Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CH 11
Загружено:
Raj HakaniОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CH 11
Загружено:
Raj HakaniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Electronic Devices
Ninth Edition
Floyd
Chapter 11
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Thyristors
Thyristors are a class of semiconductor devices characterized
by 4-layers of alternating p- and n-material. Four-layer devices
act as either open or closed switches; for this reason, they are
most frequently used in control applications.
Summary
Some thyristors and their symbols are
(c) Diac (d) Triac (a) (e) SCS (b) SCR 4-layer diode
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Thyristors
Summary
Anode
Q
1
pn junction
2
Q
2
Cathode
pn junction 3
pn junction 1
The concept of 4-layer devices is usually
shown as an equivalent circuit of a pnp
and an npn transistor. Ideally, these
devices would not conduct, but when
forward biased, if there is sufficient
leakage current in the upper pnp device,
it can act as base current to the lower
npn device causing it to conduct and
bringing both transistors into saturation.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Four-Layer Diode
The 4-layer diode (or Shockley diode) is a type of thyristor
that acts something like an ordinary diode but conducts in
the forward direction only after a certain anode to cathode
voltage called the forward-breakover voltage is reached.
The 4-layer diode has two leads, labeled the
anode (A) and the cathode (K). The symbol
reminds you that it acts like a diode. It does
not conduct when it is reverse-biased.
Summary
p
n
p
n
1
2
3
Anode (A)
Cathode (K)
A
K
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Four-Layer Diode
The characteristic curve for a 4-layer diode shows the
forward blocking region. When the anode-to-cathode
voltage exceeds V
BR
, conduction occurs. The switching
current at this point is I
S
.
Summary
On
Off
V
BR(F)
V
AK
I
H
0
I
A
I
S
Forward-
conduction
region
Forward-
blocking
region
Once conduction begins, it
will continue until anode
current is reduced to less than
the holding current (I
H
). This
is the only way to stop
conduction.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The SCR
The SCR had its roots in the 4-layer diode. By
adding a gate connection, the SCR could be
triggered into conduction. This improvement made
a much more useful device than the 4-layer diode.
Summary
The SCR can be turned on by
exceeding the forward
breakover voltage or by gate
current. Notice that the gate
current controls the amount
of forward breakover voltage
required for turning it on.
V
F
I
R
V
R
I
A
I
H0
I
H1
I
H2
I
G2
> I
G1 I
G1
> I
G0
I
G0
= 0
V
BR(F0)
V
BR(F1)
V
BR(F2)
0
A
K
G
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The SCR
Like the 4-layer diode, the SCR will conduct as long as
forward current exceeds I
H
. There are two ways to drop the
SCR out of conduction: 1) anode current interruption
and 2) forced commutation.
Summary
Anode current can be interrupted by breaking the anode
current path (shown here), providing a path around the SCR,
or dropping the anode voltage to the point that I
A
< I
H
.
R
A
G
I
A
= 0
+V
Force commutation uses an external circuit to momentarily
force current in the opposite direction to forward conduction.
SCRs are commonly used in ac circuits, which forces the
SCR out of conduction when the ac reverses.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
SCR Specifications
Summary
Forward-breakover voltage, V
BR(F)
:
This is the voltage at which the SCR
enters the forward-conduction region.
Holding current, I
H
: This is the value of
anode current below which the SCR
switches from the forward-conduction
region to the forward-blocking region.
Gate trigger current, I
GT
: This is the
value of gate current necessary to switch
the SCR from the forward-blocking
region to the forward-conduction region
under specified conditions.
Forward-
conduction
region (on)
for I
G
= 0
V
F
V
BR(F)
Forward-
blocking
region (off)
I
R
Reverse-
blocking
region
0
Reverse-
avalanche
region
V
BR(R)
V
R
I
H
I
F
Characteristic
for I
G
= 0
Three important SCR specifications are:
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
SCR Applications
Summary
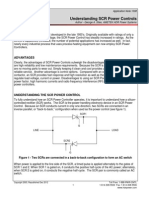
SCRs are used in a variety of power control applications.
