Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
TCP For Wireless
Загружено:
aadafull0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров16 страницedu
Оригинальное название
Tcp for Wireless
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документedu
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров16 страницTCP For Wireless
Загружено:
aadafulledu
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 16
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
TCP for Wireless Networks
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Outline
Motivation
TCP mechanisms
Indirect TCP
Snooping TCP
Mobile TCP
Fast retransmit/recovery
Transmission freezing
Selective retransmission
Transaction oriented TCP
Adapted from J. Schiller, Mobile Communications, Chapter 10
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Motivation
Transport protocols typically designed for
o Fixed end-systems
o Fixed, wired networks
TCP congestion control
o Packet loss in fixed networks typically due to
(temporary) overload situations
o Routers discard packets as soon as the buffers are full
o TCP recognizes congestion only indirectly via missing
acknowledgements
o Retransmissions unwise, they would only contribute to
the congestion and make it even worse
o Slow-start algorithm as reaction
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
TCP Slow Start
Sender calculates a congestion window for a
receiver
Start with a congestion window size equal to one
segment
Exponential increase of the congestion window up
to the congestion threshold, then linear increase
Missing acknowledgement causes the reduction of
the congestion threshold to one half of the
current congestion window
Congestion window starts again with one segment
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
TCP Fast Retransmit/Recovery
TCP sends an acknowledgement only after
receiving a packet
If a sender receives several acknowledgements
for the same packet, this is due to a gap in
received packets at the receiver
However, the receiver got all packets up to the
gap and is actually receiving packets
Therefore, packet loss is not due to congestion,
continue with current congestion window (do not
use slow-start)
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Influences of mobility on TCP
TCP assumes congestion if packets are dropped
o typically wrong in wireless networks, here we often have
packet loss due to transmission errors
o furthermore, mobility itself can cause packet loss, if e.g.
a mobile node roams from one access point (e.g. foreign
agent in Mobile IP) to another while there are still
packets in transit to the wrong access point and
forwarding is not possible
The performance of an unchanged TCP degrades
severely
o however, TCP cannot be changed fundamentally due to
the large base of installation in the fixed network, TCP
for mobility has to remain compatible
o the basic TCP mechanisms keep the whole Internet
together
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Indirect TCP I
Indirect TCP or I-TCP segments the connection
o no changes to the TCP protocol for hosts connected to
the wired Internet, millions of computers use (variants
of) this protocol
o optimized TCP protocol for mobile hosts
o splitting of the TCP connection at, e.g., the foreign agent
into 2 TCP connections, no real end-to-end connection
any longer
o hosts in the fixed part of the net do not notice the
characteristics of the wireless part
mobile host
access point
(foreign agent)
wired Internet
wireless TCP
standard TCP
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
I-TCP socket and state migration
mobile host
access point
2
Internet
access point
1
socket migration
and state transfer
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Indirect TCP II
Advantages
o no changes in the fixed network necessary, no changes
for the hosts (TCP protocol) necessary, all current
optimizations to TCP still work
o transmission errors on the wireless link do not
propagate into the fixed network
o simple to control, mobile TCP is used only for one hop
between, e.g., a foreign agent and mobile host
o therefore, a very fast retransmission of packets is
possible, the short delay on the mobile hop is known
Disadvantages
o loss of end-to-end semantics, an acknowledgement to
a sender does not any longer mean that a receiver
really got a packet, foreign agents might crash
o higher latency possible due to buffering of data within
the foreign agent and forwarding to a new foreign
