Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hemodialysis
Загружено:
Donita Meña LaroyaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Hemodialysis
Загружено:
Donita Meña LaroyaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AGRAVANTES, DENNISE
LAROYA, DONITA
REYES, VALLERIE
PRINCIPLES OF HEMODIALYSIS
11/21/11
Hemodialysis:
>Remove accumulated
metabolic waste
products
>Correct blood electrolyte
composition
>By means of exchange
between patients blood
& dialysate fluid across a
semi-permeable
membrane
11/21/11
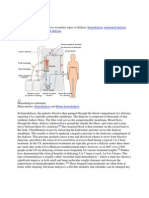
Dialyzer
>The dialyzer consists of
a bundle of semi-
permeable hollow fibers
(tubes) surrounded by a
hard plastic casing
(shell).
>The fibers are potted
into the casing with an
impermeable glue at
either end.
11/21/11
Dialyzer
>Fluid distribution caps
are then glued into place
>Blood can then flow into
one fluid distribution
cap, along the interior of
the fiber (tube-side) to
the exit distribution cap,
and thence out of the
dialyzer.
11/21/11
Dialyzer
>Dialysate, basically
distilled water with
an electrolyte and pH
composition similar
to that of blood
plasma, flows
counter-current to
the blood on the
outside of the fibers
(shell-side).
11/21/11
Dialysis CAN
Remove waste products
(e.g. urea, creatinine,
phosphorus, etc.)
Remove excess water
Correct high or imbalanced
levels of potassium, chloride,
sodium, etc. in the blood
Dialysis CANT
Automatically regulate
blood pressure
Produce hormones like
Erythropoetin (EPO)
Regulate normal calcium
levels
11/21/11
Electrolyte balance
>adding some electrolytes to
your dialysate solution
excess electrolytes are
removed as part of your
treatment
>The goal is to get the right
amount of the right
electrolytes.
11/21/11
Removing excess water
>ultrafiltration.
>the dialysis machine puts
pressure on the blood side of
the semi permeable membrane
in the dialyzer.
>This pressure forces salt and
water out of the blood and
into the dialysate.
>The used dialysate with the
blood wastes and excess fluid
is taken away and drained.
CURRENT TRENDS
New Dialysis Method Cuts
Mortality Risk
Published: Feb 16, 2013
By Michael Smith , North American
Correspondent, MedPage Today
HEMODIALYSIS ACCESS
11/21/11
ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA:
>An AV fistula requires advance
planning
>A surgeon creates an AV fistula by
connecting an artery directly to a
vein, frequently in the forearm.
>As a result, the vein grows larger and
stronger, making repeated needle
insertions for hemodialysis treatments
easier.
11/21/11
11/21/11
ARTERIOVENOUS GRAFT
The graft becomes an artificial vein that
can be used repeatedly for needle
placement and blood access during
hemodialysis.
often within 2 or 3 weeks.
Compared with properly formed fistulas,
grafts tend to have more problems with
clotting and infection and need
replacement sooner.
11/21/11
11/21/11
VENOUS CATHETER FOR TEMPORARY
ACCESS
>A catheter is a tube inserted into a vein
in your neck, chest, or leg near the
groin.
>It has two chambers to allow a two-way
flow of blood.
>Catheters are not ideal for permanent
access.
11/21/11
The most common area:
1. Internal jugular catheter
- inserted into the jugular vein on
the side of the neck.
2. Subclavian catheter -
placed into the subclavian vein
under the collar bone on the
chest.
3. Femoral catheter - placed in
the large vein in the leg near the
groin.
