam air
Diabetes
Fasting Plasma Glucose
7.0mmol/l(126mg/dl)
Or
2 hour plasma glucose 11.1 mmol/l
(200mg/dl)
OGTT
TEST TOLERANSI GLUKOSA
ORAL (T.T.G.O)
1. Makan minum seperti biasa 3 hari sebelum
pemeriksaan
2. Kegiatan jasmani dilakukan seperti biasa
3. Berpuasa 10-12 jam sebelum pemeriksaan
4. Pagi diperiksa KGD puasa
5. Minum larutan 75 gr glukosa dalam 250cc air (5 menit)
6. Pasien menunggu selama 2 jam dan tidak merokok
7. Diperiksa KGD 2 jam sesudah minum larutan glukosa
TGT
KGD puasa normal. KGD 2 jam paska pembebanan
75 gram glukosa antara 140-199 mg%
GDPT
KGD Puasa 110-125 mg%,KGD 2 j PG Normal.
GEJALA KLINIS DIABETES MELLITUS
TIPE-2
GEJALA KHAS GEJALA TIDAK KHAS
Poliuria Kesemutan
Polidipsia Gatal di daerah genital
Polifagia Keputihan
BB turun cepat Infeksi sukar sembuh
Bisul hilang timbul.
Penglihatan kabur
Cepat lelah
Mudah mengantuk
Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
Chronic Complications of
Diabetes Mellitus
Microvascular
Retinopathy
(nonproliferative/proliferat
ive)
Nephropathy
Neuropathy
Sensory and motor
(mono- and
polyneuropathy)
Autonomic
Macrovascular
Coronary artery disease
Peripheral vascular
disease
Cerebrovascular disease
Acute Complications of
Diabetes Mellitus
Hyperglycemia crisis
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Hyperglycemia
hyperosmolar State
Lactic acidosis
Hypoglycemia
GAMBARAN KLINIS DM TIPE-1
DAN DM TIPE-2
GEJALA DM tipe-1 DM tipe-2
Poliuria dan Polidipsia ++ +
Lemas dan mudah lelah ++ +
Kuat makan tapi tambah kurus ++ -
Penglihatan sering berulang kabur + ++
Gatal /radang kemaluan + ++
Neuropati periferal (kebas/kesemutan) + ++
Selalu ngompol malam (Enuresis Noct) ++ -
Sama sekali tanpa gejala - ++
KARAKTERISTIK
DM TIPE 1DAN DM TIPE 2
DM TIPE 1
Mudah terjadi ketoasidosis
Pengobatan harus dgn insulin
Onsetnya akut
Biasanya kurus /Umur muda
Terkait dgn HLA-DR3 & DR4
ICA; GADA; & IAA selalu (+)
Riwayat keluarga (+) pd 10%
30-50% kembar identik terkena
DM TIPE 2
Jarang ketoasidosis (HONK bisa)
Tidak mesti diberi insulin
Onsetlambat (pelan-pelan)
Gemuk atau tak gemuk / > 45 thn
Tak ada kaitan dengan HLA
Tak ada autoantibodi
Riwayat keluarga (+) pada 30%
100% kembar identik terkena
Kriteria Pemantauan Diabetes
Mellitus
BAIK LUMAYAN BURUK
KGD puasa 80-109 110-139> 140
KGD 2 jam pp 110-159160-199 > 200
HbA1c* 4 - 5.9% 6 8% > 8%
Kolesterol total* < 200 200-239 > 240
Kolest. LDL (PJK-)* < 130 130-159 > 160
Kolest.LDL (PJK+)* < 100 100-129 > 130
Trigliserida (PJK-)* < 200 200-249 > 250
Trigliserida (PJK+)* < 150 150-199 > 200
* = diperiksa tiap 3 hingga 6 bulan
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c)
1
PADA TIAP KUNJUNGAN HARUS
DIPANTAU
KGD Sewaktu
Tekanan darah (diukur dalam keadaan duduk)
Indeks Massa Tubuh = BB (kg) / TB (M)
2
PEMERIKSAAN BAIK LUMAYAN BURUK
TD sistolik (mmHg) < 130 130-150 >150
TD diastolik < 80 80-85 >85
IMT Pria (Kg/M2) 20-24.9 25- 27 < 20 atau >27
IMT wanita (Kg/M2) 18.5-22.9 23- 25 < 18.5 atau >25
ACUTE COMPLICATION OF
DIABETES
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
HyperOsmolar NonKetotic (HONK)/Coma
Hyperosmolar Hyperglikemic NonKetotik
Hypoglycemia
Hyperglycemia
Drowsy
Flushed
Thirsty
Diabetic Emergencies According
to Blood Glucose Level
Signs of Diabetic Coma
Kussmaul respirations
Dehydration
Fruity breath odor
Rapid, weak pulse
Normal or slightly low blood pressure
Varying degrees of unresponsiveness
Hypoglycemia
Weak, sweaty
Confused/irritable/
disoriented
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Heat
palpitations
Confusion
Tremor
