Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
GSM and Umts Networks
Загружено:
Farhan JavaidОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GSM and Umts Networks
Загружено:
Farhan JavaidАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GSM AND UMTS
NETWORKS
EVOLUTION OF MOBILE
TECHNOLOGY
PRESENTED BY: ADEEL
IQBAL
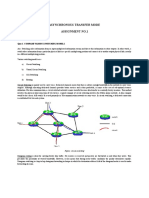
THE GSM NETWORK
2G 2.5G.
WHAT IS GSM?
GSM is an abbreviation of Global System for Mobile
communication, originally it is known as Group
Special Mobile. It is mobile telephony system that
sets the standards on how mobile
telecommunications work. It encompasses
everything in reference to mobile communications.
WHAT IS GSM?
GSM is a TDMA based wireless network technology
developed in Europe that is used throughout most of
the world. GSM phones make use of a SIM card to
identify the user's account. The use of the SIM card
allows GSM network users to quickly move their
phone number from one GSM phone to another by
simply moving the SIM card. Currently GSM
networks operate on the 850MHz, 900MHz,
1800MHz, and 1900MHz frequency bands.
WHAT IS GSM?
GSM is a second generation (2G)
telecommunications technology which is launched
early in the 90s. Eventually, it increased its speed
and added more functionality like General Packet
Radio System (GPRS) to the system which
enhanced it to 2.5G status. 2.5G has data rates up
to about 144kbit/s.
THE UMTS NETWORK
3G, 3.5G onwards
WHAT IS UMTS?
UMTS is the third generation (3G) of mobile
telecommunications technology. It is the latest
commercially available technology that mobile
phones, PDAs, and smart phones are using today.
With this development, internet access (email and
web browsing), video calling and messaging, and
text messaging (SMS) are now possible along with
traditional phone tasks.
WHAT IS UMTS?
People can now do the activities they normally do
with an internet-connected home computer while on
the trot. Imagine yourself traveling the world and still
able to email, video conference, and watch
streaming videos using your smartphone. Currently,
it can offer transfer speeds of about 3.6 Mbits per
second and even more, which can make data
transfer seamless and downloads relatively fast.
WHY UMTS?
Unlike GSM, UMTS is mainly based on CDMA
(Code Division Multiple Access) scheme and now
combines it with TDMA. However, UMTS is still new
as there are only a few areas and networks that
support the technology. Even with countries that
support it may have set different spectrum, thus
interoperability does not work fully when moving
from one nation to another nation with drastically
different spectrum.
ONE MAIN ADVANTAGE OF
GSM
There are also problems regarding the compatibility
between UMTS and GSM, which frequently led to
connections being dropped. But this is being
remedied by UMTS/GSM dual-mode devices. With
that feature, UMTS phones that go out of UMTS
network boundaries will be transferred to GSM
coverage. Transfer of network can happen mid-call.
SUMMARY
1. UMTS has faster data transfer rates than GSM.
2. GSM is 2G and 2.5G while UMTS is already 3G.
3. GSM is a rather old technology while UMTS is newer.
4. GSM is typically based on TDMA while UMTS is mainly
CDMA-based.
5. Currently, GSM is still the most widely used technology
today while UMTS is still in its infancy, slowly creeping
forward.
