Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Place of Distribution
Загружено:
Runaway ShujiИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Place of Distribution
Загружено:
Runaway ShujiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Managing
Marketing Channels
2
Explain why companies use marketing
channels and discuss the functions these
channels perform
Discuss how channel members interact and
how they organise the work of the channel
Identify the major channel alternatives open to
a company and how companies select, motivate,
and evaluate channel members
3
Explain the roles of retailers and wholesalers in the
distribution channel
Discuss the importance of marketing logistics and
integrated supply chain management
4
A value delivery network is a network made
up of the company, suppliers, distributors and
customers who partner with each other to
improve the performance of the entire system.
5
A marketing channel (also known as a
distribution channel) is a set of interdependent
organisations involved in the process of
making a product or service available for use
or consumption by the consumer or business
user.
6
7
Information
Promotion
Contact
Matching
Negotiation
Distribution
Financing
Risk taking
8
9
10
A channel conflict is a disagreement among
marketing channel members on goals and
roles.
Horizontal conflict is conflict at the same
channel level. Vertical conflict is conflict
between different levels.
11
Manufacturer
Wholesaler
Retailer
Consumer Manufacturer
Retailer
Manufacturer
W
h
o
l
e
s
a
l
e
r
12
13
A franchise organisation is the most common
type of contractual relationship, which exists
between a manufacturer, wholesaler or service
organisation and independent businesspeople
(franchisees) who buy the right to own and
operate one or more units in the franchise
system.
14
Manufacturer-sponsored
retailer franchise system
Manufacturer-sponsored
wholesaler franchise system
Service-firm-sponsored
retailer franchise system
15
Buying into a proven system
Limited capital required
Benefit of centralised purchasing power
Instant expertise available
16
Lack of control
Inconsistencies in service levels and operating standards
Fees required plus royalties and payment for management
services
17
18
Disintermediation is the elimination of a layer
of intermediaries from a marketing channel or
the displacement of traditional resellers by
radically new types of intermediaries.
19
Analysing customer needs
Setting channel objectives
Identifying channel alternatives
Evaluating channel alternatives
20
Company sales force
Manufacturers agency
Intermediaries
21
Selling and promoting
Buying and assortment
building
Bulk-breaking
Warehousing
Transportation
Financing
Risk bearing
Market information
Management services and
advice
22
Merchant wholesalers
Full-service wholesalers
Wholesale merchants
Industrial distributors
Manufacturers and
retailers branches and
offices
Agents
Manufacturers
agents
Selling agents
Purchasing agents
Commission merchants
Brokers
23
Limited-service wholesalers
Cash-and-carry
Truck
Drop shippers
Rack jobbers
Producers cooperatives
Mail-order
24
Retailing includes all the activities involved in
selling goods and services directly to final
consumers for their personal, non-business
use.
25
Amount of service
Breadth and depth of
product lines
Relative prices Organisation
26
Self-service retailers cater for
customers who are willing to perform
their own locate-compare-select process
to save money
Limited-service retailers provide more sales
assistance because they carry more shopping
goods about which consumers need information
Full-service retailers carry more specialty
goods for which customers like to be waited on
27
Specialty store
Department store
Supermarkets
Convenience stores
Superstores
Hypermarkets
Discount stores
Off-price retailer
Factory outlet
Warehouse club
28
Corporate chains
Voluntary chains
Retailer cooperatives
Franchise organisations
Merchandising conglomerates
29
Intensive distribution means stocking the product
in all possible outlets
Exclusive distribution is giving a limited number of
dealers the exclusive right to distribute the companys
products in their territories
Selective distribution is the use of more than one, but
less than all intermediaries willing to carry the product
30
Selecting channel members
Managing and motivating channel members
Evaluating channel members
31
Market logistics includes all the tasks involved
in planning, implementing and controlling the
physical flow of goods, services and related
information from points of origin to points of
consumption or use to meet customer
requirements at a profit.
32
Suppliers Company Resellers Customers
Inbound
logistics
Outbound
logistics
Reverse
logistics
33
Warehousing
Inventory management
Transportation
Logistics information management
34
Road
Rail
Water
Pipeline
Air
Internet
35
Integrated logistics management is the logistics
concept that emphasizes teamwork, both
inside the company and among all the
marketing channel organisations to maximise
the performance of the entire distribution
system.
