Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Nursing Care Plan For Client With Substance Related Disorder
Загружено:
Kireina Amanda Nuriandarie0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
39 просмотров57 страницThis document provides information on developing a nursing care plan for clients with substance use disorders. It discusses the biopsychosocial contexts of substance use, including genetic and neurobiological factors, psychological reasons for use such as coping with stress or low self-esteem, and sociocultural influences like peer pressure. It also defines key terms, outlines assessment approaches, and lists common signs and symptoms to examine for during the physical assessment of a client with a substance use disorder.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
2012-Nursing Management of Client WSubstance Related
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document provides information on developing a nursing care plan for clients with substance use disorders. It discusses the biopsychosocial contexts of substance use, including genetic and neurobiological factors, psychological reasons for use such as coping with stress or low self-esteem, and sociocultural influences like peer pressure. It also defines key terms, outlines assessment approaches, and lists common signs and symptoms to examine for during the physical assessment of a client with a substance use disorder.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
39 просмотров57 страницNursing Care Plan For Client With Substance Related Disorder
Загружено:
Kireina Amanda NuriandarieThis document provides information on developing a nursing care plan for clients with substance use disorders. It discusses the biopsychosocial contexts of substance use, including genetic and neurobiological factors, psychological reasons for use such as coping with stress or low self-esteem, and sociocultural influences like peer pressure. It also defines key terms, outlines assessment approaches, and lists common signs and symptoms to examine for during the physical assessment of a client with a substance use disorder.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 57
Nursing Care Plan for
Client with Substance
Related Disorder
Dian Wahyuni
Mental Health Nursing II
Binawan Institute of Health Science
Objectives
Discuss the Biologic, Psychologic, and
Sociocultural Context of Care
Understand the symptoms patterns
Develop nursing care plan for clients with
substance use
Understand treatment modalities
Biologic Context
Genetic predisposition
Neurobiologic origin
Low level of MAOIs
Dehydrogenase deficit
Dopamine excess/craving
Comorbid physical/mental diagnosis
Psychological Context
Depressed mood
Unmet dependency meet
Impulsive style
Inability to contend with life stress
Unmet needs of power/attention
Low self-concept/self-esteem
Inability to tolerate failure
Sociocultural Context
Peer influence/pressure
Detrimental environment
Deteriorating neighborhood
Alienating issues
Illegal behaviors
Drug trafficking
Dysfunctional family system
Terms
Substance Dependence / addiction
Continued to use despite substance-related problems, as
evidence by physiologic, cognitive, and behavioral symptoms.
Tolerance: The need for greater amount of the substance to
produced the desire effect or when the same amount of the
substance is used overtime the effect is decreased
Withdrawal: The physiologic, cognitive, and behavioral
symptoms (specific to the substance) that occur when heavy use
of the substance for over long period is stopped and the
decrease level of the substance in blood/tissues.
Compulsive use pattern: the use pattern is longer than intended
and larger is needed, the individuals want to stop the habit but
always fail, more time devoted to gain, use and recovering from
the drugs, the use of substance continues despite the physical,
legal, occupational problems.
Substance Abuse
Failure to complete obligations in home, work or school
Continued use of substance despite danger
Legal problems related to substance use
Recurrent social or interpersonal problems
Substance intoxication
A reversible substance-specific syndrome that occurs following
intake or exposure to the substance
Comorbidity / Dual Diagnosis
Substance-related disorders that occur in association with other
Axis I mental disorders in DSM-IV-TR
Other coexisting mental disorders with substance disorders are:
anxiety disorders, mood disorders, major depression, bipolar
disorders, personality disorders.
Terms
Classification (DSM-IV TR)
Substance related disorder
Substance Use Disorder Substance Induced Disorder
Substance Substance
Dependence Abuse
Substance intoxication
Substance withdrawal
Substance induced delirium
Substance induced persistent dementia
Substance induced Persisting amnestic
disorder
Substance induced Psychotic disorder
Substance induced Mod Disorder
Substance induced Anxiety Disorder
Substance induced Sexual Dysfunction
Substance induced Sleep Disorder
Klasifikasi Zat
1. Depresan SSP
Alkohol
BArbiturat
Sedatif/ Hipnotik Non
Barbiturat
Ansiolitik
Inhalan
Opioid (analgesik narkotik )
Sintetis
2.Stimulan SSP
Amfetamin
Stimulan Non Amfetamin
Nikotin
Kafein
3. Halusinogen
Fenisiklidin (PCP)
Psilosisbin (dalam jamur psilocybe)
Meskalin (dalam kaktus peyote)
Asam lisergis
4. Kanabioid
Kanabis (Mariyuana)
Hasish (hash)
Dronabinol (Marionol)
Depresan SSP
Efek muncul karena neurotransmitor inhibitor
distimulasi (GABA) atau mengubah
neurotransmiter eksitasi (dopamin dan
epineprin)
Penggunaan kronis dapat mengurangi produksi
dan suplai neurotransmitor inhibitor
Neuro eksitasi terjadi bila konsumsi dihentikan
tiba-tiba. Stimulasi Norepineprin dan dopamin
yang terjadi setelah penghentian menyebabkan
gejala putus zat.
Stimulan SSP
Meningkatkan pelepasan norepineprin dari saraf
prasinaps dan mencegah pengambilannya
kembali
Blokade prasinaps menyebabkan deplesi
katekolamin dan menyebabkan peningkatan
kebutuhan akan zat yang menstimulasi.