One of the most common applications is to use it in ac
circuits to control a dc motor or appliance because the
SCR can both rectify and control.
I
B
A
R
R
1
4
R
R
2
3
M
The SCR is triggered on the
positive cycle and turns off on
the negative cycle. A circuit
like this is useful for speed
control for fans or power tools
and other related applications.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
SCR Applications
Summary
Another application for SCRs is in crowbar circuits
(which get their name from the idea of putting a crowbar
across a voltage source and shorting it out!)
The purpose of a crowbar
circuit is to shut down a power
supply in case of over-voltage.
Once triggered, the SCR
latches on. The SCR can
handle a large current, which
causes the fuse (or circuit
breaker) to open.
SW
R
3
Fuse
DC
power supply
R
2
R
1
V
TRIG
D
2
D
1
V
OUT
"Crowbar circuit"
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Diac
Summary
The diac is a thyristor that acts like two back-to-back
4-layer diodes. It can conduct current in either
direction. Because it is bidirectional, the terminals are
equivalent and labeled A
1
and A
2
.
The diac conducts current after the
breakdown voltage is reached. At that
point, the diac goes into avalanche
conduction, creating a current pulse
sufficient to trigger another thyristor (an
SCR or triac). The diac remains in
conduction as long as the current is
above the holding current, I
H
.
A
1
A
2
V
F
V
BR(F)
I
R
0
V
BR(R)
V
R
I
H
I
F
I
H
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Triac
Summary
The triac is essentially a bidirectional SCR but the
anodes are not interchangeable. Triggering is done by
applying a current pulse to the gate; breakover triggering
is not normally used.
When the voltage on the A
1
terminal is positive with respect
to A
2
, a gate current pulse will
cause the left SCR to conduct.
When the anode voltages are
reversed, the gate current pulse
will cause the right SCR to
conduct.
A
2
A
1
G
I
G0
V
A
V
BR(F2)
I
A
V
BR(R0)
V
A
I
A
V
BR(R1)
V
BR(R2)
I
G1
I
G2
I
G0
I
G1
I
G2
V
BR(F1)
V
BR(F0)
I
H0
I
H1
I
H2
I
H2
I
H1
I
H0
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Triac Applications
Summary
Triacs are used for control of ac in applications like
electric range heating controls, light dimmers, and
small motors.
V
in
R
L
V
G
A
1
G
A
2
I
L
Triac on
Delay
angle
Conduction
angle
Like the SCR, the
triac latches after
triggering and turns
off when the current is
below the I
H
, which
happens at the end of
each alteration.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Silicon-Controlled Switch (SCS)
Summary
The SCS is similar to an SCR but with
two gates. It can be triggered on with a
positive pulse on the cathode gate, and
can be triggered off with a positive pulse
on the anode gate.
Cathode
gate
(G
K
)
Cathode (K)
Anode (A)
Anode
gate
(G
A
)
In this example, the SCS is controlling
a dc source. The load is in the cathode
circuit, which has the advantage of
one side of the load being on circuit
ground.
R
L
V
V
V
GK
GA
L
A
G
K
G
A
K
+V
CC
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Unijunction Transistor (UJT)
Summary
The UJT consists of a a block of lightly-doped
(high resistance) n-material with a p-material
grown into its side. It is often used as a trigger
device for SCRs and triacs.
The UJT is a switching device;
it is not an amplifier. When the
emitter voltage reaches V
P
(the
peak point), the UJT fires,
going through the unstable
negative resistance region to
produce a fast current pulse.
B
2
E
B
1
Negative
resistance
I
E
I
V
I
P
V
V
V
P
Peak
point
V
E
Cutoff Saturation
Valley point
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Unijunction Transistor (UJT)
Summary
The equivalent circuit for a UJT shows that looks like a
diode connected to a voltage divider. The resistance of the
lower divider (r
B1
) is inversely proportional to the emitter
current. When the pn junction is first
forward-biased, the junction
resistance of r
B1
suddenly appears
to drop, and a rush of current occurs.
r
B2
r
B1
E
B
2
B
1
+
V
EB1
+
V
pn
+
V
BB
V
BB
I
E
An important parameter is h, which is the
intrinsic standoff ratio. It represents the
ratio of r
B1
to the interbase resistance r
BB
with no current.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Unijunction Transistor (UJT) Application
Summary
A circuit using a UJT to fire an SCR is shown. When the
UJT fires, a pulse of current is delivered to the gate of the
SCR. The setting of R
1
determines when the UJT fires. The
diode isolates the UJT
from the negative part
of the ac.
