Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Kromatografi Kolom
Загружено:
Rista Siti MaarniОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Kromatografi Kolom
Загружено:
Rista Siti MaarniАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
COLUMN CHROMATOGRAPHY
SMK Negeri 13 Bandung
R+OH- + X- === R+X- + OH-
n R-H+ + Mn+ === (R)n-Mn+ + n H+
Objective
After this session the students are
expected to be able to conduct the
analysis of chemical substance using
the ion exchanger resin.
ION EXCHANGER RESIN
Definition : ion exchange from
the same charge ions between the
solution and the insoluble solid
Condition
The solid substance to exchange
should have the same ion with the ion
in solution
Molecular structure of solid has an
opened structure and permeable
(easy to be penetrated) so the solute
is easy come and out. Exchanging
process will be past and efficient
ION EXCHANGER RESIN
The solid substance is stationary
phase and the solution is mobile
phase.
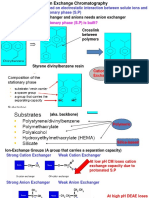
Solid ion exchanger is made of
polymer polystirene cross-linked with
divinyl benzee. Polymer with cross-
linking called resin. It has free phenyl
group easy to react with ionic
functional group (addition)
Resin used in analysis to separate
inorganic ions (cation and anion)
Ptroperties of Ion Exchanger Resin
1. Insoluble in water but has an ability to
absorbp water molecule in it structure.
2. Has a high molecular relative mass (High
Mr).
3. Resistant to chemical substance (Acid,
base, organic solvent)
4. When an ionic solution flow in to resin, it
will release an ion and at the same time it
will capture an ion of the solution.
5. Ion exchange carry out on the same type
ion (cation with cation, anion with anion).
4 types of ion exchanger resin
1. Strong acid cation exchanger. The
exchanger functional group is sulfonic
acid.
2. Weak acid cation exchanger. The
exchanger functional group is carboxilic
acid.
3. Strong base anion exchanger. The
exchanger functional group is quarterner
ammonium ion.
4. Weak base anion exchanger. The
exchanger functional group is anion group.
(Cation Exchanger Resin)
A column filled by acid / R-H
to exchange cations in
solution with H
+
ion in the
resin.
R
z
H + C
+
R
z
C
+ H
+
C
+
could be : Na
+
, K
+
, Ca
2+
,
Mg
2+
, etc.
Cation Exchanger Resin
In weak acid exchanging type, H is
carboxilic acid that only partly
ionized. The reaction is:
nR
z
CO
2
H
+
+ M
n+
(R
z
CO
2
)
n
M + nH
+
In strong acid exchanging type, H is
sulfonic acid group. It is strong acid
like sulfuric acid. The reaction is.
nR
z
SO
3-
+ M
n+
(R
z
SO
3
)
n
M + nH
+
(Cation Exchanger Resin)
(Anion Exchanger Resin)
A column filled by base / R-
OH to exchange anions in
solution with OH
-
ion in the
resin.
R
Z
OH + A
-
R
Z
A + OH
-
A
-
could be : Cl
-
, SO
4
2-
, NO
3
-
, etc.
(Anion Exchanger Resin)
In strong base anion exchanger, the
reaction is :
n
R
z
NR
3
+
OH
-
+ A
n-
(R
z
NR
3
)nA +
n
OH
-
Ion Exchanger Selectivity
There are 2 factors influence the
selectivity :
The exchanged ions properties
The ion exchanger properties.
Exchanged ions properties:
At room temperature and low
concentration, ion with higher
charge will tightly held by resin.
Ex : Al
3+
> Ca
2+
> Na
+
In the same condition for the same
charge ion :
+1 ion
Lower the size of ion, stronger the resin hold the ion.
Ex : Li
+
< H
+
< Na
+
< NH
4+
< K
+
+2 ion
Resin absorption determinated by the ion size and
dissosiation of salt .
Ex : Cd
2+
< Ba
2+
< Mn
2+
< Mg
2+
= Zn
2+
< Cu
2+
< Co
2+
Exchanged ions properties:
In strong base ion exchanger -1
anionhas the equivalent absorption
selectivity with the +1 cation. (Lower
the size of ion, stronger the resin hold
the ion)
Ex : F
-
< HCO
3-
< Cl
-
< HSO
3-
< OH
-
< Br
-
<
NO
3-
< I
-
In dilute solution -X anion (X>1)
absorbed stronger than the -1 anion.
When the charge of cations to be
exchanged is not same. Ion activity
with the higher charge is higher
when the concentration of higher
charge ion is lower.
