Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
C1 Mod 2 - Introduction To Psychoactive Substance Use
Загружено:
PUSAT LATIHAN AADK0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
73 просмотров22 страницыNOTA BENGKEL UNDERSTANDING ADDICTION SYLLABUS 1&2 SIRI 1/2014
Оригинальное название
C1 Mod 2 – Introduction to Psychoactive Substance Use
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документNOTA BENGKEL UNDERSTANDING ADDICTION SYLLABUS 1&2 SIRI 1/2014
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
73 просмотров22 страницыC1 Mod 2 - Introduction To Psychoactive Substance Use
Загружено:
PUSAT LATIHAN AADKNOTA BENGKEL UNDERSTANDING ADDICTION SYLLABUS 1&2 SIRI 1/2014
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 22
MODULE 2INTRODUCTION TO
PSYCHOACTIVE SUBSTANCE USE
Curriculum 1
Physiology and Pharmacology for
Addiction Professionals
The Colombo Plan Asian Centre for Certification and Education of Addiction Professionals Training Series
Curriculum 1
2.2
Module 2 Learning Objectives
Define psychoactive substance
List general ways in which psychoactive
substances affect mood, thoughts, and behavior
List the four main categories (classes) of
psychoactive substances and several substances
within each
List the methods of administering psychoactive
substances
Discuss the levels of progression of substance
use
2.3
Psychoactive Substances
Affect the bodys central nervous system
Change how people behave or perceive what
is happening around them
2.4
Central Nervous System
2.5
BloodBrain Barrier
Large, water-
soluble
molecules are
blocked
Small, fat-soluble
molecules can enter
2.6
Pharmacology
Studies the effects of medications and other
substances on the body and the brain
2.7
Half-Life
The amount of time it takes to eliminate half of
the original dose of a substance from the body
2.8
Other Factors
A persons age, the length of time a person
has regularly used a substance, and the
amount of a substance regularly used affect
how the body:
Absorbs psychoactive substances
Metabolizes them
Eliminates them
2.9
Psychoactive Substances
Psychoactive substances alter:
Mood
Thoughts
Sensory perceptions
Behavior
2.10
Effects of Psychoactive Substances
Can be positive or negative
Depend to a large extent on the type of
substance used
2.11
Drug Classes: Examples
Stimulants Opioids
(narcotics)
Depressants Hallucinogens
Cocaine Heroin
Alcohol
LSD
Amphetamine Morphine
Barbiturates
Mescaline
Peyote
Methamphetamine
Opium
Benzodiazepines
Ecstasy
Nicotine,
Caffeine
Demerol
Gamma-
Hydroxybutyrate
(GHB); Rohypnol
Mushrooms
2.12
Legal Substances
Just because a substance is legal does not
mean it is safer than an illegal substance
2.13
Other
Some drugs do not fit neatly into a category:
Cannabinoids (marijuana, hashish)
Khat/Miraa
Dissociative anesthetics (phencyclidine [PCP],
ketamine)
Inhalants solvents, gases, nitrites
2.14
Routes of Administration
Swallowing
Snorting
Smoking
Inhaling fumes
Intramuscular (IM) injection
Subcutaneous (SC) injection
Intravenous (IV) injection
Topical
Sublingual
2.15
Routes of Administration
The faster the drug hits the brain, the greater
and more reinforcing its effect
2.16
Speed of Action
Smoking: 710 seconds
Intravenous injecting: 1530 seconds
Injecting into the muscle or under the skin: 35
minutes
2.17
Speed of Action
Mucous membrane absorption (snorting,
rectal): 35 minutes
Swallowing: 2030 minutes
Absorbed through skin: Slowly over a long
period
2.18
Small-Group Exercise: Routes of
Administration
Form small groups
As a group, develop a list of any five
psychoactive substances
For each substance, list the most common
routes of administration used in your area
Keep in mind that some substances have
more than one route of administration
2.19
Break
15 minutes
2.20
Progression of Use
Experimental/recreational use
Circumstantial/Occasional use
Intensified/regular use
Compulsive/addictive use
2.21
Learning Assessment
Write one quiz question about todays material
on a piece of paper
2.22
Journal
What did you learn today that you did not
already know?
How might you apply what you learned to your
job?
What questions do you still have?