R
1
V
E
R
2 C
B
A
R
R
L
G
D
UJT
SCR
The UJT produces a fast,
reliable current pulse to
the SCR, so that it tends
to fire in the same place
every cycle.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT)
Summary
The PUT is a 4-layer thyristor with a gate. It is
primarily used as a sensitive switching device.
The gate pulse can trigger a sharp increase in
current at the output.
A
G
K
The characteristic of a PUT is
similar to a UJT, but the PUT
intrinsic standoff ratio can be
programmed with external
resistors and the UJT has a
fixed ratio.
V
AK
(anode-to-cathode voltage)
V
P
V
V
I
P
I
V
0 I
A
(anode current)
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT)
Summary
The principle application for a PUT is for driving SCRs and
triacs, but, like the UJT, can be used in relaxation oscillators.
For the circuit to oscillate, R
1
must be large
enough to limit current to less than the valley
current (I
V
). The period of the oscillations is
given by:
1
1
ln
1
T RC
h
where
3
2 3
R
R R
h
R
3
G
K
A
R
1
R
2
R
4
C
+V
CC
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
The Programmable Unijunction Transistor (PUT)
Summary
1
1
ln
1
T RC
h
3
2 3
10 k
20 k + 10 k
R
R R
h
R
3
G
K
A
R
1
R
2
R
4
C
+V
CC
0.01 F m
220 k
10 k
20 k
27
+20 V
What is intrinsic standoff ratio, and the period of the circuit?
0.33
1
220 k 0.01 F ln
1 0.33
0.89 ms
What is the frequency? 1.12 kHz
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Selected Key Terms
4-layer diode
Thyristor
SCR
The type of 2-terminal thyristor that conducts
current when the anode-to-cathode voltage reaches
a specified breakover value.
A class of four-layer (pnpn) semiconductor
devices.
Silicon-controlled rectifier; a type of three
terminal thyristor that conducts current when
triggered by a voltage at the single gate terminal
and remains on until anode current falls below a
specified value.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Selected Key Terms
LASCR
Diac
Triac
Light-activated silicon-controlled rectifier; a four
layer semiconductor device (thyristor) that
conducts current in one direction when activated
by a sufficient amount of light and continues to
conduct until the current falls below a specified
value.
A two-terminal four-layer semiconductor device
(thyristor) that can conduct current in either
direction when properly activated.
A three-terminal thyristor that can conduct current
in either direction when properly activated.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Selected Key Terms
SCS
UJ T
PUT
Silicon-controlled switch; a type of four-terminal
thyristor that has two gate terminals that are used
to trigger the device on and off.
Unijunction transistor; a three terminal single pn
junction device that exhibits a negative resistance
characteristic.
Programmable unijunction transistor; a type of
three terminal thyristor (physically more like an
SCR than a unijunction) that is triggered into
conduction when the voltage at the anode exceeds
the voltage at the gate.