agent
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
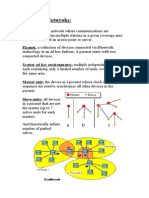
Snooping TCP I
Transparent extension of TCP within the foreign agent
buffering of packets sent to the mobile host
lost packets on the wireless link (both directions!) will be
retransmitted immediately by the mobile host or foreign
agent, respectively (so called local retransmission)
the foreign agent therefore snoops the packet flow and
recognizes acknowledgements in both directions, it also
filters ACKs
changes of TCP only within the foreign agent (+min. MH
change)
wired Internet
buffering of data
end-to-end TCP connection
local retransmission
correspondent
host
foreign
agent
mobile
host
snooping of ACKs
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Snooping TCP II
Data transfer to the mobile host
o FA buffers data until it receives ACK of the MH, FA detects
packet loss via duplicated ACKs or time-out
o fast retransmission possible, transparent for the fixed network
Data transfer from the mobile host
o FA detects packet loss on the wireless link via sequence
numbers, FA answers directly with a NACK to the MH
o MH can now retransmit data with only a very short delay
Advantages:
o Maintain end-to-end semantics
o No change to correspondent node
o No major state transfer during handover
Problems
o Snooping TCP does not isolate the wireless link well
o May need change to MH to handle NACKs
o Snooping might be useless depending on encryption schemes
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Mobile TCP
Special handling of lengthy and/or frequent
disconnections
M-TCP splits as I-TCP does
o unmodified TCP fixed network to supervisory host (SH)
o optimized TCP SH to MH
Supervisory host
o no caching, no retransmission
o monitors all packets, if disconnection detected
set sender window size to 0
sender automatically goes into persistent mode
o old or new SH reopen the window
Advantages
o maintains semantics, supports disconnection, no buffer
forwarding
Disadvantages
o loss on wireless link propagated into fixed network
o adapted TCP on wireless link
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Fast retransmit/fast recovery
Change of foreign agent often results in packet loss
o TCP reacts with slow-start although there is no congestion
Forced fast retransmit
o as soon as the mobile host has registered with a new foreign
agent, the MH sends duplicated acknowledgements on purpose
o this forces the fast retransmit mode at the communication
partners
o additionally, the TCP on the MH is forced to continue sending
with the actual window size and not to go into slow-start after
registration
Advantage
o simple changes result in significant higher performance
Disadvantage
o further mix of IP and TCP (to know when there is a new
registration), no transparent approach
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Transmission/time-out freezing
Mobile hosts can be disconnected for a longer time
o no packet exchange possible, e.g., in a tunnel, disconnection
due to overloaded cells or mux. with higher priority traffic
o TCP disconnects after time-out completely
TCP freezing
o MAC layer is often able to detect interruption in advance
o MAC can inform TCP layer of upcoming loss of connection
o TCP stops sending, but does not assume a congested link
o MAC layer signals again if reconnected
Advantage
o scheme is independent of data and TCP mechanisms (Ack,SN)
=> works even with IPsec
Disadvantage
o TCP on mobile host has to be changed, mechanism depends on
MAC layer
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Selective retransmission
TCP acknowledgements are often cumulative
o ACK n acknowledges correct and in-sequence receipt of
packets up to n
o if single packets are missing quite often a whole packet
sequence beginning at the gap has to be retransmitted
(go-back-n), thus wasting bandwidth
Selective retransmission as one solution
o RFC2018 allows for acknowledgements of single packets,
not only acknowledgements of in-sequence packet
streams without gaps
o sender can now retransmit only the missing packets
Advantage: much higher efficiency
Disadvantage
o more complex software in a receiver, more buffer needed
at the receiver
Wireless Networks Spring 2005
Transaction oriented TCP
TCP phases
o connection setup, data transmission, connection release
o using 3-way-handshake needs 3 packets for setup and release,
respectively
o thus, even short messages need a minimum of 7 packets!
