Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 1 Respiration
Загружено:
aqilajandin0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
33 просмотров26 страницbiology form 4
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документbiology form 4
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
33 просмотров26 страницChapter 1 Respiration
Загружено:
aqilajandinbiology form 4
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 26
HUMAN BREATHING MECHANISM
The chemical process whereby energy is released
from glucose or other simple substances is known as
respiration.
In cellular respiration,
Glucose + O
2
Energy + CO
2
+ Water
Our body takes in O
2
from atmosphere and releases
CO
2
.
This process which involves an exchange of gases is
known as breathing.
The role of the respiratory system is to produce energy
through three mechanism:
Breathing to obtain energy
Transport oxygen from blood to the body cells
Cellular respiration to oxidize food using oxygen in the
body cells
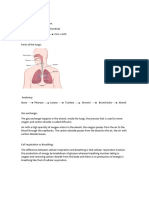
The Structure of Human Respiratory System
PART FUNCTION
Nasal cavity Moistens air that passes through
and traps dust particles in air.
Trachea Help to trap dust particles and
microorganisms in air.
Bronchi/bronchus Direct air to the lungs.
Lung Rich in blood vessels and alveoli.
Ribs Protect lungs
Diaphragm Separate the thoracic cavity from
the abdominal cavity.
Intercostal
muscles
Move ribs during the breathing
process.
The Structure of Human Lungs
Lungs is the main respiratory organ of human.
The lung is soft and spongy organ.
Located in the thoracic cavity and protected by ribs.
There are fine branches in the lung called bronchioles.
Bronchioles branch out from the bronchi.
There are many air sacs at the ends of the bronchioles
known as alveoli/alveolus.
Flow of Air from the Atmosphere
to the Lungs
Alveoli surrounded by blood capillaries.
Gaseous exchange takes place in the lungs by
diffusion.
An alveolus has the following adaptations to allow it to
exchange gases effectively.
has a very large surface area
has walls which are very thin and elastic
is surrounded by a network of blood capillaries
is moist
Breathing Mechanism
The process of taking in air into the lungs is known as
inhalation.
The air that enters the lungs is the inhaled air.
The process of expelling carbon dioxide from the lungs
into the atmosphere is known as exhalation.
The air expelled is known as exhaled air.
Model of the Human Respiratory System
Comparing Inhalation and Exhalation
TRANSPORT OF OXYGEN IN THE
HUMAN BODY
During inhalation, the concentration of O
2
in inhaled air
is higher than O
2
content in the blood capillaries.
Oxygenated air is drawn into the lungs through the
nasal cavity, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and finally
into the alveoli.
Alveoli are tiny air sacs where the exchange of gases
takes place.
During the exchange of gases, O
2
will be transported
from the alveoli to the body cells while CO
2
will be
transported from the body cells to the lungs.
Diffusion of O
2
from the Alveoli into the Blood Capillaries
Alveoli have moist surfaces, thin walls and surrounded
by blood capillaries.
O
2
in the inhaled air will dissolve on the moist surface
of alveoli.
This cause the concentration of O
2
in alveoli to
increase.
When concentration of O
2
in the alveoli is higher than
in the blood capillaries, O
2
will be transported to the
blood capillaries through diffusion.
Transport of Oxygen by Blood
Blood is a type of tissue fluid that flows in the blood
capillaries.
Blood acts as a medium of transport of oxygen due to
assistance from the haemoglobin.
Haemoglobin is the red pigment found in the red blood
cells.
Haemoglobin is an important carrier of oxygen
because it combines with oxygen easily.
Haemoglobin + Oxygen Oxyhaemoglobin
Oxyhaemoglobin will be carried from the lungs to the
other parts of the body cells that lack oxygen.
Diffusion of O
2
from Blood Capillaries to Body Cells
When oxyhaemoglobin reaches the body cells that
lack O
2
, it breaks down into O
2
and haemoglobin.
Oxyhaemoglobin Haemoglobin + Oxygen
The released O
2
will be absorbed by the body cells
while the haemoglobin will return to the lungs to
combine with the O
2
.
At the same time, CO
2
from the cells diffuses into the
blood capillaries to be carried by haemoglobin back to
the alveoli.