Bila dihentikan secara tiba-tiba, neurotransmiter
eksitasi akan sangat deplesi dan menyebabkan
depresi serta disforia yang parah
Opioid
Adalah depresan SSP dan analgesik yang
sangat kuat
Menghambat pelepasan zat p dan
menempel pada reseptor endorfin untuk
meredakan nyeri
Bila dihentikan mendadak, akan terjadi
pelepasan norepineprin yang sangat
banyak
Halusionogen
Menstimulasi reseptor prasinaps dan
menyebabkan gangguan penglihatan dan
persepsi
PCP melepaskan dopamin, norepineprin,
serotonin dan menghambat GABA
Penghentian mendadak menyebabkan
ketidakseimbangan neurotransmiter dan
menyebabkan kecemasan, insomnia dan
panik
Kanabioid
Mirip dengan halusinogen dan depresan
SSP
Menyebabkan sulit konsentrasi, euforia,
hilangnya memori jangka pendek
Penghentian yang tiba-tiba membuat efek
stimulasi berlebihan karena sifat depresan
dihentika
Inhalan
Bekerja sebagai depresan SSP, dapat
menembus sawar darah otak
Dosisnya tidak dapat dikendalikan, sangat
berbahaya
Bila dihentikan tiba-tiba, tidak
menimbulkan gejala
Assessment
Multiaxial Assessment (DSM IV TR)
Axis I: Clinical dysfunction
Axis II: Personality Disorders and Mental
Retardation
Axis III: Psychosocial and Environmental
Problems
Axis IV: Global Assessment of Functioning
(GAF)
Assessment
Autoanamnesis (client) and aloanamnesis
(parents, caregiver or any significant person)
Physical Assessment
Psychiatric Assessment
Laboratory Assessment
Fluoroscopy Assessment
Electrophysiology assessment
Psychology test
Social evaluation
Autoanamnesis
Firstly build trust relationship with client then ask
client related to substance use
If trust relationship has not been established:
Identify areas where client needs professional help
(problem at school, problems with parents, problems
in client working place, etc)
How long the problem has existed?
What efforts have been done?
Demographic data
Ask client related to what, when, why and how the client use
the substance.
Ask client related to medical complication related to drug use
Ask client related to other complication such as: insomnia,
lack of concentration, agitated, lost of appetite, etc.
Ask client related to mental disturbance: hallucination,
delusion, panic, depression
Why the client want to stop using right now? Why now?
How client use his/her leisure time?
Are there any problems with client psychosocial relationship?
How is client education, marriage and work history?
Is client have been admitted to hospital or rehabilitation
center?
Aloanamnesis
Client growth and development history
Educational, marriage, and work history
Typical behavior of client before the substance
consumption
What are behaviors changes occurred?
Are tools used for substance use found in
clients room? Or family found the substance in
clients property?
Was family members often lost their valuables?
Physical examination
(not only limited to these signs and symptoms)
Examination Sign and Symptoms Details
Consciousness
Somnolent
Stupor-coma
Delirium
Opioid intoxication, sedatif-hipnotic, alcohol,
inhalant. Amphetamines and cocaine
withdrawal.
Any substance overdose
Sedatif hipnotik or alcohol withdrawl,
amphetamine or PCP intoxication
Pulse
Rapid
Slow
LSD or amphetamine intoxication,
opioid withdrawal
Opioid; sedatif-hipnotik; alcohol;
inhalant intoxication
Body temperature
High
Low
LSD intoxication; amphetamine
intoxication. Alcohol, sedatif-hipnotic,
opioid withdrawal, infection disease
Opioid intoxication
Examination Sign and Symptoms Details
Respiratory rate
Slow
Fast and shallow
Sedatif-hipnotic, alcohol, or
opioid use
High dose sedatif hipnotic
intoxication
Blood pressure
High
Low
Amphetamin, cocaine, LSD
and Canabis use
Alcohol withdrawl. Opioid
withdrwl (BP usually high at
the beginning)
Examination Sign and Symptoms Details
Eye
Palpebra is half closed
Conjunctiva :
Red
Pale
Sclera icteric
Pupil:
Pin point
Dilatation and reactive
Dilatation and nonreactive
Eye movement:
Lateral nistagmus
Vertical or horizontal
nistagmus
Lacrimation
Diplopia
Increase blinking reflect
Opioid intoxication
Canabis intoxication
Long consumption of
amphetamine and cocain
Substance use induced hepatic
disease
Opioid intoxication
Amphetamine and LSD
intoxication
Anticolinergic drugs
Sedatif-hipnotic intoxication,
canabis intoxication
PCP intoxication
Opioid withdrawl
Sedatif-hipnotik intoxication
Sedatif-hipnotik withdrawl
Examination Sign and Symptoms Details
Nose Rinore (wet)
Ulcus or Nasal Septum
perforation
Opioid withdrawl
Inhalant cocain use
Mouth Bad breath/ dry chemical
substance
Frequent yawning
Inhalant use
Amphetamine, cocaine or hallucinogen
intoxication, opioid withdrawl
Lung Bronchitis
Tuberculosis
Fibrosis
Cancer
Tobaco and canabis use
Heavy psychoactive drug user
Psychoactive drug user (parenteral
use)
Tobacco smoker
Examination Sign and Symptoms Details
Heart
Tachycardia
Arrhythmia
Amphetamin, cocain,
hallucinogen intoxication;
opioid, sedative-hypnotic,
alcohol withdrawal
Inhalant intoxication;
sedative-hipnotic withdrawl
Stomach
Gastritis
Alcohol use
Liver
Cirrhosis hepatic
Fatty liver
B/C hepatitis
Heavy alcohol use
Overdose alcohol use
Parenteral/intravena opioid
use
Examination Sign and Symptoms Details
Stomach wall
Spasme Opioid or sedatif-hipnotic
withdrawl
Skin
Blushing
Sianosis
Over perspiration
Gooseflesh
Pruritus
Dry
Needle track
Popping scar
Paronikia, tinea, skabies, pedikulosis
Alcohol, amphetamine,
hallucinogen, and opioid use
Opioid, amphetamine,
cocaine and hallucinogen use
Amphetamine intoxication,
cocaine and opioid
withdrawal
Opioid withdrawl
Opioid use
Colinergic drug use
Intravena route of opioid,
amphetamine or barbiturate
Swallowing injection site,
usually because of opioid use
Psychotic user who doesnt
pay attention in their self care
Examination Sign and Symptoms Details
Nervi Craniales Diplopia, dismetria, dan disartri Sedatif-hipnotik, alcohol, opioid
and inhalant intoxication.
