Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
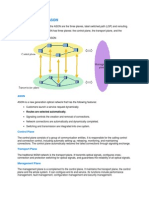
SDH Overview
Загружено:
Kavish JaggiАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SDH Overview
Загружено:
Kavish JaggiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
1
SDH Theory
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
2
What is SDH?
SDH = Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
It is a transport network
synchronous
fully standardized
with high bandwidth
for synchronous and asynchronous signals
for future broadband signals and new services
with standardized network management capabilities
with traffic protection
with a flexible multiplexing structure
direct access to tributaries
cross-connections without demultiplexing
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
3
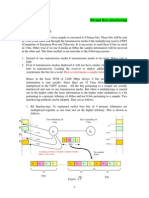
Digital Transmission System
Regenerator
recreates the signal.
Multiplexer (MUX)
Multiplexer combines data from
several lines and transmits it
over a higher-capacity data link.
No signal
60 km
R
60 km
Regenerator
MUX MUX
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
4
Add-Drop Multiplexer (ADM)
Part of the traffic is terminated.
Part of the traffic goes transparently
through.
Multiplexer Naming Conventions
TM
m/n
aggregate
ADM
m/n
aggregate
aggregate
tributaries
Terminal Multiplexer (TM)
All traffic is terminated here.
m: aggregate level
n: lowest tributary level
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
5
No traffic is terminated.
Cross-connection matrix
connects tributary
signals of one aggregate
to another aggregate.
Digital Cross-connect (DXC m/n)
PDH
MUX
PDH
MUX
PDH
MUX
PDH
MUX
DDF
SDH
Cross-Connect
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
6
PDH Bit Rates & HIERARCHY
Hierarchy level USA Europe
0 64 kbit/s T0 64 kbit/s E0
1 1.544 Mbit/s T1 (24x) 2.048 Mbit/s E1 (32x)
2 6.312 Mbit/s DS-2 (4x) 8.448 Mbit/s E2 (4x)
3 44.736 Mbit/s DS-3 (7x) 34.368 Mbit/s E3 (4x)
4 139.264 Mbit/s E4 (4x)
E1
E0
E2
E3
E4
plesiochronous
plesiochronous
plesiochronous
synchronous
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
7
SDH Bit Rates & HIERARCHY
SONET
(ANSI)
SDH
(ITU-T)
Data rate
(Mbps)
STS-1 51.84
STS-3 STM-1 155.52
STS-9 466.56
STS-12 STM-4 622.08
STS-18 933.12
STS-24 1244.16
STS-36 1866.24
STS-48 STM-16 2488.32
STM-64 9953.28
STM1
STM4
STM16
STM64
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
8
PDH vs. SDH Add & Drop Function
ADM
STM-1
STM-1
Six TMs needed
to drop E1
One ADM is
enough to drop E1.
TM TM
TM TM
TM TM
E3
E3
E3
E2
E2
E1
E1
E1
E4 E4
E1 (2.048 kbit/s)
E2
2/1 2/1
3/2
3/2
4/3 4/3
PDH
SDH
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
9
STM-1 Frame
2430 bytes/frame 8 bit/byte 8000 frame/s = 155.52 Mbit/s
transmitted from top to bottom and left to right
AU-4 pointers
MSOH
Payload
VC-4 (HO-VC)
RSOH
9
r
o
w
s
(
b
y
t
e
s
)
9
5
261
270 columns (bytes)
3
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
10
155.520 Mbit/s serial signal
9 BYTES + 261 BYTES = 270 BYTES 270 BYTES x 9 = 2430 BYTES
2430 BYTES/FRAME x 8 BITS/BYTE x 8000 FRAMES/SEC = 155.520 Mbit/s
125us
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
2 4 3 0 b y t e s
2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s 2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s
O v e r h e a d p a y l o a d
F F F F
2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s
2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s
2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s
2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s
2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s
2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s
2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s
2 6 1 b y t e s 9 b y t e s
STM -1 Frame
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
11
Pointer processing
Multiplexing
Aligning
Mapping
SDH Multiplexing Structure (ETSI)
VC-4 STM-N
N
3
1
3
7
139 264 kbit/s
44 736 kbit/s
34 368 kbit/s
6312 kbit/s
2048 kbit/s
1544 kbit/s
AUG
AU-4
TUG-3
TUG-2
TU-3
TU-2
TU-12
VC-2
VC-3
VC-12
VC-11
C-4
C-3
C-2
C-12
C-11
1
C-n Container-n
1
C Container
VC Virtual Container
TU Tributary Unit
TUG Tributary Unit Group
AU Administrator Unit
AUG Administrator Unit Group
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
12
PDH over SDH
2 Mbit/s plesiochronous stream
Justification bytes
C12
Path Overhead
VC12
Container
POH
TU Pointer
TU12
Virtual Container
Container (C)
basic payload unit
Virtual Container (VC)
C + POH (path overhead)
Tributary Unit (TU)
VC + pointer
The pointer indicates the
start of the VC and allows
dynamic alignment of the
VC within the TU frame.