Sweating
Anxiety
Hunger
Visual
disturbances
Seizure
Loss of
Consciousness
Hypoglycemia
Symptoms of hypoglycemia
Neurogenic (autonomic) Neuroglycopenia
Trembling
Palpitations
Sweating
Anxiety
Hunger
Nausea
Tingling
Difficulty concentrating
Confusion
Weakness
Drowsiness
Vision changes
Difficulty speaking
Headache
Dizziness
tiredness
Drugs associated with Hypoglycemia
ACE inhibitors
Alcohol
Antimalarials
Beta-blockers (non-cardioselective)
Disopyramide
Fluoroquinolones (e.g. gatifloxacin)
Quinidine
Salicylates (high doses only)
Hypoglycemia Treatment
Glucose
15 grams of simple carbohydrates
8oz. fruit juice
Half can regular soda
3 glucose tabs
1 tablespoon honey
Glucagon injection
Stimulates glycogen breakdown
Baseline Vital Signs
Hypoglycemia
Respirations = normal to rapid
Pulse = normal to rapid
Skin = pale and clammy
Blood pressure = low
Hyperglycemia
Respirations = deep and rapid
Pulse = normal to fast
Skin = warm and dry
Blood pressure = normal
Tujuan Pengelolaan
Diabetes Mellitus
Menghilangkan gejala
Mempertahankan rasa sehat
Memperbaiki kualitas hidup
Mencegah komplikasi (akut dan kronis)
Mengurangi laju komplikasi yang sudah ada
Menurunkan jumlah kematian
MANAGEMENT OF DM
Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring
Diet
Exercise
Drug Therapy
102
Management: Diet & Exercise
Edukasi
Tujuan:
Pencegahan Primer
Pencegahan Sekunder
Pencegahan Tertier
MICROVASCULAR
COMPLICATIONS
Hyperglycemia
Pericyte
loss
Hyperperfusion Capillary/
Endothelial
damage
Loss of
autoregulation
Capillary
occlusion
Vasoactive
factors
Loss of tight
junction
Retinal
ischemia
New vessels
-Low resistance
- No pericyte/autoregulation
Growth
factors
Macular
oedema
Pathophysiology of diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy
108
Two types of diabetic retinopathy:
Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR)
Early stage diabetic retinopathy
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
Later stage diabetic retinopathy
Treatment Eye Disease
Cataract removal
Laser surgery for
retinopathy
Nonproliferative diabetic
retinopathy (NPDR)
110
Also called background
diabetic retinopathy.
Earliest stage of diabetic
retinopathy.
Damaged blood vessels
in the retina leak extra
fluid and small amounts
of blood into the eye.
Cholesterol or other fat
deposits from blood,
called hard exudates,
may leak into retina.
Top: Healthy retina
Bottom: Retina with NPDR,
containing hard exudates
DIABETIC
NEPHROPATHY
Pathophysiology of diabetic
nephropathy
Hyperglycemia
Renal
vasodilatation
Increased
intraglomerular
capillary pressure
Protein glycation
Increased glomular
filtration rate
Hypertension
Increased
protein excretion
Microalbuminuria or
macroalbuminuria
Nephropathy
Glomurular
damage
Treatment - Nephropathy
ACE inhibitors
MNT protein
restriction
DIABETIC
NEUROPATHY
Mechanism of nerve damage in
diabetes
METABOLIC VASCULAR
glucose
sorbitol
H
2
O
nerve
oedema
myoinositol
NO
production
AGE
formation
vasoconstriction
Arterial
narrowing
Vessel
occlusion
Slow nerve
conduction
Impairing
axonal transport
Altered membrane
potensial
Burning, feeling like the feet are on fire
Freezing, like the feet are on ice,
although they feel warm to touch
Stabbing, like sharp knives
Lancinating, like electric shocks
Autonomic Neuropathy
Pathophysiology: diabetic foot ulceration
Neuropathy
Sensory
Loss of
protective
sensation
Motor
Abnormal foot
biomechanics
Autonomic
Reduced skin
compliance and
lubrication
ULCERATION
Vascular
insufficiency
Case 4
How do you know if the ulcer is infected then?
