Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chest X Ray Mediastinum Cohs Febr 2014
Загружено:
MozaLootahИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chest X Ray Mediastinum Cohs Febr 2014
Загружено:
MozaLootahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chest X ray
Mediastinum
COHS
February 2014
Goals
To understand the basic terminology and techniques
of chest x-rays
To gain familiarity with "the normal chest x-ray
To learn and practice a standardized sequence of
chest x-ray interpretation
To learn and be able to recognize several
common chest x-ray abnormalities
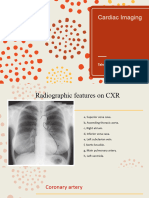
Lung zones
Pulmonary arteries
Many structures can be identified within
the mediastium;
Heart, blood vessels, main airways,
esophagus, lymph nodes, thymus ..
TWO SHADOWS/MAGNIFICATION
DISTANT STRUCTURES
SHADOWS MERGE
ADJACENT STRUCTURES
How many structures can you identify?
LV
RV
SVC
Aortic pulmonary
recess
Left
Aortic
arch
RA
LA
Right
pulmonary
artery
Right
pulmonary
artery
(lower lobe)
Vascular
pedicle
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
SVC
IVC
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
RA
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
RV
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
PA
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
LA
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
LV
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
Aorta
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
Right border
Superior vena cava
Right atrium
Inferior vena cava
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
Right border
Superior vena cava
Right atrium
Inferior vena cava
Left border
Aortic knob
Main pulmonary trunk
Left ventricle
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
Pulmonary Arteries
Right
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
Pulmonary Arteries
Right
Left
Postero-Anterior (PA) View
Pulmonary Arteries
Right
Left
Pulmonary Veins
LA
How many structures
can you identify?
Gastric air
bubble
Left upper
lobe
bronchus
IVC
Right
hemidiaphragm
LV
LA
RV
Pulmonary
outflow
tract
Aorta
Right upper
lobe bronchus
RPA
LPA
Confluence of
pulmonary
veins
Brachiocephalic
vessels
Trachea
Left
hemidiaphragm
Lateral View
RA
SVC
IVC
Lateral View
RV
Lateral View
Lateral View
LA
Lateral View
LV
Lateral View
Aorta
Lateral View
LV
Lateral View
Aorta
Main Pulmonary Artery
Inferior vena cava
Lateral View
Pulmonary Arteries
Left
Right
Pulmonary Veins
Which valve has been replaced?
Which valve has been replaced?
Aortic valve
Note the orientation of the
valve perpendicular to the
plane of the PA film.
Which valve has been replaced?
Which valve has been replaced?
Pulmonic
The pulmonary outflow
tract is more superior
and lateral than many
people think.
Last one, name the valves
Last one, name the valves
Aortic
Tricuspid
Mitral
Tricuspid
Mitral
Aortic
Found in the superior mediastinum.
Right and left margins are normally formed by the
superior vena cava and the descending portion of the
aortic arch, respectively.
A widened vascular pedicle can have several
etiologies including elevated intravascular volume,
aortic trauma, or pericardial effusion.
Vascular
pedicle
Aortic
arch
Superior
vena cava
Intravascular volume
depletion
Intravascular volume
elevation
vs.
Vascular
pedicle
Vascular
pedicle
Intravascular volume
depletion
Intravascular volume
elevation
Intravascular volume elevation resulting in an expanded SVC should not be mistaken
for hematoma, which would have a less distinct border and more opacified
appearance.
vs.
Superior
vena cava
Aorta
Superior
vena cava
Aorta
Trauma patient with an aortic transection
Note the vascular pedicles fuzzy, opacified right border.
What is happening here?
What is happening here?
Can you follow the heart borders?
What is happening here?
The wide vascular
pedicle here results
from a pericardial
effusion
The pacemaker
wires roughly
outline the right
atrium border
If you look closely you can
make out the superior
pericardial border
The left heart border
can be seen within the
effusion
effusion
effusion
Comparing this with older films can also help make the diagnosis.
