Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Electromagnetism: By: Joshua Alfred de La Cruz Nicole Marie Dela Cruz Stephen Miayo
Загружено:
10march1965Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Electromagnetism: By: Joshua Alfred de La Cruz Nicole Marie Dela Cruz Stephen Miayo
Загружено:
10march1965Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
ELECTROMAGNETISM
By:
Joshua Alfred De la Cruz
Nicole Marie Dela Cruz
Stephen Miayo
History
The origin of electricity is and
magnetism sprang from ancient mens
curiosity over the ability of two
materials, amber and lodestone to
attract other materials.
With the publication of James Clerk
Maxwell's 1873 Treatise on
Electricity and Magnetism in which
the interactions of positive and
negative charges were shown to be
regulated by one force.
History
There are four main effects
resulting from these
interactions, all of which have
been clearly demonstrated by
experiments:
Electric charges attract or repel
one another with a force
inversely proportional to the
square of the distance between
them: unlike charges attract,
like ones repel.
History
Magnetic poles attract or
repel one another in a
similar way and always come
in pairs: every north pole is
yoked to a south pole.
An electric current in a wire
creates a circular magnetic
field around the wire, its
direction depending on that
of the current.
History
A current is induced in a
loop of wire when it is
moved towards or away from a
magnetic field, or a magnet
is moved towards or away
from it, the direction of
current depending on that of
the movement.
Magnetism
It is the term used to refer to the
ability of lodestones to attract iron.
A material having this property is
called a magnet.
The modern name for lodestone or
magnetic iron ore is magnetite.
Classification
Natural
They are found in nature and are
called lodestones or magnetite.
Artificial
May be temporary or permanent.
Retentivity is the ability of a
magnetic material to retain its
magnetism after it has been
magnetized.
Classification
Electromagnet
A magnet whose magnetic field
is produced by electric current
passing through coils of wire
wrapped around a core.
Types
Ferromagnetism
Are strongly attracted be a magnet.
They include iron, cobalt, nickel, and steel.
In ferromagnetic materials, all electrons are
spinning in the same direction.
Diamagnetism
Is a weak response to magnetic field.
Materials are repelled by a magnetic field.
Metals, like bismuth, copper, gold, silver,
lead, nonmetals, water, and organic compounds
are diamagnetic.
Types
Paramagnetism
Weakly attracted to magnets.
When cooled, more magnetic.
Geomagnetism
Referred as Earths
magnetism.
William Gilbert- conducted
experiments and concluded
that the Earth was a huge
magnet.
Law of Magnetic Poles
Peter Petegrinus- same poles
repel.
William Gilbert- confirmed it.
John Michael- force of
attraction or repulsion
between poles varies inversely
as the square of the distance
between them.
Law of Magnetic Poles
Charles de Coulomb- force between two
poles is directly proportional to the
product of the poles and inversely
proportional to the square of the
distance between them.
By combining these relation, he proposed
the equation:
m
1
m
2
F= k
d
2
Where F is the force, k as the constant, m are pole
strengths in ampere, and d is the distance in meters.
Magnetic Field
Is a region of space where a
magnet is capable of
exerting a force on a
magnetic material.
Analogous to the electric
field around an electric
charge.
Magnetic Field
Is also defined in terms of
the force exerted on an
electric charge moving in the
field.
Michael Faraday- introduced
the idea that the magnetic
field is made up of lines of
force which is called the
magnetic flux.
Magnetic Field
Magnetic flux- its unit is
weber(Wb), flux per unit
area perpedicular to te fiel
is called magnetic field
intensity the SI unit for I
is tesla. Named afte Nikola
tesla.
Magnetic Effect of Current
Chistian Oersted- made a
demonstration on the heating
effect of a current.
by this , he accidentally discovered
that a current-carrying conductor
produces a magnetic field and this
was influenced the orientation of
the nearby compass.
right hand rule- the magnetic field
produced by a current may be
determined by this.