Motor nerve
Ataxia
Light tremor
Major tremor
Sedatif-hipnotik, alcohol,
inhalant, opioid intoxication.
Amfetamin, cocain, hallucinogen,
opioid withdrawl.
Sedatif-hipnotic withdrawl
Reflects Hyperreflexion
Hypo-/a-reflection
Amphetamin, cocaine, LSD use
Sedative hypnotic, alcohol or
inhalant heavy intoxication
Psychiatric Assessment
Comorbidity/dual diagnosis
Anxiety, depression, dissocial personality disorders, hyperactivity are some mental disorders
that could lead to substance abuse
Substance abuse lead to several mental disorders: panic (cannabis user), psychosis (
amphetamine or cocaine users), dementia (alcohol), depression (amphetamine and cocaine
withdrawal) delirium (alcohol or sedative-hypnotic withdrawal)
Emotional disorders:
Agitative: amphetamine, cocaine, cafeine, PCP intoxication
Aggressive: amphetamine, cocaine, PCP intoxication
Depression: Amphetamine, cocain, segdative-hypnotic, alcohol
withdrawal
Disforia/: cocaine or opioid beginners
Euforia: All psychoactive drugs intoxication
Nervous: Amphetamine, cocaine, hallucinogen, cafeine, PCP, cannabis
use. Opioid, sedative hipnotic, alcohol and nicotiine withdrawal
Impulsive: PCP intoxication
Irritabel: Alcohol intoxication, sedatif-hypnotic, inhalant intoxication.
Alcohol, sedative hypnotic, nicotine withdrawal
Labil: Sedative-hypnotic, alcohol, PCP intoxication.
Communication disorders:
Lots of talking: alcohol intoxication
Thought disorders:
Delusions: Amphetamine, cocaine, hallucinogen, cannabis intoxication;
alcohol withdrawal
Depersonalization: Hallucinogen, PCP intoxication
Perception disorders:
Hallucination: amphetamine, hallucinogen intoxication; alcohol
withdrawal
Illusion: hallucinogen intoxication
Sinestesi: Hallucinogen intoxication
Memory and Attention disturbance
Amnesia: alcohol, sedative-hypnotic withdrawal
Dementia: long time use of alcohol
Tingkah laku klien pengguna zat sedatif hipnotik
a. Menurunnya sifat menahan diri
b. Jalan tidak stabil, koordinasi motorik kurang
c. Bicara cadel, bertele-tele
d. Sering datang ke dokter untuk minta resep
e. Kurang perhatian
f. Sangat gembira, berdiam, (depresi), dan kadang
bersikap bermusuhan
g. Gangguan dalam daya pertimbangan
h. Dalam keadaan yang over dosis, kesadaran menurun,
koma dan dapat menimbulkan kematian.
i. Meningkatkan rasa percaya diri
Tingkah laku klien pengguna ganja :
a. Kontrol didi menurun bahkan hilang
b. Menurunnya motivasi perubahan diri
c. Ephoria ringan
Tingkah laku klien pengguna alcohol :
a. Sikap bermusuhan
b. Kadang bersikap murung, berdiam
c. Kontrol diri menurun
d. Suara keras, bicara cadel,dan kacau
e. Agresi
f. Minum alcohol pagi hari atau tidak kenal waktu
g. Partisipasi di lingkungan social kurang
h. Daya pertimbangan menurun
i. Koordinasi motorik terganggu, akibat cenerung mendapat kecelakaan
j. Dalam keadaan over dosis, kesadaran menurun bahkan sampai koma.
