Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Muscular Tissue
Загружено:
Steph Vee0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
88 просмотров49 страницThis document describes the three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, forming the bulk of the body's musculature. It contains repeating structural units called sarcomeres composed of actin and myosin filaments. Cardiac muscle is striated and involuntary, found only in the heart. Its cells are joined end to end by intercalated discs. Smooth muscle is non-striated and involuntary, capable of slow, sustained contractions. It lines organs like the digestive tract and blood vessels.
Исходное описание:
Muscular Tissue
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document describes the three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, forming the bulk of the body's musculature. It contains repeating structural units called sarcomeres composed of actin and myosin filaments. Cardiac muscle is striated and involuntary, found only in the heart. Its cells are joined end to end by intercalated discs. Smooth muscle is non-striated and involuntary, capable of slow, sustained contractions. It lines organs like the digestive tract and blood vessels.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
88 просмотров49 страницMuscular Tissue
Загружено:
Steph VeeThis document describes the three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated and voluntary, forming the bulk of the body's musculature. It contains repeating structural units called sarcomeres composed of actin and myosin filaments. Cardiac muscle is striated and involuntary, found only in the heart. Its cells are joined end to end by intercalated discs. Smooth muscle is non-striated and involuntary, capable of slow, sustained contractions. It lines organs like the digestive tract and blood vessels.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 49
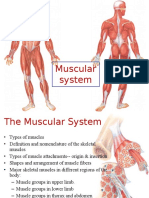
MUSCULAR TISSUE
General Characteristics of Muscle
Fiber
Elongated and oriented parallel to its direction of
action
Cell membrane is known as sarcolemma
Nucleus is elongated and is parallel to the long
axis of the muscle fiber
Cytoplasm is known as sarcoplasm
strongly acidophilic due to its myoglobin pigment
Contractility is its fundamental property
contraction generates heat
Functions of Muscles
Movements
Locomotion
Maintenance of body posture
Functional Classification
Voluntary
under the control of the CNS
Involuntary
contract in response to stimulation of the
autonomic nervous system
Structural Classification
Striated
presence of transverse or cross-striations
known as dark and light bands
Smooth
no cross-striations but with longitudinal
striations
Histological Classification
Skeletal muscles
Cardiac muscles
Smooth muscles
Skeletal Muscle
Striated and voluntary
Forms the main bulk of the body
musculature
Generally attached to the bone except
for the intrinsic muscles of the tongue,
upper esophagus and some of the facial
expression muscles
Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Long cylindrical and multinucleated cells
10-100 u
Myoblasts; satellite cells
Muscle fibers do not branch
On cross-section
fibers appear almost equal in size
nuclei are located at the periphery or
beneath the sarcolemma and may be more
than 2
Skeletal Muscle
Connective Tissue Covering
Epimysium
the dense CT surrounding the whole muscle
Perimysium
the thin septa that extend to surround each
fascicle
Endomysium
the delicate reticulum surrounding individual fibers
Skeletal Muscle Fiber
Fine longitudinal striations and cross-
striations are detectable and both are due to
the arrangement of myofibril
Longitudinal sections show heavily stained
dark bands alternating with relatively pale
bands are seen
Dark bands are designated A-bands (myosin)
H band
Lighter staining bands are I-bands (actin)
Z line
Sarcomere
Structural and functional unit of the
skeletal muscle
The segments of myofibrils between
successive Z-lines
Includes an A-band and half of the 2
contiguous I-bands
Actin (thin) myofilaments
free ends are attached to the Z-line, then
towards the A-band up to the edge of the
H-zone
Myosin (thick) myofilaments
occupy the entire A-band
Actin (thin) myofilament
Composed of F-actin, tropomyosin and
troponin complex (TnT, TnC, TnI)
Attached to the -actinin of the Z disc
Myosin (thick) myofilaments
Bound to proteins of M line and to the Z
disc by a large protein called titin (with