The Electromagnet
A magnet whose magnetic field is
produced by electric current
passing through coils of wire
wrapped around a core and the
strength depends on the number of
turns and current.
The first ever electromagnet was
made by William Sturgeon and
later improved by Joseph Henry.
Uses
They can be turn on/off.
The strength can be varied.
Very large magnetic field can be
produced.
Used in steel yards.
Essential parts in the construction of
electric meters, electric generators,
circuit breakers, motors and others.
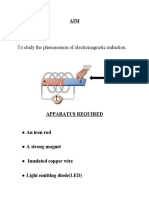
Electromagnetic Induction
Process by which a changing
magnetic flux produces electric
current.
The current and emf produce is
called induced current an induces
emf.
There are two laws describing the
electromagnet induction:
Faradays law and Lenzs law.
Electromagnetic Induction
Faradays law- states that
whenever there is a change in
the magnetic flux in a
circuit, an induced current is
produce.
Lenzs law- states that the
induced current flows in a
direction so as to oppose the
change causing it.
Application
Discovery of Faraday and
Henry paved the development
of the generator,
transformer and other
devices that made the
production of electricity
cheaper.
AC/DC Generator
Converts mechanical energy
to electrical energy.
Hyppolyte Pixii- was
credited for having made the
first electric generator.
Parts of a Simple AC generator
armature- consist of coils of
insulated wire wound around a
soft iron core.
- attached to a shaft so
that it can rotate between the
poles of the magnet.
- ends are connected to
the external circuit by means of
slip rings that rotate with the
armature.
Parts of a Simple AC generator
Slip rings- made of either brass or
copper.
- insulated from each other
and from he shaft.
- each rings slides against
the stationary brush .
Brush- collect the current and
transmit it to the external circuit.
Motor
A generator operating
reverse.
Changes electrical energy to
mechanical energy.
Has the same parts as a
simple DC generator.
Parts of a Motor
Brushes are connected to a
battery to send current to the
armature.
Magnetic field produced by this
current in the armature interacts
with the field of the magnet and
exerts a force that rotates the
armature.
A shaft attached to the armature
makes the motion for doing work.
Parts of a Motor
Transformer
a device used to raise or
lower the voltage of an AC
source.
consist primary and
secondary coils placed side
by side having a common iron
core.
Transformer
Plays a major role in power
transmission.
Whenever electricity is
transmitted , there is
always loss of power because
of the resistance of the
transmission wires.
Types of Transformer
Step down transformer-
lowers the voltage.
Step up transformer- raises
the voltage.
THANK YOU!
Вам также может понравиться
- Teresa of Avila - The Life of ST Teresa, A Carmelite Nun Reprint 1912Документ674 страницыTeresa of Avila - The Life of ST Teresa, A Carmelite Nun Reprint 1912WaterwindОценок пока нет
- Veep 4x10 - Election Night PDFДокумент54 страницыVeep 4x10 - Election Night PDFagxz0% (1)
- TG Time - Speed - DistanceДокумент46 страницTG Time - Speed - DistanceShivam Dubey80% (10)
- Electricity and MagnetismДокумент7 страницElectricity and MagnetismAlan GamingОценок пока нет
- Precision Nutrition. Nutrient TimingДокумент21 страницаPrecision Nutrition. Nutrient TimingPaolo AltoéОценок пока нет
- Group 4 CariCRIS Case SubmissionДокумент6 страницGroup 4 CariCRIS Case SubmissionKingsuk MaityОценок пока нет