36
New retail forms and short life cycles
Growth of non-store retailing
Retail convergence
Rise of mega-retailers
Growing importance of retail technology
Global expansion of retailers
Blurring of lines between retailers and wholesalers
37
What do you understand to be a firms supply
chain and how is it different from its value
delivery network?
Why do firms employ multi-channel distribution systems?
What are the main challenges facing retailers and
wholesalers who wish to remain a viable part of the
marketing channel?
38
Identify the primary challenges an organisation faces in
managing its channel members. What are some of the
methods companies use to motivate channel partners?
What factors might govern international expansion for
European retailers? Why might local retailers be well
positioned for global expansion? How will online retailing
affect global retail expansion?
Вам также может понравиться
- Assignment PPD 1Документ33 страницыAssignment PPD 1Runaway Shuji33% (3)
- Assignment PPD 1Документ33 страницыAssignment PPD 1Runaway Shuji33% (3)
- Lipton Marketing PlanДокумент15 страницLipton Marketing Planomzii100% (4)
- Sales & Distribution ManagementДокумент113 страницSales & Distribution Managementrohini jhaОценок пока нет
- Operation ManagementДокумент8 страницOperation ManagementBhaavyn SutariaОценок пока нет
- Pogo Eyewear Business PlanДокумент18 страницPogo Eyewear Business Planmodernmagnate97% (35)
- Designing and Managing Channels and DistributionДокумент72 страницыDesigning and Managing Channels and Distributionbotolaik100% (2)
- Sales & Distribution ManagementДокумент48 страницSales & Distribution ManagementChirag JainОценок пока нет
- Pricing StrategyДокумент16 страницPricing Strategyatifatanvir1758Оценок пока нет
- Distribution ManagementДокумент20 страницDistribution ManagementMatsouka Kou100% (2)
- Modern Approaches To ManagementДокумент22 страницыModern Approaches To ManagementRunaway Shuji100% (1)
- Ch8 - Distribution Management and Marketing Mix ModДокумент34 страницыCh8 - Distribution Management and Marketing Mix Moddeepak vermaОценок пока нет
- Merchant Funded Loyalty WhitepaperДокумент10 страницMerchant Funded Loyalty WhitepaperbansalrohitОценок пока нет
- CH 15 Marketing ChannelsДокумент33 страницыCH 15 Marketing ChannelsBhanu GariaОценок пока нет
- Cafe Coffee DayДокумент52 страницыCafe Coffee DayMerwyn FernandesОценок пока нет
- 7 ElevenДокумент27 страниц7 ElevenAdnan Shah100% (1)
- The Growing Consumption of Bread and Baked Goods in IndonesiaДокумент44 страницыThe Growing Consumption of Bread and Baked Goods in IndonesiaRippie RifdahОценок пока нет
- Distribution Management and Marketing MixДокумент32 страницыDistribution Management and Marketing MixVikas100% (1)
- Learning Objectives: Marketing ChannelsДокумент36 страницLearning Objectives: Marketing ChannelsVikasОценок пока нет
- MARSMAN V First CoconutДокумент3 страницыMARSMAN V First CoconutKenneth DavidОценок пока нет
- United States International University - AfricaДокумент12 страницUnited States International University - Africacobbymark100% (1)
- Distribution - MMДокумент49 страницDistribution - MMRihanshu SinghalОценок пока нет
- Marketing Channel Supply Chain ManagementДокумент36 страницMarketing Channel Supply Chain ManagementCoolest CoolОценок пока нет
- Channels of DistributionДокумент32 страницыChannels of DistributionRanzel Erika Jan Francia100% (1)
- Marketing Channels: Delivering Customer ValueДокумент29 страницMarketing Channels: Delivering Customer ValueBachtiar ThyarОценок пока нет
- Unit 09 PlaceДокумент20 страницUnit 09 PlaceKhan AshfaqueОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 Marketing Channels To Create Value For CustomersДокумент40 страницChapter 10 Marketing Channels To Create Value For Customerssunchox123Оценок пока нет
- Channels of DistributionДокумент31 страницаChannels of DistributionBloomingdale UttaraОценок пока нет
