Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Heat Treatment, Case Hardening
Загружено:
M Insan KamilОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Heat Treatment, Case Hardening
Загружено:
M Insan KamilАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name : Muhammad Insan Kamil
Class : III MA
Nim : 061230200091
Majoring : Mechanical Engineering
Subject : Mechanic of Material
Lecturer : H. Firdaus ST, MT
Heat Treatment (Perlakuan Panas)
Heat Treating defined as the controlled heating and
cooling of metals for the primary purpose of altering their
properties (strength, ductility, hardness, toughness,
machinability, etc
Can be done for Strengthening purposes such as
:converting structure to martensite.
Can be done for Softening and Conditioning Purposes
such as : annealing, tempering, etc.
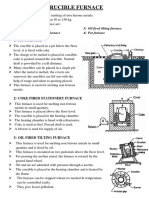
CASE HARDENING
When we want to make a material harder on the case
(just surface) than in of material.
Low carbon steels cannot be hardened by heating due
to the small amounts of carbon present.
Case hardening seeks to give a hard outer skin over a
softer core on the metal.
The addition of carbon to the outer skin is known as
carburising.
Function OF Case Hardening
In general case, every part of machine
has a characteristics. so there are some
differences to the needs of the material
such as harder output than input.
Example :
Gearbox, gear are part of the machine that
works more harder in the surface, so, for make
material is not brittle & easier break. The
solution is case hardening
CASE HARDENING METHODS
Methods to Surface Hardening
Heat Treatment
Induction
Flame
Laser
Light
Electron beam
Case Hardening
Carburizing
Cyaniding
Carbonitriding
Nitriding
Simple process of Surface Hardening
The simple process of surface hardening when
the case of material is heating quickly to more
recrystallization or what we need than its
material is cooling quickly according for what
the material we need.
Quenching media for Surface Hardening
Brine (water and salt solution)
Water
Oil
Air
Turn off furnace
Flame Hardening ( Torch Hardening)
Gas flames raise the
temperature of the
outer surface above
the upper critical
temp. The core will
heat by conduction.
Water jets quench the
component.
Flame Hardening
Induction hardening
Induced eddy
currents heat the
surface of the steel
very quickly and is
quickly followed by
jets of water to
quench the
component.
A hard outer layer is
created with a soft
core. The slideways
on a lathe are indu
ction hardened.
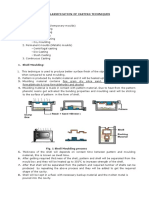
Carburizing
Pack carburising
The component is packed
surrounded by a carbon-rich
compound and placed in the
furnace at 900 degrees.
Over a period of time carbon
will diffuse into the surface of
the metal.
The longer left in the furnace,
the greater the depth of hard
carbon skin. Grain refining is
necessary in order to prevent
cracking.
Salt bath carburising. A molten salt bath (sodium
cyanide, sodium carbonate and sodium chloride) has
the object immersed at 900 degrees for an hour
giving a thin carbon case when quenched.
Gas carburising. The object is placed in a sealed
furnace with carbon monoxide allowing for fine
control of the process.
Nitriding. Nitrides are formed on a metal surface in a
furnace with ammonia gas circulating at 500 degrees
over a long period of time (100 hours). It is used for
finished components.
