Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Introduction To UMTS
Загружено:
shikhar15Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Introduction To UMTS
Загружено:
shikhar15Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
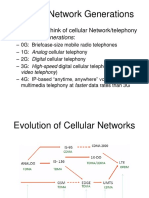
Mobile Network Evolution
1G
Analogue
2G
Digital
2.5G
Packet Data
2.75G
Enhanced Data
NMT
TACS
AMPS
GSM
CDMA
TDMA
GPRS
EDGE
CDMA 1X
WCDMA
TD-SCDMA
cdma2000
1X EV-DO
2M, 14M
2M
2.4M
384K
144K
1982-1996+ 1992-2002+ 2001+ 2004+ 2002-2004+
115K
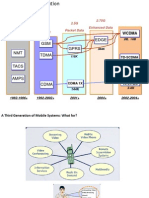
A Third Generation of Mobile Systems: What for?
A Third Generation of Mobile Systems: What for?
Concepts of 3G - Mobiles
Voice & Music phone
Mobile Audio Video
Communicator
PC / PDA PCMCIA card
Standardization Bodies
T1 ETSI TTC / ARIB TTA CWTS TIA
= 3GPP2
Standardisation of 3G cellular networks
ITU (Global guidelines and recommendations)
IMT-2000: Global standard for third generation (3G) wireless communications
3GPP is a co-operation between standardisation bodies
ETSI (Europe), ARIB/TTC (Japan), CCSA (China), ATIS (North America) and TTA (South Korea)
GSM
EDGE
UMTS
WCDMA - FDD
WCDMA - TDD
TD-SCDMA
3GPP2 is a co-operation between standardisation bodies
ARIB/TTC (Japan), CCSA (China), TIA (North America) and TTA (South Korea)
CDMA2000
CDMA2000 1x
CDMA2000 1xEV-DO
2 Mbit/s 384 kbit/s 144 kbit/s
Indoor
low mobility
Urban
reduced mobility
Rural outdoor
high mobility
Variable bit rate capability
Variable Quality Of Service (BER, delay)
Support of asymmetric traffic
Service multiplexing
High spectrum efficiency
European objective: ensure compatibility with GSM
3GPP Objectives
Added Value of UMTS
Mobile Networks and Data Services
2G Mobile
3G (UMTS)
3.5G or 3G+ (HSDPA and HSUPA)
2.5G (GPRS)
2.75G (EDGE)
3G Mobile
LTE
WiMAX
HSDPA
UMTS
EDGE
GPRS
160kbps
384Kbps
2Mbps *
14.4Mbps *
75Mbps *
100Mbps ? *
* : Per cell bandwidth (not per user)
WiMAX ("3G" or "4G" depending on manufacturer)
Future: 4G (LTE)
HSUPA 5.7Mbps *
Maximum Theoretical Bandwidth
UMTS QoS class
NRT Data Call
Background Class
PS Data Call
Interactive Class
PS Data Call
Streaming Class
PS Data Call
Conversational Class
CS Data Call
CS Data Call CS Voice Call
CS Call
RT Data Call
PS Call
Call
QoS Traffic Classes
QoS Traffic Classes
Traffic class Characteristics Example
application
Conversational Preserve time relation between
information entities of the stream.
Conversational pattern (stringent
and low delay)
Speech
Video calls
Streaming Preserve time relation between
information entities of the stream.
Real-time
streaming
video
Interactive Request-response pattern.
Preserve payload content.
Web
browsing
Background Destination is not expecting the
data within a certain time.
Preserve payload content.
