Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
EOQ With Discounts
Загружено:
prashullpИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EOQ With Discounts
Загружено:
prashullpАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EOQ WITH QUANTITY
DISCOUNTS
Objectives
To understand what quantity discounts are
To determine the optimal order quantity when
quantity discounts are present.
When carrying costs are constant
When carrying costs vary according to the
purchase price
Quantity discounts are price reductions for large
orders offered to customers to induce them to buy in
large quantities.
Potential benefits
a. reduced purchase price
b. fewer orders ordering cost decreases
Potential drawbacks
a. Increase in carrying costs due to higher
inventories
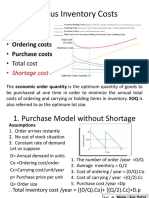
Minimize total cost, where the total cost is the sum
of carrying cost, ordering cost, and purchasing.
Total Cost,
K = Carrying Cost + Ordering Cost +
Purchasing Cost
= (Q/2)Cc + (D/Q)Co + Cp
Two general cases of the model
Carrying costs are constant (e.g. 2 $/unit)
Carrying costs are stated as a percentage of
purchase price ( e/g 20 % of unit price)
Carrying costs are constant
All curves have the same EOQ
c b, a, C *
2
c
Q
Co
Q
D
Ka
Kb
Kc
Quantity
C
o
s
t
Procedure for calculating EOQ
Compute the common EOQ.
Only one of the unit prices will have the EOQ
in its feasible range since the range do not
overlap/ Identify that range.
If the feasible EOQ is on the lowest price range,
that is the optimal order quantity.
If the EOQ is in any other range, compute the
total cost for the EOQ and for the price breaks of
all lower unit costs. Compare the total cost. The
quntity when the total cost is minimum is the
optimal order quantity.
Example
The maintenance department of
a large hospital uses about 816
cases of liquid cleanser
annually. Ordering cost is 12$,
carrying costs are 4$/cases, and
the price schedule is as follows:
Determine the optimal order
quantity and the total cost.
Range Price
1 to 49 $20
50 to 79 $18
80 to 99 17
100 16
Compute the common EOQ
Qo =
=
= 70 cases
The 70 cases can be bought at 18 $/case,
since 70 falls in the range of 50-79 cases.
(2DCo)/Cc
)}/4 {2(816)(12
The total cost to purchase 816 cases/ a year at
a rate of 70 cases/order, will be:
TC 70 = (D/Q) Co + (Q/2)Cc + Cp
= (816/70)12 + (70/12)4 + 81618
= 14 968 $
Since the cost ranges exist, each must be
checked against the minimum cost generated
by 70 cases at 18 $ each. In order to buy at
17$/case, at least 80 cases must be
purchased. The total cost at 80 cases will be
TC 80 = (816/80)12 + (80/2)4 + 81617
= 14 154 $
TC100 = (816/100)12 + (100/2)4 + 81616
= 13 354 $
Since 100 cases per order yields the lowest
total cost, 100 cases is the overall optimal
order quantity
Carrying costs are stated as a
percentage of purchase price
each curve will have a different EOQ
EOQ
a
EOQ
b
EOQ
c
Ka
Kb
Kc
CCa
CCb
carrying cost
Procedure for calculating EOQ
Beginning with the lowest price, compute
the EOQ for each price range until a
feasible EOQ is found (i.e. until an EOQ is
found that falls in the quantity range
for its price)
If the EOQ for the lowest price is feasible, it
is the optimal order quantity. If the
EOQ is not the lowest price range, compare
the total cost at the price break for all lower
prices with the total cost of the largest
feasible EOQ. The quantity that yields the
lowest total cost is the optimum quantity.
Example
Surge Electric uses 4000
toggle switches a year.
Switches are priced as
follows:
Range Unit Price
1-499 0.90 $
500-999 0.85
1000+ 0.82
It costs approximately 18 $ to prepare an
order and receive it, and carrying costs are
18% of the purchase price per unit on an
annual basis. Determine the optimal order
quantity and the annual cost.