Aplication of Materials:
Automobile: oil pump gear, drive worm screw,
brake cam, speed box gear
Motor cycle: gears, shaft, pin
Thank You for Your Attention
Вам также может понравиться
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonОт EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonОценок пока нет
- Deepesh Heat TreatmentДокумент26 страницDeepesh Heat TreatmentVaidОценок пока нет
- Surface Hardening of SteelДокумент50 страницSurface Hardening of SteelTeptep GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Case HardeningДокумент14 страницCase HardeningmasoodОценок пока нет
- Surface Hardening: - Core With Fine Pearlite, Surface MartensiticДокумент28 страницSurface Hardening: - Core With Fine Pearlite, Surface MartensiticVaibhav GuptaОценок пока нет
- HT ManualДокумент17 страницHT ManualAkhilesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Heat Treatment of MetalsДокумент8 страницHeat Treatment of MetalsDr. L. Bhanuprakash ReddyОценок пока нет
- Alloys and Types of SteelДокумент16 страницAlloys and Types of SteelRajatОценок пока нет
- Hsla SteelДокумент22 страницыHsla SteelriteshbarmanОценок пока нет
- AlloysДокумент91 страницаAlloysNiccoloОценок пока нет
- Lecture 04-CCT and TemperingДокумент17 страницLecture 04-CCT and TemperingRudy Dwi PrasetyoОценок пока нет
- Basic Information About Metals and AlloysДокумент7 страницBasic Information About Metals and AlloysMahesh JingarwarОценок пока нет
- Extrusion of Metals: Mr. Jay Vora Faculty, School of Technology, PDPU, GandhinagarДокумент27 страницExtrusion of Metals: Mr. Jay Vora Faculty, School of Technology, PDPU, GandhinagarAdityasinh DesaiОценок пока нет
- Surface TreatmentДокумент34 страницыSurface TreatmentnagarajОценок пока нет
- Chamber and Tube Furnaces 0001-G-EДокумент64 страницыChamber and Tube Furnaces 0001-G-EMutsikamahwe BrianОценок пока нет
- Theory of Non-Ferrous Metals and Alloys ProcessingДокумент83 страницыTheory of Non-Ferrous Metals and Alloys ProcessingHimanshuDeepОценок пока нет
- Aisi 305Документ3 страницыAisi 305Aditya PratapОценок пока нет
- SA253MA DetailДокумент16 страницSA253MA Detailksquare2001100% (1)
- A Model For The Graphite Formation in Ductile Cast Iron Part I Inoculation MechanismsДокумент25 страницA Model For The Graphite Formation in Ductile Cast Iron Part I Inoculation MechanismsAdams GodoyОценок пока нет
- Heat TreatmentДокумент21 страницаHeat TreatmentChernet MerknehОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Water-Hardening Tool Steels (W Series)Документ3 страницыIntroduction To Water-Hardening Tool Steels (W Series)giulior89Оценок пока нет
- Heat Treatment of Nodular Cast IronДокумент4 страницыHeat Treatment of Nodular Cast IronRoman_RomeoОценок пока нет
- Non-Ferrous Alloys: Dr. Indika de Silva Senior Lecturer Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering University of MoratuwaДокумент68 страницNon-Ferrous Alloys: Dr. Indika de Silva Senior Lecturer Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering University of MoratuwaChandima K Priyamal100% (1)
- Steel and Its AlloyДокумент23 страницыSteel and Its AlloyHemang ChopraОценок пока нет
- Theory of AlloysДокумент42 страницыTheory of Alloyskeval patel100% (1)
- Effect of Cooling Rate On Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Gray Cast Iron - IsIДокумент6 страницEffect of Cooling Rate On Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Gray Cast Iron - IsIgiokniessОценок пока нет
- Chapter 17 - CorrosionДокумент11 страницChapter 17 - CorrosionmuthuhcuОценок пока нет