Вам также может понравиться
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (Cbt) for the Treatment of Opioid Use DisorderОт EverandCognitive-Behavioral Therapy (Cbt) for the Treatment of Opioid Use DisorderОценок пока нет
- Preventing Drug AbuseДокумент176 страницPreventing Drug AbuseLauraLunguОценок пока нет
- C1 Concert ReviewДокумент81 страницаC1 Concert ReviewPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- C1 Mod 1 - Training IntroductionДокумент27 страницC1 Mod 1 - Training IntroductionPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- C2 Mod 6 Components of TXДокумент105 страницC2 Mod 6 Components of TXPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- C2 Mod 3 OutcomesДокумент26 страницC2 Mod 3 OutcomesPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Treatment and Prevention of Alcohol Problems: A Resource ManualОт EverandTreatment and Prevention of Alcohol Problems: A Resource ManualОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric Diagnosis: Challenges and ProspectsОт EverandPsychiatric Diagnosis: Challenges and ProspectsIhsan M. SalloumРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Basic Counseling Skills For Addiction Professionals: Module 6: Psychoeducation Groups For Clients and FamiliesДокумент31 страницаBasic Counseling Skills For Addiction Professionals: Module 6: Psychoeducation Groups For Clients and FamilieslissarlissaaОценок пока нет
- First Aid Tips for Anxiety: 4 Crucial Steps to Overpower AnxietyОт EverandFirst Aid Tips for Anxiety: 4 Crucial Steps to Overpower AnxietyОценок пока нет
- Internet AddictionДокумент15 страницInternet AddictionAmimie LingОценок пока нет
- Annual Review of Addictions and Offender Counseling II: Best PracticesОт EverandAnnual Review of Addictions and Offender Counseling II: Best PracticesОценок пока нет
- Comprehensive Handbook of Clinical Health PsychologyОт EverandComprehensive Handbook of Clinical Health PsychologyBret A BoyerОценок пока нет
- Study Guide to Accompany Physiological Psychology Brown/WallaceОт EverandStudy Guide to Accompany Physiological Psychology Brown/WallaceОценок пока нет
- Evaluating Alcohol and Drug Abuse Treatment Effectiveness: Recent AdvancesОт EverandEvaluating Alcohol and Drug Abuse Treatment Effectiveness: Recent AdvancesLinda Carter SobellОценок пока нет
- Out of the Silence: My Journey into Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and BackОт EverandOut of the Silence: My Journey into Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and BackОценок пока нет
- CCC Community Risk Ranking December 2018Документ24 страницыCCC Community Risk Ranking December 2018ZacharyEJWilliams100% (1)
- The Wiley-Blackwell Handbook of Addiction PsychopharmacologyОт EverandThe Wiley-Blackwell Handbook of Addiction PsychopharmacologyОценок пока нет
- Life-Span Developmental Psychology: InterventionОт EverandLife-Span Developmental Psychology: InterventionRalph R. TurnerРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- CBT Case Formulation as Therapeutic ProcessОт EverandCBT Case Formulation as Therapeutic ProcessGiovanni Maria RuggieroОценок пока нет
- Integrative Dual Diagnosis Treatment Approach to an Individual with Alcoholism and Coexisting Endogenous DepressionОт EverandIntegrative Dual Diagnosis Treatment Approach to an Individual with Alcoholism and Coexisting Endogenous DepressionРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Treating Adolescent Substance Abuse Using Family Behavior Therapy: A Step-by-Step ApproachОт EverandTreating Adolescent Substance Abuse Using Family Behavior Therapy: A Step-by-Step ApproachОценок пока нет
- Management and Administration Skills for the Mental Health ProfessionalОт EverandManagement and Administration Skills for the Mental Health ProfessionalОценок пока нет
- Assessment Strategies for Cognitive–Behavioral InterventionsОт EverandAssessment Strategies for Cognitive–Behavioral InterventionsОценок пока нет
- States and Processes for Mental Health: Advancing Psychotherapy EffectivenessОт EverandStates and Processes for Mental Health: Advancing Psychotherapy EffectivenessОценок пока нет