Find the EOQ for each price, starting with the
lowest price, until a feasible EOQ is located
Cc = 0.18(0.82)=0.1476
EOQ (0.82) =
=
= 988 switches
(2DCo)/Cc
6 18)}/0.147 {2(4000
Since 988 switches will cost 0.85 $ each
rather than 0.82 each, 988 is not feasible
EOQ. Next try 0.85 per unit.
Cc = 0.18(0.85)=0.1530
EOQ (0.85) =
= 970 switches
This is feasible; 970 falls in the 0.85 $ ranges
of 500-999.
153 . 0 / )} 18 4000 ( 2 {
TC 970 = (4000/970) 18 + (970/2) 0.153 +
0.85(4000)
= 3 548 $
TC 1000 = (4000/1000) 18 + (1000/2)
0.1476 + 0.82(4000)
= 3 426 $
Thus the minimum-cost order size is 1000
switches.
Вам также может понравиться
- Various Inventory Costs: - Holding / - Ordering Costs - Purchase Costs - Total CostДокумент28 страницVarious Inventory Costs: - Holding / - Ordering Costs - Purchase Costs - Total CostAditya Dashputre100% (2)
- June 2013 Inventory ManagementДокумент68 страницJune 2013 Inventory ManagementShasank JalanОценок пока нет
- Inventory Management (2021)Документ8 страницInventory Management (2021)JustyОценок пока нет
- Deterministic Inventory Models: TVC Ordering Cost + Carrying (Holding Cost)Документ15 страницDeterministic Inventory Models: TVC Ordering Cost + Carrying (Holding Cost)Tsegaye DebeloОценок пока нет
- Marginal Costing - Brief Cases and Solutions PDFДокумент7 страницMarginal Costing - Brief Cases and Solutions PDFKaranSinghОценок пока нет
- Sample Test Questions For EOQДокумент5 страницSample Test Questions For EOQSharina Mhyca SamonteОценок пока нет
- FFM Updated AnswersДокумент79 страницFFM Updated AnswersSrikrishnan SОценок пока нет
- NB: When The Holding Cost Per Unit Is Not Given, We Usually Take It To Be A Percentage of Purchase Price (C) Per UnitДокумент3 страницыNB: When The Holding Cost Per Unit Is Not Given, We Usually Take It To Be A Percentage of Purchase Price (C) Per UnitVans Tee100% (1)
- Managerial Accounting Sample Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент17 страницManagerial Accounting Sample Multiple Choice Questionsjen1861280% (5)
- Basic EOQ Model: Trial and Error MethodДокумент7 страницBasic EOQ Model: Trial and Error MethodROCKYОценок пока нет
- Cost Accounting 16uco513 K1-Level Questions UNIT-1Документ27 страницCost Accounting 16uco513 K1-Level Questions UNIT-1Abirami santhanamОценок пока нет
- Process Costing: Faculty: Zaira AneesДокумент76 страницProcess Costing: Faculty: Zaira AneesAnas4253Оценок пока нет
- Questions of CGSДокумент4 страницыQuestions of CGSaneel72Оценок пока нет
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) : Cost AccountingДокумент4 страницыEconomic Order Quantity (EOQ) : Cost AccountingGudeta GelanaОценок пока нет
- EOQ With Quantity DiscountsДокумент23 страницыEOQ With Quantity DiscountsCarey HillОценок пока нет
- Activity Based CostingДокумент2 страницыActivity Based CostingVivek KheparОценок пока нет
- Basic Cost Management ConceptsДокумент15 страницBasic Cost Management ConceptsKatCaldwell100% (1)
- 1 Eoq PDFДокумент12 страниц1 Eoq PDFLyber PereiraОценок пока нет
- MCQ Test 1 On Accounting ConceptsДокумент8 страницMCQ Test 1 On Accounting ConceptsFreedNathanОценок пока нет
- Cost and Management NotesДокумент279 страницCost and Management NotesRamchandra MurthyОценок пока нет
- MCQs CH 15 MicroДокумент6 страницMCQs CH 15 MicroishtiaqlodhranОценок пока нет
- Inventory Management QuizДокумент2 страницыInventory Management QuizPranav GoyalОценок пока нет
- 6.2 Standard Costing & Variance Anlysis: Cost Accounting 341Документ25 страниц6.2 Standard Costing & Variance Anlysis: Cost Accounting 341sadhaya rajanОценок пока нет