Tingkah laku klien pengguna opioda :
a. Terkantuk-kantuk
b. Bicara cadel
c. Koordinasi motorik terganggu
d. Acuh terhadap lingkungan, kurang perhatian
e. Perilaku manipulatif, untuk mendapatkan zat adiktif
f. Kontrol diri kurang
Tingkah laku klien pengguna kokain :
a. Hiperaktif
b. Euphoria, agitasi, dan sampai agitasi
c. Iritabilitas
d. Halusinasi dan waham
e. Kewaspadaan yang berlebihan
f. Sangat tegang
g. Gelisah, insomnia
h. Tampak membesar besarkan sesuatu
i. Dalam keadaan over dosis: kejang, delirium, dan paranoid
Observasi perilaku pasien
Mekanisme pertahanan diri yang biasa digunakan:
denial dari masalah
proyeksi merupakan tingkah laku untuk melepaskan diri dari tanggung
jawab
Disosiasi merupakan proses dari penggunaan zat adiktif
Data khusus
jumlah dan kemurnian zat yang digunakan
Sering menggunakan
Metode penggunaan (dirokok, intravena, Oral)
Dosis terakhir digunakan
Cara memperoleh zat (dokter, mencuri, dll)
Dampak bila tidak menggunakan
Jika over dosis, berapa beratnya
Stressor dalam hidupnya
Sistem dukungan (keluarga, social, finansial)
tingkat harga diri klien, persepsi klien terhadap zat adiktif
Tingkah laku manipulatif
Tingkah laku klien pengguna opioda :
a. Terkantuk-kantuk
b. Bicara cadel
c. Koordinasi motorik terganggu
d. Acuh terhadap lingkungan, kurang perhatian
e. Perilaku manipulatif, untuk mendapatkan zat adiktif
f. Kontrol diri kurang
Tingkah laku klien pengguna kokain :
a. Hiperaktif
b. Euphoria, agitasi, dan sampai agitasi
c. Iritabilitas
d. Halusinasi dan waham
e. Kewaspadaan yang berlebihan
f. Sangat tegang
g. Gelisah, insomnia
h. Tampak membesar besarkan sesuatu
i. Dalam keadaan over dosis: kejang, delirium, dan paranoid
Observasi perilaku pasien
Mekanisme pertahanan diri yang biasa digunakan:
denial dari masalah
proyeksi merupakan tingkah laku untuk melepaskan diri dari tanggung
jawab
Disosiasi merupakan proses dari penggunaan zat adiktif
Data khusus
jumlah dan kemurnian zat yang digunakan
Sering menggunakan
Metode penggunaan (dirokok, intravena, Oral)
Dosis terakhir digunakan
Cara memperoleh zat (dokter, mencuri, dll)
Dampak bila tidak menggunakan
Jika over dosis, berapa beratnya
Stressor dalam hidupnya
Sistem dukungan (keluarga, social, finansial)
tingkat harga diri klien, persepsi klien terhadap zat adiktif
Tingkah laku manipulatif
The Treatment
Detoxification:
Medical treatment to overcome overdose
Opioid Withdrawal:
Abrupt withdrawal
Symptomatic treatment withdrawal
Gradual withdrawal
Non Opioid substitute (clonididne)
Rapid detoxification
Long Term Medical Management
Disulfiram (Antabuse alcohol)
Naltrexon (opioid antagonis)
Methadone maintenance program (for
heroin user)
Buprenorfin maintenance program (opioid
user)
Therapeutic Community
Same with Milieu therapy
The leader is an ex user
The professionals act as consultant or advisor
Four principles:
Democratization
Permissive behaviors
Communality
Reality confrontation
Phase I: orientation
Phase II: therapy (everyday therapy or seminars)
Phase III: Community relationship
Phase IV: TC in once a week
Graduation
Treatment modalities
Abstinence VS Controlled use
Behavioral, cognitive, Traditional psychotherapy
Self-help group
Alcoholic Anonymous (AA)
12 steps of AA
Al-Anon; Naranon; Cocanon
Narcotics Anonymous (NA)
Cocaine Anonymous CA)
1. Ancaman kehidupan
a. Gangguan keseimbangan cairan: mual, muntah berhubungan
dengan pemutusan zat opioda
b. Resiko terhadap amuk berhubungan dengan intoksikasi
sedatif hipnotik
c. Resiko cidera diri berhubungan dengan intoksikasi aklkohol,
sedatif, hipnotik
d. Panik berhubungan dengan putus zat alkohol
2. Intoksikasi
a. Cemas berhubungan dengan intoksikasi ganja
b. Kerusakan komunikasi verbal berhubungan dengan
intoksikasi sedatif hipnotik, alcohol, opioda
DIAGNOSA KEPERAWATAN
DIAGNOSA KEPERAWATAN
3. Withdrawl
a. Perubahan proses pikir: waham berhubungan dengan putus zat
alcohol, sedatif, hipnotik
b. Nyeri berhubungan dengan putus zat opioda, extasy
c. Perubahan nutrisi kurang dari kebutuhan berhubungan dengan
putus zat opioda
4. Pasca detoksikasi
a. Gangguan pemusatan perhatian berhubungan dengan dampak
penggunaan zat adiktif
b. Gangguan konsep diri : harga diri rendah berhubungan dengan
tidak mampu mengenal kualitas yang positif dari diri sendiri.
c. Resiko melarikan diri berhubungan dengan ketergantungan
tehadap zat adiktif
Resiko tinggi terhadap cedera: jatuh berhubungan dengan kesulitan
keseimbangan
Perubahan nutrisi: kurang dari kebutuhan tubuh berhubungan
dengan asupan makanan yang kurang
Gangguan pola tidur berhubungan dengan sensori sistem saraf
pusat
pola tidur berhubungan dengan hipersensitifitas
Kerusakan pertukaran gas: pola nafas tidak efektif berhubungan
dengan penurunan ekspansi paru.
