Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
USD Vs INR
Загружено:
Sunny Khandelwal0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
112 просмотров27 страницThis is a ppt on USD vs INR during the month of July 2013 to August 2013.
Оригинальное название
USD vs INR
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis is a ppt on USD vs INR during the month of July 2013 to August 2013.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
112 просмотров27 страницUSD Vs INR
Загружено:
Sunny KhandelwalThis is a ppt on USD vs INR during the month of July 2013 to August 2013.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 27
Forex: The foreign exchange market (forex, FX,
or currency market) is a global decentralized market
for the trading of currencies.
Currency: Currency is anything that is used in any
circumstances, as a medium of exchange.
Repo Rate: The rate at which the RBI lends money
to commercial banks is called repo rate.
Balance Of Trade: The difference between a
country's imports and its exports.
Reverse Repo rate: The rate at which
the RBI borrows money from commercial banks.
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): The amount of funds
that the banks have to keep with the RBI.
FII: Foreign Institutional Investor, An investor or
investment fund that is from or registered in a
country outside of India.
Trade Deficit: An economic measure of a negative
balance of trade in which a country's imports exceeds
its exports. A trade deficit represents an outflow of
domestic currency to foreign markets.
INR has suffered significantly from Fed tapering implications,
trading to a new record low against the USD toward the end of
June. The sharp depreciation has also shaken fixed income and
equity markets, key financing avenues for the countrys
current account deficit.
FOREX: The foreign exchange market (forex, FX,
or currency market) is a global decentralized market for the
trading of currencies. The main participants in this market are
the larger international banks. The foreign exchange market
assists international trade and investment by enabling currency
conversion. It also supports direct speculation in the value of
currencies, and the carry trade, speculation based on the
interest rate differential between two currencies.
Currency Traded: GBP/USD, EUR/USD, USD/JPY
INDIAN RUPEE(INR):
The Indian rupee (ISO code: INR) is the official currency of
the Republic of India. The Reserve Bank manages currency in
India and derives its role in currency management on the basis
of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
Year2000 Year2004 Year2006 Year2007 Year2008 Year2009 Year2010 Year2013
USD/INR
YEAR
The Objectives of study behind this project are to learn about
the following aspects:
To understand the basic concepts of Forex
To understand the difference between forex market and other
markets.
To understand the concept of a pip (percentage in point)
To know about the currencies traded in forex market,
To study the major factors that affects the valuation of
currency in international market.
To study the recent events that lead to the depreciation of
Indian Rupee.
To understand the factors affecting price of any currency.
To understand the concept of currency forecasting i.e; value of
INR against USD.
SCOPE
This project was based on the study of Indian Rupee
depreciation against the U.S Dollar during June 2013 to
August 2013.
DATA SOURCE
Research included gathering both Primary and Secondary data.
Primary Data is the first hand data, which are selected a fresh
and thus happen to be original in character. Primary Data was
crucial to have a watch of stock market and to trace various
past and present fluctuations on Indian Rupee against the U.S.
Dollar.
Secondary Data are those which has been collected by
someone else and which already have been passed through
statistical process. Secondary data has been taken from
internet, newspaper, articles and journals from professionals,
magazines and companies web sites.
RESEARCH APPROACH
The research approach used was survey and observation
method which is a widely used method for data collection and
best suited for descriptive and conclusive type of research
survey includes research instrument like online survey either
by use of internet or by books and journals. Conclusive type of
research includes interviews from professional consultants in
the company.
In international markets, this price is decided just like the price of
any other commodity in the market, by the relative demand and
supply.
The demand for a currency is created by two factors, its exports or
the investments that people want to make in that currency or assets
denominated in that currency.
The force of market sentiment becomes far overpowering than the
ability of the monetary agencies to control the value of their
currency.
The effects of falling exports or rising imports are the reverse - they
reduce its demand and weaken the currency. Outflow of capital has
the same effect.
Currency Depreciation and Appreciation
The loss of value of a country's currency with respect to one or more
foreign reference currencies, typically in a floating exchange
rate system whereas an increase of value of a currency, is currency
appreciation.
More and more rupees are
brought in our country and dollars
are sold
More and more rupees are sold
and dollars are brought
CAUSES OF A NATION'S CURRENCY APPRECIATION
OR DEPRECIATION
Relative Product Prices: If a country's goods are relatively
cheap, foreigners will want to buy those goods. In order to buy
those goods, they will need to buy the nation's currency.