spring-like domains)
Myosin (thick) myofilaments
Consists of many myosin bundled together
along their rod-like tails with their heads
exposed and directed towards thin
filaments
Bound to proteins of M line and to the Z
disc by a large protein called titin (with
spring-like domains)
Sliding Filament Mechanism
Actin filaments slide past the myosin
filaments towards the center of the
sarcomere
H zone becomes narrow and may be
obliterated
I-band also becomes narrow
A-band remains constant during
relaxation and contraction
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Corresponds to the endoplasmic reticulum of
other cell types
Consists of membrane-bound sarcotubules
that forms a canalicular network around each
myofibril
Devoid of ribosomes
Site of sequestration of calcium during muscle
relaxation and for release into the sarcoplasm
of free calcium ions that trigger contraction in
response to a nerve impulse
Types Of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
Type I or slow, red oxidative fibers
Type IIa or fast, intermediate oxidative-
glycolytic fibers
Type IIb or fast, white glycolytic fibers
Types Of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
Type I or slow, red oxidative fibers
Many mitochondria; abundant myoglobin
Oxidative phosphorylation of fatty acids
For slow, continuous contraction for
prolonged periods such as postural muscles
at the back
Types Of Skeletal Muscle Fibers
Type IIa or fast, intermediate oxidative-
glycolytic fibers
Many mitochondria, myoglobin and
glycogen
Both oxidative and anaerobic glycolysis
For rapid contraction and short burst of
activity such as in athletes
Cardiac Muscles
Striated and involuntary
Thickest layer of the heart, the myocardium
Branching and anastomosing fiber
Generally have single nucleus per cell
Ovoid nucleus
nucleus are centrally located unlike the skeletal
muscle
Cross-section show moderate variation in the
size of muscle fibers
Cardiac Muscles
Each cell is joined end to end by a
surface specialization called intercalated
discs
Intercalated discs functions
maintain firm cohesion of successive
cellular units of the myocardium
transmits the pull of one contractile unit to
the next cellular unit along the long axis of
the myofibrils
Cardiac Muscles
Fine longitudinal striations and transverse
striations are also found
Sarcomere is also the structural and
functional unit
The component fibers have inherent
automicity and rhythmicity
Myofibrils closely resemble those of the
skeletal muscle
Sarcoplasmic reticulum is present but not as
highly developed as skeletal muscle
Purkinje Myocytes
Modified cardiac muscle fibers that
are specialized for impulse conduction
Located in the
Sinoatrial node at the junction of the
superior vena cava with the right atrium
Atrioventricular node at the lower part of
the interatrial septum
Internodal tracts and bundle of His
Smooth Muscle
Non-striated and involuntary
Capable of slow, sustained, resistant to
fatigue contraction
Muscle fiber is the structural and
functional unit
Smooth Muscle Fiber
Fusiform or spindle-shaped
Elongated nucleus situated in their
widest central portion
Vary in their length in the different
organs (20 u 500 u)
Smooth Muscle Fiber
When in bundles or in extensive layers
individual fibers are off set such that the
wide portion of the cells are adjacent to
the thin tapering end of neighboring cells
So in transverse sections
smooth muscle appear as a mosaic of
irregular polygons of varying sizes
with nuclei found only in larger cross-
sections
Smooth Muscle Fiber
3 kinds of filaments
thin actin filaments, 4-8 nm in diameter
F-actin and calmodulin insert into dense bodies
(contain -actinin)
thicker myosin filaments, 15 nm
intermediate filaments, 10 nm, generally
are desmin
Smooth Muscle Fiber
Rudimentary sarcoplasmic reticulum
T tubules are absent
During contraction the borders of the
cell become scalloped and the nucleus
distorted
Location of Smooth Muscles
Walls of the digestive tract from the middle of the
esophagus to the inner anal sphincter
Walls of the respiratory tract from the trachea to the
alveolar ducts
Walls of blood vessels
Walls of ducts of glands
Arrector pili muscle found in the hair bulb of skin
Areola of mammary glands
Subcutaneous tissue of the scrotum
Urinary bladder
Uterus
end
Вам также может понравиться
- Classification of MusclesДокумент30 страницClassification of MusclesAreej SadruddinОценок пока нет
- Muscle Tissue OutlineДокумент4 страницыMuscle Tissue OutlinePeachy PieОценок пока нет