Esophagus
Thyroid
Thymus
Lymph nodes
These are generally not seen unless there is
pathology
What could be the source of this anterior mediastinal mass?
What could be the source of this anterior mediastinal mass?
Ddx: Lymphoma/leukemia, germ cell tumors (e.g., teratoma), thymic
mass (e.g., thymoma, cyst), enlarged thyroid, vascular (e.g.,
hematoma, aortic aneurysm).
This patient has a thymoma.
How about this one?
How about this one?
This patient has a an enlarged thyroid gland.
A. Anteriorposterior chest radiograph obtained on
supine position shows mediastinal widening with
enlarged and indistinct aortic knob and
aortopulmonary window opacification (a).
B. Contrast-enhanced axial
CT scan shows a rupture
of the aorta with a
pseudoaneurysm (star)
projecting anteromedially.
Also noted are mediastinal
hematoma and bilateral
hemothoraces.
C. 3-D volume rendering
image well demonstrates a
pseudoaneurysm (arrow)
of the aorta at isthmic
portion.
B
A
Traumatic Aortic Rupture Case 1. 68/M
C
A. Chest radiograph appears normal.
B. Tc
99m
MDP scan shows hot uptake at junction
between left 1
st
rib and manubrium.
C and D. Axial (C) and 3-D reconstruction (D) CT
scans reveal fracture of calcified left 1
st
costal
cartilage, just lateral to sternocostal joint.
A C
D
B
Case 1. 49/M
Fracture of the left 1
st
Costal Cartilage
Вам также может понравиться
- Comparative Cardiac Imaging: A Case-based GuideОт EverandComparative Cardiac Imaging: A Case-based GuideJing Ping SunОценок пока нет
- Radiology of Cardiac and Vascular Structures: Cindy Chan, MDДокумент64 страницыRadiology of Cardiac and Vascular Structures: Cindy Chan, MDMohamoud MohamedОценок пока нет
- PA Projection AP ProjectionДокумент64 страницыPA Projection AP ProjectionMiaMDОценок пока нет
- Anomalies of Fetal Cardiac SystemДокумент42 страницыAnomalies of Fetal Cardiac SystemNishant RajОценок пока нет
- CHEST X-RAY Presentation CVSДокумент45 страницCHEST X-RAY Presentation CVSNorsafrini Rita Ahmad100% (1)
- Cardiovascular DiseasesДокумент49 страницCardiovascular DiseasesSHAMENI VINODОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Imaging Sept 2016tДокумент254 страницыCardiac Imaging Sept 2016tColeen Joyce NeyraОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7 - CXR Lecture SlidesДокумент72 страницыLecture 7 - CXR Lecture Slidesubcradadmin100% (1)
- CXR Interpretation WriteupДокумент32 страницыCXR Interpretation WriteupArhanОценок пока нет
- Chest Imaging IДокумент173 страницыChest Imaging Ikathi raja sekharОценок пока нет
- Basic Chest Imaging and Heart FailureДокумент57 страницBasic Chest Imaging and Heart FailureKiaa auliaОценок пока нет
- Natalya Master CardioДокумент71 страницаNatalya Master CardioTaman Hoang100% (1)
- BF - PJB - Yaf Mel Tia NiaДокумент20 страницBF - PJB - Yaf Mel Tia NiaRoberto HutapeaОценок пока нет
- Kuliah Radiologi Cardiorespiratory 2Документ99 страницKuliah Radiologi Cardiorespiratory 2Muhammad Sandy Ali YafieОценок пока нет
- Radiologi-Fotfo Toraks - No PicДокумент30 страницRadiologi-Fotfo Toraks - No PicKrisna MuhammadОценок пока нет
- Basic Fetal EchocardiographyДокумент63 страницыBasic Fetal EchocardiographyMuhammad Abeesh100% (1)
- Thorak SДокумент71 страницаThorak Srizkynugroho15Оценок пока нет
- Normal ChestДокумент82 страницыNormal ChestMonica CherladyОценок пока нет
