Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Neonatal Hypocalcemia
Загружено:
Emily EresumaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Neonatal Hypocalcemia
Загружено:
Emily EresumaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
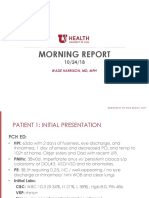
Jessica Sempler PGY3
7/30/14
7do female infant presented to the ED with
tactile fever and tonic clonic extension of her
left arm and leg x3 episodes at home
Tonic clonic episodes last 30sec-1min,
accompanied by abnormal head movement
Feeding slightly less well today
Born at 37 2/7 weeks to a 25yo G3P1102
GBS unknown
No h/o genital HSV in either parent
NSVD with clear fluids
APGARS 9/9
BW 2740g
D/C from hospital on DOL 2
Bilateral cleft lip and palate, f/u with Plastic
Surgery scheduled for the following week
T 39.4, HR 170, R 88, BP 69/38, 92% on RA, Wt 2.7Kg
GEN: Awake, alert, no acute distress
HEENT: AFOSF with no bulging, no scleral icterus, b/l
cleft lip and palate
PULM: Tachypneic, LCTAB with symmetric breath
sounds
CV: S1, S2 with no murmurs, 2+ peripheral pulses, 3sec
capillary refill
ABD: S/NT/ND, active bowel sounds, no HSM
NEURO: Appropriate tone, but with tonic clonic
activity reportedly witnessed by ED nurse and tech
FEVER:
SBI ; especially HSV
Viral illness
SEIZURE ACTIVITY:
Febrile seizure
Hypoglycemia
Electrolyte abnormality
NAT
Stroke
Infantile spasm
Metabolic disease
CT Brain
Full ROS
VRP -
WBC 10.1, 5% bands
UA with small Hgb, 2+ protein
CSF with 11 WBC, 174 RBC, Protein 94, Glucose
50
Upper limit for WBCs in CSF = 18 if >29d
CMP WNL except Ca 5.2
iCal 0.76 (1.19-1.50)
Phos 8.8 (4.8-8.2)
Mag 1.2 (1.6-2.3)
Vit D (P)
PTH (P)
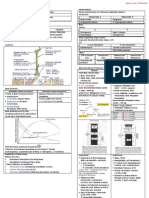
Causes of Hypocalcemia
in children
HYPOPARATHYROIDISM:
Maternal
hyperparathyroidism
HYPOVITAMINOSIS D:
Low maternal Vitamin D
MISCELLANEOUS:
Sepsis/critical illness
View the chart in UpToDate article:
Etiology of hypocalcemai in
infants and children.
(Unable to publish due to copyright. )
Ampicillin
Cefotaxime
Acyclovir
Load with 10mg/Kg IV Phenobarbital
CaGluconate IV
MagSulfate IV
Ingestion of excessive phosphate from
evaporated milk or modified cow milk
formulas
Marked tissue breakdown resulting in release
of intracellular phosphate
Renal failure
Formation of poorly soluble
CaPhos salts
22q11 deletion syndrome
Conotruncal cardiac anomalies
Hypoplastic thymus
Hypocalcemia (d/t parathyroid hypoplasia)
Occurs in 1:4,000 births
Most common form of dysgenesis of
parathyroid glands in neonates and infants
Disturbed migration of cervical neural crest
cells
Renal wasting
GI losses
Magnesium depletion causes impaired
synthesis or secretion of parathyroid hormone
(Suh et al 1973)
Magnesium corrected after repletion in ED
Calcium remained low despite repeated IV
repletion
Vitamin D 16 (L)
~8 beats of clonus, jittery infant
1. Start PO Calcium supplements and Vitamin D
suppplements
Ca Carbonate
Calcitriol
Cholecalciferol
2. Await results of PTH prior to testing for
DiGeorge
Due to copyright restriction view
algorithm in UpToDate article:
Overview of vitamin D
PTH 20 (15-65); c/w hypoparathyroidism
Cleft palate alone is more common than cleft
lip with cleft palate
Genomic SNP microarray; to capture a wider
array of genomic imbalances beyond del22q11,
which would be picked up with FISH
Discharged to home on Ca supplements and
Vit D
Diagnosis of late neonatal hypocalcemia,
defined as occuring after the 2
nd
or 3
rd
day of
life, usually at the end of the first week
Plan to test Mom for hyperparathyroidism if
SNP microarray normal
Neonatal hypocalcemia http://www.uptodate.com/contents/neonatal-
hypocalcemia?source=search_result&search=neonatal+hypocalcemia&selectedTitle=1%7
E11
DiGeorge syndrome: Clinical features and diagnosis
http://www.uptodate.com/contents/digeorge-syndrome-clinical-features-and-
diagnosis?source=search_result&search=DiGeorge&selectedTitle=1%7E62
Overview of vitamin D http://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-vitamin-
d?source=search_result&search=Vitamin+D&selectedTitle=2%7E150
Sanjad-Sakati syndrome in Omani children
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3191633/
Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/mitochondrial-encephalomyopathy-lactic-acidosis-
and-stroke-like-episodes
Hypocalcemia in the neonate and infant https://www.inkling.com/read/sperling-
pediatric-endocrinology-4th/chapter-18/hypocalcemia
Pathogenesis of Hypocalcemia in Primary Hypomagnesemia: Normal End-Organ
Responsiveness to Parathyroid Hormone, Impaired Parathyroid Gland Function
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC302237/
Вам также может понравиться
- Food Challenge 03.20.2019Документ17 страницFood Challenge 03.20.2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Kidney Disorders 03.27.2019Документ33 страницыKidney Disorders 03.27.2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Morning Report Case Presentation: APRIL 1, 2019Документ14 страницMorning Report Case Presentation: APRIL 1, 2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Hypertension Noon Conference 03.20.2019Документ44 страницыPediatric Hypertension Noon Conference 03.20.2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Dangers of Vaping 03.15.2019Документ23 страницыDangers of Vaping 03.15.2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Ophtho Pearls 03.13.2019Документ17 страницOphtho Pearls 03.13.2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Board Prep Metabolics Feb 2019Документ23 страницыBoard Prep Metabolics Feb 2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Chronic Granulomatous Disease 01.23.2019Документ10 страницChronic Granulomatous Disease 01.23.2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Board Prep Emergency Ingestions Dec.2018Документ46 страницBoard Prep Emergency Ingestions Dec.2018Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Tachycardia How To Keep Your Patient Alive in The Middle of The NightДокумент30 страницTachycardia How To Keep Your Patient Alive in The Middle of The NightEmily Eresuma100% (1)
- Case Presentation: Tad MiyaДокумент41 страницаCase Presentation: Tad MiyaEmily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Bells Palsy or Stroke 02.06.2019Документ19 страницBells Palsy or Stroke 02.06.2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Investing 101 For Residents: RJ Nemeyer MDДокумент12 страницInvesting 101 For Residents: RJ Nemeyer MDEmily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Board Prep Genetics Dec 2018Документ62 страницыBoard Prep Genetics Dec 2018Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Somatization 01.28.2019Документ28 страницSomatization 01.28.2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Pertussis 01.14.2019Документ29 страницPertussis 01.14.2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Board Prep GI Jan 2019Документ32 страницыBoard Prep GI Jan 2019Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Morning Report: Melanie Nelson, PGY-2Документ25 страницMorning Report: Melanie Nelson, PGY-2Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Anemia: Erika Franz-O'Neal PGY-2 Pediatric ResidentДокумент16 страницAnemia: Erika Franz-O'Neal PGY-2 Pediatric ResidentEmily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Jaundice 11.28.2018Документ13 страницJaundice 11.28.2018Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Limping 12.10.2018Документ32 страницыLimping 12.10.2018Emily Eresuma100% (1)
- Morning Report: JANUARY 7, 2019 Katie Mailey, Pgy2Документ24 страницыMorning Report: JANUARY 7, 2019 Katie Mailey, Pgy2Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Wilderness Medicine 11.20.2018Документ12 страницWilderness Medicine 11.20.2018Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Halloween Safety: Dominique ChevalierДокумент21 страницаHalloween Safety: Dominique ChevalierEmily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Foster Care in Utah: Marlayna DespresДокумент11 страницFoster Care in Utah: Marlayna DespresEmily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Urology Topics Relating To Infants & Toddlers: Danielle Brady, Pgy-2Документ35 страницPediatric Urology Topics Relating To Infants & Toddlers: Danielle Brady, Pgy-2Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Ventilators 11.07.2018Документ38 страницVentilators 11.07.2018Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- MysteryCase 10.22.18Документ10 страницMysteryCase 10.22.18Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Morning Report: Lindsey Gakenheimer-Smith MD PGY3Документ20 страницMorning Report: Lindsey Gakenheimer-Smith MD PGY3Emily EresumaОценок пока нет