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
13
Multiplexing of AU into STM-N
AUG
AUG
AUG
AUG
STM-4
SOH
AU-4
AU-4
AU-4
AU-4
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
14
No. of Columns used for Tributary Unit
TU11 TU12 TU2 TU3
3 4 12 86
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
15
KLM Coordinates
AU-4 pointers
MSOH
Payload
VC-4 (HO-VC)
RSOH
V
C
-
4
P
O
H
VC-12
VC-12
K
L
TU12-1 TU12-2 TU12-3
TUG3-1 TUG3-2 TUG3-3
TUG2-6
TUG2-7
TUG2-5
TUG2-4
TUG2-3
TUG2-1
TUG2-2
TUG-3 number (values 1-3)
TUG-2 number (values 1-7)
TU-12 number (values 1-3)
KLM: 271 KLM: 152 KLM: 300
VC-3
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
16
Termination of Sections
Path
Multiplexing Sections Multiplexing Sections
Regenerator Sections
TM TM
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
17
Regenerates the optical signal.
Terminates RSOH.
REG
STM-N STM-N
Regenerator
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
18
Terminal Multiplexer
TM
STM-N
or
PDH
STM-M
Terminates RSOH and MSOH.
May terminate HOP and LOP overhead.
Multiplexes/maps tributary signals.
Includes timing and management functions.
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
19
STM-N or PDH
STM-M STM-M
ADM
Add/drop Multiplexer
Terminates RSOH and MSOH.
May terminate HOP and LOP overhead.
Includes connection function between the two aggregates.
Multiplexes/maps tributary signals.
Includes a connection function for allocation of TUs within
the STM frame.
Includes timing and management functions.
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
20
Cross-connect
Terminates RSOH and MSOH.
Includes connection function between the aggregates.
Can have tributary ports, for which it may terminate HOP
and LOP overhead.
Includes timing and management functions.
STM-N or PDH
STM-M STM-M DXC
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
21
STM-16
STM-4
STM-1
STM-16
STM-4
STM-1
SDXC 4/1
Example of Cross-connect (XC)
16 x
4 x
1 x
16 x
4 x
1 x
SDH
multiplexer
AUG
VC-4
34 (45) Mbit/s 2(1.5) Mbit/s
VC-12 VC-3
HO
XC
LO
XC
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
22
SDH Overhead
Overheads carry information for monitoring, maintaining
and controlling the operation of network.
Overhead types
POH for end-to-end monitoring of payload signal (VC-12, VC-3
and VC-4)
Block errors, far end alarms, trace and payload type
SOH is used for monitoring of signal between SDH equipment.