CO
2
will be expelled out of the lungs during exhalation.
THE IMPORTANCE OF A HEALTHY
RESPIRATION SYSTEM
Our respiratory system will be affected if it is exposed
to the air pollutants.
Most pollutants are toxic and carcinogenic.
Toxicity is a nature of substance that can harm living
cells.
Carcinogenicity leads to the production of cancerous
cells.
Toxic substances are known as toxins.
Carcinogenic substances are known as carcinogens.
The Effects of Harmful Substances
We must avoid taking up smoking which can damage
the respiratory system.
An activity to show the effects of cigarette smoke on
white cotton wool can be conducted as follows:
The white cotton is used as an analogy of the lung
tissues.
At the end of the activity, it is found that:
Thermometer reading increases cigarette smoke can
increase the temperature of lung.
White cotton wool turns brownish and contains black
particles cigarette smoke contains tar.
Cotton wool has very strong nicotine smell nicotine
from the cigarette smoke condense on the cotton wool.
Hydrogen carbonate indicator turns yellow nitrogen
oxide in cigarette smoke dissolves in it and makes it
acidic.
Improving the Quality of the Air
Banning open burning of rubbish.
Using unleaded petrol in motor vehicles.
Conducting campaigns for the preservation and
conservation of good air quality.
Вам также может понравиться
- Chapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismДокумент4 страницыChapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismWindy SanОценок пока нет
- Respiratory System For PowelДокумент41 страницаRespiratory System For PowelNikko Bondoc ManaloОценок пока нет
- Lec 17 Circulatory SystemДокумент21 страницаLec 17 Circulatory SystemEnmuskОценок пока нет
- 11 Biology Notes ch17-pdf1Документ9 страниц11 Biology Notes ch17-pdf1LishaОценок пока нет
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesДокумент5 страницBreathing and Exchange of Gaseslpc4944Оценок пока нет
- What Is Respiration?Документ8 страницWhat Is Respiration?Waleed Bin KhalidОценок пока нет
- Breathing & Exchange of GasesДокумент5 страницBreathing & Exchange of GasesMamta TiwariОценок пока нет
- Respiratory System in Human BeingsДокумент11 страницRespiratory System in Human BeingsSarada KasyapОценок пока нет
- Human Respiratory System: When InhalingДокумент4 страницыHuman Respiratory System: When InhalingMohanasundari MuniandyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Science Form 1Документ19 страницChapter 1 Science Form 1Che SalОценок пока нет
- Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPДокумент8 страницMaterial Downloaded From SUPERCOPfast-track for n2021Оценок пока нет
- Gas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsДокумент7 страницGas Exchange in Plants and AnimalsMarvin MelisОценок пока нет
- 11 Biology Notes Ch17 Breathing and Exchange of GasesДокумент4 страницы11 Biology Notes Ch17 Breathing and Exchange of GasesParimala deviОценок пока нет
- The Respiratory SystemДокумент5 страницThe Respiratory SystemmvslikavОценок пока нет
- COPD Case ICUДокумент19 страницCOPD Case ICUKim Vizcarra100% (1)
- The Respiratory SystemДокумент2 страницыThe Respiratory SystemNicole PinedaОценок пока нет
- The Human Respiratory SystemДокумент2 страницыThe Human Respiratory SystemWei Ling KuahОценок пока нет
- Respiratory SystemДокумент10 страницRespiratory SystemSudip NeupaneОценок пока нет
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationДокумент3 страницыRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoОценок пока нет
- Breathing & Exchange of Gases NotesДокумент7 страницBreathing & Exchange of Gases NotesKankana Biswas100% (1)
- Respiratory SystemДокумент3 страницыRespiratory SystemjoimaciascorreaОценок пока нет
- Genbio2 RespirationДокумент1 страницаGenbio2 RespirationArvie Jane Mendoza DeTorresОценок пока нет