- Morning Report: Wade Harrison, MD, MPHДокумент13 страницMorning Report: Wade Harrison, MD, MPHEmily EresumaОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Inflammation and Vitamin D: The Infection ConnectionДокумент17 страницInflammation and Vitamin D: The Infection ConnectionBreBotОценок пока нет
- Electrolyte Imbalance ArcherДокумент111 страницElectrolyte Imbalance ArcherDanica Chiara Motia100% (2)
- Department of Periodontics and Implantology: Calcium MetabolismДокумент63 страницыDepartment of Periodontics and Implantology: Calcium Metabolismrasagna reddy100% (1)
- Hypocalcemia in NewbornsДокумент2 страницыHypocalcemia in NewbornsEunice Lan ArdienteОценок пока нет
- Regulasi CA, MG and PO4Документ16 страницRegulasi CA, MG and PO4siskaОценок пока нет
- (PDF Copy) PSGSMMC Lecture - Reviewing Head and Neck Surgery 2021Документ65 страниц(PDF Copy) PSGSMMC Lecture - Reviewing Head and Neck Surgery 2021Patrick PengosroОценок пока нет
- Vitamin D Metabolism... Mechanism of Action and Clinical Appllications.Документ11 страницVitamin D Metabolism... Mechanism of Action and Clinical Appllications.asalizwa ludlalaОценок пока нет
- Mini Mock Exam - QДокумент9 страницMini Mock Exam - QHana maeОценок пока нет
- 2.3 HYPOCALCEMIA and HYPERCALCEMIAДокумент7 страниц2.3 HYPOCALCEMIA and HYPERCALCEMIABooz Waief CaluzaОценок пока нет
- The Bioavailability of Dietary CalciumДокумент18 страницThe Bioavailability of Dietary CalciumtvmedicineОценок пока нет
- Common Metabolic Diseases of Cattle: Ketosis, Milk Fever, Grass Tetany, and Downer Cow Complex ZДокумент18 страницCommon Metabolic Diseases of Cattle: Ketosis, Milk Fever, Grass Tetany, and Downer Cow Complex ZHikmat UllahОценок пока нет
- 2020-Biochem-Activity-16 - BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONESДокумент32 страницы2020-Biochem-Activity-16 - BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONESGabrielle John HernaezОценок пока нет
- Passmedicine MRCP Mcqs-RheumatologyДокумент110 страницPassmedicine MRCP Mcqs-RheumatologyMayar Wael50% (2)
- Electrolytes SummaryДокумент23 страницыElectrolytes SummaryDjdjjd SiisusОценок пока нет
- Animal Anatomy and Physiology: Figure Q.18Документ25 страницAnimal Anatomy and Physiology: Figure Q.18hager atefОценок пока нет
- Fluid, Electrolyte, Acid Base BalanceДокумент42 страницыFluid, Electrolyte, Acid Base BalanceSutrisno YangОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisДокумент5 страницPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Parathyroid HormoneДокумент120 страницParathyroid HormoneLaura TapiaОценок пока нет
- Adime 3Документ9 страницAdime 3api-279537861Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 Endocrine SystemДокумент18 страницLesson 2 Endocrine SystemMARY JANE ANGELICA SEVAОценок пока нет
- (CC Lab) Calcium & MagnesiumДокумент6 страниц(CC Lab) Calcium & MagnesiumDennisse San JoseОценок пока нет
- Inergetix 6 Software and Hardware Installation Jan 2013Документ116 страницInergetix 6 Software and Hardware Installation Jan 2013kisgallcsaba100% (1)
- Ms Test-Questio 2Документ24 страницыMs Test-Questio 2Jackie AbarraОценок пока нет
- 3.physiology Emrcs2016Документ106 страниц3.physiology Emrcs2016Farah FarahОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology 2 Final Exam 2021-NkДокумент16 страницPharmacology 2 Final Exam 2021-NkT'amo HanashОценок пока нет
- ENDOCRINOLOGY For BCPSДокумент59 страницENDOCRINOLOGY For BCPSInzamamul Haque ShihabОценок пока нет
- Part A Sample McqsДокумент7 страницPart A Sample McqssmartherbtОценок пока нет
- Musculoskeletal SystemДокумент22 страницыMusculoskeletal SystemKeyna DizonОценок пока нет
- Calcium MetabolismДокумент28 страницCalcium MetabolismAhmedkhaed100% (1)
- A Handbook of Oral Physiology and Oral BiologyДокумент87 страницA Handbook of Oral Physiology and Oral Biologyamirmaafi100% (1)