RSOH: block errors, trace
MSOH: block errors, synchronization, and far-end alarms
P
O
H
RSOH
MSOH
POINTER
9 260
270
3
5
9
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
23
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
RSOH 1 A1 A1 A1 A2 A2 A2 J0 NU1 NU2
RSOH 2 B1 R1 R2 E1 R3 U1 F1 NU3 NU4
RSOH 3 D1 R4 R5 D2 R6 U2 D3 U3 U4
PTR 4 H1 Y1 Y2 H2 1 1 H3 H3 H3
MSOH 5 B2 B2 B2 K1 U5 U6 K2 U7 U8
MSOH 6 D4 U9 U10 D5 U11 U12 D6 U13 U14
MSOH 7 D7 U15 U16 D8 U17 U18 D9 U19 U20
MSOH 8 D10 U21 U22 D11 U23 U24 D12 U25 U26
MSOH 9 S1 Z12 Z13 Z21 Z22 M1 E2 NU5 NU6
RSOH
A1, A2 framing patterns (F6H), (28H)
J0 regenerator section Trail Trace Identifier (TTI)
B1 BIP-8 parity byte
E1 RS orderwire channel (service telephone)
F1 user (network operator) data channel
D1, D2, D3 regenerator section Data Communication Channel (DCCR)
NU1, NU2, NU3, NU4 bytes reserved for national use
R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 media specific bytes (e.g. radio link)
U1, U2, U3, U4 bytes with no defined use
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
24
MSOH
B2 BIP-24 parity bytes
K1, K2 Automatic Protection Switching (APS) channel,
D4 to D12 multiplex section Data Communication Channel (DCCM)
S1 synchronization status
M1 Remote Error Indication (REI)
E2 MS orderwire channel (service telephone)
NU5, NU6 bytes reserved for national use
U5 to U26 bytes with no defined use
Z12, Z13, Z21, Z22 bytes with no defined use
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
RSOH 1 A1 A1 A1 A2 A2 A2 J0 NU1 NU2
RSOH 2 B1 R1 R2 E1 R3 U1 F1 NU3 NU4
RSOH 3 D1 R4 R5 D2 R6 U2 D3 U3 U4
PTR 4 H1 Y1 Y2 H2 1 1 H3 H3 H3
MSOH 5 B2 B2 B2 K1 U5 U6 K2 U7 U8
MSOH 6 D4 U9 U10 D5 U11 U12 D6 U13 U14
MSOH 7 D7 U15 U16 D8 U17 U18 D9 U19 U20
MSOH 8 D10 U21 U22 D11 U23 U24 D12 U25 U26
MSOH 9 S1 Z12 Z13 Z21 Z22 M1 E2 NU5 NU6
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
25
VC-4 POH
POH
J 1
B3
C2
G1
F2
H4
F3
K3
N1
J1 Trail Trace Identifier
B3 Parity BIP-8
C2 Signal label (C2), used for payload type identification
G1 Path status
F2 Network operator (user) channel
H4 Multiframe indicator, a sequence indicating TU-multiframe
phase (position of VC-12)
F3 Network operator (user) channel
K3 Automatic Protection Switching
N1 Tandem Connection Monitoring TCM, optional use in
multioperator environments
SDH Theory (Fibcom)
26
Thanks
Вам также может понравиться
- SDH BasicsДокумент48 страницSDH BasicsHipolitomvn100% (3)
- Training Module On Transmission Network and Testing Concep 1Документ638 страницTraining Module On Transmission Network and Testing Concep 1kltowerОценок пока нет
- Passive Optical Networks: Principles and PracticeОт EverandPassive Optical Networks: Principles and PracticeРейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (2)
- Fundamental of SDH TechnologyДокумент467 страницFundamental of SDH TechnologyNishad Patil100% (1)
- LTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencyОт EverandLTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencySeppo HämäläinenОценок пока нет
- ALC SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideДокумент46 страницALC SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideFrancisco Salvador MondlaneОценок пока нет
- SDH AlarmsДокумент42 страницыSDH Alarmspriyanka joshi83% (6)
- Backhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsОт EverandBackhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsKazi Mohammed Saidul HuqОценок пока нет
- SDH Transport SystemsДокумент185 страницSDH Transport SystemsMofasser Ahmed (Tamal)94% (16)
- SDH TheoryДокумент34 страницыSDH Theorythe_emp_eror100% (2)
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkОт EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkОценок пока нет
- WDM PrincipleДокумент54 страницыWDM PrincipleRandy Dookheran100% (1)
- SDH ProtectionДокумент6 страницSDH Protectionzylyz71% (7)
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksОт EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Eo SDHДокумент33 страницыEo SDHapi-3806249Оценок пока нет