Monetary Policy: Countries with expansionary (easy)
monetary policies will be increasing the supply of their
currencies, which will cause the currency to depreciate and
vice versa.
Income Changes: Indian consumers purchase
more U.S. goods, the quantity of U.S. dollars demanded will
exceed the quantity supplied and the U.S. dollar will
appreciate.
Short-term Factors
Interest rates: A government may decide to lower interest rates in an
attempt to stimulate growth in the economy.
Trade flows: A trade surplus will make the currency stronger whereas a
trade deficit will usually weaken the currency.
Links to commodity based currencies: Currencies such as Canadian
dollar are commodity linked currencies and their exchange rates tend to
increase in value when there is a rise in commodities such as oil.
Long-term Factors
Long term inflation: Inflation wears away the purchasing power of
money in that country. So higher inflation in a country typically
weakens its currency.
Economic growth: It can take many years for an economy to recover
i.e. the subprime crisis in the US took place over three years ago, and it
has taken many years for the US economy to recover to the level it's
currently at.
FII outflow touches record high USD 7 Billion in June,2013
FIIs offload USD 3 Billion worth equities in July,2013.
RBI kept interest rates unchanged.
Increase in Crude prices.
Increase in Fiscal Deficit of India.
Unchanged Interest Rates BY RBI.
USA initiated process of slowing down Bond Buying
programme.
Strengthening of US Dollar against major world currencies
High Current Account Deficit
High Fiscal Account Deficit
High Cost of Subsidies
Lack Of Intervention From RBI
Continued Global Uncertainty
Persistent Inflation
Interest Rate Difference
Advantages:
Beneficial to the Exporters
Good News for NRIs
Benefits to investors invested in International Funds
Benefits to Tourism Industry
Disadvantages:
Imports become extremely expensive
Reduction in Purchasing Power Parity
Oil Price will increase
Rise in Inflation
Effect on FMGC goods
CURRENCY TRENDS
FX
Rate
Spot
June
13Q1 13Q2 13Q3 13Q4 14Q1 14Q2 14Q3 14Q4
USD
INR
60.2 54.3 60.2 58.6 58.5 58.0 57.5 57.0 56.5
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
13Q1 13Q2 13Q3 13Q4 14Q1 14Q2 14Q3 14Q4
U
S
D
I
N
R
Currency Trends
58
58.5
59
59.5
60
60.5
61
Date wise data of USD/INR
(20
th
June 2013 to 31
st
July 2013)
Average (Last 12 Months) 54.56
Average (Last 10 Years) 46.18
High (Last 12 Months) 55.94 (June, 2012)
Low (Last 12 Months) 52.96 (October, 2012)
High (Since January, 1973) 55.94 (June, 2012)
Low (Since January, 1973) 7.27 (June, 1973)
Indian Rupee (INR) Currency Exchange Forecast
Target
Month
Forecast HDTFA
Forecast for the currency
exchange rate of the Indian Rupee
for the target month indicated,
shown in Rupees per US Dollars
(USD/INR).
May 2014 56 4.01
The 12 month forecast for the Indian Rupee is in the table at the top of
this page. The forecast is that the exchange rate for the Indian
Rupee will be roughly 55.99 Indian Rupees to the USD.
The table shows a HDTFA of 4.01 which suggests that the May, 2014
currency exchange rate could easily fall between 60.01 and 51.98
USD/INR.
Lack of prior research study on the topic.
Lack of availability of required data.
Lack of measures used to collect the data.
Limited scope of study.
Limited time to watch the market and to collect the
required data.
Lack of availability of primary data
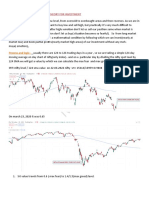
The rupee, sank by a staggering 137 paisa to its lifetime low of
60.76 against the US dollar, in the opening day at 58.39 and
was still becoming weak.
INR Depreciation: The Indian National Rupee (INR) has
depreciated 15% in past two months.
Overall, USD/INR displays a bullish trend: We estimate
USD/INR to likely continue this trend in FY2013 and target a
58-60 level. We expect the worst case USD/INR pair to make
a base around 52.10 levels in the next one year.
Indian GDP: We expect Indias GDP to likely to slow down
further to around 6% and below.
Emerging Markets: India will likely remain an
Underperformer across all Emerging Markets.
International Currencies: We believe international currencies to
remain weak with the Euro having a target of 1.16, GBP 1.50, Yen
85 and the Australian Dollar Parity.