Diagnosa keperawatan lain yang mungkin muncul
Nursing Diagnosis
Growth and development, altered
Infection, risk for
Injury, risk for
Nutrition, altered
Self-care deficit
Sensory/Perceptual Alteration
Sexual dysfunction
Sleep pattern disturbance
Knowledge deficit
Management therapeutic regimen, individuals or families: ineffective
Noncompliance
Anxiety
Communication, impaired verbal
Family process, altered
Social isolation
Self-esteem disturbance
Violence, risk for
Powerlessness
Spiritual distress
RENCANA KEPERAWATAN
1. Kondisi overdosis
Tujuan : Klien tidak mengalami ancaman kehidupan
Rencana tindakan:
- Oservasi tanda tanda vital, kesadaran pada 15 menit pada 3
jam pertama, 30 menit pada 3 jam kedua tiap 1 jam pada 24 jam
berikutnya
- Bekerja sama dengan dokter untuk pemberian obat
- Observasi keseimbangan cairan
- Menjaga keselamatan diri klien
- Menemani klien
- Fiksasi bila perlu
2. Kondisi intoksikasi
Tujuan: intoksikasi pada klien dapat diatasi, kecemasan
berkurang/hilang
Rencana tindakan:
a. Membentuk hubungan saling percaya
b. Mengkaji tingkat kecemasan klien
c. Bicaralah dengan bahasa yang sederhana, singkat mudah
dimengerti
d. Dengarkan klien berbicara
e. Sering gunakan komunikasi terapeutik
f. Hindari sikap yang menimbulkan rasa curiga, tepatilah janji, memberi
jawaban nyata, tidak berbisik di depan klien, bersikap tegas, hangat
dan bersahabat
RENCANA KEPERAWATAN
3. Kondisi withdrawl
a. Observasi tanda- tanda kejang
b. Berikan kompres hangat bila terdapat kejang pada perut
c. Memberikan perawatan pada klien waham, halusinasi: terutama
untuk menuunkan perasaa yang disebabkan masalah ini: takut,
curiga, cemas, gembira berlebihan, benarkan persepsi yang salah
d. Bekerja sama dengan dokter dalam memberikan obat anti nyeri
4. Kondisi detoksikasi
a. Melatih konsentrasi: mengadakan kelompok diskusi pagi
b. Memberikan konseling untuk merubah moral dan spiritual klien
selama ini yang menyimpang, ditujukan agar klien menjadi manusia
yang bertanggung jawab, sehat mental, rasa bersyukur, dan optimis
c. Mempersiapkan klien untuk kembali ke masyarakat, dengan bekerja
sama dengan pekerja social, psikolog.
RENCANA KEPERAWATAN
INTERVENSI KEPERAWATAN
Dx: Resiko tinggi terhadap cedera: jatuh berhubungan dengan kesulitan
keseimbangan
Kriteria hasil:
- mendemonstrasikan hilangnya efek-efek penarikan diri yang memburuk
- tidak mengalami cedera fisik
Intervensi:
Mandiri
1.Identifikasi tingkat gejala putus alkohol, misalnya tahap I diasosiasikan
dengan tanda/gejala hiperaktivitas (misalnya tremor, tidak dapat
beristirahat, mual/muntah, diaforesis, takhikardi, hipertensi); tahap II
dimanifestasikan dengan peningkatan hiperaktivitas ditambah dengan
halusinogen; tingkat III gejala meliputi DTs dan hiperaktifitas autonomik
yang berlebihan dengan kekacauan mental berat, ansietas, insomnia,
demam.
2.Pantau aktivitas kejang. Pertahankan ketepatan aliran udara. Berikan
keamanan lingkungan misalnya bantalan pada pagar tempat tidur.
3.Periksa refleks tenton dalam. Kaji cara berjalan, jika memungkinkan
4.Bantu dengan ambulasi dan aktivitas perawatan diri sesuai kebutuhan
Kolaborasi
5. Berikan cairan IV/PO dengan hati-hati sesuai petunjuk
6. Berikan obat-obat sesuai petunjuk: benzodiazepin, oksazepam,
fenobarbital, magnesium sulfat.
Rasional:
1. Pengenalan dan intervensi yang tepat dapat menghalangi terjadinya
gejala-gejala dan mempercepat kesembuhan. Selain itu perkembangan
gejala mengindikasikan perlunya perubahan pada terapi obat-obatan
yang lebih intensif untuk mencegah kematian.
2. Kejang grand mal paling umum terjadi dan dihubungkan dengan
penurunana kadar Mg, hipoglikemia, peningkatan alkohol darah atau
riwayat kejang.
3. Refleksi tertekan, hilang, atau hiperaktif. Nauropati perifer umum
terjadi terutama pada pasien neuropati
4. mencegah jatuh dengan cedera
5. mungkin dibutuhkan pada waktu ekuilibrium, terjadinya masalah
koordinasi tangan/mata.
6. Penggantian yang berhati-hati akan memperbaiki dehidrasi dan
meningkatkan pembersihan renal dari toksin sambil mengurangi resiko
kelebihan hidrasi.
PERAN PERAWAT
Perawat harus mengetahui masalah yang
berkaitan dengan penggunaan NAPZA agar
dapat memberikan perawatan kepada klien
secara efektif.
Perawat harus memahami perasaan seseorang
tentang alkohol sehingga perawat dapat bekerja
secara efektif. Perawat jiwa juga membantu
dalam mendampingi klien NAPZA dan keluarga
dalam melaksanakan terapi. Serta memberikan
pendidikan kesehatan agar klien bisa
berkomunikasi efektif dan berpersepsi positif
Laboratory Assessment
Urine analysis
Should be done before 48 hours after the
last use
Ineffective individual coping
Expected outcomes:
The patient will abstain from using all mood-altering chemicals
Short-term goals:
The patient will substitute healthy coping responses for
substance abusing behaviors
The patient will assume responsibility for behaviors
The patient will identify and use social support system
Intervention:
Build trust relationship with the patient
Help the patient to identify the substance abuse problem
Involve the patient in describing situations that lead to
substance-abusing behaviors
Consistently offer support and the expectation hat the patient
has the strength to overcome the problem
Intervention (Cont.)