Example :
M
+2
in solution and M
+1
in resin will
effectively exchanged at low
concentration
M
+1
in solution and M
+2
in resin will
effectively exchanged at high
concentration.
Ion exchanger properties
Quantitatively, afinity of ion exchanger resin
to the exchanged ions terms as distribution
coefficient (D):
sama yang pelat pada larutan dalam sampel Kuantitas
entu pelat tert pada resin dalam sampel Kuantitas
D
Complexing agent
Complexing agent is anions like Cl
-
, Br
-
and I
-
which
have ligand nature. The complexion is influenced by
pH value.
Many metals could be separated in anion exchanger
column after transformed to anion by complexing
agent.
Metal separation in anion exchanger column carry
out by addition of high concentration acid to
transform metal ion to be complex anion.
Example
Concentrated HCL forms complex anion with most
metal except alkali and earth alkali metal.
Al(III), Ni(II), dan Cr(III) form complex anion with
Cl
-
.
Almost all complex anion of metal absorbed by
quarternar ammonium resin.
Resin Regeneration
Amount of cation and anion to be exchanged
by resin depends on the resin capacity.
When resin absorb amount of ion more than
its capacity, resin is exhausted. It should be
regenerated.
Regeneration of anion exchanger resin :
Acid : HCl, H
2
SO
4
.
Reaction : Rz C + H
+
Rz H + C
+
Regeneration of cation exchanger resin :
Base : NaOH.
Reaction : Rz A + OH
-
Rz OH + A
-
Resin Column
a
.
Вам также может понравиться
- Fluid Mechanics Chapter 1-5Документ32 страницыFluid Mechanics Chapter 1-5Kristine Ann Reclosado38% (8)
- SP 2 Ion - Exchange-RevДокумент44 страницыSP 2 Ion - Exchange-Revgeevitha raoОценок пока нет
- Co - Cu Part 1 - Column Separation Sp14 FINALДокумент10 страницCo - Cu Part 1 - Column Separation Sp14 FINALDaniel Arul NesanОценок пока нет
- ION EXCHANGEjashДокумент9 страницION EXCHANGEjashJash SapariyaОценок пока нет
- 7 Ion Exchange 2020Документ51 страница7 Ion Exchange 2020a.ayseselimmОценок пока нет
- Ion ExchangeДокумент50 страницIon ExchangeSiti Nurshahira100% (1)
- Ce 480 - IoxДокумент22 страницыCe 480 - IoxNTEYE CHITONGEОценок пока нет
- Kuliah Ion ExchangeДокумент46 страницKuliah Ion ExchangeNila Fitra AndiniОценок пока нет
- Principles of Ion ExchangeДокумент5 страницPrinciples of Ion ExchangeYsabelle JimeneaОценок пока нет
- Ion Exchange SДокумент28 страницIon Exchange SHamza SawalmehОценок пока нет
- Ion ExchangeДокумент63 страницыIon ExchangeChuah Chong YangОценок пока нет
- Chrom-Lect 4-Ion ExchДокумент22 страницыChrom-Lect 4-Ion ExchPramudia PutraОценок пока нет
- Experiment 13 Results and Discussion Report: Determination of Total Ion Concentration Using Ion Exchange ChromatographyДокумент3 страницыExperiment 13 Results and Discussion Report: Determination of Total Ion Concentration Using Ion Exchange ChromatographyNathalie Dagmang100% (3)
- Ion ExchangeДокумент15 страницIon ExchangeEmon KhanОценок пока нет
- Ion ExchangerДокумент23 страницыIon ExchangerMuhammad AlghitanyОценок пока нет
- 9 Ion ExchangeДокумент68 страниц9 Ion ExchangeThiago CangussuОценок пока нет
- Soil Chemistry - Engchem Lec PDFДокумент39 страницSoil Chemistry - Engchem Lec PDFDanika Kaye GornesОценок пока нет
- Ion Exchange ResinsДокумент5 страницIon Exchange ResinsAJITHОценок пока нет
- 1 IER FundamentalsДокумент54 страницы1 IER FundamentalsAdam FendrychОценок пока нет
- Ion Exchange and Carbon Adsorption - Riska Ristiyanti 21030116410011Документ27 страницIon Exchange and Carbon Adsorption - Riska Ristiyanti 21030116410011Riska RistiyantiОценок пока нет
- Acids and BasesДокумент15 страницAcids and Baseslebogang0% (1)
- Acid - Base ChemistryДокумент63 страницыAcid - Base ChemistryAlyssa BaltazarОценок пока нет
- Ion ExchangeДокумент22 страницыIon ExchangePrateek MallОценок пока нет
