Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
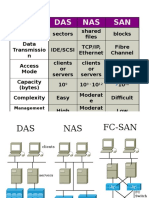
Storage Area Network
Загружено:
Sanjeev ShuklaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Storage Area Network
Загружено:
Sanjeev ShuklaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Storage Area Network
Network Topology
DAS Direct Area Storage
NAS Network Area Storage
SAN Storage Area Network
DAS
DAS
Direct-Attached Storage (DAS)
Storage connects directly to servers
Applications access data from DAS using block-
level access protocols
Examples:
Internal HDD of a host,
Tape libraries, and
Directly connected external HDD
DAS Benefits
Ideal for local data provisioning
Quick deployment for small environments
Simple to deploy
Reliability
Low capital expense
Low complexity
DAS Challenges
limited scalability
Number of connectivity ports to hosts
Number of addressable disks
Distance limitations
For internal DAS, maintenance requires
downtime
Limited ability to share resources (unused
resources cannot be easily re-allocated)
Array front-end port, storage space
Resulting in islands of over and under
utilized storage pools
Areas Where DAS Fails
Just-in-time information to business users
Integration of information infrastructure with business
processes
Flexible and resilient storage architecture
The Solution?
Storage Networking
FC SAN
NAS
IP SAN
What is a SAN ?
Dedicated high speed
network of servers and
shared storage devices
Provide block level data
access
What is a SAN ?
Resource Consolidation
Centralized storage and
management
Scalability
Theoretical limit: Appx.
15 million devices
Secure Access
Fibre Channel
Latest FC
implementations
support 16Gb/s
Fibre Channel
A high-speed network
technology that runs on
high-speed optical fiber
cables (for front-end SAN
connectivity)
Fibre Channel
and serial copper
cables (for back-end
disk connectivity)
FC SAN Evolution
Components of SAN
Three basic components:
Servers,
Network infrastructure, and
Storage,
Can be further broken down into the following key
elements:
Node Ports,
Cabling,
Interconnecting devices (such as FC switches or
hubs),
Storage arrays, and
SAN management software
Components of SAN: Node
ports
Examples of nodes
Hosts, storage and tape library
Ports are available on:
HBA in host Front-end adapters in storage
Each port has transmit (Tx) link and receive (Rx) link
HBAs perform low-level
interface functions
automatically to
minimize impact on host
performance
Components of SAN: Cabling
Copper cables for short distance
Optical fiber cables for long distance
Single-mode
Can carry single beams of light
Distance up to 10 KM
Multi-mode
Can carry multiple beams of light
simultaneously
Distance up to 500 meters
Components of SAN: Cabling
Components of SAN: Cabling
(connectors)
Node Connectors:
SC Duplex Connectors
LC Duplex Connectors
Patch panel Connectors:
ST Simplex Connectors
Components of SAN:
Interconnecting devices
Hubs
Switches and
Directors
Components of SAN: Storage
array
storage consolidation
and centralization
provides
High
Availability/Redundancy
Performance
Business
Continuity Multiple
host connect
Components of SAN: SAN
management software
A suite of tools used in a SAN to manage the
interface between host and storage arrays
Provides integrated management of SAN
environment
Web based GUI or CLI
SAN Interconnectivity Options: FC-
AL
Devices must arbitrate to gain control
Devices are connected via hubs
Supports up to 127 devices
Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL)
SAN Interconnectivity Options: FC-
SW
Dedicated bandwidth between devices
Support up to 15 million devices
Higher availability than hubs
Fabric connect (FC-SW)
IP SAN
In FC SAN transfer of block level data takes place
over Fibre Channel
Emerging technologies provide for the transfer
of block-level data over an existing IP network
infrastructure
Driver for IP SAN
Easier management
Existing network infrastructure can be leveraged
Reduced cost compared to new SAN hardware and
software
Supports multi-vendor interoperability
Many long-distance disaster recovery solutions already
leverage IP-based networks
Many robust and mature security options are available
for IP networks
Why IP?