- PrinciplesofMarketing 12 PlaceДокумент23 страницыPrinciplesofMarketing 12 PlaceHOSSAIN SAIFANОценок пока нет
- M R, W, L: Anaging Etailing Holesaling AND OgisticsДокумент34 страницыM R, W, L: Anaging Etailing Holesaling AND OgisticsTejas DesaiОценок пока нет
- Session 10 - Place DecisionsДокумент20 страницSession 10 - Place DecisionsEshan JainОценок пока нет
- ChannelДокумент57 страницChannelSahil M JohnОценок пока нет
- Supply Chains and The Value Delivery NetworkДокумент4 страницыSupply Chains and The Value Delivery NetworkJennyОценок пока нет
- Session7 - Channel ManagementДокумент38 страницSession7 - Channel ManagementMadhav VakhariaОценок пока нет
- Marketing Channels and Supply Chain Management: Principles of Marketing Philip Kotler, Gary ArmstrongДокумент25 страницMarketing Channels and Supply Chain Management: Principles of Marketing Philip Kotler, Gary ArmstrongShadman Sakib FahimОценок пока нет
- Marketing Channels and Supply Chain Management: A Global PerspectiveДокумент30 страницMarketing Channels and Supply Chain Management: A Global PerspectiveAzeem AhmedОценок пока нет
- Marketing Channels and Supply Chain Management: Chapter ObjectivesДокумент16 страницMarketing Channels and Supply Chain Management: Chapter ObjectivesAni SinghОценок пока нет
- 4-Channel ManagementДокумент41 страница4-Channel ManagementArunKumarОценок пока нет
- UNIT III - PlaceДокумент66 страницUNIT III - PlaceRevati RathodОценок пока нет
- 201 MM Unit 3-PlaceДокумент36 страниц201 MM Unit 3-PlaceAjay KareОценок пока нет
- What Major Types of Marketing Intermediaries Occupy This Sector?Документ5 страницWhat Major Types of Marketing Intermediaries Occupy This Sector?ankita_shreeramОценок пока нет
- 18.marketing ChannelsДокумент42 страницы18.marketing Channelsalmasy99Оценок пока нет
- Physical DistributionДокумент16 страницPhysical DistributionpapaiyajayОценок пока нет
- Managing Retailing Wholesaling and Market LogisticsДокумент20 страницManaging Retailing Wholesaling and Market Logisticsmido beveickОценок пока нет
- Managing Retailing, Wholesaling, and Market LogisticsДокумент20 страницManaging Retailing, Wholesaling, and Market Logisticsmido beveickОценок пока нет
- Place Aka "Distribution" "Marketing Channels"Документ42 страницыPlace Aka "Distribution" "Marketing Channels"时家欣Оценок пока нет
- Designing and Managing Value Networks and ChannelsДокумент17 страницDesigning and Managing Value Networks and ChannelspRiNcE DuDhAtRa100% (1)
- Marketing Channels and Supply Chain Management: A Global PerspectiveДокумент30 страницMarketing Channels and Supply Chain Management: A Global Perspectiveddaga_1Оценок пока нет
- Marketing Channels: Sobia Irum, PHD Management College of Business Administration University of BahrainДокумент65 страницMarketing Channels: Sobia Irum, PHD Management College of Business Administration University of BahrainYesfoo Al RiffaayОценок пока нет
- Marketing ChannelsДокумент40 страницMarketing ChannelsNeesha NazОценок пока нет
- Objective 4.08: Acquire Foundational Knowledge of Channel Management To Understand Its Role in MarketingДокумент29 страницObjective 4.08: Acquire Foundational Knowledge of Channel Management To Understand Its Role in MarketingYash AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Managing Integrated Marketing ChannelДокумент21 страницаManaging Integrated Marketing Channelade_k012Оценок пока нет
- Channel DecisionsДокумент30 страницChannel Decisionsuzmatabassum1996Оценок пока нет
- Chapter Eight ChannelДокумент22 страницыChapter Eight ChannelwaleОценок пока нет
- Marketing Channels and Supply Chain ManagementДокумент22 страницыMarketing Channels and Supply Chain ManagementNikunj SharmaОценок пока нет
- What Is Logistics Management?Документ383 страницыWhat Is Logistics Management?Shreya GoyalОценок пока нет
- Kotler 15Документ19 страницKotler 15Nafees Hasan ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Integration of Sales and Distribution Strategies Final 2003Документ24 страницыIntegration of Sales and Distribution Strategies Final 2003Sukesh Kumar50% (2)