- Quantity Discounts For The Eoq ModelДокумент13 страницQuantity Discounts For The Eoq Modelnatalie clyde matesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Process Costing Average Fifo CostingДокумент22 страницыChapter 5 Process Costing Average Fifo CostingMosharraf Hussain100% (1)
- Practice of Cost Volume Profit Breakeven AnalysisДокумент4 страницыPractice of Cost Volume Profit Breakeven AnalysisHafiz Abdulwahab100% (1)
- Exercise 1 - Decision Theory PDFДокумент5 страницExercise 1 - Decision Theory PDFKaran Kakkar0% (1)
- Inventory Valuation ProblemsДокумент7 страницInventory Valuation ProblemsRahul SinghОценок пока нет
- Assignment ModelДокумент9 страницAssignment ModelHamzaОценок пока нет
- ADL 56 Cost & Management Accounting 2V3Документ20 страницADL 56 Cost & Management Accounting 2V3Deepesh100% (1)
- Cost Accounting Sample Question Paper (100 Marks & 75 MarksДокумент5 страницCost Accounting Sample Question Paper (100 Marks & 75 MarksVishnuNadar50% (2)
- Job and Batch CostingДокумент7 страницJob and Batch CostingDeepak R GoradОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 3 Transportatiofor Night ClassДокумент10 страницCHAPTER 3 Transportatiofor Night ClassHACHALU FAYE100% (1)
- Multiple Choice: Circle One Answer For Each Question. Transfer All You Answer To The Attached Answer Sheet and Email Back To Me On April 16Документ3 страницыMultiple Choice: Circle One Answer For Each Question. Transfer All You Answer To The Attached Answer Sheet and Email Back To Me On April 16Joshua RamirezОценок пока нет
- Chapter 03 TP EndДокумент43 страницыChapter 03 TP EndMesfin MekuriaОценок пока нет
- Strategic Cost ManagementДокумент5 страницStrategic Cost ManagementBharat BhojwaniОценок пока нет
- Ratio Analysis: Profitability RatiosДокумент10 страницRatio Analysis: Profitability RatiosREHANRAJОценок пока нет
- Cost & Management Accounting - MGT402 Quiz 3Документ34 страницыCost & Management Accounting - MGT402 Quiz 3JocyReyes100% (1)
- Relevant CostДокумент22 страницыRelevant Costkhawajafzal100% (2)
- MGT705 - Advanced Cost and Management Accounting Midterm 2013Документ1 страницаMGT705 - Advanced Cost and Management Accounting Midterm 2013sweet haniaОценок пока нет
- Sample Level 2 Operations Management ExamДокумент23 страницыSample Level 2 Operations Management ExamAnonymous d6Etxrtb100% (3)
- Aggregate Production PlanningДокумент110 страницAggregate Production Planningzakria100100Оценок пока нет
- Question Bank - Aggregate PlanningДокумент6 страницQuestion Bank - Aggregate Planningm3gp13 yo100% (1)
- Chap 13 Inventory ManagementДокумент43 страницыChap 13 Inventory ManagementAcyslz50% (2)
- InventoryДокумент46 страницInventoryAnkit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Seminar 15 - Life Cycle Costing (Questions)Документ3 страницыSeminar 15 - Life Cycle Costing (Questions)Asfa ahmedОценок пока нет
- Overheads: Faculty: Zaira AneesДокумент59 страницOverheads: Faculty: Zaira AneesVishal MalhiОценок пока нет
- A Numerical Example of Target and Lifecycle CostingДокумент2 страницыA Numerical Example of Target and Lifecycle CostingAtulSinghОценок пока нет
- Inventory ManagementДокумент27 страницInventory ManagementsaloniОценок пока нет
- Brkeven Ex2 PDFДокумент1 страницаBrkeven Ex2 PDFSsemakula Frank0% (1)
- LKAS 19 2021 UploadДокумент31 страницаLKAS 19 2021 Uploadpriyantha dasanayake100% (1)
- Accounting CONCEPTS Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент7 страницAccounting CONCEPTS Multiple Choice Questionspatsjit50% (2)