- The LTE-Advanced Deployment Handbook: The Planning Guidelines for the Fourth Generation NetworksОт EverandThe LTE-Advanced Deployment Handbook: The Planning Guidelines for the Fourth Generation NetworksРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- SNCP ProtectionДокумент6 страницSNCP Protectionhekri100% (2)
- Tejas NetworksДокумент59 страницTejas Networksfranckkiemde50% (2)
- Training PDH SDH DWDMДокумент112 страницTraining PDH SDH DWDMjayakumar_s_9993% (14)
- Alu DWDM PDFДокумент39 страницAlu DWDM PDFShewan Alam SuhreedОценок пока нет
- Intoducion A OtnДокумент72 страницыIntoducion A OtnGustavo CazaresОценок пока нет
- SDH Anomalies, Defects, Failures, and Alarms DefinitionsДокумент10 страницSDH Anomalies, Defects, Failures, and Alarms DefinitionsAhmed IsmailОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts of ASONДокумент20 страницBasic Concepts of ASONAnonymous H0SJWZE80% (1)
- OTA058001 ASON Features and Application Introduction: Issue 1.0Документ62 страницыOTA058001 ASON Features and Application Introduction: Issue 1.0Ho Anh TuanОценок пока нет
- SDH Overhead and PointerДокумент23 страницыSDH Overhead and PointerMahmoud TahaОценок пока нет
- HCIA-Transmission V2.0 Mock ExamДокумент6 страницHCIA-Transmission V2.0 Mock ExamAhmed ElseliniОценок пока нет
- Basic DWDM Components.Документ16 страницBasic DWDM Components.Pradeep Kumar SahuОценок пока нет
- 01 WDM Technology ComponentsДокумент109 страниц01 WDM Technology ComponentskalphieОценок пока нет
- DWDM vs OTN: Understanding the Difference Between Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing and Optical Transport NetworksДокумент4 страницыDWDM vs OTN: Understanding the Difference Between Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing and Optical Transport Networkschaidar_lakareОценок пока нет
- Types of DWDMДокумент21 страницаTypes of DWDMKoshy GeojiОценок пока нет
- SDH ProtectionДокумент46 страницSDH Protectionapi-3806249100% (8)
- DWDM 101 - Introduction To DWDM 2 PDFДокумент107 страницDWDM 101 - Introduction To DWDM 2 PDFanon_249773183Оценок пока нет
- DWDMДокумент33 страницыDWDMrealiserОценок пока нет
- Basics On SDH From STM-1 Up ToДокумент124 страницыBasics On SDH From STM-1 Up Tojangid_mohanОценок пока нет
- Microwave Transmission LineДокумент43 страницыMicrowave Transmission LineNasirul Islam SabujОценок пока нет
- ASON ProtocolДокумент18 страницASON ProtocolPasham ShivaОценок пока нет
- Optical Power Adjustment GuideДокумент17 страницOptical Power Adjustment GuideJuancarlos ArrietaОценок пока нет
- Training Course WDM Principle V1.0-20080902Документ92 страницыTraining Course WDM Principle V1.0-20080902ZannatoonОценок пока нет
- Narrowband Interference Suppression (RAN15.0 - 01) PDFДокумент21 страницаNarrowband Interference Suppression (RAN15.0 - 01) PDFSam FicherОценок пока нет
- MW Links Planning With Pathloss IVДокумент232 страницыMW Links Planning With Pathloss IVsonibox100% (1)
- Mapping OTNДокумент35 страницMapping OTNEduard IsturizОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Synchronization: Synchronous AsynchronousДокумент91 страницаIntroduction To Synchronization: Synchronous AsynchronousAkhtar Mehmood100% (1)
- Ethernet Over SDHДокумент5 страницEthernet Over SDHEng SugaalОценок пока нет
- Advanced DWDM TrainingДокумент144 страницыAdvanced DWDM TrainingShaytaanОценок пока нет
- ASON-WSON Fundamentals Rev9Документ56 страницASON-WSON Fundamentals Rev9mettlemaster100% (4)
- SDH & PDHДокумент5 страницSDH & PDHMohammad Faruque Hossain100% (4)
- FECДокумент63 страницыFECSanjay YadavОценок пока нет
- DWDM TopologiesДокумент11 страницDWDM TopologiesAbdillah Arifin Rahman LubisОценок пока нет
- Tejas SDH Bvtig - Hol.esДокумент9 страницTejas SDH Bvtig - Hol.esShine JosephОценок пока нет
- Optical Transport NetworkДокумент28 страницOptical Transport NetworkshawnОценок пока нет
- Basic Microwave PropagationДокумент35 страницBasic Microwave PropagationOmar AyoubОценок пока нет
- SDH Principle PDFДокумент51 страницаSDH Principle PDFSharka SanaullahОценок пока нет