THANK YOU
Вам также может понравиться
- Chapter 1 Networking UnsecuredДокумент58 страницChapter 1 Networking UnsecuredAnandganesh PolisettiОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Keynote Sigos Product Guide 2013 PDFДокумент68 страницKeynote Sigos Product Guide 2013 PDFSantha KumarОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Telecom IndustryДокумент126 страницTelecom Industrymmrksamy100% (1)
- Digital Bangladesh & ICTДокумент49 страницDigital Bangladesh & ICTRaihan PervezОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- 1 WCDMA Principle.Документ40 страниц1 WCDMA Principle.biju_teleОценок пока нет
- Vendor Presentation-3 (Hardware Product Portfolio) - 0801Документ61 страницаVendor Presentation-3 (Hardware Product Portfolio) - 0801btsupersuper100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- ITU-Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2006Документ240 страницITU-Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2006Abu Ahsan SiddiqueОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- CV Mohsin RF LatestДокумент5 страницCV Mohsin RF LatestHakeem Mohsin SaifОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Capacity Case Study - ShortenedДокумент11 страницCapacity Case Study - Shortenedcyo3fff100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- 4G LTE TO 3G HANDOVER FAILURE WITH CAUSE CODE RANAP (SGSN Issue Huawei)Документ5 страниц4G LTE TO 3G HANDOVER FAILURE WITH CAUSE CODE RANAP (SGSN Issue Huawei)budiОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Balance Score Card On Telecomm SectorДокумент15 страницBalance Score Card On Telecomm Sectortushartutu67% (6)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Mobile Computing NotesДокумент36 страницMobile Computing NotesMINCY SABU50% (2)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Term Paper On CDMAДокумент5 страницTerm Paper On CDMATaufeeq Malik100% (1)
- Flexem'S User'S Manual of The Fbox DevicesДокумент143 страницыFlexem'S User'S Manual of The Fbox Devicesbassit82Оценок пока нет
- DHI-MXVR4104: 4 Channels H.265 1 HDD Mobile Video RecorderДокумент2 страницыDHI-MXVR4104: 4 Channels H.265 1 HDD Mobile Video RecorderJuan Pablo Cisternas FortuneОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- 3G V/s Wi-Fi: Seminar Report ONДокумент20 страниц3G V/s Wi-Fi: Seminar Report ONPriyanka TalwarОценок пока нет
- 3d InternetДокумент25 страниц3d Internetphani98Оценок пока нет
- Introducing 5G Networks - Characteristics and UsagesДокумент8 страницIntroducing 5G Networks - Characteristics and Usagesashishsinghchouhan100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode Assignment No.1: Ques 1. Compare Various Switching ModelsДокумент6 страницAsynchronous Transfer Mode Assignment No.1: Ques 1. Compare Various Switching Modelsjkj2010Оценок пока нет
- What Are The Differences Between 2G, 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G Networks?Документ4 страницыWhat Are The Differences Between 2G, 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G Networks?savsen6720Оценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- IoT NotesДокумент97 страницIoT Notestrupti.kodinariya9810Оценок пока нет
- 18 08 29Документ22 страницы18 08 29Florian MuellerОценок пока нет
- Advances in Security and Payment Methods For Mobile CommerceДокумент364 страницыAdvances in Security and Payment Methods For Mobile CommerceDyan Lilo100% (1)
- Airtel Mumbai 3G Tariff PlansДокумент1 страницаAirtel Mumbai 3G Tariff PlanstechwhackОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Guowang Miao - Jens Zander - Ki Won Sung - Slimane Ben Slimane - Fundamentals of Mobile Data Networks-Cambridge University Press (2016)Документ323 страницыGuowang Miao - Jens Zander - Ki Won Sung - Slimane Ben Slimane - Fundamentals of Mobile Data Networks-Cambridge University Press (2016)belial belial100% (1)
- Business Strategy Case Study - DoCoMoДокумент18 страницBusiness Strategy Case Study - DoCoMoRobinHood TiwariОценок пока нет
- Encardio Combined ManualsДокумент785 страницEncardio Combined ManualsMostafa AdelОценок пока нет
- YM19 Yimiyanguang (2400words) Without MarkДокумент12 страницYM19 Yimiyanguang (2400words) Without Markvincent MburuОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- (Potraz) : Postal and Telecommunications Regulatory Authority of ZimbabweДокумент25 страниц(Potraz) : Postal and Telecommunications Regulatory Authority of ZimbabweJoseph MutitiОценок пока нет
- Presentation About 3G, 4G, Next Generation Mobile TechnologyДокумент24 страницыPresentation About 3G, 4G, Next Generation Mobile Technologyshadman88% (8)