- Magnetism & ElectromagnetismДокумент38 страницMagnetism & ElectromagnetismganapathiОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Induction ArmanДокумент12 страницElectromagnetic Induction ArmanMalikОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentДокумент13 страницMagnetic Effect of Electric Currentanjupal100% (4)
- Bago Project CharterДокумент6 страницBago Project CharterLarize BautistaОценок пока нет
- Electricity and Magnetism: Sonny P. de Leon MT1Документ58 страницElectricity and Magnetism: Sonny P. de Leon MT1iMer22100% (1)
- Magnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Документ43 страницыMagnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Heidi QuiranteОценок пока нет
- Advanced Finite Element Model of Tsing Ma Bridge For Structural Health MonitoringДокумент32 страницыAdvanced Finite Element Model of Tsing Ma Bridge For Structural Health MonitoringZhang ChaodongОценок пока нет
- Delta Robot KinematicsДокумент11 страницDelta Robot KinematicssekinОценок пока нет
- Motionless Pulsed SystemsДокумент0 страницMotionless Pulsed SystemsmatijahОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Induction: Name - Kunal Agrawal Roll No. - 20Документ22 страницыElectromagnetic Induction: Name - Kunal Agrawal Roll No. - 20Kunal AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentДокумент18 страницMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentMayurItankarОценок пока нет
- Culture and Creative Industries in TanzaniaДокумент70 страницCulture and Creative Industries in TanzaniaYana ArsyadiОценок пока нет
- 03 Network TOPCIT PDFДокумент80 страниц03 Network TOPCIT PDFJayson AguilarОценок пока нет
- The Prodigious MuseДокумент466 страницThe Prodigious Musesleepyninjitsu100% (1)
- SSPC - Guia 12Документ6 страницSSPC - Guia 12José Alvaro Herrera Ramos50% (2)
- Science ReviewerДокумент5 страницScience ReviewerShaine RectoОценок пока нет
- MagnetismДокумент4 страницыMagnetismnicoaviles725Оценок пока нет
- Electricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismДокумент51 страницаElectricity Magnetism and ElectromagnetismJun OrbitaОценок пока нет
- Mag ElectromagДокумент38 страницMag ElectromagJames Paul Micael GargantaОценок пока нет
- Electricuty and MagneДокумент51 страницаElectricuty and MagneVandana SharmaОценок пока нет
- Science 10-Lesson 10Документ34 страницыScience 10-Lesson 10afloresОценок пока нет
- Pajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Документ4 страницыPajunar J Jonna P. - Assignment 2Jonna PajunarОценок пока нет
- Final Exam in ElectricityДокумент7 страницFinal Exam in ElectricityNiko Igie Albino PujedaОценок пока нет
- Submitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - MbaДокумент7 страницSubmitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - Mbashailesh singhОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic InductionДокумент18 страницElectromagnetic Inductionwakki 10Оценок пока нет
- Electromagnetism For Printing ModuleДокумент24 страницыElectromagnetism For Printing ModuleBob PhigglebottomОценок пока нет
- Basic Principle of ElectricityДокумент5 страницBasic Principle of ElectricityFavour OgbonnaОценок пока нет
- KN Phy Project 12Документ13 страницKN Phy Project 12Mariappan NatarajanОценок пока нет
- Reviewer: Build A Motor Activity: Topic: MagnetismДокумент14 страницReviewer: Build A Motor Activity: Topic: MagnetismOP GAMINGОценок пока нет
- Powerpoint ElectronicsДокумент30 страницPowerpoint Electronicsjanine jaboneteОценок пока нет