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
1. The 4-layer (Shockley) diode can conduct current if
a. the anode-to-cathode voltage exceeds V
BR
b. a current pulse is applied to the gate
c. both a and b are correct
d. none of the above
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
2. The SCR can conduct current if
a. the anode-to-cathode voltage exceeds V
BR
b. a current pulse is applied to the gate
c. both a and b are correct
d. none of the above
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
3. A bidirectional thyristor is the
a. 4-layer diode
b. SCR
c. triac
d. silicon-controlled switch
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
4. A thyristor that looks like two back-to-back 4-layer
diodes is the
a. SCR
b. triac
c. SCS
d. diac
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
5. An SCR turns off when the
a. gate trigger current drops below a specified level
b. anode current drops below the holding current
c. both a and b are true
d. none of the above
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
6. The purpose of a crowbar circuit is to protect a load from
a. excessive ripple
b. low-voltage
c. over-voltage
d. all of the above
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
7. A diac and triac are similar in that both devices
a. can use breakover triggering
b. can be used in ac circuits
c. are bidirectional
d. all of the above
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
8. A device that has an unstable negative resistance region
is the
a. UJT
b. diac
c. triac
d. SCS
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
9. The symbol for a silicon-controlled switch (SCS) is
(a) (b) (c) (d)
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
10. A programmable unijunction transistor (PUT) is
programmed by choosing the
a. RC time constant
b. gate resistors
c. power supply voltage
d. cathode resistor
2012 Pearson Education. Upper Saddle River, NJ, 07458.
All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices, 9th edition
Thomas L. Floyd
Quiz
Answers:
1. a
2. c
3. c
4. d
5. b
6. c
7. d
8. a
9. d
10. b
Вам также может понравиться
- CH 11Документ34 страницыCH 11Ahmed ElsharkawyОценок пока нет
- ThyristorДокумент22 страницыThyristorBharat100% (1)
- IECD Capsule NotesДокумент59 страницIECD Capsule NotesANANTHU PRADEEPОценок пока нет
- Thyristors PDFДокумент51 страницаThyristors PDFRobert Stephen NuñezОценок пока нет
- RF Active DevicesДокумент13 страницRF Active DevicesRaj PatelОценок пока нет
- Slides Lec 1-2Документ26 страницSlides Lec 1-2ali tariqОценок пока нет
- Edc Special DevicesДокумент50 страницEdc Special DevicesSurekha PittaОценок пока нет
- Silicon Controlled RectifierДокумент9 страницSilicon Controlled RectifierMahendraNath Reddy EОценок пока нет
- SCR, Traic, Diac ReportДокумент19 страницSCR, Traic, Diac ReportPravin Gareta60% (5)
- SCR 1Документ21 страницаSCR 1Prasun MoyraОценок пока нет
- Silicon Controlled RectifierДокумент9 страницSilicon Controlled RectifierFarishat Nusabbee An Nafs100% (1)
- BE 5 UnitДокумент23 страницыBE 5 Unit08sunnyjaganОценок пока нет
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier DefinitionДокумент10 страницSilicon Controlled Rectifier DefinitionishmamОценок пока нет
- THYRISTOR StudentДокумент30 страницTHYRISTOR StudentgggggОценок пока нет
- Ch05 Transistor Bias Circuits (37 PP)Документ19 страницCh05 Transistor Bias Circuits (37 PP)junaidnazirОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9: Thyristors Thyristors: (C) Diac (D) Triac (A) (E) SCS (B) SCR 4-Layer DiodeДокумент5 страницChapter 9: Thyristors Thyristors: (C) Diac (D) Triac (A) (E) SCS (B) SCR 4-Layer DiodeAngel CondiОценок пока нет
- CH11 ThyristorsДокумент86 страницCH11 Thyristorsmiathegirl9Оценок пока нет
- Electronics Devices & Circuit Lab ManualДокумент53 страницыElectronics Devices & Circuit Lab Manualbiswajit7sarkar100% (1)