- Emergency UltrasoundДокумент32 страницыEmergency UltrasoundChoga ArlandoОценок пока нет
- Radioanatomi Jantung Kel 9bДокумент42 страницыRadioanatomi Jantung Kel 9bMuhamad KeanuОценок пока нет
- Materi Foto ThoraksДокумент90 страницMateri Foto ThoraksArif Rahman Wardhani100% (1)
- Radiography of The Thorax: BY Abubakar AДокумент70 страницRadiography of The Thorax: BY Abubakar AJameeluh TijjanyОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Imaging - 8 - Radiological Pathology - Lung Pathologies and Radiology in Specific Cases - Prof - Dr.i̇smet TAMERДокумент35 страницDiagnostic Imaging - 8 - Radiological Pathology - Lung Pathologies and Radiology in Specific Cases - Prof - Dr.i̇smet TAMERAly MssreОценок пока нет
- Interpretation of Chest Imaging1Документ91 страницаInterpretation of Chest Imaging1Brooke TurnerОценок пока нет
- Cardiac RadiologyДокумент17 страницCardiac Radiologytam meiОценок пока нет
- Mitral Stenosis-RarestДокумент9 страницMitral Stenosis-RarestWen Jie LauОценок пока нет
- in The Given Chest X-Ray, Normal Cardiothoracic Ratio IsДокумент63 страницыin The Given Chest X-Ray, Normal Cardiothoracic Ratio Is李建明Оценок пока нет
- Chest X-Ray Analysis 2023Документ63 страницыChest X-Ray Analysis 2023CHARLOTTE DU PREEZОценок пока нет
- Crash Course Interpretation of Chest X-Ray PDFДокумент144 страницыCrash Course Interpretation of Chest X-Ray PDFMechkar KatherinОценок пока нет
- Interpretation Chest X RayДокумент127 страницInterpretation Chest X RayVimal NishadОценок пока нет
- CXR ABC by DR ShamolДокумент139 страницCXR ABC by DR Shamolazar103100% (3)
- CARDIOVASCULAR Mettler RadiologíaДокумент25 страницCARDIOVASCULAR Mettler RadiologíaDavid ReyesОценок пока нет
- Medical Investigations PDFДокумент136 страницMedical Investigations PDFFathy ElsheshtawyОценок пока нет
- Murtazasegmentalanalysis 171214123424Документ90 страницMurtazasegmentalanalysis 171214123424Arifin SiregarОценок пока нет
- How To Read X-RayДокумент8 страницHow To Read X-RayPeterson Wachira HscОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Imaging-AnatomyДокумент27 страницCardiac Imaging-AnatomyfatimaОценок пока нет
- Radial Anatomy of The ThoraxДокумент46 страницRadial Anatomy of The ThoraxElijah KamaniОценок пока нет
- Final EchocardiographyДокумент55 страницFinal EchocardiographyAdarshBijapur100% (1)
- DR - Sakher-Alkhaderi: Consultant Radiologist AmcДокумент50 страницDR - Sakher-Alkhaderi: Consultant Radiologist AmcAswin Rajasekaran100% (1)
- Congenital Heart Disease: Patent Ductus ArteriosusДокумент43 страницыCongenital Heart Disease: Patent Ductus ArteriosusanandafirstyОценок пока нет
- Basic Chest RadiologyДокумент81 страницаBasic Chest RadiologynasirimbbОценок пока нет
- Mbbs Review1486647513581205409Документ179 страницMbbs Review1486647513581205409Cvam SahОценок пока нет
- Adult Congenital Heart DiseaseДокумент45 страницAdult Congenital Heart DiseaseCatur UtamiОценок пока нет
- By Dr. Chia Kok KingДокумент84 страницыBy Dr. Chia Kok KingLokanath SeepanaОценок пока нет
- Adult Chest X-RayДокумент60 страницAdult Chest X-RayAnil DasОценок пока нет