- Unit 11 Electricity & MagnetismДокумент60 страницUnit 11 Electricity & Magnetismtheswag9876Оценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic InductionДокумент25 страницElectromagnetic Inductionnivasan aОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 FinalДокумент15 страницChapter 8 Finalsaleamlak wendmnewОценок пока нет
- Unit 11aДокумент45 страницUnit 11aGramoz CubreliОценок пока нет
- CH 13Документ12 страницCH 13charanОценок пока нет
- Artikel Listrik MagnetДокумент7 страницArtikel Listrik MagnetAgnes NovitaОценок пока нет
- ProjectДокумент8 страницProjectRaV anОценок пока нет
- Barrera, Jasper Owen Albeso - Chapters 4-6Документ13 страницBarrera, Jasper Owen Albeso - Chapters 4-6Jade BaliolaОценок пока нет
- Kashish Physics ProjectДокумент6 страницKashish Physics ProjectNirmit JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Charge Particles: Science Terms Photo/ ImageДокумент5 страницCharge Particles: Science Terms Photo/ ImageJireh Joy BaliliОценок пока нет
- Physics AbhinavДокумент22 страницыPhysics AbhinavabhinavОценок пока нет
- ElectromagnetsДокумент51 страницаElectromagnetsRoanne Mae MañalacОценок пока нет
- PHYSICSДокумент7 страницPHYSICSMohamed Mounir MYP3Оценок пока нет
- Reading Comprehension Worksheet - 10th GradeДокумент4 страницыReading Comprehension Worksheet - 10th GradeAngelica Calamba CalicaОценок пока нет
- Physics Investigatory ProjectДокумент9 страницPhysics Investigatory ProjectKURRA DIVIT SOSHОценок пока нет
- MagnetismДокумент45 страницMagnetismPatel DipenОценок пока нет
- BEX20903 Chapter 1 EMTДокумент18 страницBEX20903 Chapter 1 EMTHameed SareaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Class - X ScienceДокумент18 страницChapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current: Class - X ScienceGovind DabralОценок пока нет
- Archt 33Документ17 страницArcht 33Kean Matthew SantiagoОценок пока нет
- Art Integerated Project Science by Shivam Adinath Munde 10th-f.Документ22 страницыArt Integerated Project Science by Shivam Adinath Munde 10th-f.Chaynamo GamingОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic InductionДокумент10 страницElectromagnetic InductionKatrinaОценок пока нет
- Physics Project: Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentДокумент10 страницPhysics Project: Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentananditaОценок пока нет
- 3-5 Physics Elec MagДокумент34 страницы3-5 Physics Elec MagPrecious BalgunaОценок пока нет
- Physics ProjectДокумент20 страницPhysics Projectblah68194Оценок пока нет
- Magnetic Effects Class 10 Cbse NotesДокумент20 страницMagnetic Effects Class 10 Cbse NotesAsmita PandeyОценок пока нет
- Project Sciencegroup4Документ19 страницProject Sciencegroup4Sean Matthew Del cruzОценок пока нет
- Eddy CurrentsДокумент5 страницEddy CurrentsDivyanshu KaushikОценок пока нет
- ELECTRICITYДокумент6 страницELECTRICITYsamuel rojasОценок пока нет
- Class X Science (Magnetic Effect of Electric Current)Документ10 страницClass X Science (Magnetic Effect of Electric Current)Mohammad RezaullahОценок пока нет
- AC GeneratorДокумент16 страницAC Generatorsheikhiyad60Оценок пока нет
- Physics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairaneДокумент18 страницPhysics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairanePrerana PorechaОценок пока нет
- 3rd Quarter Week 4 Electricity and MagnetismДокумент22 страницы3rd Quarter Week 4 Electricity and MagnetismStephanie AquinoОценок пока нет
- SciiДокумент7 страницSciimae condeОценок пока нет
- Phy PRJДокумент9 страницPhy PRJStudies 123Оценок пока нет
- Ja303 Automotive ElectricalДокумент23 страницыJa303 Automotive ElectricalMohd SyazwanОценок пока нет