- Slides Chapter 1,2 & 3Документ63 страницыSlides Chapter 1,2 & 3Moin UddinОценок пока нет
- BUS 311 Chapter 12Документ40 страницBUS 311 Chapter 12osmanincekara2002Оценок пока нет
- Marketing Channels and Supply Chain ManagementДокумент25 страницMarketing Channels and Supply Chain ManagementKushal LokeshОценок пока нет
- Marketing Indicator 3.05: Acquire Foundational Knowledge of Channel Management To Understand Its Role in MarketingДокумент29 страницMarketing Indicator 3.05: Acquire Foundational Knowledge of Channel Management To Understand Its Role in Marketingsanchita22Оценок пока нет
- Chapter - Five 5.3 PLACE /distributionДокумент18 страницChapter - Five 5.3 PLACE /distributionMasresha TasewОценок пока нет
- DistributionДокумент11 страницDistributionSHREYASH DESHPANDEОценок пока нет
- Chapter 17Документ16 страницChapter 17Rozan FarizqyОценок пока нет
- 11 Place & DIstribution DecisionsДокумент23 страницы11 Place & DIstribution DecisionsNitinKhareОценок пока нет
- Block B MP Week 4.2 Distribution TutenДокумент25 страницBlock B MP Week 4.2 Distribution Tutenyalan dunyaОценок пока нет
- Distribution Planning ControlДокумент54 страницыDistribution Planning ControlMir Mansoor Ali MagamiОценок пока нет
- Distribution Channels and Logistics ManagementДокумент41 страницаDistribution Channels and Logistics ManagementMdk blore100% (1)
- Marketing ChannelsДокумент37 страницMarketing ChannelsAnubhav SinghОценок пока нет
- Designing and Managing Integrated Marketing ChannelsДокумент50 страницDesigning and Managing Integrated Marketing ChannelsanuradhakampliОценок пока нет
- Place: Distribution Strategies: Principles of MarketingДокумент14 страницPlace: Distribution Strategies: Principles of Marketing4 กานติมา วงค์เปี้ยОценок пока нет
- Business Game ScheduleДокумент2 страницыBusiness Game ScheduleRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- APC 309 ABC Mock Exam Solution A and BДокумент3 страницыAPC 309 ABC Mock Exam Solution A and BRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- NX0472 / LD0472: Developing Global Management Competencies I (BI Strand)Документ5 страницNX0472 / LD0472: Developing Global Management Competencies I (BI Strand)Runaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Assignment MAAR 1Документ28 страницAssignment MAAR 1Runaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Financial Analysis For Boa CoffeeДокумент2 страницыFinancial Analysis For Boa CoffeeRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Company Profile of PumaДокумент1 страницаCompany Profile of PumaRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- The Main Barrier of Marketing Plan For Cie: Name: Tran Anh Dung (Jay) Lecturer: Mr. Frederick IgnacioДокумент23 страницыThe Main Barrier of Marketing Plan For Cie: Name: Tran Anh Dung (Jay) Lecturer: Mr. Frederick IgnacioRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Discuss Definitions of Quality in Terms of Business and Services ProvisionДокумент10 страниц1.1 Discuss Definitions of Quality in Terms of Business and Services ProvisionRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Assignment Guiide OBДокумент5 страницAssignment Guiide OBRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Individual Behavior at WorkДокумент22 страницыIndividual Behavior at WorkRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- The Relationship Between Educational Attainment and Professional Attainment in DanangДокумент3 страницыThe Relationship Between Educational Attainment and Professional Attainment in DanangRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Tran Anh Dung: ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыTran Anh Dung: ObjectivesRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Event Date Lunch Set Menu 11 December 2014: Time Venue Number of Guest 10:00 Lemongrass Rest 43 Studen + 5 Staff MemberДокумент3 страницыEvent Date Lunch Set Menu 11 December 2014: Time Venue Number of Guest 10:00 Lemongrass Rest 43 Studen + 5 Staff MemberRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