11/21/11
Вам также может понравиться
- Hydrocele, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHydrocele, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Hemodialysis 1Документ25 страницHemodialysis 1Jasmine KaurОценок пока нет
- HemodialysisДокумент22 страницыHemodialysisAlyssa Agravante100% (3)
- DIALYZERДокумент2 страницыDIALYZERassilamorОценок пока нет
- Dialysis DocumentДокумент3 страницыDialysis DocumentLucelle ArellanoОценок пока нет
- DialysisДокумент14 страницDialysisAndriKusumaОценок пока нет
- Peritoneal DialysisДокумент23 страницыPeritoneal Dialysismakyofrancis20Оценок пока нет
- Peritoneal DialysisДокумент723 страницыPeritoneal DialysisErvandy RangganataОценок пока нет
- Hemodialysis, Phosphorus and Calcium, Peritoneal DialysisДокумент29 страницHemodialysis, Phosphorus and Calcium, Peritoneal DialysisTrizha MaeОценок пока нет
- DialysisДокумент34 страницыDialysisAntonio Junior CastroОценок пока нет
- TypesДокумент3 страницыTypesProser Faith TabaculdeОценок пока нет
- Dialysis: Duaa Farooq Khan 11634 Amina Bashir 11283 Syed Uzair Iftikhar 13608 Qamar Ud Din 13071Документ11 страницDialysis: Duaa Farooq Khan 11634 Amina Bashir 11283 Syed Uzair Iftikhar 13608 Qamar Ud Din 13071Aimal SafdarОценок пока нет
- Hemodialysis: By: Liana Lee SenciónДокумент14 страницHemodialysis: By: Liana Lee SenciónKavidu KeshanОценок пока нет
- Dialysis Basics: DR - Ashutosh Ojha MD, DNB (Gen Med) PDCC-Nephro (Student) GMCH..GuwahatiДокумент36 страницDialysis Basics: DR - Ashutosh Ojha MD, DNB (Gen Med) PDCC-Nephro (Student) GMCH..GuwahatiManish Arya JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Myths of DialysisДокумент26 страницMyths of DialysisSijo Muthukad M100% (1)
- HemodialysisДокумент13 страницHemodialysisEthel Gretchen Casalla100% (2)
- Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Insertion - OriginalДокумент11 страницPeritoneal Dialysis Catheter Insertion - OriginalZul HazmiОценок пока нет
- Peritoneal DialysisДокумент5 страницPeritoneal DialysisLisette TupasОценок пока нет
- HemodialysisДокумент19 страницHemodialysisMox Aban100% (1)
- What You Should Know About Dialyzer Reuse: A Guide For Hemodialysis Patients and Their FamiliesДокумент8 страницWhat You Should Know About Dialyzer Reuse: A Guide For Hemodialysis Patients and Their FamiliesDewiyanti TodingОценок пока нет
- Hemodialysis and The Artificial KidneyДокумент48 страницHemodialysis and The Artificial KidneyRI NAОценок пока нет
- Dialysis: Notes MS Vol. 2 Krizza Myrrh Gomera Balcita, RNДокумент52 страницыDialysis: Notes MS Vol. 2 Krizza Myrrh Gomera Balcita, RNWhimsey CipresОценок пока нет
- Hemodialysis: NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Injury, Risk For (Loss of Vascular Access) Risk Factors May IncludeДокумент10 страницHemodialysis: NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Injury, Risk For (Loss of Vascular Access) Risk Factors May IncludeChevelle Valenciano-GaanОценок пока нет
- Renal Replacement TherapyДокумент50 страницRenal Replacement TherapyMalueth Angui100% (1)
- Cannulation Camp: Basic Needle Cannulation Training For Dialysis StaffДокумент7 страницCannulation Camp: Basic Needle Cannulation Training For Dialysis Staffcharlenetan18100% (3)
- Hemodialysis MachineДокумент15 страницHemodialysis MachineLuis Alberto Díaz OlmedoОценок пока нет
- Hemodialysis Training ProgramДокумент5 страницHemodialysis Training Programsakuraleeshaoran100% (1)
- Peritoneal DialysisДокумент5 страницPeritoneal DialysisJulienne Sanchez-SalazarОценок пока нет
- HD TaskДокумент3 страницыHD Taskenrique magpilyОценок пока нет
- B.Reprocessing of DialyzerДокумент4 страницыB.Reprocessing of DialyzerKyara Mara Gabrielle AnditОценок пока нет
- Core Curriculum For The Dialysis Nurse - Module 1Документ7 страницCore Curriculum For The Dialysis Nurse - Module 1green_archerОценок пока нет
- Catheter Care Guidelines (By ANZUS)Документ19 страницCatheter Care Guidelines (By ANZUS)cateterdoblejota100% (1)
- DACUM Competency Profile For Hemodialysis TechnicianДокумент5 страницDACUM Competency Profile For Hemodialysis Technicianmanishbabu100% (1)
- Dialyzer Reprocessing Flow ChartДокумент1 страницаDialyzer Reprocessing Flow ChartGrafe ChuaОценок пока нет
- Prepared By, Gayathri R 2 Yr MSC (N) UconДокумент41 страницаPrepared By, Gayathri R 2 Yr MSC (N) UconGayathri RОценок пока нет
- DialyzerДокумент10 страницDialyzerfatima rasheedОценок пока нет