Assessing foot ulcers for the presence of infection is vital. All
open wounds are likely to get colonised with microorganisms,
such as Staphylococcus aureus, and not necessarily infected.
Therefore, the presence of infection needs to be defined
clinically rather than microbiologically.
An infected ulcer
Signs suggesting
infection include;
1. purulent
secretions
2. presence of friable
tissue
3. undermined edges
4. foul odour
Page 120 of 67
Assessment Infected Ulcers
Chronic Complications-
Microvascular
Amputation of Toes
Charcot foot
grossly disordered
architecture and
biomechanics
midfoot ulceration
instability of midfoot
note previous minor
amputations
still well-vascularised
Bone resorption and destruction
Bone regeneration on antibiotic therapy
Doctor treating a patient in his surgery: 17
th
Century, after Teniers the younger (by kind
permission of National Gallery, London)
Does it need antibiotics,
doctor?
You must be joking mate!
Debridement and offloading more
like it!
Besides, they wont be
discovered for another 300 years!
Autonomic Neuropathy
DM-related autonomic neuropathy can involve multiple
systems, including the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal,
genitourinary, sudomotor, and metabolic systems.
Autonomic neuropathies affecting the cardiovascular
system cause a resting tachycardia and orthostatic
hypotension.
Gastroparesis and bladderemptying abnormalities are
often caused by the autonomic neuropathy seen in DM
(discussed below).
Hyperhidrosis of the upper extremities and anhidrosis of
the lower extremities result from sympathetic nervous
system dysfunction.
Anhidrosis of the feet can promote dry skin with
cracking, which increases the risk of foot ulcers.
Autonomic neuropathy may reduce counterregulatory
hormone release, leading to an inability to sense
hypoglycemia appropriately ((hypoglycemia
unawareness)
Chronic Complications-Microvascular
Sexual problems for men
erectile dysfunction
retrograde ejaculation
Sexual problems for women
decreased vaginal lubrication
decreased sexual response
Urologic problems for men and
women
urinary tract infections
neurogenic bladder
MACROVASCULAR
COMPLICATIONS
5. KOMPLIKASI DIABETES
Diabetic
Retinopathy
Leading cause
of blindness
in working age
adults
1
Diabetic
Nephropathy
Leading cause of
end-stage renal disease
2
Cardiovascular
Disease
Stroke
2 to 4 fold increase in
cardiovascular
mortality and stroke
3
Diabetic
Neuropathy
Leading cause of
non-traumatic lower
extremity amputations
5
8/10 diabetic patients
die from CV events
4
1
Fong DS, et al. Diabetes Care 2003; 26 (Suppl. 1):S99S102.
2
Molitch ME, et al. Diabetes Care 2003; 26 (Suppl. 1):S94S98.
3
Kannel WB, et al. Am Heart J 1990; 120:672676.
4
Gray RP & Yudkin JS. In Textbook of Diabetes 1997.
5
Mayfield JA, et al. Diabetes Care 2003; 26 (Suppl. 1):S78S79.