- Copper in Heat Exchangers - WikipediaДокумент11 страницCopper in Heat Exchangers - Wikipediaramthecharm_46098467Оценок пока нет
- Heat Treatment of SteelДокумент11 страницHeat Treatment of SteelMohamed El-gammalОценок пока нет
- @standardsharin - ASME STP-NU-044-2011-12Документ62 страницы@standardsharin - ASME STP-NU-044-2011-12EricОценок пока нет
- Welding FundametalsДокумент55 страницWelding Fundametalsyadavmihir63Оценок пока нет
- Iron Carbon Phase DiagramДокумент4 страницыIron Carbon Phase DiagramMizanur RahmanОценок пока нет
- FRP Flange Repair Procedure.Документ1 страницаFRP Flange Repair Procedure.Donbandan0% (1)
- Selecting Tubing Materials For Power Generation Heat ExchangersДокумент20 страницSelecting Tubing Materials For Power Generation Heat ExchangersPing Apiwat100% (1)
- Induction PWHTДокумент6 страницInduction PWHTMallinatha PNОценок пока нет
- Alloy SteelsДокумент9 страницAlloy SteelsAileen Joy CananiaОценок пока нет
- Stainless Steel Technical PresentationДокумент23 страницыStainless Steel Technical PresentationRavi Teja100% (1)
- 06-Fatigue and Creep of Materials - F17 PDFДокумент23 страницы06-Fatigue and Creep of Materials - F17 PDFsabavoonОценок пока нет
- Welding PDFДокумент6 страницWelding PDFNavneet ChaubeyОценок пока нет
- The TEMPCORE ProcessДокумент15 страницThe TEMPCORE ProcessShanna Lee100% (1)
- Physical MetallurgyДокумент101 страницаPhysical MetallurgySheikh Sabbir Sarforaz100% (1)
- Aircraft Materials and ProcessesДокумент15 страницAircraft Materials and ProcessesRajesh KumarОценок пока нет
- The Science of Welding Metallurgy: A Brief Word On Filler MetalsДокумент2 страницыThe Science of Welding Metallurgy: A Brief Word On Filler MetalsSandro FerreiraОценок пока нет
- Thermanit 17-06 (Boehler)Документ1 страницаThermanit 17-06 (Boehler)queno1Оценок пока нет
- Crucible Furnace Some MoreДокумент2 страницыCrucible Furnace Some MorePrashanth BnОценок пока нет
- Pneumatic Steelmarking - Chapter IV AOD ProcessingДокумент6 страницPneumatic Steelmarking - Chapter IV AOD Processinggau3koОценок пока нет
- Classification of Casting TechniquesДокумент16 страницClassification of Casting TechniquesRehan SharmaОценок пока нет
- Types of Welding DefectsДокумент7 страницTypes of Welding DefectsPradip Erande100% (1)
- Unit 2-Chapter 6 - Heat Treatment of MetalsДокумент55 страницUnit 2-Chapter 6 - Heat Treatment of Metalssainath reddy kesam reddyОценок пока нет
- Uts Material SuperplastisДокумент10 страницUts Material SuperplastisHandrizaHanifAsyrafiОценок пока нет
- Effects of MN Content and Heat TreatmentДокумент5 страницEffects of MN Content and Heat TreatmentTrần Xuân VịnhОценок пока нет
- 03 - Iron - Iron CarbideДокумент35 страниц03 - Iron - Iron CarbidebotobotoakbarОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Residual StressДокумент61 страницаCharacteristics of Residual Stressعزت عبد المنعمОценок пока нет
- Special Metals Joining (WeldingWorld) PDFДокумент52 страницыSpecial Metals Joining (WeldingWorld) PDFاکبر کرمیОценок пока нет
- 1 - Intro To MetllurgyДокумент37 страниц1 - Intro To Metllurgyapi-342177144Оценок пока нет
- Chip Formation and Tool LifeДокумент37 страницChip Formation and Tool LifeSquakx BescilОценок пока нет
- MCM AllДокумент7 страницMCM AllPalanisamy RajaОценок пока нет
- Department of Petrochemical Collage of Technical Engineering Duhok Polytechnic UniversityДокумент13 страницDepartment of Petrochemical Collage of Technical Engineering Duhok Polytechnic UniversityIbrahimОценок пока нет
- Extrusion and Its ApplicationДокумент28 страницExtrusion and Its ApplicationLakhan GuptaОценок пока нет