- Muscle PhysiologyДокумент50 страницMuscle PhysiologyJoyce Adjei-boateng100% (1)
- Chapter 9 - Muscular System: Three Types of Muscle TissuesДокумент73 страницыChapter 9 - Muscular System: Three Types of Muscle TissuesRafie HusniОценок пока нет
- 3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiДокумент19 страниц3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiОценок пока нет
- NeoplasiaДокумент21 страницаNeoplasiabpt2Оценок пока нет
- Tissues 4Документ65 страницTissues 4marianisie448100% (3)
- Integumentary System: Functions of SkinДокумент7 страницIntegumentary System: Functions of SkinSoniyaJI84Оценок пока нет
- Bone Physiology: By: Sandesh. A. PДокумент75 страницBone Physiology: By: Sandesh. A. PAnalhaq ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Anatomy 3. Semester TestsДокумент19 страницAnatomy 3. Semester TestsTamil IniyanОценок пока нет
- Cardiac OutputДокумент31 страницаCardiac OutputanojОценок пока нет
- 1-Bones of The Upper Limb Final-2Документ18 страниц1-Bones of The Upper Limb Final-2DrVasu Mudiraj100% (1)
- Histology Notes 2Документ13 страницHistology Notes 2Lukas BüchlerОценок пока нет
- Anatomy & Physiology Unit 1Документ29 страницAnatomy & Physiology Unit 1Priyanjali SainiОценок пока нет
- Development of Branchial ArchesДокумент4 страницыDevelopment of Branchial ArchesFidz Lianko100% (1)
- 2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inДокумент19 страниц2.1 (B) - Role of Muscles, Ligaments & Tendons inliefeng81100% (1)
- Development of HeartДокумент15 страницDevelopment of Heartash ashОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System: Na ShaoДокумент79 страницThe Nervous System: Na ShaoArvindhanОценок пока нет
- 11-Acid-Base BalanceДокумент28 страниц11-Acid-Base BalanceKathlene BarasiОценок пока нет
- Histology and Physiology of Bones: OsteonДокумент54 страницыHistology and Physiology of Bones: OsteonAnwar815100% (2)
- Connective TissueДокумент13 страницConnective TissueHelena Allguter100% (3)
- Histology, Lecture 6, Connective Tissues (Lecture Notes)Документ6 страницHistology, Lecture 6, Connective Tissues (Lecture Notes)Ali Al-Qudsi100% (3)
- Bilaminar and Trilaminar Germ DiscДокумент40 страницBilaminar and Trilaminar Germ DiscjabirОценок пока нет
- Fracture Healing: Dow University of Health SciencesДокумент15 страницFracture Healing: Dow University of Health SciencesZaheer KhanОценок пока нет
- Membrane TransportДокумент24 страницыMembrane Transportolawandeilo123Оценок пока нет
- Complete Histology of Respiratory SystemДокумент66 страницComplete Histology of Respiratory Systemhassam qaziОценок пока нет
- DR Jagdish Narayan Assistant Professor Department of PhysiologyДокумент75 страницDR Jagdish Narayan Assistant Professor Department of PhysiologyYordanos GetachewОценок пока нет
- Lecture Cartilage and Bone 2009Документ46 страницLecture Cartilage and Bone 2009Danti Nelfa Riza100% (1)
- Action Potential - Communication Within NeuronsДокумент6 страницAction Potential - Communication Within NeuronsPeehuОценок пока нет
- Degeneration & Regeneration of Nerve FibreДокумент29 страницDegeneration & Regeneration of Nerve FibreSana FatimaОценок пока нет
- Motor System 1Документ30 страницMotor System 1api-36993610% (1)
- Nervous System - QuizДокумент65 страницNervous System - QuizrmmmsОценок пока нет
- Diseases of The Temporomandibular JointДокумент27 страницDiseases of The Temporomandibular JointJustDen090% (1)
- Upper Limb: Organization FunctionДокумент33 страницыUpper Limb: Organization FunctionAhmed Nabiel El-Jaliel100% (1)
- Cartilage and BoneДокумент54 страницыCartilage and BoneAGolosinoОценок пока нет
- PARASYMPATHETIC GANGLION in Head and NeckДокумент53 страницыPARASYMPATHETIC GANGLION in Head and NeckDEEP SABОценок пока нет
- 4.3 Bone TissueДокумент80 страниц4.3 Bone TissueManjunathОценок пока нет
- HIS 6 - Haemoglobin Recall Oxygen Binding Properties of HB: Iron (II) - Protoporphyrin IXДокумент2 страницыHIS 6 - Haemoglobin Recall Oxygen Binding Properties of HB: Iron (II) - Protoporphyrin IXKristin DouglasОценок пока нет
- The Gut Tube and Body CavitiesДокумент31 страницаThe Gut Tube and Body CavitiesGeoffreyОценок пока нет
- Hip JointДокумент25 страницHip JointHashim OmarОценок пока нет
- The Fate of Metabolism Andmabolic PathwaysДокумент25 страницThe Fate of Metabolism Andmabolic PathwaysXuân Vi100% (1)
- Development of The FaceДокумент76 страницDevelopment of The Facedr parveen bathla100% (1)