- Slides Lec2Документ22 страницыSlides Lec2Aijaz HussainОценок пока нет
- Silicon Controlled RectifierДокумент148 страницSilicon Controlled RectifierSrinivasRaoОценок пока нет
- Raw 7Документ14 страницRaw 7syafruddinr_68006517Оценок пока нет
- Eto Handout1 DiodeДокумент20 страницEto Handout1 DiodedawitОценок пока нет
- Silicon-Controlled Rectifier: A High Power SCRДокумент8 страницSilicon-Controlled Rectifier: A High Power SCRPaarthibba KumarОценок пока нет
- Edc U-2 Scr&ujtДокумент18 страницEdc U-2 Scr&ujtRAVEE396Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 11: ThyristorsДокумент11 страницChapter 11: ThyristorsJohn Paul GaelaОценок пока нет
- Pe FINALДокумент131 страницаPe FINALAnonymous R4WpNxОценок пока нет
- Full Wave RectifierДокумент10 страницFull Wave Rectifierdheerajguptaandro20% (5)
- ELECTRON DEVICES-Power DevicesДокумент58 страницELECTRON DEVICES-Power DevicesSekar GanapathyОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Thyristors PDFДокумент9 страницIntroduction To Thyristors PDFAnnie BordsОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesДокумент24 страницыPower Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesTapobroto ChatterjeeОценок пока нет
- Lecture 04Документ15 страницLecture 04Roy Jonathan Adorna AvilaОценок пока нет
- Lab SheetДокумент29 страницLab SheetKennedy KoluteОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual Power ElectronicsДокумент39 страницLab Manual Power ElectronicsZainab AnwarОценок пока нет
- Experiment 2Документ4 страницыExperiment 2Emre YavuzОценок пока нет
- EEE 121 Circuit Theory 1: Circuit Theorems & Apllication To DC CircuitsДокумент29 страницEEE 121 Circuit Theory 1: Circuit Theorems & Apllication To DC CircuitsKamarul Syaril AzzahariОценок пока нет
- Een 11 Prelim Lec3Документ31 страницаEen 11 Prelim Lec3Miggy VelasquezОценок пока нет
- Names: Thyristor Thyr IstorДокумент30 страницNames: Thyristor Thyr IstorNaty SeyoumОценок пока нет
- Scr-Diac-Triac-UjtДокумент11 страницScr-Diac-Triac-Ujtmmuz.backup4Оценок пока нет
- Publication 12 4813 82Документ10 страницPublication 12 4813 82rasmksjiОценок пока нет
- Thyristor Family PSDДокумент18 страницThyristor Family PSDHiren H. Patel100% (1)
- Electronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)Документ14 страницElectronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)em2200139Оценок пока нет
- Beee 150426070534 Conversion Gate02Документ12 страницBeee 150426070534 Conversion Gate02Amit KumarОценок пока нет
- Thyristors and Triacs PDFДокумент30 страницThyristors and Triacs PDFCristianОценок пока нет
- Handout - Thyristor and Other DevicesДокумент8 страницHandout - Thyristor and Other DevicesAngel CondiОценок пока нет
- Unit 2Документ22 страницыUnit 2SUSHMAGUPTAОценок пока нет
- AEC Module1 Clipping and ClampingДокумент43 страницыAEC Module1 Clipping and ClampingVinay kumar havinalОценок пока нет
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Semiconductor DiodesДокумент35 страницElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Semiconductor DiodesEzsilvasilva SilvaОценок пока нет
- Two Terminal Electronic DevicesДокумент28 страницTwo Terminal Electronic DevicesFahad GhanyОценок пока нет
- Batangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentДокумент15 страницBatangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentKarenMacalaladTanangОценок пока нет
- Special Semiconductor Devices: Mr. Jay Mehta Asst. Professor St. Francis Institute of TechnologyДокумент35 страницSpecial Semiconductor Devices: Mr. Jay Mehta Asst. Professor St. Francis Institute of Technologyjay mehtaОценок пока нет
- Flip-Flop Electronics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopedДокумент16 страницFlip-Flop Electronics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopednatcutОценок пока нет
- Circuit Lab AssignmentДокумент20 страницCircuit Lab AssignmentYeab SraОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Lab ManualДокумент47 страницPower Electronics Lab Manualshaan_patil100% (1)