- Huawei - DWDM Basic OTN Product IntroДокумент89 страницHuawei - DWDM Basic OTN Product Intromartin100% (10)
- Huawei DWDM SDHДокумент31 страницаHuawei DWDM SDHKevin SalvatierraОценок пока нет
- T Rec G.654 201210 I!!pdf e PDFДокумент22 страницыT Rec G.654 201210 I!!pdf e PDFKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Quick Start Guide: 300 Series Managed SwitchesДокумент16 страницQuick Start Guide: 300 Series Managed SwitchesVinícius AraújoОценок пока нет
- Accessories 12 Dbi Omni Antenna: High Power Wi-Fi With Indoor/Outdoor Omni AntennaДокумент2 страницыAccessories 12 Dbi Omni Antenna: High Power Wi-Fi With Indoor/Outdoor Omni AntennaKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Arindam Das-20080706 - 1Документ4 страницыArindam Das-20080706 - 1Kavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Firepro Router Tech Support PDFДокумент14 страницFirepro Router Tech Support PDFRaj50% (2)
- Chapter 3-Bit and Byte InterleavingДокумент2 страницыChapter 3-Bit and Byte InterleavingKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Fiberoptic 101Документ38 страницFiberoptic 101Manisha KumariОценок пока нет
- DWDM TutorialДокумент14 страницDWDM TutorialRohit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Networking Essentials PDFДокумент16 страницNetworking Essentials PDFfatospeci100% (5)
- Application Form of Physically Handicapped Persons For Issue of Identify CertificateДокумент1 страницаApplication Form of Physically Handicapped Persons For Issue of Identify CertificateKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- STM 1 ConfigurationДокумент11 страницSTM 1 Configurationrohit0072260% (5)
- Guidelines on Probation ManagementДокумент15 страницGuidelines on Probation ManagementAshutosh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Application Form of Physically Handicapped Persons For Issue of Identify CertificateДокумент1 страницаApplication Form of Physically Handicapped Persons For Issue of Identify CertificateKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Arindam Das-20080706 - 1Документ4 страницыArindam Das-20080706 - 1Kavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- NPS Pension CalculatorДокумент6 страницNPS Pension CalculatorKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- OFC Inspection Report IAA-PEP Drum LossДокумент1 страницаOFC Inspection Report IAA-PEP Drum LossKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Application Form of Physically Handicapped Persons For Issue of Identify CertificateДокумент1 страницаApplication Form of Physically Handicapped Persons For Issue of Identify CertificateKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- SDH Pocket GuideДокумент74 страницыSDH Pocket GuideTanzim TajОценок пока нет
- User Guide To Fiber OpticsДокумент11 страницUser Guide To Fiber Opticsmisr1972Оценок пока нет
- XDM 100 Product NoteДокумент8 страницXDM 100 Product NoteKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- TJ1500-R3 System GuideДокумент50 страницTJ1500-R3 System GuideRajesh Sharma100% (3)
- 07 - 6345-6350 EM Commissioning A NEДокумент21 страница07 - 6345-6350 EM Commissioning A NEKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- SDH PG Opt TM Ae 1005 PDFДокумент0 страницSDH PG Opt TM Ae 1005 PDFokisoundОценок пока нет
- Ha NetworksДокумент6 страницHa Networksgule mariamОценок пока нет
- VatДокумент3 страницыVatKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Surge ProtectionДокумент3 страницыSurge ProtectionKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Chapter Xiii OfcДокумент60 страницChapter Xiii OfcKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Reliability and MTBF OverviewДокумент10 страницReliability and MTBF OverviewA. Lukas Priya UtamaОценок пока нет
- SDH PDH MappingДокумент3 страницыSDH PDH MappingKavish JaggiОценок пока нет
- Configuring InterVLAN Routing in AOS - Quick Configuration Guide Netvanta AdtranДокумент11 страницConfiguring InterVLAN Routing in AOS - Quick Configuration Guide Netvanta AdtranJonОценок пока нет
