Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Barefoot Walking
Загружено:
Jon Lewis0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
105 просмотров36 страницPresentation on barefoot walking
Оригинальное название
Barefoot walking
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документPresentation on barefoot walking
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
105 просмотров36 страницBarefoot Walking
Загружено:
Jon LewisPresentation on barefoot walking
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 36
By Jon Lewis
What do we need our feet to do?
1. Absorb shock during loading
2. Adjust to different terrains
3. Become a rigid lever capable of forward propulsion
FLEXIBLE
RIGID
Barefoot Biomechanics
The ankle
Made up of:
Tibia
Fibula
Talus
Hinge Joint
PF/DF
The ankle
+ External
Rotation
+ Internal
Rotation
Subtalar Joint
Formed by Talus and
calcaneus
3 articulating facets
Important for walking on
uneven ground
The Subtalar Joint
Triplanar Joint
Midtarsal Joint
Articulations:
Talonavicular Joint
calcaneocuboid joint
Movements:
Abd Add
Circumduction
PF DF
= PRO/SUPINATION
Ankle, subtalar, Midtarsal Complex
Mitred Hinge
Arches
Arches
Arches 3D
The foot is a tripod
Concave zone of
stability
Arches
Arches
Higher arches =
Bones lock together
Higher mechanical stability
Less stress on Tie beam
Tensile strength/rigid
Lower Arches =
Bones unlock
Less stable
Stress on tie beam
Shock absorbing
Function of the foot
Rigid lever for Propulsion Shock absorbant/flexible
Muscles acting on foot
Types: Intrinsic & Extrinsic
Function: Propulsion & alter
rigidity of arches during gait cycle
Force couples
Force Couples with opposing actions:
Tib Post : peroneus longus: rigidity transverse arch
Windlass Mechanism
Contraction EHL/EDL
Passive tension of
Flexors and P.Fascia
Sesmoids move
anteriory increasing
tension of FDL
Raise arch strong tie
beam - RIGID
Somatosensory Feedback
Gait Cycle
Pro Pronation Supination Sup
Shoes prevent all these mechanisms
from happening properly
Act as cast restricting foots natural biomechanics
Cushions feet dampening sensory feedback and reflex
activity
Alters biomechanics up kinetic chain
Results in:
Muscle/Bone atrophy
Faulty remodeling
Weakened biomechanics
Footwear Pathologies
Caused of foot pathologies:
Genetics
Footwear
Pathologies:
Metatarsalgia
Plantar Fasciitis
Hallux valgus
Heel Spurs
Neuromas
Achilles tendonitis
Shin Splints
PTFM probs
Hip/Back Pain
Footwear Design Characteristics
Heels
Shift centre of mass forward
Adjustments to keep
upright
Problems up kinetic chain
Heels
Unequal WB Heel
forefoot
Increased speed of Pro/PF
=> Shock absorbing (Slap)
Increased pressure on
forefoot
Shortening TA reducing
efficiency of propulsion
Heels
Toe Spring
Compensates for reduced sole flexibility at ball
Raised toes create a rocker
FHL, FDL inhibition
=> reduced propulsion, muscle atrophy
Shoe flexibility
Barefoot flexes at ball
All shoes flex 30-80% less
Sole creates flex resistance
=> fatigue
Stair climbing in elderly
Shoe Fit
Evidence that no footwear fits properly
Sizing system 630 years old
90% all shoes built snug (for support)
Restrictive toe box
Natural expansion of foot (pronation)
Poorly formed arches
Restricted Natural Biomechanics
SHOD
BAREFOOT
Great toe DF = Windlass
Mechanism
Lacing prevents arch raising
Stiff upper preventing hindfoot
supination
MT DFd relative to midfoot
Posterior sesamoids
Stress on Plantar tie beam
Great toe DF =
MT PF
Anterior sessamoids
Dome shaped arch
Free hindfoot
Tension on soft tissue
Arch support
Stabilise subtalar by
supporting arch
Shod vs unshod
No difference in
alignment except heel
height.