- Budget AnswersДокумент6 страницBudget AnswersSushant MaskeyОценок пока нет
- 4 5931788210203003021Документ139 страниц4 5931788210203003021Issa Boy100% (1)
- Managerial Accounting SolutionДокумент18 страницManagerial Accounting Solutionfarizimran100% (1)
- Flexible Budget Examples Chapter 18Документ9 страницFlexible Budget Examples Chapter 18Surbhi JainОценок пока нет
- Appraising A Project by Discounting and Non-Discounting CriteriaДокумент55 страницAppraising A Project by Discounting and Non-Discounting CriteriaVaidyanathan Ravichandran100% (5)
- Container AccountsДокумент9 страницContainer AccountsNelsonMoseM100% (3)
- Quantity DiscountДокумент22 страницыQuantity Discountkevin royОценок пока нет
- Inventario Qd. Inglés.Документ28 страницInventario Qd. Inglés.Edgar VelozОценок пока нет
- SSRN Id2374621Документ8 страницSSRN Id2374621prashullpОценок пока нет
- Leader and Power PoliticsДокумент4 страницыLeader and Power PoliticsprashullpОценок пока нет
- Advertising Budgeting & Media Planning: Nijaz NДокумент13 страницAdvertising Budgeting & Media Planning: Nijaz NprashullpОценок пока нет
- Unit 6 Learning: ObjectivesДокумент17 страницUnit 6 Learning: ObjectivesSujy CauОценок пока нет
- Advertising EthicsДокумент4 страницыAdvertising EthicsprashullpОценок пока нет
- Ethical Issues in Functional AreasДокумент33 страницыEthical Issues in Functional Areasprashullp56% (9)
- Campaignplanning 111128112331 Phpapp01Документ26 страницCampaignplanning 111128112331 Phpapp01prashullpОценок пока нет
- Innovation, Creativity and EntrepreneurshipДокумент19 страницInnovation, Creativity and EntrepreneurshipprashullpОценок пока нет
- Business Plan TemplateДокумент9 страницBusiness Plan TemplatePalo Alto Software93% (61)
- Business QuizДокумент66 страницBusiness QuizS.S.RulesОценок пока нет
- Management FunctionsДокумент4 страницыManagement FunctionsprashullpОценок пока нет
- Business EnvironmentДокумент3 страницыBusiness EnvironmentprashullpОценок пока нет
- Cap PlanningДокумент17 страницCap PlanningprashullpОценок пока нет
- ForecastingДокумент16 страницForecastingprashullpОценок пока нет
- Set TheoryДокумент15 страницSet TheoryprashullpОценок пока нет
- Exercise: © Copy Right: Rai University 11.502 85Документ1 страницаExercise: © Copy Right: Rai University 11.502 85prashullpОценок пока нет
- Lecture 18Документ6 страницLecture 18prashullpОценок пока нет
- MatricesДокумент11 страницMatricesprashullpОценок пока нет
- 1 T&DДокумент61 страница1 T&DprashullpОценок пока нет
- Lecture 19Документ16 страницLecture 19prashullpОценок пока нет
- Time Series AnalysisДокумент13 страницTime Series AnalysisprashullpОценок пока нет
- Agreement: Offer + Acceptance Agreement. Every Promise or Set of Promises Forming Consideration or Each OtherДокумент18 страницAgreement: Offer + Acceptance Agreement. Every Promise or Set of Promises Forming Consideration or Each OtherprashullpОценок пока нет
- Chapter 01Документ12 страницChapter 01prashullpОценок пока нет
- Org DescriptionДокумент11 страницOrg DescriptionprashullpОценок пока нет
- CLIFFORD PROCTOR'S NURSERIES LIMITED - Company Accounts From Level BusinessДокумент7 страницCLIFFORD PROCTOR'S NURSERIES LIMITED - Company Accounts From Level BusinessLevel BusinessОценок пока нет
- 1 Why The Working Class?: Education For SocialistsДокумент32 страницы1 Why The Working Class?: Education For SocialistsDrew PoveyОценок пока нет