- Unidad II - Tomografia de ToraxДокумент97 страницUnidad II - Tomografia de ToraxJoyce MoreiraОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6 - Cardiac Anatomy SlidesДокумент57 страницLecture 6 - Cardiac Anatomy Slidesubcradadmin100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Pathology: Professor Mircea BuruianДокумент174 страницыCardiovascular Pathology: Professor Mircea BuruianDiana PopoviciОценок пока нет
- OS205 Cardiac ImagingДокумент7 страницOS205 Cardiac ImagingLaurisse ManaloОценок пока нет
- Chest X RaysДокумент31 страницаChest X RaysEmma CatterallОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Congenital DiseaseДокумент27 страницCardiac Congenital Diseasenovitafitri123Оценок пока нет
- Congenital Heart Disease: Kriti Puri, MD Hugh D. Allen, MD Athar M. Qureshi, MDДокумент30 страницCongenital Heart Disease: Kriti Puri, MD Hugh D. Allen, MD Athar M. Qureshi, MDhari ilman toniОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Anatomy Using CTДокумент39 страницCardiac Anatomy Using CTDyah KumalasariОценок пока нет
- Tte and Tee Assessment For Asd Closure 2Документ88 страницTte and Tee Assessment For Asd Closure 2Avinash GutheОценок пока нет
- Radiologi Thorax NormalДокумент15 страницRadiologi Thorax NormalVina RatnasariОценок пока нет
- Chest Anatomy. Chest AnatomyДокумент70 страницChest Anatomy. Chest AnatomydrelvОценок пока нет
- Thorax NormalДокумент15 страницThorax Normaldody haikalОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Pathology FINALДокумент45 страницCardiovascular Pathology FINALIanОценок пока нет
- CardiovascularДокумент80 страницCardiovascularhajarhaniyahОценок пока нет
- Nutrition of Children With Inborn Errors of MetabolismДокумент28 страницNutrition of Children With Inborn Errors of MetabolismMozaLootahОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology CH 01 Introduction, Cell Injury, Adaptaion, DeathДокумент8 страницPathophysiology CH 01 Introduction, Cell Injury, Adaptaion, DeathMozaLootahОценок пока нет
- Case Study 12Документ2 страницыCase Study 12MozaLootahОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology CH 02 Inflammation-V2Документ24 страницыPathophysiology CH 02 Inflammation-V2MozaLootahОценок пока нет
- Data CollectionДокумент6 страницData CollectionMozaLootahОценок пока нет
- Physics UOS Ch1 PPT HSДокумент39 страницPhysics UOS Ch1 PPT HSMozaLootahОценок пока нет
- DigestionДокумент21 страницаDigestionHoang Ba HaiОценок пока нет
- Body Tissues Histology 101Документ25 страницBody Tissues Histology 101MozaLootahОценок пока нет
- Cohen Chapter 2Документ5 страницCohen Chapter 2MozaLootahОценок пока нет
- PubmedДокумент30 страницPubmedMozaLootahОценок пока нет
- EMail Using It Effectivley 2013Документ45 страницEMail Using It Effectivley 2013MozaLootahОценок пока нет
- CN&D Program - Conceptual FrameworkДокумент22 страницыCN&D Program - Conceptual FrameworkMozaLootahОценок пока нет
- 1.9 Problem Solving Chapter 1Документ16 страниц1.9 Problem Solving Chapter 1MozaLootahОценок пока нет
- Physiology of The Normal Heart: Key PointsДокумент5 страницPhysiology of The Normal Heart: Key PointsGustavo TejerinaОценок пока нет
- Doppler Venoso MMIIДокумент23 страницыDoppler Venoso MMIIAdriana KimuraОценок пока нет
- Endothelium: What Is The Basic Structure of Endothelium?Документ2 страницыEndothelium: What Is The Basic Structure of Endothelium?Aurelia AlexandraОценок пока нет
- Step by Step Pediatric Echocardiography PDFДокумент141 страницаStep by Step Pediatric Echocardiography PDFDiana_anca6100% (1)