Cushioning
Dissapates vertical shock
=> 10% at best
Pronation control more important for shock absorption
Cushioning proprioception for pronation
Desensitisation
Cushioning Rigid soles Arch supports
Inhibits sensory stimulus needed to align bones for
stability
Chronicly unstable=>degen up Kintetic chain
Expensive protective running shoes => more injuries
Unshod population = No foot pathologies
Unhealthy Bone Remodelling
Wolfes law
Chinese foot binding
Restrictive toe boxes
Weakened bony arch structure
Childrens feet negatively affected by 6 yo
Physiotherapy
Rx for foot related pathologies
Cushioning
Not as effective as efficient pronation
Orthotics
Plantar contact angle
Short term
Exercise therapy
Not functional => low compliance
Concentrates on flexors
Вам также может понравиться
- Improving Ankle and Knee Joint Stability: Proprioceptive Balancefit Discs DrillsОт EverandImproving Ankle and Knee Joint Stability: Proprioceptive Balancefit Discs DrillsОценок пока нет
- Functional Movement Presentation-Jostone4Документ43 страницыFunctional Movement Presentation-Jostone4paulОценок пока нет
- The 7 Functional Movement Patterns For Strength TrainingДокумент19 страницThe 7 Functional Movement Patterns For Strength TrainingGalvez, Anya Faith Q.Оценок пока нет
- Liebenson - Functional Training Handbook ReviewДокумент3 страницыLiebenson - Functional Training Handbook ReviewJoaoPncs SilvaОценок пока нет
- Hamstring Injury - Diagnosis and Injury Management DiagnosisДокумент5 страницHamstring Injury - Diagnosis and Injury Management Diagnosisgemichan26Оценок пока нет
- Biomechanics of The Tennis Serve Implications For.4Документ6 страницBiomechanics of The Tennis Serve Implications For.4Paulo Tsuneta100% (1)
- Compton - PsoasДокумент25 страницCompton - PsoasiruizmolinaОценок пока нет
- Isokinetic Strength Training of Kinetic Chain Exercises of A Professional Tennis Player With A Minor Partial Internal Abdominal Oblique Muscle TearДокумент7 страницIsokinetic Strength Training of Kinetic Chain Exercises of A Professional Tennis Player With A Minor Partial Internal Abdominal Oblique Muscle Tear壮Оценок пока нет
- A Teaching Progression For Squatting Exercises.7Документ9 страницA Teaching Progression For Squatting Exercises.7Rhiannon CristinaОценок пока нет
- Posture EvaluationДокумент12 страницPosture EvaluationpaconscribdОценок пока нет
- Restricted Ankle Dorsiflexion: Methods To Assess and Improve Joint FunctionДокумент9 страницRestricted Ankle Dorsiflexion: Methods To Assess and Improve Joint FunctionJorge Lucas JimenezОценок пока нет
- Aquatic TherapyДокумент37 страницAquatic TherapyMustafa Mabrouk100% (1)
- Step 4 Your Body's PowerДокумент8 страницStep 4 Your Body's PowerhumpreydumpyОценок пока нет
- Core Stability Rippetoe PDFДокумент4 страницыCore Stability Rippetoe PDFSylvia GraceОценок пока нет
- NRCBooklet HealthyFeet v1 PDFДокумент72 страницыNRCBooklet HealthyFeet v1 PDFemilio_camacho_13Оценок пока нет
- Neuro-Developmental Clinical ObservationsДокумент2 страницыNeuro-Developmental Clinical ObservationsAmitesh NarayanОценок пока нет
- Gray Cook Self Limiting ExerciseДокумент7 страницGray Cook Self Limiting ExerciseWaldir Martins NetoОценок пока нет
- Lactic Acid and Exercise Performance - Culprit or FriendДокумент14 страницLactic Acid and Exercise Performance - Culprit or FriendFaris Nasir100% (1)
- Saving My Knee Guide by The Stone Clinic Copy (New)Документ11 страницSaving My Knee Guide by The Stone Clinic Copy (New)Aleksandra LSОценок пока нет
- Nutrition and Sports PerformanceДокумент29 страницNutrition and Sports PerformanceMomenHamedОценок пока нет
- The Strength Coachx27s Guide To Shoulder TrainingДокумент86 страницThe Strength Coachx27s Guide To Shoulder TrainingZhopa100% (1)
- Rehab of Patients With HemiplegiaДокумент2 страницыRehab of Patients With HemiplegiaMilijana D. DelevićОценок пока нет
- ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 Edition: Functional Programming For Stability-Mobility and MovementДокумент94 страницыACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 Edition: Functional Programming For Stability-Mobility and MovementManjunatha GayakwadОценок пока нет