- Supervising Addiction Specialist: Passbooks Study GuideОт EverandSupervising Addiction Specialist: Passbooks Study GuideОценок пока нет
- CV Vivek Benegal 0610Документ16 страницCV Vivek Benegal 0610bhaskarsg0% (1)
- Forensic Mental Health Assistant: Passbooks Study GuideОт EverandForensic Mental Health Assistant: Passbooks Study GuideОценок пока нет
- Addiction Reform: The Organic Processes of Substance Use BehaviorОт EverandAddiction Reform: The Organic Processes of Substance Use BehaviorОценок пока нет
- Healing Inside Out And Outside In: Finding Zen through Spriritual HealingОт EverandHealing Inside Out And Outside In: Finding Zen through Spriritual HealingОценок пока нет
- Current Topics in Clinical and Community Psychology: Volume 3От EverandCurrent Topics in Clinical and Community Psychology: Volume 3Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Origins of Phobias and Anxiety Disorders: Why More Women than Men?От EverandOrigins of Phobias and Anxiety Disorders: Why More Women than Men?Оценок пока нет
- Rights and Responsibilities in Behavioral Healthcare: For Clinical Social Workers, Consumers, and Third PartiesОт EverandRights and Responsibilities in Behavioral Healthcare: For Clinical Social Workers, Consumers, and Third PartiesОценок пока нет
- Sexual Assault Risk Reduction and Resistance: Theory, Research, and PracticeОт EverandSexual Assault Risk Reduction and Resistance: Theory, Research, and PracticeLindsay M. OrchowskiОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Forensic Assessment: Psychological and Psychiatric PerspectivesОт EverandHandbook of Forensic Assessment: Psychological and Psychiatric PerspectivesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Somatoform and Other Psychosomatic Disorders: A Dialogue Between Contemporary Psychodynamic Psychotherapy and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy PerspectivesОт EverandSomatoform and Other Psychosomatic Disorders: A Dialogue Between Contemporary Psychodynamic Psychotherapy and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy PerspectivesChristos CharisОценок пока нет
- Cannabis Use and Mental Health: A Critical Review of Risks and BenefitsОт EverandCannabis Use and Mental Health: A Critical Review of Risks and BenefitsОценок пока нет
- Network Monitoring 6Документ22 страницыNetwork Monitoring 6PUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Rangkaian ICT - 12Документ41 страницаRangkaian ICT - 12PUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Panduan Pembangunan ModulДокумент19 страницPanduan Pembangunan ModulPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- 1 Govnet 1Документ12 страниц1 Govnet 1PUSAT LATIHAN AADK100% (1)
- AntivirusДокумент12 страницAntivirusPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Islamic 12 StepДокумент9 страницIslamic 12 StepPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- IP Addressing 4Документ33 страницыIP Addressing 4PUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Participant Curriculum 01Документ209 страницParticipant Curriculum 01PUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
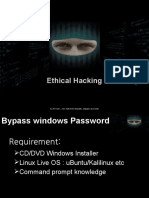
- Ethical HДокумент4 страницыEthical HPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- C1 Mod 1 - Training IntroductionДокумент27 страницC1 Mod 1 - Training IntroductionPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Agen Proveketeur Dan PeranannyaДокумент20 страницAgen Proveketeur Dan PeranannyaPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- C1 Concert ReviewДокумент81 страницаC1 Concert ReviewPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- C1 Mod 2 - Introduction To Psychoactive Substance UseДокумент22 страницыC1 Mod 2 - Introduction To Psychoactive Substance UsePUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Agen Proveketeur Dan PeranannyaДокумент20 страницAgen Proveketeur Dan PeranannyaPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- C2 Mod 3 OutcomesДокумент26 страницC2 Mod 3 OutcomesPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Trainer Curriculum 02Документ576 страницTrainer Curriculum 02PUSAT LATIHAN AADK100% (1)