- "Why Some Firms Outperform Others" Resource Possession & Exploitation Resources & CapabilitiesДокумент1 страница"Why Some Firms Outperform Others" Resource Possession & Exploitation Resources & CapabilitiesJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Emerging Trends in Recruitment and Talent AcquisitionДокумент3 страницыEmerging Trends in Recruitment and Talent Acquisitionpallavi1289Оценок пока нет
- 40 Days of ProsperityДокумент97 страниц40 Days of ProsperityGodson100% (3)
- Sales Philippine Law (Articles 1458 - 1510)Документ17 страницSales Philippine Law (Articles 1458 - 1510)Ellen Glae Daquipil100% (4)
- Ebook PDF Data Mining For Business Analytics Concepts Techniques and Applications With Xlminer 3rd Edition PDFДокумент41 страницаEbook PDF Data Mining For Business Analytics Concepts Techniques and Applications With Xlminer 3rd Edition PDFpaula.stolte522100% (35)
- EBO 2 - Worldwide Energy Scenario - FINALДокумент15 страницEBO 2 - Worldwide Energy Scenario - FINALmodesto66Оценок пока нет
- Pietro Mascagni and His Operas (Review)Документ7 страницPietro Mascagni and His Operas (Review)Sonia DragosОценок пока нет
- 富達環球科技基金 說明Документ7 страниц富達環球科技基金 說明Terence LamОценок пока нет
- 10 Biggest LiesДокумент12 страниц10 Biggest LiesJose RenteriaОценок пока нет
- HR Practice NTPCДокумент10 страницHR Practice NTPCMayuri Das100% (3)
- Compiled Reports From 57th JCRC AY1314Документ44 страницыCompiled Reports From 57th JCRC AY1314keviiagm1314Оценок пока нет
- Laffitte 2nd Retrial Motion DeniedДокумент6 страницLaffitte 2nd Retrial Motion DeniedJoseph Erickson100% (1)
- PDFДокумент26 страницPDFAjay Kumar GantiОценок пока нет
- District MeetДокумент2 страницыDistrict MeetAllan Ragen WadiongОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Lesson 3 - The Human PersonДокумент5 страницIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Lesson 3 - The Human PersonPaolo AtienzaОценок пока нет
- Tin Industry in MalayaДокумент27 страницTin Industry in MalayaHijrah Hassan100% (1)
- AMGPricelistEN 09122022Документ1 страницаAMGPricelistEN 09122022nikdianaОценок пока нет
- Learn Hindi Through TamilДокумент3 страницыLearn Hindi Through TamilMohana Krishnan Janakiraman53% (15)
- Reviewer For Fundamentals of Accounting and Business ManagementДокумент4 страницыReviewer For Fundamentals of Accounting and Business ManagementAngelo PeraltaОценок пока нет
- Mauricio Hernandez Santiago, A206 706 192 (BIA April 22, 2016)Документ10 страницMauricio Hernandez Santiago, A206 706 192 (BIA April 22, 2016)Immigrant & Refugee Appellate Center, LLC100% (1)
- © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaДокумент24 страницы© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaPraveen Reddy DevanapalleОценок пока нет
- Zambia National Holdings Limtied and United National Independence Party (Unip) v. The Attorney-General (1994) S.J. 22 (S.C.) SupreДокумент12 страницZambia National Holdings Limtied and United National Independence Party (Unip) v. The Attorney-General (1994) S.J. 22 (S.C.) SupreNkumbu kaluweОценок пока нет
- The Dawn of IslamДокумент2 страницыThe Dawn of IslamtalhaОценок пока нет
- G12 Pol Sci Syllabus FinalДокумент8 страницG12 Pol Sci Syllabus FinalChrisjohn MatchaconОценок пока нет
- National Park PirinДокумент11 страницNational Park PirinTeodor KrustevОценок пока нет
- Assignment Accounting For BusinessДокумент5 страницAssignment Accounting For BusinessValencia CarolОценок пока нет
- Group 1 KULOT RevisedДокумент15 страницGroup 1 KULOT RevisedFranchesca Mekila TuradoОценок пока нет
- University of Education Lahore (Bank Road Campus)Документ11 страницUniversity of Education Lahore (Bank Road Campus)Shabana ArifОценок пока нет