US 10-year Treasury yield: We estimate yield should witness 1.20%
in FY2013.
How to control this situation?
RBI should sell Forex reserves and buy rupees in an immediate
action in order to arrest the further decline in the value of rupees
Government should create a stable political and economic
environment in order to make India an attractive destination for
foreign investments.
Government should increase the limit of FDI in the existing sectors.
The Govt. increased import duty on gold import to 8 % from 6 %.
RBI creates Demand for rupee by sucking excess rupee liquidity.
http://www.dailyfx.com/forex_market_news/forecasts
http://www.linkedin.com/company/inforay-consultants-pvt-ltd
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Currency_appreciation_and_depreciation
http://www.markets.com/education/fundamental-analysis/main-economic-
indicators.html
http://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/06/forexcommodities.asp
http://www.wantchinatimes.com/news-
subclasscnt.aspx?id=20130528000046&cid=1102
http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/AnnualReportPublications.aspx?Id=1080
http://www.forecast-chart.com/usd-indian-rupee.html
http://www.moneycontrol.com/mccode/currencies/
http://www.moneycontrol.com/news/rupee/how-depreciating-rupee-
impacts-middle-class-indians_932002.html
Вам также может понравиться
- Currency Option Strat PDFДокумент11 страницCurrency Option Strat PDFssinha122Оценок пока нет
- Macroeconomic Factors Affecting USD INRДокумент16 страницMacroeconomic Factors Affecting USD INRtamanna210% (1)
- USDINR Option StrategyДокумент1 страницаUSDINR Option Strategynarendra_pОценок пока нет
- Standard Deviation (Volatility) : AverageДокумент7 страницStandard Deviation (Volatility) : AverageSachin SahooОценок пока нет
- Forex Business Plan.01Документ8 страницForex Business Plan.01Kelvin Tafara SamboОценок пока нет
- Trading StrategyДокумент17 страницTrading StrategyxrashexОценок пока нет
- Otion Trading StrategyДокумент59 страницOtion Trading StrategySurendra Singh Bhadouriya100% (1)
- Central Pivot Range (CPR)Документ10 страницCentral Pivot Range (CPR)Jaideep PoddarОценок пока нет
- Trader PyramidДокумент12 страницTrader Pyramidramji3115337Оценок пока нет
- DRIVATIVES Options Call & Put KKДокумент134 страницыDRIVATIVES Options Call & Put KKAjay Raj ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Advance Options StrategiesДокумент14 страницAdvance Options StrategiesMahbubul Islam KoushickОценок пока нет
- Option Strategy Final EditnДокумент58 страницOption Strategy Final EditnHarshit Shah100% (1)
- Swaps and Indian Swap MarketДокумент16 страницSwaps and Indian Swap Marketrajde100% (3)
- Strategy Guide: Bull Call SpreadДокумент14 страницStrategy Guide: Bull Call SpreadworkОценок пока нет
- Mastering Expiry Day Trading PDFДокумент126 страницMastering Expiry Day Trading PDFpr9cdfrz7pОценок пока нет
- Fib Retracement ToolДокумент9 страницFib Retracement ToolSharma compОценок пока нет
- FinIdeasBackUp Basic Option Trader BrochureДокумент8 страницFinIdeasBackUp Basic Option Trader Brochurekrana26Оценок пока нет
- 17.forecasting of Forex Market Using Technical AnalysisДокумент65 страниц17.forecasting of Forex Market Using Technical Analysisharrydeepak100% (1)
- Doji Pattern: NeutralДокумент4 страницыDoji Pattern: NeutralKrishnadeep KhakhriaОценок пока нет
- Presentation Usdinr - FinalДокумент45 страницPresentation Usdinr - FinalBhavin Karia100% (1)
- CourseOutline TAMДокумент5 страницCourseOutline TAMJyoti BudhiaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4-Hedging With FuturesДокумент36 страницLecture 4-Hedging With FuturesNIAZ ALI KHANОценок пока нет
- Tweezer TopДокумент5 страницTweezer Topkarthick sudharsanОценок пока нет
- WWW Investopedia Com MACD PrimulДокумент10 страницWWW Investopedia Com MACD PrimulAvram Cosmin GeorgianОценок пока нет
- Date Open High Low Close PP Gain/ (Loss)Документ6 страницDate Open High Low Close PP Gain/ (Loss)Mrdilipa DilipaОценок пока нет