- How Does Hemodialysis WorkДокумент19 страницHow Does Hemodialysis WorkMaxence KouessiОценок пока нет
- HydronephrosisДокумент7 страницHydronephrosisNaqash NobleОценок пока нет
- 1 PDFДокумент94 страницы1 PDFJohn Louie SolitarioОценок пока нет
- Assessment of The Breast: Jonalyn Sotero Esco RN., MANДокумент41 страницаAssessment of The Breast: Jonalyn Sotero Esco RN., MANVan MaverickОценок пока нет
- Intradialytic ComplicationsДокумент5 страницIntradialytic Complicationskane1978Оценок пока нет
- Hemodialysis MachineДокумент17 страницHemodialysis MachineMehdi MohammedОценок пока нет
- Nephro - CVC Tip SheetДокумент6 страницNephro - CVC Tip Sheetsam m0% (1)
- How Does Haemodialysis WorkДокумент19 страницHow Does Haemodialysis Workhello_khay100% (1)
- Complications of HemodialysisДокумент34 страницыComplications of HemodialysisElza GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Hemodialysis Adequacy DwiДокумент27 страницHemodialysis Adequacy Dwiryo_ninukОценок пока нет
- Intradialytic Stretching Exercises On Fatigueand Muscle CrampsДокумент6 страницIntradialytic Stretching Exercises On Fatigueand Muscle CrampsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Kidney Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент6 страницKidney Anatomy and PhysiologyJohn Wilbert BirungОценок пока нет
- LESSON 9 Organ Donation ActДокумент56 страницLESSON 9 Organ Donation ActnullОценок пока нет
- Understanding HemodialysisДокумент16 страницUnderstanding HemodialysisIsha MohantyОценок пока нет
- Renal Replacement Therapies Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisДокумент86 страницRenal Replacement Therapies Hemodialysis and Peritoneal DialysisSabita Tripathi100% (2)
- DialysisДокумент34 страницыDialysisdaisy100% (2)
- Urinary EliminationДокумент9 страницUrinary EliminationTuTitОценок пока нет
- CAUTIДокумент46 страницCAUTImahesh sivaОценок пока нет
- Gastrostomy and JejunostomyДокумент43 страницыGastrostomy and JejunostomyLeslie Anne Alcibar TababaОценок пока нет
- Complications Dialysis 12 09Документ47 страницComplications Dialysis 12 09irish_meg316557100% (2)
- Hemodialysis: Navigation SearchДокумент14 страницHemodialysis: Navigation SearchepingОценок пока нет
- Hemodialysis Power PointДокумент40 страницHemodialysis Power Pointahmad_taher_9Оценок пока нет
- Dialysis PrescriptionДокумент23 страницыDialysis PrescriptionMercy Juliana Jacqualine100% (1)
- DialysisДокумент20 страницDialysisShiela Mae Lopez100% (1)
- Pdfpage 2 PDFДокумент1 страницаPdfpage 2 PDFDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology WithДокумент14 страницAnatomy and Physiology WithDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Acute Gastroenteritis NCPДокумент2 страницыAcute Gastroenteritis NCPXhla Ng78% (18)
- Patient - S Daily Progress in The HospitalДокумент5 страницPatient - S Daily Progress in The HospitalDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент14 страницAnatomy and PhysiologyDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент14 страницAnatomy and PhysiologyDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study SP Area - Dexa and InderalДокумент12 страницDrug Study SP Area - Dexa and InderalDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology WithДокумент14 страницAnatomy and Physiology WithDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент14 страницAnatomy and PhysiologyDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology WithДокумент14 страницAnatomy and Physiology WithDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент14 страницAnatomy and PhysiologyDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент14 страницAnatomy and PhysiologyDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology WithДокумент14 страницAnatomy and Physiology WithDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- SocioДокумент9 страницSocioDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- High Carb DishДокумент3 страницыHigh Carb DishDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- High Carb DishДокумент3 страницыHigh Carb DishDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- High in Vitamins and Minerals DishДокумент1 страницаHigh in Vitamins and Minerals DishDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Plot - A Rose For EmilyДокумент1 страницаPlot - A Rose For EmilyDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- DoorДокумент2 страницыDoorDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Genogram On Case Study JBLДокумент1 страницаGenogram On Case Study JBLDonita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Lola Camellia: Vehicular Accident (2009)Документ3 страницыLola Camellia: Vehicular Accident (2009)Donita Meña LaroyaОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Review Mcqs (From The Official Biochemistry Study Guide)Документ5 страницEnzyme Review Mcqs (From The Official Biochemistry Study Guide)Mrs Rehan100% (1)