Encourage the patient to participate in a treatment
program
Develop with the patient a written contract for behavioral
changes that is signed by the nurse and patient
Help the patient to identify and adopt healthier coping
responses.
Identify and assess social support systems that are
available to the patients
Provide support to significant others
Educate the patient and significant others about the
substance abuse problem and available resources
Refer the patient to appropriate resource and provide
support until the patient is involved in the program
Motivational approaches
(Stuart&Laraia, 2001, p.513)
Principles
Express emphaty trough reflective listening
Develop discrepancy between patients goal or values and their current
behaviors
Avoid arguments and direct confortation
Roll with resistance
Support self-efficacy
FRAMES approach
Feedback
Responsibility for change
Advice; nonjudgmental
Menus of self-directed change
Emphatic Counseling
Self-efficacy; optimistic empowerment
Decisional balance grid
The Treatment
Detoxification:
Medical treatment to overcome overdose
Opioid Withdrawal:
Abrupt withdrawal
Symptomatic treatment withdrawal
Gradual withdrawal
Non Opioid substitute (clonididne)
Rapid detoxification
Long Term Medical Management
Disulfiram (Antabuse alcohol)
Naltrexon (opioid antagonis)
Methadone maintenance program (for
heroin user)
Buprenorfin maintenance program (opioid
user)
Therapeutic Community
Same with Milieu therapy
The leader is an ex user
The professionals act as consultant or advisor
Four principles:
Democratization
Permissive behaviors
Communality
Reality confrontation
Phase I: orientation
Phase II: therapy (everyday therapy or seminars)
Phase III: Community relationship
Phase IV: TC in once a week
Graduation
Treatment modalities
Abstinence VS Controlled use
Behavioral, cognitive, Traditional psychotherapy
Self-help group
Alcoholic Anonymous (AA)
12 steps of AA
Al-Anon; Naranon; Cocanon
Narcotics Anonymous (NA)
Cocaine Anonymous CA)
Вам также может понравиться
- Sentence Starters-1Документ2 страницыSentence Starters-1api-172950733100% (1)
- Drugs and Substance AbuseДокумент68 страницDrugs and Substance AbuseIano IanoОценок пока нет
- Substance AbuseДокумент45 страницSubstance AbuseKimberly Anne SP Padilla100% (1)
- Substance Abuse PresentationДокумент50 страницSubstance Abuse PresentationGabrielle KattОценок пока нет
- The 9 Secrets of Your Matrix (Sample Numerology Reading)Документ17 страницThe 9 Secrets of Your Matrix (Sample Numerology Reading)NumberOneNumerology72% (18)
- 8 Key Competencies - For Youthpass in EVSДокумент1 страница8 Key Competencies - For Youthpass in EVSMoșneagu Beatrice100% (1)
- Developmental PsychologyДокумент6 страницDevelopmental PsychologyMuhammad Adeel0% (1)
- Substance AbuseДокумент70 страницSubstance AbuseAnonymous nz9rhH100% (1)
- Substance Related Disorders: Brian Smart, M.D. Harborview Medical CenterДокумент70 страницSubstance Related Disorders: Brian Smart, M.D. Harborview Medical CenterFahrika Luthfi Afiqoh100% (1)
- Substance Related DisordersДокумент29 страницSubstance Related DisordersAnonymous nz9rhHОценок пока нет
- Psychoactive Substance UseДокумент48 страницPsychoactive Substance UsesiputamaliaputriОценок пока нет
- Substance Abuse VidebeckДокумент48 страницSubstance Abuse VidebeckFatima Hyghia Himpon100% (1)
- Substance AbuseДокумент25 страницSubstance AbuseAadil AminОценок пока нет
- Substance AbuseДокумент34 страницыSubstance AbuseAbigael Patricia GutierrezОценок пока нет
- PSYC 2300 042523 Lecture SlidesДокумент19 страницPSYC 2300 042523 Lecture SlidesCristinaОценок пока нет
- Group 6 Problem 4Документ50 страницGroup 6 Problem 4DessyОценок пока нет
- Patient Seeking Medically Supervised WithdrawalДокумент3 страницыPatient Seeking Medically Supervised WithdrawalLauren EОценок пока нет
- Common Psychosocial Problem in Adolescence: - Substance Abuse - Juvenile Delinquency - Smoking and AlcoholismДокумент59 страницCommon Psychosocial Problem in Adolescence: - Substance Abuse - Juvenile Delinquency - Smoking and AlcoholismSamjhana GautamОценок пока нет
- SUBSTANCE DISORDER AND TREATMENT OPTIONSДокумент63 страницыSUBSTANCE DISORDER AND TREATMENT OPTIONSBagus Cahya WibawaОценок пока нет
- Substance AbuseДокумент19 страницSubstance AbuseVrushank RamОценок пока нет
- Related Disorders 2017 Handout KKKДокумент12 страницRelated Disorders 2017 Handout KKKFu Xiao ShanОценок пока нет
- Module 14: Understanding Substance Use DisordersДокумент5 страницModule 14: Understanding Substance Use DisordersLiz EvermoreОценок пока нет
- Substance Abuse and AddictionДокумент55 страницSubstance Abuse and Addictionnikolamatejic100% (1)