- OÊÊ Ê OÊÊ Ê Oêê Ê OÊÊ ÊДокумент18 страницOÊÊ Ê OÊÊ Ê Oêê Ê OÊÊ ÊRudi Sutanto TanОценок пока нет
- Utility Assignment: Ion Exchanger Arranged byДокумент7 страницUtility Assignment: Ion Exchanger Arranged byFaris Rahmansya NurcahyoОценок пока нет
- Utility Assignment: Ion Exchanger Arranged byДокумент7 страницUtility Assignment: Ion Exchanger Arranged byFaris Rahmansya NurcahyoОценок пока нет
- T.Y.B.sc. PPT Ion ExchangeДокумент31 страницаT.Y.B.sc. PPT Ion ExchangeMohammed Munawar pОценок пока нет
- Lect.12 Ion Exchange FinalДокумент39 страницLect.12 Ion Exchange FinalDr.D.SELVI100% (5)
- Soil ChemistryДокумент97 страницSoil ChemistryGel Mi AmorОценок пока нет
- How A Stationary Phase (S.P) Is Built?: Cations Needs A Cation Exchanger and Anions Needs Anion ExchangerДокумент49 страницHow A Stationary Phase (S.P) Is Built?: Cations Needs A Cation Exchanger and Anions Needs Anion ExchangerKanchanОценок пока нет
- Ion ExchangeДокумент66 страницIon ExchangeTsebe HermanОценок пока нет
- 6e. Aquatic GeochemistryДокумент46 страниц6e. Aquatic GeochemistrysudhakarОценок пока нет
- Laporan KPiДокумент18 страницLaporan KPimiaw713Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Equilibrium 1Документ49 страницChemical Equilibrium 1samarthasai2006Оценок пока нет
- Ionic EquilibriumДокумент13 страницIonic EquilibriumTrupti ChavanОценок пока нет
- Ion Exchange 2Документ26 страницIon Exchange 2api-3737745100% (3)
- Soil ChemistryДокумент30 страницSoil ChemistryRavindra BirlaОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Work Precipitation TitrationДокумент16 страницLaboratory Work Precipitation TitrationMythri Metallizing Pvt Ltd ProjectsОценок пока нет
- Chem 18.1 Experiment 9 'Ion Exchange ChromatographyДокумент6 страницChem 18.1 Experiment 9 'Ion Exchange ChromatographyNat DabuétОценок пока нет
- Ion Exchange ResinДокумент7 страницIon Exchange ResinAnup Bajracharya75% (4)
- Ion ExchangeДокумент24 страницыIon ExchangeDr. M. Prasad NaiduОценок пока нет
- Discussion For Anion ExchangeДокумент2 страницыDiscussion For Anion ExchangeEzekielОценок пока нет
- Soil ChemistryДокумент30 страницSoil ChemistryNIksОценок пока нет
- Ion Exchange ResinsДокумент7 страницIon Exchange ResinsVirgilMaroОценок пока нет
- Madhuriassignment1 170811023927 PDFДокумент4 страницыMadhuriassignment1 170811023927 PDF16_dev5038Оценок пока нет
- Experiment ID: 3b: Ion ExchangeДокумент14 страницExperiment ID: 3b: Ion ExchangeMetehan GazioğluОценок пока нет
- Gas Chromatography and Ion Exchage Chromatography Sem VI U-IIДокумент36 страницGas Chromatography and Ion Exchage Chromatography Sem VI U-IInoobdaadam003Оценок пока нет
- Ion Exchangechromatography 19102515412854Документ30 страницIon Exchangechromatography 19102515412854chinmayeeОценок пока нет
- Principles of Ion ExchangeДокумент4 страницыPrinciples of Ion ExchangeGOWTHAM GUPTHAОценок пока нет
- Ion Exchange - Treatment-2Документ86 страницIon Exchange - Treatment-2Shabbir OsmaniОценок пока нет
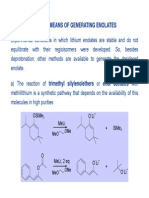
- 1.3. Other Means of Generating Enolates: Osime Meli O Li + SimeДокумент14 страниц1.3. Other Means of Generating Enolates: Osime Meli O Li + SimeVirendra Singh RajputОценок пока нет
- SoilДокумент33 страницыSoilFrancis PadulОценок пока нет
- Ion Exchange ResinsДокумент8 страницIon Exchange ResinsabdulanisОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactions - How Far and How FastДокумент18 страницChemical Reactions - How Far and How FastDoris GladiaОценок пока нет
- Pertukaran Kation Budi 17 Nov 2020Документ39 страницPertukaran Kation Budi 17 Nov 2020Nugi Al MaulanaОценок пока нет
- Nirav Sir: 2 + - (S) + (Aq) - (Aq)Документ19 страницNirav Sir: 2 + - (S) + (Aq) - (Aq)api-233404189Оценок пока нет
- Inorganic 1122Документ6 страницInorganic 1122Saira Falak SherОценок пока нет