- BreakoutДокумент0 страницBreakoutjavamateОценок пока нет
- Delta Gamma Neutral StrategyДокумент2 страницыDelta Gamma Neutral StrategyakrathiОценок пока нет
- Options Stratergies Payoff ChartДокумент2 страницыOptions Stratergies Payoff ChartAbhijit ButalaОценок пока нет
- Laththur Arasu Trading Company: Nifty Option Day Trading Plan Nifty TrendДокумент1 страницаLaththur Arasu Trading Company: Nifty Option Day Trading Plan Nifty Trend9952090083Оценок пока нет
- Option Chain Excel Sheet Required FilesДокумент1 страницаOption Chain Excel Sheet Required Filesudhaya kumar100% (1)
- Value Research Stock Advisor - Sterlite TechnologiesДокумент32 страницыValue Research Stock Advisor - Sterlite TechnologiesjesprileОценок пока нет
- Option Trading StrategiesДокумент32 страницыOption Trading StrategiesNikhil Gauns DessaiОценок пока нет
- The Camarilla Equation ExplainedДокумент9 страницThe Camarilla Equation ExplainedSAM SMITHОценок пока нет
- Fundamental AnalysisДокумент6 страницFundamental Analysismanoj_mmmОценок пока нет
- The Architect Program CatalogueДокумент16 страницThe Architect Program CatalogueTrevor HanniganОценок пока нет
- Hedging StrategiesДокумент10 страницHedging StrategiesLakshman Kumar YalamatiОценок пока нет
- Delta Hedging Dayton ManufacturingДокумент10 страницDelta Hedging Dayton ManufacturingMeet JivaniОценок пока нет
- Implied VolatilityДокумент15 страницImplied VolatilityAjit SinghОценок пока нет
- Derpo Class 1& 2Документ5 страницDerpo Class 1& 2laale dijaanОценок пока нет
- Algorithm Trading in Indian Financial MarketsДокумент3 страницыAlgorithm Trading in Indian Financial MarketswakhanОценок пока нет
- Strategy Portfolio: Dravyaniti Consulting LLPДокумент13 страницStrategy Portfolio: Dravyaniti Consulting LLPChidambara StОценок пока нет
- Echange Rate Mechanism: 1. Direct Quote 2. Indirect QuoteДокумент4 страницыEchange Rate Mechanism: 1. Direct Quote 2. Indirect QuoteanjankumarОценок пока нет
- KKДокумент34 страницыKKgoud mahendharОценок пока нет
- Hedging Strategies Using Futures PDFДокумент11 страницHedging Strategies Using Futures PDFRishabh GuptaОценок пока нет
- Welcome To Momentum Trading SetupДокумент12 страницWelcome To Momentum Trading SetupSunny Deshmukh0% (1)
- Power Pivots 80 ManualДокумент11 страницPower Pivots 80 ManualANIL1964Оценок пока нет
- Bullish: Option Strategies For Bullish ViewДокумент10 страницBullish: Option Strategies For Bullish ViewAshutosh ChauhanОценок пока нет
- SlidesДокумент77 страницSlidesSuneel HoodaОценок пока нет
- Market Moves From High Level To Low Level, From Oversold To Overbought Areas and Then Reverses. As We Are inДокумент3 страницыMarket Moves From High Level To Low Level, From Oversold To Overbought Areas and Then Reverses. As We Are inroughimОценок пока нет
- Moving Average Indicator Checklist: Tradingwithrayner PresentsДокумент8 страницMoving Average Indicator Checklist: Tradingwithrayner PresentsHimanshu Singh RajputОценок пока нет
- Nifty Options ProfitДокумент16 страницNifty Options ProfitMohanОценок пока нет
- A Presentation On: Trading StrategiesДокумент26 страницA Presentation On: Trading StrategiessumitkjhamОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Technical Analysis: Andrew WilkinsonДокумент37 страницIntroduction To Technical Analysis: Andrew WilkinsonsmslcaОценок пока нет
- Forex Risk ManagementДокумент242 страницыForex Risk ManagementParvesh AghiОценок пока нет
- Lynden Reabow FX Trader PSG Online: Derivatives Trading - Currency FuturesДокумент33 страницыLynden Reabow FX Trader PSG Online: Derivatives Trading - Currency FuturesManoj KumarОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Trading Types Fundamental TradersДокумент11 страницAn Introduction To Trading Types Fundamental TradersGopi KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Currency Markets: by DVKДокумент74 страницыIntroduction To Currency Markets: by DVKSaubhagya Suri100% (1)