- Brass Microstructure For Metallurgy LabДокумент7 страницBrass Microstructure For Metallurgy LabSelvaraj0% (1)
- 1367 6 PDFДокумент20 страниц1367 6 PDFIrshad Khan100% (1)
- Knottex Spare Part ManualДокумент39 страницKnottex Spare Part ManualKarthhic Mukil57% (7)
- MEC 322 Manufacturing Lec Week 1Документ63 страницыMEC 322 Manufacturing Lec Week 1Danyal ChaudhryОценок пока нет
- Interview QuestionДокумент22 страницыInterview QuestionsugeshОценок пока нет
- ISO System of Limits and Fits (Tolerances)Документ6 страницISO System of Limits and Fits (Tolerances)skakerОценок пока нет
- Stair Treads and Fast NersДокумент1 страницаStair Treads and Fast Nersparag7676Оценок пока нет
- CastingДокумент18 страницCastingNeelu TiruvayipatiОценок пока нет
- Instruments Set For Upper Limb (Small Bone Fragment) Rp. 16.034.000Документ4 страницыInstruments Set For Upper Limb (Small Bone Fragment) Rp. 16.034.000SOFIANTITALIBOОценок пока нет
- Knuth Lathe DL E Heavy 620 - 3000Документ8 страницKnuth Lathe DL E Heavy 620 - 3000martin_jaitmanОценок пока нет
- Bolt Marking & Identification - Metric & UNC/UNF: BM BMДокумент14 страницBolt Marking & Identification - Metric & UNC/UNF: BM BMNorco TilesОценок пока нет
- Surface GrindingДокумент6 страницSurface GrindingAnonymous YkDJkSqОценок пока нет
- Bollhoff Helicoil Tangless Inserts 2Документ3 страницыBollhoff Helicoil Tangless Inserts 2Ace Industrial SuppliesОценок пока нет
- Flexco Bolt Solid Plate Fastening System: The Cement Industry Standard For Strong, Long-Lasting SplicesДокумент4 страницыFlexco Bolt Solid Plate Fastening System: The Cement Industry Standard For Strong, Long-Lasting SplicesBanksyОценок пока нет
- Din 965Документ10 страницDin 965PacoОценок пока нет
- Laser Marking StationДокумент2 страницыLaser Marking Stationsedat atalayОценок пока нет
- Lost Wax Casting ProcessДокумент2 страницыLost Wax Casting ProcessgabaldoniОценок пока нет
- 4.0 Manufacturing Process Roll FormingДокумент4 страницы4.0 Manufacturing Process Roll FormingMuhd NadzriОценок пока нет
- Material GradesДокумент20 страницMaterial GradesEmreОценок пока нет
- Catalog Materiale de Adaos FileurДокумент193 страницыCatalog Materiale de Adaos FileurRogo CatalinОценок пока нет
- Ifi-100-107 1Документ58 страницIfi-100-107 1diegosc2200Оценок пока нет
- CNC Part ProgrammingДокумент53 страницыCNC Part ProgrammingmsshahenterОценок пока нет
- 011 Repl of Kiln Shell Under TyreДокумент32 страницы011 Repl of Kiln Shell Under TyreddОценок пока нет
- NG 414 - NG 464: Pos. Code Q.ty Descrizione Description Description BeshreibungДокумент6 страницNG 414 - NG 464: Pos. Code Q.ty Descrizione Description Description BeshreibungheyОценок пока нет
- GN4 - Hand Tools and Power Tools - Heavy Equipment SafetyДокумент123 страницыGN4 - Hand Tools and Power Tools - Heavy Equipment SafetyNavi AgeinОценок пока нет
- Hacksaws & FilesДокумент27 страницHacksaws & FilesCiwing CiwingОценок пока нет
- Select Arc Brochure On Ni Alloy Welding ProductsДокумент6 страницSelect Arc Brochure On Ni Alloy Welding Productsharan2000Оценок пока нет
- Caulking Vs FulleringДокумент2 страницыCaulking Vs FulleringVimal ThomasОценок пока нет
- Instapdf - in Advanced Manufacturing Process MCQ 553Документ12 страницInstapdf - in Advanced Manufacturing Process MCQ 553s170252 P.ASHOK sklmОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5 - DistortionДокумент22 страницыLesson 5 - DistortionKhepa BabaОценок пока нет
- DJF21012 Sand Casting 1006Документ15 страницDJF21012 Sand Casting 1006Sakinah KamalОценок пока нет