E-mail
File
downloading
Demanding
Delay
Jitter
Demanding
Bit rate
Jitter
Tolerant
Delay and bit rate
can vary
Integrity
Easiest
Delay and bit rate
can vary
Integrity
QoS for different services
QoS Differentiation
Conversational RAB
Streaming RAB
Interactive RAB
Interactive RAB
Background RAB
MMS
Web
browsing
Push-to-talk
Streaming
Video
telephony
Each service gets the treatment it requires according to the QoS profile
Network resources are shared according to the service needs
Network resources can be used more efficiently
UMTS Network Structure
GSM /GPRS BSS
BTS
BSC
PCU
SS7
SCP
SMS
SCE
PSTN/other PLMN
Internet,
Intranet
MSC/VLR GMSC
HLR/AUC
SGSN
CG
BG
GGSN
PS backbone
Other PLMN
CS domain
PS domain
NodeB
RNC
UTRAN
Iu-CS
Iu-PS
A
G
b
GERAN
WCDMA Interfaces
A Interface
A-bis
Um
MSC
BSC
BTS
UE
SGSN
Gb
GSM
Iub
Uu
MSC
RNC
NodeB
UE
SGSN
Iu-PS
Iu-CS
Iub
Uu
RNC
NodeB
UE
Iur
WCDMA
UTRAN
BSS
GERAN
Radio Network Interfaces
Iu
Iu PS
Connection to the packet switched core network domain
SGSN/GGSN
Iu CS
Connection to the circuit switched core network domain
MSC
Protocol RANAP
Iur
RNC interconnection
[eg: for SHO support ]
Protocol RNSAP
Iub
Connection for the RBS to the RNC
Protocol NBAP
Uu
Air Interface to the UE
Protocol RRC, RLC, MAC
Core Network
RNC
RNC
Iu
Iur
Iub
Uu
Node
B
Node
B
Node
B
UE
Thank you
Вам также может понравиться
- 3G Wcdma: Aditya K. Jagannatham Indian Institute of Technology KanpurДокумент30 страниц3G Wcdma: Aditya K. Jagannatham Indian Institute of Technology KanpurFaisal MalikОценок пока нет
- Evolution From GSM To UMTSДокумент32 страницыEvolution From GSM To UMTSnattynafОценок пока нет
- 1.Lf Bt1001 E01 1 Lte Overview 76Документ76 страниц1.Lf Bt1001 E01 1 Lte Overview 76Roghib AshfahaniОценок пока нет
- Enhanced Data-Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE) : An OverviewДокумент72 страницыEnhanced Data-Rates For Global Evolution (EDGE) : An OverviewPrashant SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- 21 Final 3GДокумент41 страница21 Final 3GSubhi RosdianОценок пока нет
- Digital Network - Lecturer6Документ40 страницDigital Network - Lecturer6Jumanne AllyОценок пока нет
- Presentation ON 4G-Technology: Presented By: Ajay Kanwal 2K8/COE/108Документ22 страницыPresentation ON 4G-Technology: Presented By: Ajay Kanwal 2K8/COE/108Ajay KanwalОценок пока нет
- 01 LTE Overview 65Документ65 страниц01 LTE Overview 65Tharindu Wijegoonasekara100% (1)
- 3G & Mobile Data Networks: Overview of Architecture, Design & Case StudiesДокумент48 страниц3G & Mobile Data Networks: Overview of Architecture, Design & Case StudiesteertageОценок пока нет
- GPRS EngДокумент286 страницGPRS EngMd Zaki AhmedОценок пока нет
- GSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless CommunicationДокумент45 страницGSM To 3G: A Journey of Wireless Communicationsrshelke100% (1)
- Overview of 3G Technologies and ApplicationsДокумент41 страницаOverview of 3G Technologies and ApplicationsMosab MohammadОценок пока нет
- LTE Session 1 11122015Документ33 страницыLTE Session 1 11122015srinvas_107796724Оценок пока нет
- Presentation 1Документ12 страницPresentation 1Ali AliОценок пока нет
- Mobile GenerationДокумент24 страницыMobile GenerationPhantom FireОценок пока нет
- UmtsДокумент53 страницыUmtsNicholas WilsonОценок пока нет
- General Packet Oriented Radio ServiceДокумент29 страницGeneral Packet Oriented Radio ServiceHusnainОценок пока нет