- Electronics Devices & Circuits Unit I:Semiconductor Diodes and ApplicationsДокумент31 страницаElectronics Devices & Circuits Unit I:Semiconductor Diodes and ApplicationsGurvinderpal Singh MultaniОценок пока нет
- ODD II YR 2 MarksДокумент99 страницODD II YR 2 MarksjesudosssОценок пока нет
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesОт EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (7)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- Koyama Iros02-Multi Fingered Exoskeleton Haptic DeviceДокумент6 страницKoyama Iros02-Multi Fingered Exoskeleton Haptic DeviceRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- Advance Vacuum Cleaner: ABSTRACT: Autonomous Cleaning Robot Will Perform Task LikeДокумент4 страницыAdvance Vacuum Cleaner: ABSTRACT: Autonomous Cleaning Robot Will Perform Task LikeRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- News Paper Cutting 29.11.2015Документ26 страницNews Paper Cutting 29.11.2015Raj HakaniОценок пока нет
- Faq1 - Abu Robocon 2016 - 26 Oct 15Документ15 страницFaq1 - Abu Robocon 2016 - 26 Oct 15Raj HakaniОценок пока нет
- IJSRDV2I11275Документ2 страницыIJSRDV2I11275Raj HakaniОценок пока нет
- Global Navigation Satellite System and Augmentation: KctswamyДокумент20 страницGlobal Navigation Satellite System and Augmentation: KctswamyRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- Print NET 2014Документ88 страницPrint NET 2014Raj HakaniОценок пока нет
- News Paper Cutting 17.10.2015Документ14 страницNews Paper Cutting 17.10.2015Raj HakaniОценок пока нет
- World Book Day - ActivityДокумент2 страницыWorld Book Day - ActivityRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- Design & Simulation of Low Loss Circular Corrugated Waveguide For 42 GHZ, 200Kw GyrotronДокумент5 страницDesign & Simulation of Low Loss Circular Corrugated Waveguide For 42 GHZ, 200Kw Gyrotronbaban1_jpgОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: C I C C CДокумент3 страницыGujarat Technological University: C I C C CRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- MATLAB: An Introduction: Adapted From An Introductory Manual by John Buck, MIT 27 May 1989Документ15 страницMATLAB: An Introduction: Adapted From An Introductory Manual by John Buck, MIT 27 May 1989dineshkagОценок пока нет
- Index: Remaining Student Have To Present and Do Their Design Eng WorkДокумент1 страницаIndex: Remaining Student Have To Present and Do Their Design Eng WorkRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- 4a4 1285Документ5 страниц4a4 1285Meenakshi DhasmanaОценок пока нет
- Topic: Choppers: Class: 5 Sem. (EE)Документ89 страницTopic: Choppers: Class: 5 Sem. (EE)ankit407Оценок пока нет
- Yeni-2 Power Electronic ExperimentsДокумент7 страницYeni-2 Power Electronic ExperimentsRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- GK 7Документ13 страницGK 7Raj HakaniОценок пока нет
- 633937171401169110Документ16 страниц633937171401169110Raj HakaniОценок пока нет
- 8086 CPU Complete SureshДокумент89 страниц8086 CPU Complete SureshRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- Presentation 6Документ44 страницыPresentation 6SeverusManiОценок пока нет
- Assembler, Linker and LoaderДокумент6 страницAssembler, Linker and LoaderSyed Shiyaz MirzaОценок пока нет
- MOSFET Structure: Source Gate Drain Field Oxide Gate OxideДокумент12 страницMOSFET Structure: Source Gate Drain Field Oxide Gate OxideRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- APP1008 - Understanding SCR Power ControllersДокумент4 страницыAPP1008 - Understanding SCR Power ControllersRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- MOSFET Structure: Source Gate Drain Field Oxide Gate OxideДокумент12 страницMOSFET Structure: Source Gate Drain Field Oxide Gate OxideRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- Tracking PositionДокумент16 страницTracking PositionRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- Tracking PositionДокумент16 страницTracking PositionRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- NSIT FormДокумент4 страницыNSIT FormRaj HakaniОценок пока нет