- Substance RelatedДокумент12 страницSubstance RelatedJoyce VillalesОценок пока нет
- Addiction Management: Anas Elshafei & Shailee Trivedi Internal Medicine Core Rotation August 9, 2010 To October 29, 2010Документ29 страницAddiction Management: Anas Elshafei & Shailee Trivedi Internal Medicine Core Rotation August 9, 2010 To October 29, 2010sgolbariОценок пока нет
- DRUG ABUSE: CAUSES, SIGNS AND TREATMENT OPTIONSДокумент27 страницDRUG ABUSE: CAUSES, SIGNS AND TREATMENT OPTIONSRahul SharmaОценок пока нет
- Disorders Related to Substance Use and Their TreatmentsДокумент41 страницаDisorders Related to Substance Use and Their TreatmentsRizki MaulanaОценок пока нет
- Gr. 9 - Types of Drugs Slide ShowДокумент43 страницыGr. 9 - Types of Drugs Slide ShowdhairyapbОценок пока нет
- Ethics Da2Документ5 страницEthics Da2hemaОценок пока нет
- HLSC 1F90 November 7Документ5 страницHLSC 1F90 November 7Michael TruongОценок пока нет
- Substance Use and Addiction DisordersДокумент4 страницыSubstance Use and Addiction DisorderskgjtertijОценок пока нет
- SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS: UNDERSTANDING ALCOHOL ABUSEДокумент60 страницSUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS: UNDERSTANDING ALCOHOL ABUSEAndika DamarnegaraОценок пока нет
- Drug Education: Prevention, Signs, Effects and RehabilitationДокумент37 страницDrug Education: Prevention, Signs, Effects and Rehabilitationjohn lesterОценок пока нет
- I. Objectives: GeneralДокумент36 страницI. Objectives: GeneralSharlaine CabanayanОценок пока нет
- Substance Disorder 2020Документ59 страницSubstance Disorder 2020dennyzpsОценок пока нет
- Finals Topic: Substance Related DisordersДокумент26 страницFinals Topic: Substance Related Disordersエニエルカム オレーバンОценок пока нет
- Substance AbuseДокумент10 страницSubstance AbuseAdriano SonnyОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Chapter 6 Mental HealthДокумент47 страницUnit 2 Chapter 6 Mental HealthedriansamaОценок пока нет
- Provisional Diagnosis: Differential DiagnosesДокумент7 страницProvisional Diagnosis: Differential Diagnoseshernandez2812Оценок пока нет
- Abuse You LoseДокумент16 страницAbuse You LoseJayla BeckwithОценок пока нет
- Drug Awareness Seminar: Police Community Relations LectureДокумент93 страницыDrug Awareness Seminar: Police Community Relations LectureQuelly100% (3)
- Drug EducationДокумент26 страницDrug EducationVincent EucaporОценок пока нет
- Adolscence Disorder: BY-Devraj ShindeДокумент43 страницыAdolscence Disorder: BY-Devraj ShindecharudevОценок пока нет
- Drug EducationДокумент50 страницDrug EducationrtuppilОценок пока нет
- Mechanisms of AddictionДокумент26 страницMechanisms of AddictionAmantle DutaОценок пока нет
- Drug Addiction SignsДокумент12 страницDrug Addiction SignsZohrahLiaqatОценок пока нет
- Drug-Addiction-Biology ProjectДокумент37 страницDrug-Addiction-Biology ProjectAhalya Bai SahooОценок пока нет
- Substance Abuse-Prevention StrategiesДокумент31 страницаSubstance Abuse-Prevention StrategiesWasim KakrooОценок пока нет
- Drugs, Drug Abuse and Related LawsДокумент47 страницDrugs, Drug Abuse and Related LawsMiyangОценок пока нет
- Biology Investigatory ProjectДокумент17 страницBiology Investigatory ProjectAnonymous CreationsОценок пока нет
- Army Public School: Drug AddictionДокумент17 страницArmy Public School: Drug AddictionLl PlurkОценок пока нет
- Alcohol and Drug AddictionДокумент19 страницAlcohol and Drug Addictionchuna ramОценок пока нет
- 2 - Substance Abuse - LAGДокумент65 страниц2 - Substance Abuse - LAGBritneyОценок пока нет
- Drugs - of - Abus1.docx Filename - UTF-8''Drugs of Abus1Документ7 страницDrugs - of - Abus1.docx Filename - UTF-8''Drugs of Abus1Arvy JohnОценок пока нет
- Common Signs and Symptoms of Drug Dependence and AddictionДокумент4 страницыCommon Signs and Symptoms of Drug Dependence and AddictionAbbygail WasilОценок пока нет
- Substance Related Disorder Powerpoint 1 1 1Документ72 страницыSubstance Related Disorder Powerpoint 1 1 1amir ARSHADОценок пока нет
- DRUG AND ALCOHOL ABUSE (AutoRecovered)Документ10 страницDRUG AND ALCOHOL ABUSE (AutoRecovered)betsyОценок пока нет
- MapehДокумент7 страницMapehTala GinezОценок пока нет
- Final FY Presentation1Документ45 страницFinal FY Presentation1SamОценок пока нет
- Review of the Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002 (RA 9165Документ7 страницReview of the Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002 (RA 9165Mauii TejidorОценок пока нет
- Addiction DisordersДокумент32 страницыAddiction Disordersgideon gideonОценок пока нет
- Addictive DisorderДокумент7 страницAddictive DisorderMaham SohailОценок пока нет