- 1 Scope: Release As The Present DocumentДокумент37 страниц1 Scope: Release As The Present DocumentchandankumohantyОценок пока нет
- Presentation ON 4G-Technology: Presented By: Sonia Choudhary B. E. Ivth Year I.T GvsetДокумент25 страницPresentation ON 4G-Technology: Presented By: Sonia Choudhary B. E. Ivth Year I.T Gvsetaskiran1237807Оценок пока нет
- 3G Mobile CommunicationДокумент27 страниц3G Mobile CommunicationTechy GuyОценок пока нет
- QoS Wireless Networks Techniques 3G StandardsДокумент30 страницQoS Wireless Networks Techniques 3G StandardsDeva Prasad Sakala100% (1)
- GSM Architecture and Concepts GuideДокумент11 страницGSM Architecture and Concepts GuideMauricio Benavente MaytaОценок пока нет
- 1xEV DO TechnologyДокумент220 страниц1xEV DO TechnologyYu LeОценок пока нет
- Explain m13 - 1 Other Technologies Tetra Gprs Edge UmtsДокумент30 страницExplain m13 - 1 Other Technologies Tetra Gprs Edge UmtsMiguel Andres Vanegas GОценок пока нет
- Presentation ON 4G-Technology: Presented By: Sonia Choudhary B. E. Ivth Year I.T GvsetДокумент25 страницPresentation ON 4G-Technology: Presented By: Sonia Choudhary B. E. Ivth Year I.T GvsetShahbaz AlamОценок пока нет
- SeminarДокумент25 страницSeminarSatasa Samannita0% (1)
- GPRS ReportДокумент26 страницGPRS ReportSarita Vijay Kharia VermaОценок пока нет
- UMTS ... : 3G Technology and ConceptsДокумент83 страницыUMTS ... : 3G Technology and ConceptsAimad SadounОценок пока нет
- Lecture2 Intro Mobiel Generations UMS 2021 Last v3Документ81 страницаLecture2 Intro Mobiel Generations UMS 2021 Last v3بليغ عبدالله صبريОценок пока нет
- Mobile CommunicationsДокумент33 страницыMobile Communicationsgenesis619Оценок пока нет
- Driving Broadband Innovation in UAE Du LTE EvolutionДокумент28 страницDriving Broadband Innovation in UAE Du LTE EvolutionashishОценок пока нет
- GPRS Architecture and GTP Protocol OverviewДокумент57 страницGPRS Architecture and GTP Protocol OverviewShriraj07Оценок пока нет
- 3G TrainingДокумент359 страниц3G TrainingVikash Yadav100% (3)
- An Overview of Wireless Data CommunicationsДокумент63 страницыAn Overview of Wireless Data CommunicationsebinVettuchirayilОценок пока нет
- 3G Services in Asia - Here and Now!: CDMA (1xEV-DO)Документ37 страниц3G Services in Asia - Here and Now!: CDMA (1xEV-DO)Ajay NagarОценок пока нет
- An Overview of Wireless Data Communications TechnologiesДокумент63 страницыAn Overview of Wireless Data Communications TechnologiesnahuОценок пока нет
- Foreword: Error! No Text of Specified Style in Document. Error! No Text of Specified Style in DocumentДокумент38 страницForeword: Error! No Text of Specified Style in Document. Error! No Text of Specified Style in DocumentchandankumohantyОценок пока нет
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Документ32 страницыGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS)Ojas_Bhatia_2380Оценок пока нет
- Mobile Communications GuideДокумент33 страницыMobile Communications Guidekarlo_stuОценок пока нет
- MC-04 LTE and BeyondДокумент28 страницMC-04 LTE and BeyondIp PangОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Services in 3G Network: Lecture Notes Dea Misi 1 March 04Документ81 страницаEvolution of Services in 3G Network: Lecture Notes Dea Misi 1 March 04Hao NguyenОценок пока нет
- The GPRS Network: ContentsДокумент13 страницThe GPRS Network: ContentsChidhuro OwenОценок пока нет