Transaction oriented TCP
o RFC1644, T-TCP, describes a TCP version to avoid this
overhead
o connection setup, data transfer and connection release can be
combined
o thus, only 2 or 3 packets are needed
Advantage
o efficiency
Disadvantage
o requires changed TCP
o mobility no longer transparent
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- PW160-7K S 0411Документ890 страницPW160-7K S 0411ado_22100% (2)
- NV200 Manual Set - Section 2 - Field Service ManualДокумент13 страницNV200 Manual Set - Section 2 - Field Service ManualBogicevic DejanОценок пока нет
- Design and Implementation of Real Time FacialДокумент8 страницDesign and Implementation of Real Time FacialaadafullОценок пока нет
- Data WarehouseДокумент63 страницыData WarehouseaadafullОценок пока нет
- Research 1 PDFДокумент6 страницResearch 1 PDFaadafullОценок пока нет
- Emotion Recognition From Facial Expressions Using Multilevel HMMДокумент7 страницEmotion Recognition From Facial Expressions Using Multilevel HMMaadafullОценок пока нет
- Research PaperДокумент7 страницResearch PaperaadafullОценок пока нет
- Facial RegonitionДокумент4 страницыFacial RegonitionaadafullОценок пока нет
- Research 1 PDFДокумент13 страницResearch 1 PDFaadafullОценок пока нет
- Mobile Computing Gsm4049Документ76 страницMobile Computing Gsm4049aadafullОценок пока нет
- Broadcast Systems1Документ24 страницыBroadcast Systems1aadafullОценок пока нет
- Dabengpre V2Документ24 страницыDabengpre V2aadafullОценок пока нет
- 2009 M.tech. Cse Mobile and Wireless Communication 2nd Sem.Документ3 страницы2009 M.tech. Cse Mobile and Wireless Communication 2nd Sem.shailygoyalОценок пока нет
- 2012 M.tech. Cse Soft Computing 2nd Sem.Документ2 страницы2012 M.tech. Cse Soft Computing 2nd Sem.amitrathee09Оценок пока нет
- Mobile Computing Gsm4049Документ76 страницMobile Computing Gsm4049aadafullОценок пока нет
- GSM Architecture: Project ReportДокумент40 страницGSM Architecture: Project ReportaadafullОценок пока нет
- JSP (Java Server Pages)Документ8 страницJSP (Java Server Pages)aadafullОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент1 страницаAssignmentaadafullОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ59 страницUnit 1aadafullОценок пока нет
- SNA Unit-1Документ57 страницSNA Unit-1aadafullОценок пока нет
- Unit-2 Networking Lecture-10: Introduction To Networking:: Connecting To A ServerДокумент20 страницUnit-2 Networking Lecture-10: Introduction To Networking:: Connecting To A ServeraadafullОценок пока нет
- Finger (-B) (-F) (-H) (-I) (-L) (-M) (-P) (-Q) (-S) (-W) (Username)Документ14 страницFinger (-B) (-F) (-H) (-I) (-L) (-M) (-P) (-Q) (-S) (-W) (Username)aadafullОценок пока нет
- Program: 1. Calculation of Average of NumbersДокумент4 страницыProgram: 1. Calculation of Average of NumbersAjay AyyaduraiОценок пока нет
- Child Development and PedagogyДокумент3 страницыChild Development and PedagogyaadafullОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 CSДокумент6 страницChapter 11 CSaadafullОценок пока нет
- Constraint Satisfaction Problems: Version 1 CSE IIT, KharagpurДокумент17 страницConstraint Satisfaction Problems: Version 1 CSE IIT, KharagpurRohan AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Asia Indian Society & Culture HierarchyДокумент5 страницAsia Indian Society & Culture HierarchyaadafullОценок пока нет
- Lesson 01 - Iit - Iartificial Intelligence 2 AI PDFДокумент11 страницLesson 01 - Iit - Iartificial Intelligence 2 AI PDFVille4everОценок пока нет