- Inflammation PPT - OdpДокумент82 страницыInflammation PPT - OdpBhanu PraseedhaОценок пока нет
- Histology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTДокумент108 страницHistology Lecture: Minerva Diana A. Dichoso, RMTVernadel ApolloОценок пока нет
- CellДокумент7 страницCellPrashant PandeyОценок пока нет
- Connective TissueДокумент7 страницConnective TissueSheena Pasion100% (1)
- Anatomy - Skull FeaturesДокумент6 страницAnatomy - Skull FeaturesAkhil BansalОценок пока нет
- PhysiologyДокумент31 страницаPhysiologyraza20100% (1)
- Ana 201 (Axilla N Axillary Artery) - 1Документ119 страницAna 201 (Axilla N Axillary Artery) - 1Favour OnyeaboОценок пока нет
- Connective TissuesДокумент45 страницConnective TissuesAbrar osmanОценок пока нет
- The Human ThoraxДокумент71 страницаThe Human Thoraxbayenn100% (2)
- Upper Extremities Ortho SG3Документ119 страницUpper Extremities Ortho SG3Nuhu Bankwhot100% (1)
- Thyroglossal Duct CystДокумент2 страницыThyroglossal Duct CystPulkitОценок пока нет
- Muscular System OutlineДокумент6 страницMuscular System Outlineapi-294104473Оценок пока нет
- Humb1000 Compendium NotesДокумент9 страницHumb1000 Compendium NotesZeba ZiaОценок пока нет
- Nerve and Muscle PhysiologyДокумент82 страницыNerve and Muscle PhysiologychandsriОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive System HistologyДокумент23 страницыFemale Reproductive System Histologyjmizai100% (1)
- Muscular TissueДокумент6 страницMuscular TissueChezkaMayC.OliverosОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)Документ21 страницаAnatomy Lec 9 (Muscles)HumrazОценок пока нет
- Sir FayyazДокумент49 страницSir FayyazSara ZaraОценок пока нет
- 7.nervous TissueДокумент76 страниц7.nervous TissueSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Microbiology ReviewerДокумент8 страницMicrobiology ReviewerSteph Vee100% (6)
- Nematode Table PDFДокумент1 страницаNematode Table PDFFarlogyОценок пока нет
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) By: Rod Rhais CambroneroДокумент17 страницVitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) By: Rod Rhais CambroneroMaureen Peralta TagsaОценок пока нет
- HemaДокумент59 страницHemaSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Streak Plate Cultivation TechniqueДокумент16 страницStreak Plate Cultivation TechniqueSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Biochem TestsДокумент27 страницBiochem TestsSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Nervous System ReviewerДокумент6 страницNervous System ReviewerSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Reviewer CH11 - MUSCULAR SYSTEMДокумент9 страницReviewer CH11 - MUSCULAR SYSTEMSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) By: Rod Rhais CambroneroДокумент17 страницVitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) By: Rod Rhais CambroneroMaureen Peralta TagsaОценок пока нет
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) By: Rod Rhais CambroneroДокумент17 страницVitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) By: Rod Rhais CambroneroMaureen Peralta TagsaОценок пока нет
- Research Lecture 1 by Ma'am Jasmen PasiaДокумент79 страницResearch Lecture 1 by Ma'am Jasmen PasiaSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Trace Elements by WhoДокумент178 страницTrace Elements by WhoSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Mycoviro Part 1Документ69 страницMycoviro Part 1Steph VeeОценок пока нет
- BAsic Guide On Ilokano LanguageДокумент8 страницBAsic Guide On Ilokano LanguageSteph Vee83% (6)
- CD Marker HandbookДокумент47 страницCD Marker HandbookSteph Vee100% (1)
- Midterm Subcut-Sys-OpportunisticДокумент84 страницыMidterm Subcut-Sys-OpportunisticSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- The Brief HistoryДокумент11 страницThe Brief HistorySteph VeeОценок пока нет
- BMLS 3 AntigensДокумент51 страницаBMLS 3 AntigensSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- MTSTS Midterm2012Документ86 страницMTSTS Midterm2012Steph VeeОценок пока нет
- Citric Acid CycleДокумент22 страницыCitric Acid CycleSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids and ProteinsДокумент48 страницAmino Acids and ProteinsSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Citric Acid Cycle-With Quiz BiochemistryДокумент24 страницыCitric Acid Cycle-With Quiz BiochemistrySteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids and ProteinsДокумент48 страницAmino Acids and ProteinsSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- MTSTS Midterm2012Документ86 страницMTSTS Midterm2012Steph VeeОценок пока нет