PEMBULUH DARAH KECIL PEMBULUH DARAH BESAR
KONTROL Kadar Gula Darah
ADEKWAT
TERBUKTI MENURUNKAN RISIKO
KOMPLIKASI KRONIS
100
75
50
25
0
-12 -10 -6 -2 0 2 6 10 14
Fungsi sel
Beta (%)
Tahun Sejak Diagnosis
TGT
Hiperglikemi
Postprandial
Fase I
DM tipe 2
Fase II
DM tipe 2
Fase III
DM tipe 2
Hubungan kegagalan terapi dg Stadium pada DM
Tipe 2 dan Fungsi Sel Beta Pankreas
Strategy to Prevent the Deterioration
of Type 2 Diabetes
Years from Diagnosis
Lebovitz H. Diabetes Review 1999;7:139-53
T2DM phase III
Beta Cell
Function
(%)
IGT Postprandial
Hyperglycemia
T2 DM
phase I
T2DM
phase II
-12 10 -6 -2 0 2 6 10 14
Monotherapy
Life Style
Oral Hypo(s)
Combination
Insulin with
or without
Oral Hypo
Glycemic agent
Matching Pharmacology to
Pathophysiology
Hyperglycemia
Biguanides
(TZD)
TZD
(Biguanides)
Alpha-glucosidase
inhibitors
Sulfonylureas
Meglitinides
Nateglinide
Glucose influx
Peripheral
glucose uptake
Insulin
secretion
Hepatic
glucose
output
Site & Mode of Action of OADs
136 www.drsarma.in
Adapted from DeFronzo R. Ann Intern Med 1999;131:281
Site of action MOA Agents
Insulin
secretion
Sulfonylureas
Repaglinide
Nateglinide
HGO
production
Biguanides
Glitazones
Slow CHO
Digestion
a- glucosidase
inhibitors
Peripheral
insulin sensitivity
Glitazones
Biguanides
SUS: Mechanism of action
Others:
Dec glucagon
Secretion
Binding to
Extrapancreatic
SU receptors
in K channels
Dr.Sarma@works
Actions of Metformin
REPAGLINIDE:
Mechanism of action
Meglitinides: have 2 common binding sites
w/ SU and 1 unique binding site
THIAZOLIDINEDIONES: MOA
PPAR-g activators
Insulin sensitizers
delay from 4-12 weeks in
the onset of their therapeutic
benefits
LIVER, MUSCLE, FAT
Activate insulin-responsive genes
regulating
- Glc and lipid metab
- Insulin signalling
- Adipocyte differentiation
INCRETIN-BASED TX
GLP-1 Mimetics: Exenatide (Byetta)
DPP-IV inhibitors:
Sitagliptin (Januvia)
Vildagliptin
GLP-1 MIMETIC:
EXENATIDE
SC injections: absorbed equally from arm,
abdomen, thigh
Peak: 2 hrs
Duration: up to 10 hrs
DPP-IV INHIBITORS
Sitagliptin
When to start insulin?
BMI : > 23 Metformin, AGI, TZD, DPP-IV
Inh.
BMI: 18 23 Metformin, SU/glinid, AGI, DPP-IV
Inh.
BMI: < 18 Insulin
HbA1c :
< 7 life style modification
7 8 single/combination oral drugs
8 9 combination oral drugs
> 9 oral drug + insulin combination
intensive insulin
Sejarah Insulin
1921 Insulin ditemukan
oleh Banting dan Best
1922 Leonard Thompson
adalah pasien pertama yang
mendapat suntikan insulin
1923 Novo Nordisk mulai
produksi Insulin Hewan
(Sapi dan Babi)
1973 Insulin Hewan
Monokomponen
1987 Insulin Human
1990 Insulin Analog
INDIKASI PENGGUNAAN INSULIN
1. DM tipe 1
2. Penurunan berat badan yg cepat
3. Hiperglikemia yg berat disertai dg ketosis
4. Ketoasidosis diabetik
5. Hiperglikemia hiperosmolar non ketotik
6. Hiperglikemia dg asidosis laktat
7. Gagal dg kombinasi OHO dosis hampir max
8. Stress berat
9. Kehamilan dg DM atau DM Gestasional
10. Gangguan fs. ginjal atau hati yg berat
11. Kontraindikasi dan atau alergi thp OHO
KEGUNAAN METABOLIK TERAPI INSULIN
Menurunkan kadar GD puasa & pp
Supresi produksi glukosa oleh hati
Stimulasi utilisasi glukosa perifer
oksidasi gluk / penyimpanan di otot
Perbaiki komposisi lipoprotein abnormal
Mengurangi glucose toxicity
Perbaiki kemampuan sekresi endogen
Mengurangi glycosilated end products
KAPAN INSULIN DIPERLUKAN?