- Pendanaan Pelayanan Kesehatan: Sebuah Perspektif InternasionalДокумент24 страницыPendanaan Pelayanan Kesehatan: Sebuah Perspektif InternasionalKireina Amanda NuriandarieОценок пока нет
- Bing GrisДокумент1 страницаBing GrisKireina Amanda NuriandarieОценок пока нет
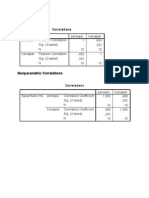
- Hasil Spearman RhoДокумент1 страницаHasil Spearman RhoKireina Amanda NuriandarieОценок пока нет
- Grafik Di Atas Menunjukan Informasi Tentang 3 PerbandingДокумент1 страницаGrafik Di Atas Menunjukan Informasi Tentang 3 PerbandingKireina Amanda NuriandarieОценок пока нет
- 2012 Kuliah XII Vitamin & Mineral DR ErwinДокумент35 страниц2012 Kuliah XII Vitamin & Mineral DR ErwinKireina Amanda NuriandarieОценок пока нет
- Faktor Dominan BRHBG DGN Kualitas TidurДокумент16 страницFaktor Dominan BRHBG DGN Kualitas TidurKireina Amanda NuriandarieОценок пока нет
- Bing GrisДокумент1 страницаBing GrisKireina Amanda NuriandarieОценок пока нет
- MRДокумент11 страницMRKireina Amanda NuriandarieОценок пока нет
- ADHD Non-Medication Treatments and Skills For Children and Teens 162 Tools, Techniques, Activities Handouts A Workbook For Clinicians and Parents by Burdick, Debra EДокумент359 страницADHD Non-Medication Treatments and Skills For Children and Teens 162 Tools, Techniques, Activities Handouts A Workbook For Clinicians and Parents by Burdick, Debra EBunmamp Tran Minh Phuc71% (7)
- 16 PPG WAJ3102 Topic 9 Writing Different Text TypesДокумент7 страниц16 PPG WAJ3102 Topic 9 Writing Different Text TypesNorfaiza Abu BakarОценок пока нет
- The Roles of Emotion in Consumer ResearchДокумент9 страницThe Roles of Emotion in Consumer Researchm_taufiqhidayat489Оценок пока нет
- Eat That FrogДокумент1 страницаEat That FroghalimОценок пока нет
- Sensorimotor Stage: Approx. Age Piaget: Cognitive DevelopmentДокумент2 страницыSensorimotor Stage: Approx. Age Piaget: Cognitive DevelopmentChristineAlaОценок пока нет
- Easter Exam Practice Word No MS.Документ9 страницEaster Exam Practice Word No MS.Lucy MilnerОценок пока нет
- How Positive Thinking Builds Your Skills, Speaking. AriatnaДокумент7 страницHow Positive Thinking Builds Your Skills, Speaking. AriatnaHutasoitAsjgnОценок пока нет
- Syllabus of INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATIONAL NEUROSCIENCEДокумент3 страницыSyllabus of INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATIONAL NEUROSCIENCEViraj Panara100% (1)
- Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook For Diagnosis and Treatment (4th Ed.)Документ4 страницыAttention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook For Diagnosis and Treatment (4th Ed.)JANICE JOSEPHINE TJONDROWIBOWO 11-S3Оценок пока нет
- Final Thesis Edited PartДокумент50 страницFinal Thesis Edited Partjessie james hijosОценок пока нет
- What is shopping addictionДокумент2 страницыWhat is shopping addictionClaire MusikasОценок пока нет
- Ia - Nature of Science ConpttДокумент27 страницIa - Nature of Science Conpttapi-423322065Оценок пока нет
- Borang Kritikan VideoДокумент2 страницыBorang Kritikan VideonuvedaaОценок пока нет
- Human Design Profile References Line 6Документ1 страницаHuman Design Profile References Line 6JRNОценок пока нет
- Study Master Life Skills Grade 5 Teacher S GuideДокумент415 страницStudy Master Life Skills Grade 5 Teacher S GuideNadine100% (1)
- Observations, Interviews, and Questionnaires (Book 2 en Ethnographer'S Toolkit) - Walnut Creek, Ca: Altamira PressДокумент5 страницObservations, Interviews, and Questionnaires (Book 2 en Ethnographer'S Toolkit) - Walnut Creek, Ca: Altamira PressAndrada DaianaОценок пока нет
- Internet Access Boosts Learning at Hibubullao National HighДокумент3 страницыInternet Access Boosts Learning at Hibubullao National HighJomarian MercadoОценок пока нет
- Midterm 1Документ10 страницMidterm 1JeliliОценок пока нет
- Essay Language AwarenessДокумент3 страницыEssay Language AwarenessElizabeth Qu O0% (1)
- Chap 1 TO 3 SOCIAL MEDIA For Final DefenseДокумент50 страницChap 1 TO 3 SOCIAL MEDIA For Final DefensePaul Christian Villaverde0% (1)
- The Birthday Presents - LiteracyДокумент3 страницыThe Birthday Presents - Literacyapi-270064896Оценок пока нет
- Edu 355 Edtpa Task 2 - Justin RiveraДокумент3 страницыEdu 355 Edtpa Task 2 - Justin Riveraapi-448989844Оценок пока нет
- Denis Lawton Model of The Curriculum ProcessДокумент1 страницаDenis Lawton Model of The Curriculum ProcessOwlyHeartfelia75% (4)
- Williams-Top 10 Principles-Reading (1986)Документ4 страницыWilliams-Top 10 Principles-Reading (1986)mariangoud100% (1)
- Weather Lesson First GradeДокумент6 страницWeather Lesson First Gradeapi-306779366Оценок пока нет
- INLP 30 Day Action Plan Ver 1.9Документ32 страницыINLP 30 Day Action Plan Ver 1.9Jennette CronkОценок пока нет