- Investigatory Project On TransformersДокумент16 страницInvestigatory Project On Transformers10march196588% (8)
- For Mohar Enterprisese PropДокумент2 страницыFor Mohar Enterprisese Prop10march1965Оценок пока нет
- Fganh D (KK : Eqdr Ikb LkexzhДокумент4 страницыFganh D (KK : Eqdr Ikb Lkexzh10march1965Оценок пока нет
- Present G.M.Документ6 страницPresent G.M.10march1965Оценок пока нет
- Information For 2014 - 2016 MBA ProgrammeДокумент1 страницаInformation For 2014 - 2016 MBA Programme10march1965Оценок пока нет
- Company Interview ExperiencesДокумент3 страницыCompany Interview Experiences10march1965Оценок пока нет
- Kritika Bahl: Phone No.: 9711958723 E-Mail Address: H.no 40, Pocket-28, Sector-24, Rohini, Delhi-85Документ2 страницыKritika Bahl: Phone No.: 9711958723 E-Mail Address: H.no 40, Pocket-28, Sector-24, Rohini, Delhi-8510march1965Оценок пока нет
- Best MarksheetsДокумент478 страницBest Marksheets10march1965Оценок пока нет
- Adeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFДокумент12 страницAdeyinka Wulemat Olarinmoye - The Images of Women in Yoruban Folktales PDFAngel SánchezОценок пока нет
- Liquid Holdup in Large-Diameter Horizontal Multiphase PipelinesДокумент8 страницLiquid Holdup in Large-Diameter Horizontal Multiphase PipelinessaifoaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Consumer Behavior: by Dr. Kevin Lance JonesДокумент18 страницIntroduction To Consumer Behavior: by Dr. Kevin Lance JonesCorey PageОценок пока нет
- The "Write" Way: A Judicial Clerk's Guide To Writing For The CourtДокумент92 страницыThe "Write" Way: A Judicial Clerk's Guide To Writing For The Courtunknown07blackstarОценок пока нет
- Pdf-To-Word EditedДокумент48 страницPdf-To-Word EditedJames Genesis Ignacio LolaОценок пока нет
- Revised Market Making Agreement 31.03Документ13 страницRevised Market Making Agreement 31.03Bhavin SagarОценок пока нет
- Oc ch17Документ34 страницыOc ch17xavier8491Оценок пока нет
- Learning Objectives: Understanding The Self Module 1 - Sexual SelfДокумент11 страницLearning Objectives: Understanding The Self Module 1 - Sexual SelfMiss MegzzОценок пока нет
- Michelle Kommer Resignation LetterДокумент1 страницаMichelle Kommer Resignation LetterJeremy TurleyОценок пока нет
- Who Di 31-4 Atc-DddДокумент6 страницWho Di 31-4 Atc-DddHenderika Lado MauОценок пока нет
- Constitutional Law Sem 5Документ5 страницConstitutional Law Sem 5Ichchhit SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Why We're Still Learning New Things About The JFK AssassinationДокумент8 страницWhy We're Still Learning New Things About The JFK AssassinationNolan SОценок пока нет
- Dnyanadeep's IAS: UPSC Essay Series - 7Документ2 страницыDnyanadeep's IAS: UPSC Essay Series - 7Rahul SinghОценок пока нет
- Comparative Analysis of Severe Pediatric and Adult Leptospirosis in Sa o Paulo, BrazilДокумент3 страницыComparative Analysis of Severe Pediatric and Adult Leptospirosis in Sa o Paulo, BrazilShofura AzizahОценок пока нет
- PracticeProbs (5 - 27 - 07) - CMOS Analog ICs PDFДокумент70 страницPracticeProbs (5 - 27 - 07) - CMOS Analog ICs PDFmyluvahanОценок пока нет
- IDLC Finance Limited: Assignment (Research Report)Документ29 страницIDLC Finance Limited: Assignment (Research Report)Nishat ShimaОценок пока нет
- Agvan DorzhievДокумент7 страницAgvan DorzhievMichael FelicianoОценок пока нет
- Unit 9:: What Did You See at The Zoo?Документ11 страницUnit 9:: What Did You See at The Zoo?ARiFin MoHaMedОценок пока нет
- The First Converts in Chin Hills - Ni Kong HongДокумент7 страницThe First Converts in Chin Hills - Ni Kong HongLTTuangОценок пока нет