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideОт EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionОт EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionОценок пока нет
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Fourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974От EverandFourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974V. GutmannОценок пока нет
- 1st Yr Lec3Документ16 страниц1st Yr Lec3abhijeetnarkhede69198Оценок пока нет
- Astm C 295-2019Документ9 страницAstm C 295-2019Mohammed Ali100% (1)
- Pioglitazone NaopaticlesДокумент11 страницPioglitazone NaopaticlesAtiq Ur-RahmanОценок пока нет
- Paraquat - Hoja de SeguridadДокумент3 страницыParaquat - Hoja de SeguridadCLARENA ALEJANDRA GUZMÁN RUIZОценок пока нет
- 410 Stainless Steel: Form of SupplyДокумент3 страницы410 Stainless Steel: Form of SupplyDeepak SinghОценок пока нет
- FT Schedule RM Phase 1Документ1 страницаFT Schedule RM Phase 1Virat ValiОценок пока нет
- Nta Abhyas Test-65 CДокумент5 страницNta Abhyas Test-65 CMIITY EDUОценок пока нет
- Guía para Seleccionar Columnas HPLCДокумент52 страницыGuía para Seleccionar Columnas HPLCDiana Lilibet Sánchez MontesОценок пока нет
- Ramabulana Et Al. 2021 MN and MetPA - Chemical Space of Four Momordica Plant SpeciesДокумент15 страницRamabulana Et Al. 2021 MN and MetPA - Chemical Space of Four Momordica Plant SpeciesFernanda SantosОценок пока нет
- Bs en 357 - 2004 Glass-Frp ClassДокумент16 страницBs en 357 - 2004 Glass-Frp ClassKwong chi hoОценок пока нет
- Brochures WSM2-Y PDFДокумент16 страницBrochures WSM2-Y PDFkunkzОценок пока нет
- Radioactive Contamination at The Jana Elementary School Hazelwood MOДокумент26 страницRadioactive Contamination at The Jana Elementary School Hazelwood MOArmi EasterbyОценок пока нет
- GUIDE-MQA-017-006 (Good Manufacturing Practice For Assemblers of Medicinal Products)Документ15 страницGUIDE-MQA-017-006 (Good Manufacturing Practice For Assemblers of Medicinal Products)William ChandraОценок пока нет
- Plant Cell WallДокумент2 страницыPlant Cell WallShiela BelandresОценок пока нет
- 自來水管埋設工程施說明書Документ187 страниц自來水管埋設工程施說明書富山Оценок пока нет
- Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice WorksheetДокумент3 страницыProtons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice WorksheetAnthony Gio L. AndayaОценок пока нет
- Flares ImДокумент25 страницFlares ImBaba JohnehОценок пока нет
- Heat Capacity Lab ReportДокумент8 страницHeat Capacity Lab ReportLiHong Khaw100% (1)
- Is 8224Документ16 страницIs 8224Ankit YadavОценок пока нет
- Viking Sprinkler Shield & GuardДокумент4 страницыViking Sprinkler Shield & Guardshankar_04Оценок пока нет
- Electrooculography and It's ApplicationsДокумент48 страницElectrooculography and It's ApplicationsRose Edward50% (6)
- Nitrogen, Total, TNT, 0 To 25.0, Persulfate Digestion Method 10071Документ9 страницNitrogen, Total, TNT, 0 To 25.0, Persulfate Digestion Method 10071Dwiyana YogasariОценок пока нет
- Cytech Products Data SheetsДокумент71 страницаCytech Products Data Sheetslinga2014Оценок пока нет
- Aeroquip HoseДокумент0 страницAeroquip Hosegbm2246Оценок пока нет
- 70 Penetration Grade BitumenДокумент1 страница70 Penetration Grade BitumenJohn SnowОценок пока нет
- WPS Vessel 1Документ4 страницыWPS Vessel 1Naqqash SajidОценок пока нет
- Experiments 11 15 NotesДокумент16 страницExperiments 11 15 Notesforisko05Оценок пока нет
- SilicaMix Product Brochure2Документ12 страницSilicaMix Product Brochure2rajni phОценок пока нет
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Tumbuhan: Ihsan Tria Pramanda, M.SДокумент19 страницAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Tumbuhan: Ihsan Tria Pramanda, M.SReva RahmafitriОценок пока нет