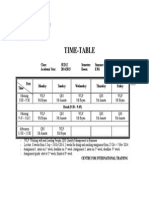
- Time-Table: Class: SUD12 Semester: Summer (From 1 Sep - 7 Nov 2014) Academic Year: 2014/2015 Room: E301Документ1 страницаTime-Table: Class: SUD12 Semester: Summer (From 1 Sep - 7 Nov 2014) Academic Year: 2014/2015 Room: E301Runaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Define QualityДокумент14 страницDefine QualityRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Assignment TQM 1Документ13 страницAssignment TQM 1Runaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Similarities N Different Deming Juran N CrosbyДокумент4 страницыSimilarities N Different Deming Juran N CrosbyRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Danang University of Economics Btec HND in Business (Management)Документ8 страницDanang University of Economics Btec HND in Business (Management)Runaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Danang University of Economics Btec HND in Business (Management)Документ7 страницDanang University of Economics Btec HND in Business (Management)Runaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Arvo Li Incident ReportsДокумент10 страницArvo Li Incident ReportsRunaway ShujiОценок пока нет
- Apna BazarДокумент14 страницApna BazarkishkashОценок пока нет
- Case ZaraДокумент13 страницCase ZaraVipul Bharadwaj100% (1)
- Republishing and Book Expo Display Proposal For Mrs. Victoria Kapuni WordДокумент4 страницыRepublishing and Book Expo Display Proposal For Mrs. Victoria Kapuni WordArnotte MarohombsarОценок пока нет
- Google Shopping Free Visibility EbookДокумент25 страницGoogle Shopping Free Visibility EbookSilvian NaneaОценок пока нет
- B2B Marketing Unit 1Документ38 страницB2B Marketing Unit 1K Memcha SinghaОценок пока нет
- Evolve Digital Level 2A Vocabulary ListsДокумент14 страницEvolve Digital Level 2A Vocabulary ListsKarla ArmasОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTIONДокумент13 страницINTRODUCTIONIrfan KhaziОценок пока нет
- 4 Mapping The Spatiality of Informal Street VendingДокумент21 страница4 Mapping The Spatiality of Informal Street VendingHEENNAH IA SIMBULANОценок пока нет
- The Markstrat Challenge: - Introduction IДокумент36 страницThe Markstrat Challenge: - Introduction ITaanОценок пока нет
- Donald F. Blankertz - Cases and Problems in Marketing ResearchДокумент360 страницDonald F. Blankertz - Cases and Problems in Marketing Researchalmar_dgz_268340Оценок пока нет
- Companies: Reliance RetailДокумент2 страницыCompanies: Reliance RetailPallavi PrakashОценок пока нет
- Report On SquireДокумент21 страницаReport On SquireNiladri HasanОценок пока нет
- Traffic Restraint and Retail VitalityДокумент4 страницыTraffic Restraint and Retail VitalityparkingeconomicsОценок пока нет
- Vice President Apparel Design in NYC NY Resume Susan GrantДокумент3 страницыVice President Apparel Design in NYC NY Resume Susan GrantSusanGrant1Оценок пока нет
- Push and Pull Strategy in Supply Chain Management - A Comprehensive GuideДокумент3 страницыPush and Pull Strategy in Supply Chain Management - A Comprehensive GuideSakshi ThapliyalОценок пока нет
- Localization Strategy in Vietnamese Market: The Cases ofДокумент25 страницLocalization Strategy in Vietnamese Market: The Cases ofHồng Thy NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Welcome To The World ofДокумент10 страницWelcome To The World ofAniket MehareОценок пока нет
- Coatings SA - December - 19Документ36 страницCoatings SA - December - 19Long An ĐỗОценок пока нет
- Groceries Project by Saurav FinalДокумент49 страницGroceries Project by Saurav FinalMuskan GuptaОценок пока нет
- TOLEDO Business Model Upd. 1Документ12 страницTOLEDO Business Model Upd. 1Iif SyarifОценок пока нет