- Mobility-WPS Office (Copy)Документ22 страницыMobility-WPS Office (Copy)Ghost GamerxОценок пока нет
- Fascia Book ReviewДокумент4 страницыFascia Book ReviewÁgnes LovasОценок пока нет
- Hydrotherapy Knee OA Exercise SheetДокумент6 страницHydrotherapy Knee OA Exercise SheetMuhammad Faishal Imam AfifОценок пока нет
- Reactive Wall Push-Up: ExecutionДокумент36 страницReactive Wall Push-Up: Executioncoach_noeОценок пока нет
- Power Plate PilatesДокумент4 страницыPower Plate PilateselenfelОценок пока нет
- Tennis Recovery Coaches BookletДокумент28 страницTennis Recovery Coaches BookletsharvinОценок пока нет
- Final Tspine EbookДокумент13 страницFinal Tspine EbookLuz Marina Castro Mora100% (1)
- Barefoot RunningДокумент43 страницыBarefoot Runningjigar00775100% (1)
- Strengthening Versus Stabilisation Exercise Programmes for Preventing and Reducing Low Back Pain in FemalesОт EverandStrengthening Versus Stabilisation Exercise Programmes for Preventing and Reducing Low Back Pain in FemalesОценок пока нет
- Proprioception in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. Part 2: Clinical Assessment and InterventionДокумент10 страницProprioception in Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. Part 2: Clinical Assessment and InterventionAlejandra VasquezОценок пока нет
- Fascia Training: Michol DalcourtДокумент65 страницFascia Training: Michol DalcourtSanket SawantОценок пока нет
- Hip Assessment Worksheet Page2Документ1 страницаHip Assessment Worksheet Page2David GoodwinОценок пока нет
- Effects of Open Kinetic Chain and Closed Kinetic Chain Exercises After Ligament Reconstruction-1Документ12 страницEffects of Open Kinetic Chain and Closed Kinetic Chain Exercises After Ligament Reconstruction-1vardhanrajharshОценок пока нет
- RTC ManualДокумент15 страницRTC Manualgleko1Оценок пока нет
- Step 3 Your Body's Power ZoneДокумент4 страницыStep 3 Your Body's Power ZonehumpreydumpyОценок пока нет
- Drills For A Beginner CoachДокумент2 страницыDrills For A Beginner Coachapi-443437521Оценок пока нет
- Tendon Problems in Athletic IndividualsДокумент15 страницTendon Problems in Athletic IndividualsMuhammadskОценок пока нет
- Nike Plus Run Club John Smith Traning PlanДокумент20 страницNike Plus Run Club John Smith Traning PlanxiaokiaОценок пока нет
- Common Posture Mistakes and Fixes - NHSДокумент1 страницаCommon Posture Mistakes and Fixes - NHSDiana MushtahaОценок пока нет
- Weight Training - Pre-Adolescent Strength Training - Just Do It!Документ4 страницыWeight Training - Pre-Adolescent Strength Training - Just Do It!João P. Tinoco MaiaОценок пока нет
- 2012 C Liebenson - Hip Mobility TrainingДокумент2 страницы2012 C Liebenson - Hip Mobility TrainingLuis VargasОценок пока нет
- My Teaching MetaphorДокумент2 страницыMy Teaching Metaphorapi-455489482Оценок пока нет
- Eric Hörst's Training For Climbing Program: Antagonist and Stabilizer Training Exercises Core Training ExerciseДокумент30 страницEric Hörst's Training For Climbing Program: Antagonist and Stabilizer Training Exercises Core Training ExerciseTodorОценок пока нет
- Worlds Greatest StretchДокумент1 страницаWorlds Greatest StretchRoberto HernandezОценок пока нет
- Hamstring Rehab: Program Objectives: 1. Photos Notes Photos NotesДокумент5 страницHamstring Rehab: Program Objectives: 1. Photos Notes Photos NotesSai Teja Reddy CherukuОценок пока нет
- Chondromalacia Patella RehabДокумент1 страницаChondromalacia Patella Rehabjntownsend3404Оценок пока нет
- First Aid For TennisДокумент27 страницFirst Aid For TennisAnonymous GJuRvp9A5TОценок пока нет
- Lumbar Core StrenghtДокумент8 страницLumbar Core StrenghtMattia BressanОценок пока нет
- A Novel Sensorimotor Movement and Walking Intervention To Improve Balance and Gait in WomenpdfДокумент6 страницA Novel Sensorimotor Movement and Walking Intervention To Improve Balance and Gait in WomenpdfCarmen LlerenasОценок пока нет
- 4 Essential Strategies For The Correction of Anterior Pelvic TiltДокумент10 страниц4 Essential Strategies For The Correction of Anterior Pelvic TiltAlexander NarváezОценок пока нет