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesДокумент5 страницBreathing and Exchange of Gasessonu kumarОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology CopdДокумент15 страницAnatomy and Physiology CopdAssenav May100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology CopdДокумент15 страницAnatomy and Physiology CopdAssenav MayОценок пока нет
- Science Senior 2Документ4 страницыScience Senior 2ajichristianbaniadamОценок пока нет
- Respiration 8c RevisionДокумент4 страницыRespiration 8c RevisionJelle MustefaОценок пока нет
- Respiratory System: (A Written Report)Документ16 страницRespiratory System: (A Written Report)hellofrom theothersideОценок пока нет
- Breathing and Gas Exchange: RespirationДокумент4 страницыBreathing and Gas Exchange: RespirationAbubakar Siddiq RaminОценок пока нет
- Res (Iratory SystemДокумент2 страницыRes (Iratory SystemJosielyn ValladolidОценок пока нет
- BreathingДокумент5 страницBreathingKekeletsoОценок пока нет
- Respiratory SystemДокумент10 страницRespiratory Systemapi-305592242Оценок пока нет
- Respiratory System of FrogДокумент3 страницыRespiratory System of Frogaparajuli089Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The LungsДокумент3 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of The LungsMayownski TejeroОценок пока нет
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Chapter II - Respiratory SystemДокумент3 страницыChapter II - Respiratory SystemIndranil SinhaОценок пока нет
- 4 RespirationДокумент6 страниц4 Respirationनिरज न्यौपानेОценок пока нет
- Gas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Документ13 страницGas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Archel GalorportОценок пока нет
- Form 3 Science Chapter 1Документ25 страницForm 3 Science Chapter 1Mukilan MurugasanОценок пока нет
- CH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansДокумент4 страницыCH 11 Gas Exchange in HumansPranitha RaviОценок пока нет
- Respiration NotesДокумент7 страницRespiration NotesTamisha JacobsОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderДокумент15 страницChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disordercrabby_chicОценок пока нет
- HSB Week 9Документ18 страницHSB Week 9EmilyОценок пока нет
- Oxygen Insufficiency.Документ54 страницыOxygen Insufficiency.Josephine George JojoОценок пока нет
- RespiratorychempowerpointДокумент10 страницRespiratorychempowerpointapi-252255196Оценок пока нет
- Respiration & BreathingДокумент18 страницRespiration & BreathingKristal CampbellОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersДокумент5 страницChapter 8 Exercise Question and AnswersPooja AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Educational ProgramsДокумент28 страницEducational ProgramsEsha KuttiОценок пока нет
- Respiratory SystemДокумент2 страницыRespiratory Systemsouha kahilОценок пока нет
- Respiration: Human Respiratory SystemДокумент4 страницыRespiration: Human Respiratory SystemSheehan MathurОценок пока нет
- The Human Breathing SystemДокумент5 страницThe Human Breathing SystemHarry Cianne Luther Sayon100% (1)
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases BIOLOGY CLASS 11Документ6 страницBreathing and Exchange of Gases BIOLOGY CLASS 11AvinashОценок пока нет
- Case Study COPDДокумент16 страницCase Study COPDRegine Cimafranca Macalaguing100% (5)
- Anatomy and Physiology (Respiratory System)Документ3 страницыAnatomy and Physiology (Respiratory System)Kirstin del CarmenОценок пока нет
- Group2 (Respiration)Документ12 страницGroup2 (Respiration)dinaОценок пока нет
- Dayacus, Nicole T.: Prof. Irene Aquino: Beed 2B: Topic 6 TsegДокумент3 страницыDayacus, Nicole T.: Prof. Irene Aquino: Beed 2B: Topic 6 TsegNicole VerdaderoОценок пока нет
- Anatomi Saluran PernapasanДокумент6 страницAnatomi Saluran PernapasanfidyaОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes - Respiratory SystemДокумент9 страницBiology Notes - Respiratory SystemnoorbdeirОценок пока нет