Data UKPDS :
50% DMT2 perlu insulin setelah 6
tahun
Fungsi B-cell yg rendah pd saat
diagnosis risiko kegagalan OHO
lebih tinggi
Marre M. Int J Obesity (2002) ; 26 (Suppl 3) : S25-S30
Modern "Aggressive" Rx of Type 2
DM from Time of Diagnosis
HbA1c > 10 %
or
FPG >260 mg/dl
or
Symptomatic
or
Ketotic
IMMEDIAT
E INSULIN
Modern "Aggressive" Rx 4
HbA1c not < 7% by
6 months
Start
Insulin
www.drsarma.in 151
Rapidity of Action Insulin preparation
Ultra- rapid-action
Onset 10 -20 Peak 30 min
Lispro (Humalog), Glulisin (Apidra)
Aspart (Novolog)
Short Acting
Onset 30 to 60, Peak 2 hr
Regular (Human) Insulin
Humulin R, Novolin R
Intermediate Acting (Human)
or Analog 1 -4 h, Peak 4 -10 h
NPH (Human) Humulin N, Novolin N
Insulin Detemir (analog) - Levemir
Long Acting 1-3 No Peak 24 h Insulin Glargine (Lantus)
Mixtures (Human)1 h, P 3-12 h 70/30 or 50/50 Humulin, 70/30 Novolin
Mixtures (Analog)
Onset 30-1h, Peak 3-12 h
75/25 or 50/50 Humalog (NPL + Lispro)
70/30 Novolog neutral (Protamin + Aspart
Insulin Preparations
A chain
Gly II
e
Val Glu Gln Cys Cys Thr Ser Ile Cys Ser Leu Tyr Glu Leu Glu Asn Tyr Cys Asn
1 5 10 15 21
S S
1 5 10
15
20
25
30
B chain
S
S S
S
Phe Val Asn Gln His Leu Cys Gly Ser His Leu Val Glu Ala Leu Tyr Leu Val Cys Gly
Glu Arg
Gly
Phe
Phe
Ty
r
Thr
Lys
Pro
The
Phe
HUMAN INSULIN
Human insulin
A chain 21 amino acids
B chain 30 amino acids
JENIS INSULIN
Natural (animal) insulin : ekstraksi dari pankreas hewan
Semisynthetic human insulin : insulin dari hewan yg dimodifikasi secara
enzimatik
Biosynthetic human insulin : dibuat dengan DNA rekombinan
menggunakan ragi atau bakteri
Insulin analog : biosynthetic human insulin yg direkayasa dgn
mempertukarkan posisi asam amino atau menambahkan satu atau lebih
asam amino/asam lemak pada rantai molekul insulin
Tipe insulin berdasarkan puncak dan
jangka waktu kerjanya :
1. Insulin kerja sangat cepat : NovoRapid
, Humalog
,
Apidra
2. Insulin kerja pendek : , Humulin R
3. Insulin kerja sedang : , Humulin N
4. Insulin campur : , Humulin 30/70
, NovoMix 30
,
Humalog 25
5. Insulin kerja panjang : Levemir
, Lantus
Adanya anggapan :
Sekali dimulai, tidak pernah bisa berhenti
Akan membatasi aktivitas sehari-hari
Memulai terapi Insulin berarti:
Saya telah gagal
DM-nya sudah menjadi serius
Suntikan insulin akan sangat sakit/nyeri
Suntikan insulin menyebabkan kebutaan
Franks story: Jika anda tidak bekerja keras, anda
akan saya suntik insulin lho
Kendala Terapi Insulin
Prinsip Terapi
Insulin Basal menurunkan gula darah
puasa
Insulin Bolus menurunkan gula darah
post prandial (setelah makan)
Insulin Premixed menurunkan GD
puasa dan GD 2 jam PP
Macam-macam Rejimen Insulin
Basal Bolus
4 suntikan per hari (3 bolus dan 1 basal)
Satu kali suntikan insulin basal pada malam
hari ditambah dengan obat oral
Premixed Insulin, sekali sampai 3 kali sehari,
sebelum makan.