- Kemahiran Asas KaunselingДокумент42 страницыKemahiran Asas KaunselingPUSAT LATIHAN AADK100% (1)
- Tatacara Pemeriksaan PelawatДокумент12 страницTatacara Pemeriksaan PelawatPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Tatacara Pemeriksaan PelawatДокумент12 страницTatacara Pemeriksaan PelawatPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- ASESSMENTДокумент49 страницASESSMENTPUSAT LATIHAN AADK0% (1)
- Konsep Penagihan DadahДокумент54 страницыKonsep Penagihan DadahPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- Konsep Penagihan DadahДокумент54 страницыKonsep Penagihan DadahPUSAT LATIHAN AADKОценок пока нет
- GcsДокумент38 страницGcsFikar DarwisОценок пока нет
- Taking NotesДокумент3 страницыTaking Notesapi-247620221Оценок пока нет
- Religion and Mysticism in Emily Brontë' S Wuthering HeightsДокумент18 страницReligion and Mysticism in Emily Brontë' S Wuthering HeightsIoana Margineanu100% (1)
- Manuscrip RES1BДокумент19 страницManuscrip RES1BJohn Patrick Tolosa NavarroОценок пока нет
- Values, Attitudes and Job SatisfactionДокумент26 страницValues, Attitudes and Job SatisfactionMarjon DimafilisОценок пока нет
- The Impact of Human Resource Management Practices On Turnover of Bank Employees in BangladeshДокумент13 страницThe Impact of Human Resource Management Practices On Turnover of Bank Employees in BangladeshMuhammad AhmadОценок пока нет
- Course Handbook Strategic ManagementДокумент5 страницCourse Handbook Strategic ManagementAroojОценок пока нет
- Handout - Networks - Effective Feedback Skills ExerciseДокумент2 страницыHandout - Networks - Effective Feedback Skills ExerciseJepney50% (2)
- The Will in Psychotherapy - Alberto Alberti PDFДокумент8 страницThe Will in Psychotherapy - Alberto Alberti PDFWill NoyesОценок пока нет
- GCB Pbis HandbookДокумент21 страницаGCB Pbis Handbookapi-256174152100% (1)
- Psych20110400002 86391610 PDFДокумент5 страницPsych20110400002 86391610 PDFshobaОценок пока нет
- What Is Political InstitutionДокумент3 страницыWhat Is Political InstitutionAllan Michelle BarreteОценок пока нет
- Beebe John Energies and Patterns in Psyc PDFДокумент4 страницыBeebe John Energies and Patterns in Psyc PDFapsleunamaОценок пока нет
- An Analysis of Student Difficulties Understanding in Concept Reading CompherentionДокумент3 страницыAn Analysis of Student Difficulties Understanding in Concept Reading CompherentionAlexāŋder KhārapaОценок пока нет
- MPOB Unit 2 NOTESДокумент3 страницыMPOB Unit 2 NOTESDivyanjali SinghОценок пока нет
- Neuroplasticity in Children: Nandini MundkurДокумент3 страницыNeuroplasticity in Children: Nandini MundkurluizetteОценок пока нет
- Article DesignДокумент24 страницыArticle DesignJ.C.VОценок пока нет
- Community Integration Questionnaire Testing FormДокумент4 страницыCommunity Integration Questionnaire Testing FormriddhiОценок пока нет
- RPH BodyДокумент19 страницRPH BodyOren JaОценок пока нет
- Topic 05 All Possible QuestionsДокумент9 страницTopic 05 All Possible QuestionsMaxamed Cabdi KariimОценок пока нет
- Central Auditory Processing Disorder Case StudyДокумент19 страницCentral Auditory Processing Disorder Case StudyChris Sanchez100% (1)
- Caregiver Burden ScaleДокумент8 страницCaregiver Burden ScaleAzizul Fatharoni TofatОценок пока нет
- 21 Habits of Happy People Spirit Science and Metaphysics PDFДокумент5 страниц21 Habits of Happy People Spirit Science and Metaphysics PDFlinteringОценок пока нет
- Holy Spirit School of Tagbilaran Home School Sessions and Task Practical Research 2Документ10 страницHoly Spirit School of Tagbilaran Home School Sessions and Task Practical Research 2Johnrey Gentiles LaciaОценок пока нет
- Single Parenting and TodayДокумент12 страницSingle Parenting and Todaygelli joy corpuz67% (3)
- PPP Lesson PlanДокумент9 страницPPP Lesson Planmaster_bass77Оценок пока нет
- Philo of Man CapSLET LC 1.1Документ9 страницPhilo of Man CapSLET LC 1.1mjОценок пока нет
- Gabarro PDFДокумент4 страницыGabarro PDFGordanaMrđaОценок пока нет
- Cross-Case AnalysisДокумент16 страницCross-Case AnalysiswaiОценок пока нет
- Pom - Organisation NotesДокумент5 страницPom - Organisation NotesShodan IddyaОценок пока нет