- 8086 ArchitectureДокумент36 страниц8086 ArchitectureVaibhav GodboleОценок пока нет
- Advanced Microprocessor NotesДокумент25 страницAdvanced Microprocessor NotesPrashant AngirasОценок пока нет
- Pocket Sized Soldering Kit Cold Heat HackДокумент18 страницPocket Sized Soldering Kit Cold Heat HackDraganОценок пока нет
- Super Copier System EA Dashboard and Input DocsДокумент2 страницыSuper Copier System EA Dashboard and Input DocsZayminhtet McОценок пока нет
- AC & DC WindingДокумент29 страницAC & DC WindingSattar BalochОценок пока нет
- Manual CRT SS7900 ENG-3Документ23 страницыManual CRT SS7900 ENG-3Dante NeroОценок пока нет
- Bose: Competing by Being Truly DifferentДокумент4 страницыBose: Competing by Being Truly DifferentAngela AngelesОценок пока нет
- AD712Документ12 страницAD712samОценок пока нет
- A Seminar Reporton System VerilogДокумент29 страницA Seminar Reporton System Verilograkeshcusat890% (1)
- Mitsubishi E700 Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) Instruction ManualДокумент322 страницыMitsubishi E700 Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) Instruction ManualMROstop.com75% (4)
- User'S Manual: MODEL: MMA160/200Документ9 страницUser'S Manual: MODEL: MMA160/200Vlaovic GoranОценок пока нет
- Ashok Leyland LimitedДокумент19 страницAshok Leyland LimitedgsОценок пока нет
- PC7 PDFДокумент225 страницPC7 PDFDiego Umaña100% (1)
- Single Side BandДокумент12 страницSingle Side BandApril RodriquezОценок пока нет
- Higher Voltage Capacitance Becomes Increasingly ImportantДокумент2 страницыHigher Voltage Capacitance Becomes Increasingly ImportantdevrajОценок пока нет
- Manual Motor Starter MS132: Data SheetДокумент12 страницManual Motor Starter MS132: Data SheetHELLOGREGОценок пока нет
- 120542A Manual Instalación Antenas HDTF - Es PDFДокумент2 страницы120542A Manual Instalación Antenas HDTF - Es PDFCarloMagnoCurtisОценок пока нет
- Работа №1 Переведите: The Concept of Electrical CurrentДокумент5 страницРабота №1 Переведите: The Concept of Electrical CurrentлюдмилаОценок пока нет
- NTDCL 2023 InterviwesДокумент12 страницNTDCL 2023 InterviwesAehtsham Ul HaqОценок пока нет
- Bunn ULTRA Service and Repair ManualДокумент73 страницыBunn ULTRA Service and Repair ManualAldo MorenoОценок пока нет
- BC556, B BC557, A, B, C BC558, B: MccsemiДокумент5 страницBC556, B BC557, A, B, C BC558, B: MccsemiRogerio Morais Do NascimentoОценок пока нет
- Answer of QuestionsДокумент3 страницыAnswer of QuestionsItaakОценок пока нет
- EDO-MNL-CNS-COR-INT-XXX-021-921-1880-Rev-A HSG100 EX TYPE SPARK UP MANUALДокумент6 страницEDO-MNL-CNS-COR-INT-XXX-021-921-1880-Rev-A HSG100 EX TYPE SPARK UP MANUALErol DAĞОценок пока нет
- D BlockДокумент48 страницD BlockHarshit GuptaОценок пока нет
- Electronics Corporation of India LTD GET Exam Pattern 2018 1Документ2 страницыElectronics Corporation of India LTD GET Exam Pattern 2018 1Dhruv BhadaniyaОценок пока нет
- Microstrip Cascade Trisection FilterДокумент3 страницыMicrostrip Cascade Trisection FilterRasoul jafari sharif abadiОценок пока нет
- Example of A Simple ReportДокумент7 страницExample of A Simple ReportZuwaidah Ahmad SuhaimiОценок пока нет
- Digital Electronics Ece 213 PDFДокумент15 страницDigital Electronics Ece 213 PDFAlisha AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Honeywell Diff P Switch DPSДокумент2 страницыHoneywell Diff P Switch DPSFrinaru CiprianОценок пока нет
- 5 32848 Parallel ResonanceДокумент2 страницы5 32848 Parallel ResonanceDwarakaBobbyОценок пока нет
- SicДокумент32 страницыSicMohit BhansaliОценок пока нет
- RR58 Good 3 Phase Regulator Rectifier DiagramДокумент2 страницыRR58 Good 3 Phase Regulator Rectifier DiagramMick BurnsОценок пока нет