- Anatomy MCQДокумент9 страницAnatomy MCQMido TooОценок пока нет
- 11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemДокумент85 страниц11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemJaps De la CruzОценок пока нет
- CVD InfactionДокумент3 страницыCVD InfactionDaryl James MedilloОценок пока нет
- Amali Jantung 2Документ23 страницыAmali Jantung 2Tengku ShazlinОценок пока нет
- 2016 ESC-EAS Lečenje DislipidemijaДокумент65 страниц2016 ESC-EAS Lečenje DislipidemijaМилан Лабудовић100% (1)
- Solution Manual For High Acuity Nursing 7th Edition WagnerДокумент25 страницSolution Manual For High Acuity Nursing 7th Edition WagnerJamesThomasngec100% (31)
- Buerger's DiseaseДокумент8 страницBuerger's DiseaseGayle Bautista100% (1)
- Sclerotherapy: Treatment of Varicose Telangiectatic Leg VeinsДокумент439 страницSclerotherapy: Treatment of Varicose Telangiectatic Leg VeinsjesussalvadorsuazaОценок пока нет
- Epistaxis: "Bleeding From Inside The Nose"Документ12 страницEpistaxis: "Bleeding From Inside The Nose"Farrukh Mehmood100% (1)
- Hypertension - Student HandoutДокумент4 страницыHypertension - Student HandoutEliesther RiveraОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3Документ6 страницAssignment 3ticticОценок пока нет
- K51 - Anestesi Pada CV System (Anastesi)Документ77 страницK51 - Anestesi Pada CV System (Anastesi)Dwi Meutia IndriatiОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4 Blood VesselsДокумент14 страницLesson 4 Blood VesselsCarolyn D MayugaОценок пока нет
- 10.1007@s11906 020 1017 9Документ18 страниц10.1007@s11906 020 1017 9Isamar AgostoОценок пока нет
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramДокумент3 страницыMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramAbi Habiling100% (3)
- Human System 2 ReviewДокумент14 страницHuman System 2 Reviewn.misovicОценок пока нет
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease With Decreased Pulmonary Blood FlowДокумент7 страницCyanotic Congenital Heart Disease With Decreased Pulmonary Blood FlowdrhomiedanОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemДокумент4 страницыAnatomy and Physiology: Circulatory SystemJordz PlaciОценок пока нет
- Cvs 253Документ253 страницыCvs 253CHALIE MEQUОценок пока нет
- 11رسالة د احمد شاهين معدلة (m)Документ75 страниц11رسالة د احمد شاهين معدلة (m)ahmedshahin199090Оценок пока нет
- Blood Vessels and CirculationДокумент45 страницBlood Vessels and CirculationLloyd RebusiОценок пока нет
- Medical Supplies Philippine Heart Center 2015Документ146 страницMedical Supplies Philippine Heart Center 2015Emmeline Roy DoblaОценок пока нет
- Cardio Vascular PDFДокумент148 страницCardio Vascular PDFStefana RoxanaОценок пока нет
- New England Journal Medicine: The ofДокумент11 страницNew England Journal Medicine: The ofahmadto80Оценок пока нет
- Assessment of Knowledge and Attitude of Pharmacists Toward The Side Effects of Anesthetics in Patients With Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional StudyДокумент9 страницAssessment of Knowledge and Attitude of Pharmacists Toward The Side Effects of Anesthetics in Patients With Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional StudyMediterr J Pharm Pharm SciОценок пока нет
- AnginaДокумент12 страницAnginaDr-Sanjay SinghaniaОценок пока нет