Block Storage over IP - iSCSI
SCSI over IP
IP encapsulation
Ethernet NIC card
iSCSI HBA
Hardware-based
gateway to Fibre
Channel storage
Used to connect servers
Block Storage over IP - FCIP
Fibre Channel-to-IP
bridge / tunnel
(point to point)
Fibre Channel end
points
Used in DR
implementations
IP based protocol used to connect host and
storage
Carries block-level data over IP-based network
Encapsulate SCSI commands and transport as
TCP/IP packet
iSCSI ?
iSCSI host initiators
Host computer using a NIC or iSCSI HBA to connect to storage
iSCSI initiator software may need to be installed
iSCSI targets
Storage array with embedded iSCSI capable network port
FC-iSCSI bridge
LAN for IP storage network
Interconnected Ethernet switches and/or routers
Components of iSCSI
No FC components
Each iSCSI port on the array is configured with an IP
address and port number
iSCSI Initiators Connect directly to the Array
Bridge device translates iSCSI/IP to FCP
Standalone device
Integrated into FC switch (multi-protocol router)
iSCSI initiator/host configured with bridge as target
Bridge generates virtual FC initiator
Array provides FC and iSCSI connectivity natively
No bridge devices needed
FCIP is an IP-based storage networking technology
Combines advantages of Fibre Channel and IP
Creates virtual FC links that connect devices in a different
fabric
FCIP is a distance extension solution
Used for data sharing over geographically dispersed SAN
FCIP (Fibre Channel over
IP)?
FCIP (Fibre Channel over
IP)?
Thanks
Вам также может понравиться
- Storage Area Network, An Introduction of Basic Concepts: Antonella Corno - CCIE Storage CMДокумент40 страницStorage Area Network, An Introduction of Basic Concepts: Antonella Corno - CCIE Storage CMSachidananda SahuОценок пока нет
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewОт EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- Storage Area Network, An Introduction of Basic ConceptsДокумент39 страницStorage Area Network, An Introduction of Basic Conceptsa10b11Оценок пока нет
- Storage Area Network, An Introduction of Basic Concepts: Antonella Corno - CCIE Storage CMДокумент40 страницStorage Area Network, An Introduction of Basic Concepts: Antonella Corno - CCIE Storage CMtakeit 123Оценок пока нет
- Storage BasicsДокумент29 страницStorage BasicsdSolarianОценок пока нет
- Configuration of Microsoft ISA Proxy Server and Linux Squid Proxy ServerОт EverandConfiguration of Microsoft ISA Proxy Server and Linux Squid Proxy ServerОценок пока нет
- San NasДокумент44 страницыSan NasAnaparthi Naveen Kumar100% (1)
- DAS NAS SAN: Management Cost (Per GB)Документ21 страницаDAS NAS SAN: Management Cost (Per GB)lucky526526Оценок пока нет
- Cloud Storage Infrastructures: DAS, NAS, SAN ComparisonДокумент40 страницCloud Storage Infrastructures: DAS, NAS, SAN ComparisonNikhil Kumar100% (1)
- Cisco CCNA Short Course OverviewДокумент32 страницыCisco CCNA Short Course OverviewNamwangala Rashid NatinduОценок пока нет
- Storage Area Network: By: Syeda NazreenДокумент16 страницStorage Area Network: By: Syeda Nazreenneha shanbhagОценок пока нет
- SAN BasicДокумент44 страницыSAN BasicAnonymous kHqLhBB2CОценок пока нет
- Implementing Enterprise Storage SolutionsДокумент36 страницImplementing Enterprise Storage SolutionsSanitaracОценок пока нет
- R MOD 05-Host Integration BasicsДокумент38 страницR MOD 05-Host Integration Basicsshyco007Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Storage: Overview of The Storage SubsystemДокумент33 страницыIntroduction To Storage: Overview of The Storage SubsystemReddy NagarjunaОценок пока нет
- CCIE DC Storage Section 002 Hardware ArchitectureДокумент5 страницCCIE DC Storage Section 002 Hardware Architecturejama99Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - San SchoolДокумент17 страницChapter 1 - San Schoolapk.khedekarОценок пока нет
- SAN Training Objectives and ComponentsДокумент53 страницыSAN Training Objectives and ComponentsSachin ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- SAN Module - 2Документ27 страницSAN Module - 2Paramesh ThangarajОценок пока нет
- Wireless Captive PortalsДокумент16 страницWireless Captive PortalsLuka O TonyОценок пока нет