- Commodity Derivatives Study NotesДокумент24 страницыCommodity Derivatives Study NotesAkshaya Investmentz100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - Stress ManagementДокумент8 страницChapter 3 - Stress ManagementSunny KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- Business Plan On CafeДокумент16 страницBusiness Plan On CafeSunny KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- On NpaДокумент14 страницOn NpaSunny KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- Roles and SkillsДокумент11 страницRoles and SkillsSunny KhandelwalОценок пока нет
- Urban Farm Business PlanДокумент77 страницUrban Farm Business PlanZartosht Matthijs100% (11)
- Chapter 1-5Документ6 страницChapter 1-5Bien BibasОценок пока нет
- 7399352Документ30 страниц7399352Amit BhagatОценок пока нет
- CSR Strategy For Sustainable Business Samy Odemilin and BamptonДокумент16 страницCSR Strategy For Sustainable Business Samy Odemilin and BamptonabbakaОценок пока нет
- Rural Marketing MixДокумент4 страницыRural Marketing MixEditor IJTSRDОценок пока нет
- Small Cap & Special SituationsДокумент3 страницыSmall Cap & Special SituationsAnthony DavianОценок пока нет
- ST8 Pu 15 PDFДокумент58 страницST8 Pu 15 PDFPolelarОценок пока нет
- Kumpulan Soal Listening Part 2 & 3Документ13 страницKumpulan Soal Listening Part 2 & 3Martallena DwinandaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3: One Lecture 3: One - Period Model Period Model Pricing PricingДокумент69 страницLecture 3: One Lecture 3: One - Period Model Period Model Pricing PricingJordanSykesОценок пока нет
- Neoclassical Theory of The State Summary (North)Документ3 страницыNeoclassical Theory of The State Summary (North)Guille FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Let ReviewerДокумент5 страницLet ReviewerJo-Mar Arellano Avena100% (1)
- Ijcbm: An Overview of Indian Alcohol IndustryДокумент7 страницIjcbm: An Overview of Indian Alcohol IndustryAbhishek SharmaОценок пока нет
- Mem Chapter 6 - Rational InsanityДокумент18 страницMem Chapter 6 - Rational InsanityHarleen queenzelОценок пока нет
- Unit 3: Foreign Direct Investment: ECON 401 The Changing Global EconomyДокумент52 страницыUnit 3: Foreign Direct Investment: ECON 401 The Changing Global Economyjacklee1918Оценок пока нет
- JSW Steel: (Jswste)Документ8 страницJSW Steel: (Jswste)XYZОценок пока нет
- A Self-Reliant and Independent Economic OrderДокумент14 страницA Self-Reliant and Independent Economic OrderJen DeeОценок пока нет
- Managerial Economic 2Документ20 страницManagerial Economic 2Ahmad Hirzi AzniОценок пока нет
- Current Liabilities in Financial AccountingДокумент2 страницыCurrent Liabilities in Financial AccountingdmugalloyОценок пока нет
- Excel Crash CourseДокумент3 страницыExcel Crash CourseAniya SharmaОценок пока нет
- Questions With Answers On is-LM ModelДокумент12 страницQuestions With Answers On is-LM ModelAkshay Singh67% (3)
- Irfan Habib Capital Accumulation Pre Colonial IndiaДокумент25 страницIrfan Habib Capital Accumulation Pre Colonial IndiaNajaf HaiderОценок пока нет
- Keynes Presentation - FINALДокумент62 страницыKeynes Presentation - FINALFaith LuberasОценок пока нет
- SwensensДокумент21 страницаSwensensBé LinhОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент4 страницыNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentRajni KumariОценок пока нет
- Levelized Cost of Energy Calculation - BV - ENДокумент16 страницLevelized Cost of Energy Calculation - BV - ENpankajmayОценок пока нет
- M&M PizzaДокумент1 страницаM&M Pizzasusana3gamito0% (4)
- InvoiceДокумент1 страницаInvoiceNabeel Shaikh0% (1)
- Final Examination BUSCOMДокумент21 страницаFinal Examination BUSCOMToni Marquez100% (1)
- Tim Roberts Building A BrandДокумент39 страницTim Roberts Building A BrandMaliha KhanОценок пока нет
- IB Economics SL15 - Economic IntegrationДокумент2 страницыIB Economics SL15 - Economic IntegrationTerran100% (3)