- Comparatives and SuperlativesДокумент2 страницыComparatives and Superlativesjcarlosgf60% (5)
- Kevin Coleman's Sentencing MemoДокумент26 страницKevin Coleman's Sentencing MemoThe Valley IndyОценок пока нет
- Public Places 9 & 10Документ2 страницыPublic Places 9 & 10kaka udinОценок пока нет
- Research News: Sedimentation Velocity of Solids in Finite Size VesselsДокумент4 страницыResearch News: Sedimentation Velocity of Solids in Finite Size VesselskorangaprakashОценок пока нет
- Conut Shell: A Substitute For Aggregate in Mix Proportioning of CementДокумент17 страницConut Shell: A Substitute For Aggregate in Mix Proportioning of CementStephanie SilaoОценок пока нет
- 'Last Season's Man'Документ7 страниц'Last Season's Man'Bishal Kumar SahuОценок пока нет
- Tumor Saluran Kemih (Tumors/Malignancy of Urinary Tract) : Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuДокумент22 страницыTumor Saluran Kemih (Tumors/Malignancy of Urinary Tract) : Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuLuthfiAhmadОценок пока нет
- Civrev2 2019 Case TitlesДокумент3 страницыCivrev2 2019 Case TitlesAnne VallaritОценок пока нет
- Prevent Cross Contamination and Mix UpДокумент2 страницыPrevent Cross Contamination and Mix UpPrince Moni100% (1)
- Recipe For SuccesДокумент27 страницRecipe For Successtefany alvarezОценок пока нет
- P2 Nursing InfoДокумент14 страницP2 Nursing InfoMargarita Limon BalunesОценок пока нет
- BPT Notes Applied PsychologyДокумент36 страницBPT Notes Applied PsychologyVivek Chandra0% (1)
- Resume PLPДокумент2 страницыResume PLPapi-302180779Оценок пока нет
- Black and Decker Vaporera Electrica RecetarioДокумент17 страницBlack and Decker Vaporera Electrica RecetarioFabio AtenógenesОценок пока нет
- Carbonyl Compounds: Unit 4 Rates, Equilibria and Further Organic ChemistryДокумент5 страницCarbonyl Compounds: Unit 4 Rates, Equilibria and Further Organic ChemistryKirusaanth SathiyathasanОценок пока нет
- HSE Issues Tracker - DAFДокумент28 страницHSE Issues Tracker - DAFMohd Abdul MujeebОценок пока нет
- 10 Effective Ayurvedic Treatment For Hair LossДокумент9 страниц10 Effective Ayurvedic Treatment For Hair Lossrpav77Оценок пока нет
- CH - 3 DrainageДокумент3 страницыCH - 3 DrainageVeena VermaОценок пока нет
- Primary Health Care: Mr. John Michael M. Pitoy, B.S.N., R.NДокумент44 страницыPrimary Health Care: Mr. John Michael M. Pitoy, B.S.N., R.NJohn Michael Manlupig Pitoy100% (9)
- Material Science & Metallurgy: Third Semester B.E. Degree (CBCS) Examination, Dec.2016/Jan.2017Документ2 страницыMaterial Science & Metallurgy: Third Semester B.E. Degree (CBCS) Examination, Dec.2016/Jan.2017Shaikh MuzaffarОценок пока нет
- July 15, 2011 Strathmore TimesДокумент24 страницыJuly 15, 2011 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesОценок пока нет
- Identification of Plastics Identification of PlasticsДокумент41 страницаIdentification of Plastics Identification of PlasticsSoumickОценок пока нет
- Hindustan Coca-Cola Beverages PVT LTD B-91 Mayapuri Industrial Area Phase-I New DelhiДокумент2 страницыHindustan Coca-Cola Beverages PVT LTD B-91 Mayapuri Industrial Area Phase-I New DelhiUtkarsh KadamОценок пока нет
- Presented By: Priteshi Patel: Previously: Kentucky Fried ChickenДокумент33 страницыPresented By: Priteshi Patel: Previously: Kentucky Fried Chickensandip_1Оценок пока нет
- ISO 9001: 2015 Certified Semen Freezing LaboratoryДокумент43 страницыISO 9001: 2015 Certified Semen Freezing LaboratoryShubhamОценок пока нет
- Water Quality Parameters A Case Study of Karnafully - Dr. A K MajumderДокумент6 страницWater Quality Parameters A Case Study of Karnafully - Dr. A K MajumderMd. Badrul IslamОценок пока нет
- Flexible Learnin G: Group 3 Bsed-Math 2Документ48 страницFlexible Learnin G: Group 3 Bsed-Math 2Niña Gel Gomez AparecioОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ6 страницChapter 4Aung MyatОценок пока нет
- Soil Mechanics Lecture 1Документ86 страницSoil Mechanics Lecture 1Ammar Ayub100% (2)