Premixed dikombinasi dengan short acting
4 Suntikan per Hari
3 Short + 1 Intermediate/Long Acting
(Basal Bolus)
6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 5
Breakfast Lunch Evening Meal Sleep
time
Dua kali Suntikan Premixed Insulin Per Hari
6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3 4 5
Breakfast Lunch Evening Meal Sleep
time
45 - 60 31 - 45
61 - 75 16 - 30
75 - 90 1 - 15
Tempat Penyuntikan Insulin Subkutan :
Searah Jarum Jam
Continuous IV insulin infusion
Used to maintain glycemic control in
hospitalized patients with high blood
glucose levels; in DKA and HHNS
Regular insulin may be used IV
May also be given preoperatively or
postoperatively
More frequent BS monitoring ( q1-2
hours per agency protocol)
Efek Samping Insulin
Hipoglikemia (kadar glukosa darah terlalu
rendah)
Peningkatan berat badan
Reaksi Alergi (kemerahan, gatal-gatal di tempat
penyuntikkan)
Lipodistrofi
DIABETES
DAN PERAN INSULIN DALAM PENANGANANNYA
Dr. SUHAEMI, SpPD, FINASIM
Leonard Thompson
1922 1923
Meninggal tahun 1935
Perkembangan Terakhir Injeksi Insulin
Trans-dermal insulin delivery
Oral insulin delivery
Buccal insulin delivery Pulmonary insulin delivery
Non-Injectable Insulin
Insulin Delivery Devices 3
Inhaled Insulin
Exubera
Inhaled Insulin
1-1-08
voluntary discontinuation
4-6-08
Cancer Warning
Exubera (Inhaled Insulin)
171 www.drsarma.in
Insulin Blisters
for Aerosol
Other Injectable Drugs 1
Exenatide (Byetta)
insulin secretagogue
peptide
gila monster saliva
use with other drugs
no hypoglycemia
bid
Exenatide (Byetta)
www.drsarma.in 173
Other Injectable Drugs 1
Pramlintide (Symlin)
analogue of hormone
amylin
polypetide
slows gastric
emptying
induces satiety
opposes glucagon
reduces posprandial
BG
give with meals
used with insulin
Exenatide
www.drsarma.in 175
We have two hormones in intestines - Incretins
GLP-1 (Glucagon Like Peptide-1) and
GIP (Glucose dependent Insulinotropic Polypetide)
Normally Incretins are degraded by DPP IV enzyme
Exenatide is a synthetic analog of GLP-1 Mimetic
It is very similar to the GLP-1 in venom of Gila mon.
This is resistant to degradation by DPP IV enzyme
Exenatide inj. enhances postprandial insulin secretion
Liraglutide
www.drsarma.in 176
Modified GLP-1
Binds to albumin
Injection form only
Can reduce fasting and PP hyperglycemia
It is an additional Rx. option
Can be combined with OADs
Does not cause hypoglycemia.
SitagLiptin
www.drsarma.in 177
Normally Incretins are degraded by DPP IV enzyme
Liptins are compounds which inhibit the DDP IV
Liptins increase the action of natural GLP-1
These are oral drugs hence advantageous
These postprandial insulin secretion via GLP-1
Sitag-liptin, Vildag-liptin, Sexag-liptin are useful Rx
They are 2
nd
line agents. Combined with OADs
Do not cause hypoglycemia.
Future Therapies
www.drsarma.in 178
1. RIMONABANT CB1- R blocker Obesity thus
DM
2. GLITAZARs Dual PPAR activator Glycemia,
Lipids
Muraglitazar, Tesaglitazar, Ragaglitazar
3. VOGLIBOSE New a-GI Inhibitor - PPBG
4. ACIPIMOX FFA and IR - FBG
5. PIMAGIDINE AGPs & prevents DM complications
6. ZENERESTAT Sorbitol & Fructose DM PNP
7. ZOPOLRESTAT Aldose Red. DM PNP
8. Acetyl L-Carnitine NCV DM PNP/ ANP
9. BIMOCLOMOL Heat Shock Proteins DR & DKD
10. EXO- 226 Glycation of Proteins DKD
11. Insu. Like GF, HIM 2 (oral), Englitazone New TZD
Future Diagnostic Tests
www.drsarma.in 179
Glucose sensors to be applied on to skin
Peel of patch tests Read the Sugar in sweat
Micro needle inserted continuous monitors
Antibodies to insulin for insulin resistance
HbA1c monitors like glucose monitors
SMBG
Value in Type 2 DM
not established
Useful for titrating
insulin
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c)
2
Insulin
Acute
Complication:
Hypoglycemia
Tx: (15/15 or 20/20
Rule)
Give 15/20 g simple
carb and recheck
BG in 15/20 minutes
Insulin Acute Complication
Hypoglycemia
Hyperglycemia
How to prevention
Complications of Diabetes ?