- Virtual Trunking ProtocolДокумент13 страницVirtual Trunking Protocolhassan007Оценок пока нет
- Vsphere Distributed Switch Best PracticesДокумент30 страницVsphere Distributed Switch Best PracticesnewbeoneОценок пока нет
- Huawei NetEngine AR600 Series Enterprise Routers DatasheetДокумент13 страницHuawei NetEngine AR600 Series Enterprise Routers DatasheetpepitolavoeОценок пока нет
- Brkarc 3190Документ81 страницаBrkarc 3190ahmedОценок пока нет
- Windows 7 TweaksДокумент17 страницWindows 7 TweaksochaerryОценок пока нет
- Apollo OPT X: Extending Otn/Packet Switching To The Network EdgeДокумент2 страницыApollo OPT X: Extending Otn/Packet Switching To The Network Edgerobert adamsОценок пока нет
- Solar Data Logger ManualДокумент4 страницыSolar Data Logger ManualMihirОценок пока нет
- SS7 Whitepaper Ver 1.41Документ19 страницSS7 Whitepaper Ver 1.41Anonymous Ie0oEXP2eОценок пока нет
- Ucm62xx UsermanualДокумент391 страницаUcm62xx Usermanualkevinesco_barca9Оценок пока нет
- 350 401 New Qfrom June 23rd, 2020 To 20th Jan 2021 Digitaltut HasДокумент102 страницы350 401 New Qfrom June 23rd, 2020 To 20th Jan 2021 Digitaltut HasSudhanshuОценок пока нет
- 20345-1 Administering Microsoft Exchange Server 2016: Length Days: 5Документ4 страницы20345-1 Administering Microsoft Exchange Server 2016: Length Days: 5debut finОценок пока нет
- Arm Users Manual Ver 84Документ180 страницArm Users Manual Ver 84Test NetcomОценок пока нет
- WimaxДокумент18 страницWimaxshrishti.bhatiaОценок пока нет
- Forticonverter v6.2.1 Release NotesДокумент16 страницForticonverter v6.2.1 Release Noteslee zwagerОценок пока нет
- Cisco Me3600x - 3800x - Vho - 3600x - 3600xДокумент5 страницCisco Me3600x - 3800x - Vho - 3600x - 3600xLarry TembuОценок пока нет
- ONTAP9 Fundamentals - ONTAP Cluster FundamentalsДокумент51 страницаONTAP9 Fundamentals - ONTAP Cluster FundamentalsFelipe Nieto Concha100% (1)
- Anybus X Gateway DatasheetДокумент3 страницыAnybus X Gateway Datasheetfabroto88Оценок пока нет
- M MGW Introduction R3Документ64 страницыM MGW Introduction R3Araina GoelОценок пока нет
- Computer Network - CS610 Power Point Slides Lecture 27Документ30 страницComputer Network - CS610 Power Point Slides Lecture 27Ibrahim ChoudaryОценок пока нет
- 3.5.5 Packet Tracer - Investigate The TCP-IP and OSI Models in ActionДокумент4 страницы3.5.5 Packet Tracer - Investigate The TCP-IP and OSI Models in ActionEthan WilsonОценок пока нет
- BIG-IP Advanced Firewall Manager Operations Guide (PDFDrive)Документ122 страницыBIG-IP Advanced Firewall Manager Operations Guide (PDFDrive)mohammadОценок пока нет
- Connecting To Container Databases (CDB) and Pluggable Databases (PDB)Документ4 страницыConnecting To Container Databases (CDB) and Pluggable Databases (PDB)Ahmed NagyОценок пока нет
- MTCTCE English PDFДокумент110 страницMTCTCE English PDFHani BahwalОценок пока нет
- TCP/IP Protocols ExplainedДокумент58 страницTCP/IP Protocols ExplainedJezreel ReyesОценок пока нет
- Servicing The Lenovo RackSwitich G8272 PDFДокумент37 страницServicing The Lenovo RackSwitich G8272 PDFAlejandro Suaza CampoОценок пока нет
- FP H800 - FT48924EN02GLA0 - Overview PDFДокумент42 страницыFP H800 - FT48924EN02GLA0 - Overview PDFfidarehmanОценок пока нет
- EasyIO Wi-Fi Controller Offers Wireless BMS ExtensionДокумент2 страницыEasyIO Wi-Fi Controller Offers Wireless BMS ExtensionPrestoneKОценок пока нет
- 1 Network ComponentsДокумент4 страницы1 Network Componentsapi-326862497Оценок пока нет
- Yeastar TA410&TA810 User Manual enДокумент55 страницYeastar TA410&TA810 User Manual enNestor Daniel MorniroliОценок пока нет
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksОт EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoОт EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptОт EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksОт EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksОценок пока нет
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensОт EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensОценок пока нет