- Characterization of Lipids PDFДокумент12 страницCharacterization of Lipids PDFSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Respiratory SytemДокумент37 страницRespiratory SytemSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Classifications of SoftwareДокумент1 страницаClassifications of SoftwareSteph VeeОценок пока нет
- Muscular SystemДокумент26 страницMuscular Systemlubnab75% (4)
- Basic and Applied Cell Physiology: Reference BooksДокумент28 страницBasic and Applied Cell Physiology: Reference Booksjamila ilОценок пока нет
- Utilization of Phosphates in Meat ProductsДокумент4 страницыUtilization of Phosphates in Meat ProductsPrincess Dian RamirezОценок пока нет
- Meat Quality and FabricationДокумент37 страницMeat Quality and FabricationJessa PabilloreОценок пока нет
- Myosin, Actin & Contraction NotesДокумент4 страницыMyosin, Actin & Contraction NotesGhazali BalochОценок пока нет
- 11 Physical Education Keynotes Ch08 Fundamental of AnatomyДокумент3 страницы11 Physical Education Keynotes Ch08 Fundamental of AnatomyAkashОценок пока нет
- Comparative Proteomics Kit I: Protein Profiler Module: Biotechnology ExplorerДокумент50 страницComparative Proteomics Kit I: Protein Profiler Module: Biotechnology ExplorerHidayat FadelanОценок пока нет
- 7.the Physiology of MuscleДокумент124 страницы7.the Physiology of MuscleHenok SamuelОценок пока нет
- Electrical Muscle Stimulation and Its Use For Sports Training Programs: A ReviewДокумент32 страницыElectrical Muscle Stimulation and Its Use For Sports Training Programs: A ReviewMiguel Martín Del CampoОценок пока нет
- Chemistry of MeatДокумент6 страницChemistry of MeatSamaiza KhanОценок пока нет
- Musculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Документ22 страницыMusculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Anonymous vwR8xcIxОценок пока нет
- Muscle Contraction & Sliding Filament TheoryДокумент9 страницMuscle Contraction & Sliding Filament TheoryvishnuОценок пока нет
- (Carte) Handbook of Meat ProcessingДокумент604 страницы(Carte) Handbook of Meat ProcessingddddddpОценок пока нет
- Lab 2 - Muscle Physiology - Student - SДокумент7 страницLab 2 - Muscle Physiology - Student - SfilchibuffОценок пока нет
- Skeletal MuscleДокумент3 страницыSkeletal Musclekrystal1994Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology Test 2 PrepДокумент21 страницаAnatomy and Physiology Test 2 PrepNicholas SirunoОценок пока нет
- Muscle Tissues: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarДокумент65 страницMuscle Tissues: Mrs. Ofelia Solano SaludarYulius SamuelОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 11 Physical Education Sample Paper 02 (2019-20) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 18Документ18 страницCBSE Class 11 Physical Education Sample Paper 02 (2019-20) : Material Downloaded From - 1 / 18Samridh GuptaОценок пока нет
- Sarcomere Structure and ContractionДокумент4 страницыSarcomere Structure and ContractionkellyОценок пока нет
- Muscle TissueДокумент5 страницMuscle TissueSheena PasionОценок пока нет
- Tortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент6 страницTortora Principles of Anatomy and PhysiologybebeОценок пока нет
- Muscular System Outline PDFДокумент102 страницыMuscular System Outline PDFAlok Singh100% (1)
- Sliding Filament Theory LessonДокумент36 страницSliding Filament Theory LessonKajetano GraucosОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент21 страницаAnatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFhuonghuyen2cp9ez100% (11)
- Muscle Physiology NotesДокумент20 страницMuscle Physiology NotesPisiform90100% (1)
- CH 6 Muscular SystemДокумент51 страницаCH 6 Muscular SystemNAMERAH GOTEОценок пока нет
- Fish Protein Hydrolysates Production, Biochemical and Functional PropertiesДокумент40 страницFish Protein Hydrolysates Production, Biochemical and Functional PropertiesIoana MoldovanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Human Factors and Ergono ExtractДокумент39 страницIntroduction To Human Factors and Ergono ExtractSHAN ABISHAОценок пока нет
- KINE-311-4 Neuromuscular Clase 4Документ40 страницKINE-311-4 Neuromuscular Clase 4Gonzalo RetamalОценок пока нет
- Control and Co-Ordination 2021-2022 A Level Biology 9700 Notes by Mr. ADEEL AHMADДокумент21 страницаControl and Co-Ordination 2021-2022 A Level Biology 9700 Notes by Mr. ADEEL AHMADADEEL AHMADОценок пока нет