www.drsarma.in 185
1. Weight reduction, Exercise
2. Strict control hyperglycemia
3. Achieving lipid profile targets
4. Smoking cessation
5. Rx. of Hypertension with ACEi/ ARB
6. Low dose aspirin therapy
7. Statin therapy for all T2DM
8. ACEi or ARB for all with MAU
9. Early detection and evaluation
Treatment of Dyslipidemia
www.drsarma.in 186
Every T2DM must get 10 mg of Atorvastatin
LDL is raised Statin or Statin+ Ezetemibe
TG is raised Fenofibrate
HDL is low Niacin
Combined dyslipidemia Combinations
Lp(a) is raised Niacin
hs-CRP is raised Aspirin & Statin (already)
Take Home A B C D E
www.drsarma.in 187
A A1c target of < 7%; Better 6%
Aspirin for all DM
ACEi or ARB for all DM
B Blood Pressure target of 130/80
Blood Glucose monitoring
C Cholesterol LDL <100, Statin for all DM
D Diet modifications, Do not smoke
E Exercise 45 every day, Education on DM
Equivalent to having CAD is DM
KRITERIA PENGENDALIAN DM
Konsensus PERKENI 2006
Gula Darah Puasa
Gula Darah 2 JSM
HbA
1C
(%)
Kolesterol Total
Kolesterol LDL
Kolesterol HDL
Trigliserida
BMI
Tekanan Darah
80 - 100
80 - 144
< 6,5
< 200
< 100
> 45
< 150
18,5 - 22,9
< 130 / 80
BAIK
100 - 125
145 - 179
6.5 - 8
200 - 239
100 - 129
150 - 199
23 - 25
130-140/ 80-90
SEDANG
> 126
> 180
> 8
> 240
> 130
> 200
> 25
> 140 / 90
BURUK
Вам также может понравиться
- Aturan Minum FitbellyДокумент1 страницаAturan Minum FitbellyTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Jurnal 4Документ9 страницJurnal 4Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Brosur Penyuluhan Gizi Anak SekolahДокумент2 страницыBrosur Penyuluhan Gizi Anak SekolahTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Jurnal 2Документ9 страницJurnal 2Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Jurnal 3Документ10 страницJurnal 3Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Jurnal 4Документ9 страницJurnal 4Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Daftar PustakaДокумент1 страницаDaftar PustakaTia AriantiОценок пока нет
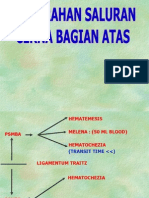
- Perdarahan Saluran Cerna Atas Dan BawahДокумент24 страницыPerdarahan Saluran Cerna Atas Dan BawahTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- 2014 ESC Management of Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation 1Документ25 страниц2014 ESC Management of Antithrombotic Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation 1Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Jurnal 1Документ13 страницJurnal 1Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Aids KulДокумент71 страницаAids KulTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Penyakit Jantung HipertensiДокумент24 страницыPenyakit Jantung HipertensiTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- The Effect of Carvedilol On Morbidity and Mortality in Patients With Heart FaliureДокумент7 страницThe Effect of Carvedilol On Morbidity and Mortality in Patients With Heart Faliurecobby174Оценок пока нет
- Demam 2Документ30 страницDemam 2Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- PedNas TB 2011-Isi A PDFДокумент59 страницPedNas TB 2011-Isi A PDFYesi SaputriОценок пока нет
- 12-Lead EKG Analysis Fall 20021Документ48 страниц12-Lead EKG Analysis Fall 20021Yesi SaputriОценок пока нет
- Soal Ujian EkgДокумент12 страницSoal Ujian EkgTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- KOLELITIASIS1Документ37 страницKOLELITIASIS1Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Demam Tifoid. KulДокумент60 страницDemam Tifoid. KulTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Falciparum Malaria by DR SarmaДокумент65 страницFalciparum Malaria by DR SarmaTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Cirrhosis 22008 Bajar Musica Gratis Descargar Musica Gratis Online Descargar Musica Gratis para CelularesДокумент72 страницыCirrhosis 22008 Bajar Musica Gratis Descargar Musica Gratis Online Descargar Musica Gratis para CelularesYeni Chie Aneuk TuleutОценок пока нет
- Hepatic EncephalopathyДокумент16 страницHepatic EncephalopathyTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- 09 Diuretics Upd 2Документ42 страницы09 Diuretics Upd 2Ritari KimyunjongОценок пока нет