- Breathing and RespirationДокумент30 страницBreathing and Respirationhamzahazard527Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Respiration Doc1Документ6 страницChapter 1 Respiration Doc1api-248021925Оценок пока нет
- Muscles and Muscle Tissue: Chapter 9 Part AДокумент82 страницыMuscles and Muscle Tissue: Chapter 9 Part ADon KeyОценок пока нет
- Laporan Kasus OAДокумент34 страницыLaporan Kasus OARosmana PuteraОценок пока нет
- Auricular Acupuncture 2013 SummerДокумент89 страницAuricular Acupuncture 2013 Summerdoringrama100% (3)
- Clinical Significance: Dermatomes of The Head, Face, and NeckДокумент7 страницClinical Significance: Dermatomes of The Head, Face, and NeckAni Xiomara Armero PreciadoОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Retained Mucus Secretion As Evidenced by Unproductive CoughДокумент1 страницаIneffective Airway Clearance Related To Retained Mucus Secretion As Evidenced by Unproductive Coughdana93% (30)
- Alakliphiles ProjДокумент24 страницыAlakliphiles ProjReshmi Jadwani100% (2)
- USMLE Step 1 High Yield TopicsДокумент13 страницUSMLE Step 1 High Yield TopicsNixon GoyalОценок пока нет
- Cricopharyngeal DysphagiaДокумент8 страницCricopharyngeal Dysphagiataner_soysurenОценок пока нет
- Hons 2 - Protozoa BB2Документ50 страницHons 2 - Protozoa BB2nigeldkdcОценок пока нет
- Toyota 1GR-FE Engine ControlДокумент18 страницToyota 1GR-FE Engine ControlMaster Xeoto89% (9)
- Important Question For Dialysis TechnicianДокумент7 страницImportant Question For Dialysis Technicianhunbaitmiki hinge100% (1)
- Unit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFДокумент47 страницUnit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFanuksha aroraОценок пока нет
- Spa Esprit Facial MenuДокумент1 страницаSpa Esprit Facial MenuMichelle YeoОценок пока нет
- Sufixe Si PrefixeДокумент14 страницSufixe Si Prefixeseaofdreams6Оценок пока нет
- Computational Models For The Human Body PDFДокумент679 страницComputational Models For The Human Body PDFGuilherme AyresОценок пока нет
- NSTSE Class 3 Answer Key Updated Paper Code 449Документ3 страницыNSTSE Class 3 Answer Key Updated Paper Code 449G KumarОценок пока нет
- Behaviours Learned Through Classical ConditioningДокумент6 страницBehaviours Learned Through Classical Conditioningapi-314561050Оценок пока нет
- PSQIДокумент4 страницыPSQIPd Ibi Propinsi DiyОценок пока нет
- AnginaДокумент59 страницAnginaVevi InakuОценок пока нет
- Exercise 6 Frog Embryology - 1Документ10 страницExercise 6 Frog Embryology - 1ANNE MARGUERITE BARETEОценок пока нет
- BIO-Zoology PracticalДокумент38 страницBIO-Zoology PracticalveeramaniОценок пока нет
- Lab Activity 2 - Chordate ClassificationДокумент2 страницыLab Activity 2 - Chordate ClassificationRio Geline EdralinОценок пока нет
- Yerba Mate - An Overview of Physiological Effects in HumansДокумент13 страницYerba Mate - An Overview of Physiological Effects in HumansJuanManuelCabarcosОценок пока нет
- Writing Practice Nursing-2Документ4 страницыWriting Practice Nursing-2Twila Abuedo100% (5)
- Bio Abhyasa Deepika PDFДокумент93 страницыBio Abhyasa Deepika PDFArogya Raju Pudhota82% (17)
- MnemonicДокумент33 страницыMnemonicyanot0206Оценок пока нет
- Vomiting: Compendium (Yardley, PA) February 2009Документ10 страницVomiting: Compendium (Yardley, PA) February 2009Vini SasmitaОценок пока нет
- DR Ara Khan Marwat: Join My Watssap Group For Part-1 Books, Papers and UpdatesДокумент25 страницDR Ara Khan Marwat: Join My Watssap Group For Part-1 Books, Papers and UpdatesmisdduaaОценок пока нет
- Sphaerotilus NДокумент2 страницыSphaerotilus NLuis M. Telleria CondeОценок пока нет
- Ascent of Sap: 3 Theories: (A) Godlewski S Relay-Pump TheoryДокумент11 страницAscent of Sap: 3 Theories: (A) Godlewski S Relay-Pump TheoryRahulBansumanОценок пока нет