- A1 3G Mechanism Technology Analysis and ComparisonДокумент51 страницаA1 3G Mechanism Technology Analysis and ComparisonAdeniji AdeyemiОценок пока нет
- A Vision Ahead : Presented by Intramantra Global Solution PVT LTD, IndoreДокумент27 страницA Vision Ahead : Presented by Intramantra Global Solution PVT LTD, IndoreDeepak RathoreОценок пока нет
- Evolution From GSM To UMTSДокумент40 страницEvolution From GSM To UMTSNgoy SaroОценок пока нет
- Day1 Session1Документ75 страницDay1 Session1MohsenОценок пока нет
- Gprs SlideДокумент52 страницыGprs SlideBrajendra MohanОценок пока нет
- Evolution to 3G and BeyondДокумент33 страницыEvolution to 3G and BeyondVikash YadavОценок пока нет
- WIMAXДокумент206 страницWIMAXammezzОценок пока нет
- Ae2m32mks2012 UmtsДокумент78 страницAe2m32mks2012 Umtsakifiqbal11Оценок пока нет
- 3G VN WCDMA Workshop - QualcommДокумент175 страниц3G VN WCDMA Workshop - QualcommoxcnvnОценок пока нет
- Evolution to 3G Networks: Understanding the Transition from 2G to 3GДокумент33 страницыEvolution to 3G Networks: Understanding the Transition from 2G to 3GNavaneeth KrishnanОценок пока нет
- General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is A: Services OfferedДокумент5 страницGeneral Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Is A: Services Offeredrenuka_ec694456Оценок пока нет
- WCDMA FundamentalsДокумент68 страницWCDMA FundamentalsYoussef YK100% (1)
- GSM, GPRS and EDGE Performance: Evolution Towards 3G/UMTSОт EverandGSM, GPRS and EDGE Performance: Evolution Towards 3G/UMTSTimo HalonenОценок пока нет
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationОт EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- GSM/EDGE: Evolution and PerformanceОт EverandGSM/EDGE: Evolution and PerformanceDr. Mikko SailyОценок пока нет
- Amip62204611 - 2014 10 14 - 13 37 18Документ1 страницаAmip62204611 - 2014 10 14 - 13 37 18shikhar15Оценок пока нет
- First Quarter Review of Monetary Policy 2012-13: Reserve Bank of IndiaДокумент18 страницFirst Quarter Review of Monetary Policy 2012-13: Reserve Bank of IndiaProfessor Sameer KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Electricity Bill PDFДокумент1 страницаElectricity Bill PDFshikhar15Оценок пока нет
- Electricity Bill PDFДокумент1 страницаElectricity Bill PDFshikhar15Оценок пока нет
- PDP Context Activation GuideДокумент124 страницыPDP Context Activation GuideUmar Abbas BabarОценок пока нет
- Table of ContentДокумент2 страницыTable of Contentshikhar15Оценок пока нет
- Shubb AraoДокумент4 страницыShubb Araoshikhar15Оценок пока нет
- Aanchal Sharma Case Study On MPДокумент5 страницAanchal Sharma Case Study On MPshikhar15Оценок пока нет
- SIX SIGMA AT MOTOROLA - HOW IT INNOVATED QUALITYДокумент12 страницSIX SIGMA AT MOTOROLA - HOW IT INNOVATED QUALITYshikhar15Оценок пока нет
- GSM Gprs Edge: 2G Digital 2.5G Packet Data 2.75G Enhanced DataДокумент17 страницGSM Gprs Edge: 2G Digital 2.5G Packet Data 2.75G Enhanced Datashikhar15Оценок пока нет
- 03.WCDMA RRM and Cell ProcedureДокумент43 страницы03.WCDMA RRM and Cell Procedureshikhar15100% (1)
- 02.WCDMA Fundamantels and ChannelsДокумент49 страниц02.WCDMA Fundamantels and Channelsshikhar15Оценок пока нет
- Optimization Guidelines ACCESSIBILITY Ericsson Rev01Документ27 страницOptimization Guidelines ACCESSIBILITY Ericsson Rev01Ömer AlbatОценок пока нет