- EKG BacaДокумент59 страницEKG BacaTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Hepatitis (DR - Lukmanhakim Usu)Документ36 страницHepatitis (DR - Lukmanhakim Usu)Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Fatty Liver Disease: A Growing EpidemicДокумент31 страницаFatty Liver Disease: A Growing EpidemicTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- RLCirrhosisPortal HTNMunireddy0207Документ41 страницаRLCirrhosisPortal HTNMunireddy0207Tia AriantiОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart Failure CHF: Nik Nikam, M.DДокумент94 страницыCongestive Heart Failure CHF: Nik Nikam, M.DTia AriantiОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Card 1Документ2 страницыCard 1nalessОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Gestational DMДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology of Gestational DMAnonymous GtR96jCОценок пока нет
- Volume38 - Issue 3 - June Sept 2018Документ107 страницVolume38 - Issue 3 - June Sept 2018wahyulan mОценок пока нет
- Meglitinide Analogues Are Classified As Insulin Secretagogues and Have Actions andДокумент6 страницMeglitinide Analogues Are Classified As Insulin Secretagogues and Have Actions andRifqoh Aulia AlthofunnisaОценок пока нет
- Censo Sospechosos 2017Документ121 страницаCenso Sospechosos 2017KarlaОценок пока нет
- Mild Diabetic Ketoacidosis2Документ10 страницMild Diabetic Ketoacidosis2GorgieОценок пока нет
- 32 PDFДокумент22 страницы32 PDFniallvvОценок пока нет
- Senior Project Research PaperДокумент16 страницSenior Project Research Paperapi-309345535100% (1)
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer Assessment ToolsДокумент16 страницDiabetic Foot Ulcer Assessment ToolsShity Shita ShituОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Care.: Daftar PustakaДокумент3 страницыDiabetes Care.: Daftar PustakaariОценок пока нет
- Presentation 1Документ6 страницPresentation 1Maya RentinaОценок пока нет
- A Comparative Study of Serum Ascorbate Between Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetics and Long Standing Type 2 Diabetics On TreatmentДокумент4 страницыA Comparative Study of Serum Ascorbate Between Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetics and Long Standing Type 2 Diabetics On TreatmentIJAR JOURNALОценок пока нет
- NovorapidДокумент16 страницNovorapidRADITA MAULASARIОценок пока нет
- The Hospital Management of Hypoglycaemia in Adults With Diabetes Mellitus 3rd EditionДокумент40 страницThe Hospital Management of Hypoglycaemia in Adults With Diabetes Mellitus 3rd EditionRumahSehat N-CareОценок пока нет
- Persistence of Islet Autoantibodies After Type 1 Diabetes DiagnosisДокумент7 страницPersistence of Islet Autoantibodies After Type 1 Diabetes DiagnosisrafaelplОценок пока нет
- Interpretation: S03 - FPSC DILSHAD COLONY (C004263143) J-50 Dilshad Colony, DelhiДокумент6 страницInterpretation: S03 - FPSC DILSHAD COLONY (C004263143) J-50 Dilshad Colony, DelhiAll VIDEOS TechОценок пока нет
- Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023: 14. Children and AdolescentsДокумент24 страницыStandards of Care in Diabetes-2023: 14. Children and AdolescentsFranklin MatuteОценок пока нет
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyДокумент5 страницDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case Studyjc_albano29100% (7)
- Carolina TrialДокумент59 страницCarolina TrialDr. Abhas ShahОценок пока нет
- Screening of Antidiabetic Drugs: Presented ByДокумент35 страницScreening of Antidiabetic Drugs: Presented BysharonОценок пока нет
- Vol 27 No 1 April 2014 Medicinus 1Документ68 страницVol 27 No 1 April 2014 Medicinus 1Natasya DelarespitaОценок пока нет
- Diabetes The NumbersДокумент24 страницыDiabetes The NumbersSasikala RajendranОценок пока нет
- Handayanijeki@yahoo - Co.id: Ijms - Indonesian Journal On Medical Science - Volume 6 No. 1 - Januari 2019Документ5 страницHandayanijeki@yahoo - Co.id: Ijms - Indonesian Journal On Medical Science - Volume 6 No. 1 - Januari 2019Abu Bilal IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring As A Screening Tool of Neonatal Hypoglycemia in Infant With Diabetic MotherДокумент7 страницContinuous Glucose Monitoring As A Screening Tool of Neonatal Hypoglycemia in Infant With Diabetic MotherraniaulfahОценок пока нет
- Estimation of Blood GlucoseДокумент16 страницEstimation of Blood GlucoseAhmed MohamadОценок пока нет
- South-East Asia Trend P-A M-1 L-12: Number of People Suffering From DM in SEA Region Is Also IncreasingДокумент1 страницаSouth-East Asia Trend P-A M-1 L-12: Number of People Suffering From DM in SEA Region Is Also IncreasingtanzirОценок пока нет
- Anti DiabeticДокумент34 страницыAnti DiabeticEJ GabaoОценок пока нет
- Agency PresentationДокумент17 страницAgency Presentationapi-316466073Оценок пока нет
- DIABETES InfographicДокумент1 страницаDIABETES InfographicDail Xymere YamioОценок пока нет
- Diabetes CCP Slides2Документ72 страницыDiabetes CCP Slides2Pandu WibowoОценок пока нет