- HTML NotesДокумент22 страницыHTML NotesaadafullОценок пока нет
- Google Glass: AbstractДокумент8 страницGoogle Glass: AbstractaadafullОценок пока нет
- NTДокумент10 страницNTaadafullОценок пока нет
- Performance Tips and Tricks With ABLДокумент23 страницыPerformance Tips and Tricks With ABLJulio Cuevas CasanovaОценок пока нет
- Campbell-Walsh Urology, 10th Edition 2012Документ1 страницаCampbell-Walsh Urology, 10th Edition 2012Annisa Chaerani BurhanuddinОценок пока нет
- Sony Ericsson ProductДокумент34 страницыSony Ericsson ProductGnana SekaranОценок пока нет
- Bul 36628Документ13 страницBul 36628Γεωργια ΛεμενιτακηОценок пока нет
- Samsung WQHD 32 SD850 Manual PDFДокумент114 страницSamsung WQHD 32 SD850 Manual PDFwbsmithiiОценок пока нет
- S Đ Main GA-H61M-S2-B3Документ31 страницаS Đ Main GA-H61M-S2-B3nguyenОценок пока нет
- Microcontroller BasicsДокумент14 страницMicrocontroller BasicsholaОценок пока нет
- Cover PageДокумент8 страницCover PageALEJANDROОценок пока нет
- Software Developer or Software Engineer or Computer Programmer oДокумент3 страницыSoftware Developer or Software Engineer or Computer Programmer oapi-77545596Оценок пока нет
- 4650 and 4850 Section 40Документ8 страниц4650 and 4850 Section 40josephmw0308Оценок пока нет
- c9372 - Manual Rectificadora Discos y TamboresДокумент28 страницc9372 - Manual Rectificadora Discos y TamboresAnonymous f5wOfuB6DYОценок пока нет
- Commands PDFДокумент261 страницаCommands PDFSenan Alkaaby100% (1)
- Chief Architect x8 Users Guide House TutorialДокумент42 страницыChief Architect x8 Users Guide House TutoriallsatchithananthanОценок пока нет
- Ghi DiaДокумент8 страницGhi Diaapi-3758127Оценок пока нет
- GamesДокумент43 страницыGamesSunil KumarОценок пока нет
- Exor PLIO06 OI Module SpecsheetДокумент4 страницыExor PLIO06 OI Module SpecsheetElectromateОценок пока нет
- FpartsДокумент3 страницыFpartsCastillo HectorОценок пока нет
- BT PresentationДокумент5 страницBT PresentationArmando GonzálezОценок пока нет
- Isp Flash Microcontroller Programme:8051 ProgrammerrДокумент4 страницыIsp Flash Microcontroller Programme:8051 ProgrammerrTol Man ShresthaОценок пока нет
- The Ultimate Truth About Coils!: Commander LoohanДокумент20 страницThe Ultimate Truth About Coils!: Commander LoohanAbimanyu Aryo100% (2)
- PRODUCTS: DH61BE, DH61CR, DH61DL, DH61WW (Standard BIOS) : BIOS Update Release NotesДокумент2 страницыPRODUCTS: DH61BE, DH61CR, DH61DL, DH61WW (Standard BIOS) : BIOS Update Release NotesEfigenio SobrinhoОценок пока нет
- Test BenchesДокумент7 страницTest BenchesAnderson LondonОценок пока нет
- IHACRES 2.1 UserGuide SecondEditionДокумент55 страницIHACRES 2.1 UserGuide SecondEditionJunior BerrocalОценок пока нет
- Contoh RAB POMPAДокумент2 страницыContoh RAB POMPAZipronОценок пока нет
- KG-UV920R Service ManualДокумент38 страницKG-UV920R Service ManualErik JirikОценок пока нет
- AS380S Series Elevator Integrated Controller Operation Manual V2.0Документ126 страницAS380S Series Elevator Integrated Controller Operation Manual V2.0Francisco Javier Burgos0% (1)
- Foxboro 870ITPH Electrochemical Transmitter For PH, ORPДокумент60 страницFoxboro 870ITPH Electrochemical Transmitter For PH, ORPGabriel SilvaОценок пока нет
- D All Product Smartphone Y Series Y520-U22 HUAWEI Y520 Smart Phone Product Description V1.0Документ15 страницD All Product Smartphone Y Series Y520-U22 HUAWEI Y520 Smart Phone Product Description V1.0XXXXОценок пока нет