- PilatesДокумент3 страницыPilatesJustina BatesОценок пока нет
- Coordination of Posture and MovementДокумент10 страницCoordination of Posture and MovementZsófia GörbeОценок пока нет
- Laterality in Sports: Theories and ApplicationsОт EverandLaterality in Sports: Theories and ApplicationsFlorian LoffingОценок пока нет
- Lewis ManagementfullДокумент7 страницLewis ManagementfullJon LewisОценок пока нет
- The ChairДокумент3 страницыThe ChairJon LewisОценок пока нет
- The ChairДокумент3 страницыThe ChairJon LewisОценок пока нет
- Basic Routine InfographicДокумент1 страницаBasic Routine InfographicJon LewisОценок пока нет
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2017Документ31 страницаAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2017Phoenix royale100% (1)
- OpticathДокумент28 страницOpticathFrancesca MazzolaniОценок пока нет
- Dinosaur Manual 1.3 - The HomebreweryДокумент33 страницыDinosaur Manual 1.3 - The HomebreweryNicholas WrightОценок пока нет
- The Jungle Excerpts 1 and 2Документ3 страницыThe Jungle Excerpts 1 and 2api-325596297Оценок пока нет
- PE FormДокумент1 страницаPE Formannalou-mascarinas-1701Оценок пока нет
- Yoon-Suin The Purple LandДокумент324 страницыYoon-Suin The Purple LandРелигия Ружья и Коробки100% (3)
- Avaliação Bimestral 9º Ano 2º BimestreДокумент5 страницAvaliação Bimestral 9º Ano 2º BimestreJuliane GuedesОценок пока нет
- Apeshit - Carlton Mellick IIIДокумент320 страницApeshit - Carlton Mellick IIIVíctor Santana50% (2)
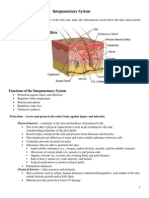
- Integumentary System HandoutДокумент18 страницIntegumentary System HandoutbarchlrОценок пока нет
- Tooth-Support Over Dentures: An Approach To Preventive ProsthodonticsДокумент5 страницTooth-Support Over Dentures: An Approach To Preventive ProsthodonticsAdvanced Research PublicationsОценок пока нет
- 1 TISSUES Online Teaching - REVISED 2021 AnaphyДокумент38 страниц1 TISSUES Online Teaching - REVISED 2021 AnaphySerendipity ParkОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Translocation in The GutДокумент29 страницBacterial Translocation in The GutdonkeyendutОценок пока нет
- Osce EmergenciesjДокумент31 страницаOsce EmergenciesjTess WilliamsОценок пока нет
- L10 ToleranceДокумент19 страницL10 Tolerancesara garciaОценок пока нет
- Thirty Minute Therapy For Anxiety WorksheetsДокумент37 страницThirty Minute Therapy For Anxiety WorksheetsAnonymous Ax12P2srОценок пока нет
- Feather Follicle Cyst in ChickensДокумент4 страницыFeather Follicle Cyst in ChickensShah NawazОценок пока нет
- Stuart Little 1 ScriptДокумент40 страницStuart Little 1 Scriptazlanamirul100% (1)
- Kamus ManusiaДокумент822 страницыKamus ManusiaAhmad Abdullah100% (1)
- Mahasiswa STIKES RS. Baptis KediriДокумент8 страницMahasiswa STIKES RS. Baptis Kedirigia hisbian ladzianiОценок пока нет
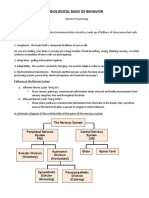
- Biological Basis of BehaviorДокумент6 страницBiological Basis of BehaviorLyanna MormontОценок пока нет
- Small IntestineДокумент2 страницыSmall Intestineiron100% (1)
- Natural Selection Lab-Phet Simulation Astrid 10DДокумент8 страницNatural Selection Lab-Phet Simulation Astrid 10DMary Fatima LlanesОценок пока нет
- Prosthodontics IIIДокумент8 страницProsthodontics IIICyril Almario CunananОценок пока нет
- Artritis Gout in Aviation MedicineДокумент22 страницыArtritis Gout in Aviation MedicineBuyungОценок пока нет
- QC ABO RH BloodДокумент62 страницыQC ABO RH BloodrhoderickОценок пока нет
- ST Louis Cty FairДокумент36 страницST Louis Cty FairGarrett RossОценок пока нет
- Paragonimus WestermaniДокумент3 страницыParagonimus WestermaniHanisha EricaОценок пока нет
- Topographic Anatomy of Abdominal OrgansДокумент18 страницTopographic Anatomy of Abdominal OrgansHasnain IdreesОценок пока нет
- Wiki Origin of The Domestic DogДокумент38 страницWiki Origin of The Domestic DogDe-hai CayolemОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Medicine 1 50Документ33 страницыRespiratory Medicine 1 50Ahmed Kh. Abu WardaОценок пока нет