- Module - 03 - Mise en Oeuvre Des Solutions de StockageДокумент33 страницыModule - 03 - Mise en Oeuvre Des Solutions de StockageTeguebzanga ZidaОценок пока нет
- 20740B 03Документ34 страницы20740B 03HaydeMartìnezDiazОценок пока нет
- Fibre Channel SAN Workloads: Live Webcast February 12, 2020 10:00 AM PTДокумент52 страницыFibre Channel SAN Workloads: Live Webcast February 12, 2020 10:00 AM PTll chiaОценок пока нет
- Data Center Topology GuideДокумент6 страницData Center Topology GuideMauro De GrandeОценок пока нет
- Storage Area NetworksДокумент13 страницStorage Area Networksnalluri_08Оценок пока нет
- BRKCRS 2000Документ88 страницBRKCRS 2000Javed HashmiОценок пока нет
- Storage Area Network (SAN)Документ81 страницаStorage Area Network (SAN)Rajat SinghalОценок пока нет
- When Should I Deploy Fiber Channel Instead of iSCSI?Документ5 страницWhen Should I Deploy Fiber Channel Instead of iSCSI?Subham MandalОценок пока нет
- Introducing MikrotikДокумент23 страницыIntroducing Mikrotikkarthong4057Оценок пока нет
- Numerous Pcs Running Graphics-Intensive ApplicationsДокумент24 страницыNumerous Pcs Running Graphics-Intensive ApplicationsLeu NameОценок пока нет
- R MOD 05-Host Integration BasicsДокумент38 страницR MOD 05-Host Integration Basicsnilber_morianoОценок пока нет
- Storage Basics: The Storage Area NetworkДокумент8 страницStorage Basics: The Storage Area NetworkrakeshsadanandanОценок пока нет
- Audience: Accelerated SAN Essentials (UC434S)Документ6 страницAudience: Accelerated SAN Essentials (UC434S)Atal AfghanОценок пока нет
- Overview: Hardware, Software, NetworkДокумент46 страницOverview: Hardware, Software, Networkandy accgamingОценок пока нет
- Storage Area Network (SAN) : Serving InformationДокумент60 страницStorage Area Network (SAN) : Serving Informationsubham duttaОценок пока нет
- Unit IVДокумент54 страницыUnit IVChetan SaiОценок пока нет
- Intranets, Extranets, WANs ExplainedДокумент78 страницIntranets, Extranets, WANs ExplainedEL MAMOUN ABDELLAHОценок пока нет
- HPE 5820 TAA-compliant Switch Series: Key FeaturesДокумент12 страницHPE 5820 TAA-compliant Switch Series: Key FeaturesJamesSmith2014Оценок пока нет
- Storage Architectures: Nases SansДокумент5 страницStorage Architectures: Nases SansSrinivas GollanapalliОценок пока нет
- 2015 Course Outline CompTIA Storage Powered by SNIAv3Документ6 страниц2015 Course Outline CompTIA Storage Powered by SNIAv3Muqeemuddin SyedОценок пока нет
- San BasicsДокумент64 страницыSan BasicsRajesh MkОценок пока нет
- HW & SW Optimisations for Embedded Systems DesignДокумент33 страницыHW & SW Optimisations for Embedded Systems DesignfjwoemcuОценок пока нет
- Infiniband Architecture Overview: Components, Layers, Packet Format, Verbs and Potential ImprovementsДокумент17 страницInfiniband Architecture Overview: Components, Layers, Packet Format, Verbs and Potential Improvementsvpacketbits999Оценок пока нет
- CheatSheets - Google - Professional ArchitectДокумент48 страницCheatSheets - Google - Professional Architectdevop journeyОценок пока нет
- Infini BandДокумент22 страницыInfini Bandtarunr1Оценок пока нет
- Xiplink: Xa-Appliances OverviewДокумент4 страницыXiplink: Xa-Appliances OverviewMuhammad Nauman KhanОценок пока нет
- HP Storageworks: Eva Iscsi Connectivity OptionДокумент11 страницHP Storageworks: Eva Iscsi Connectivity Optionwhizzer666Оценок пока нет
- Computer Evolution and PerformanceДокумент37 страницComputer Evolution and PerformanceMAHNOOR ATIFОценок пока нет
- CCNA2 M1 WANs and RoutersДокумент17 страницCCNA2 M1 WANs and RoutersRechelle Marie SusonОценок пока нет
- CCNA Guide To Cisco Networking: Chapter 5: WAN ConceptsДокумент44 страницыCCNA Guide To Cisco Networking: Chapter 5: WAN ConceptsJiang Shi FengОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor & Computer Architecture (Μpca) : Unit 4: Usb, Pci, Scsi,Amba And Asb Bus ArchitectureДокумент12 страницMicroprocessor & Computer Architecture (Μpca) : Unit 4: Usb, Pci, Scsi,Amba And Asb Bus ArchitecturePranathi PraveenОценок пока нет
- Jarkom 2 (Vlan) Lan Design: Tasmi, S.Si,. M.Kom, MTCNA, MTCREДокумент26 страницJarkom 2 (Vlan) Lan Design: Tasmi, S.Si,. M.Kom, MTCNA, MTCREBagus wirawanОценок пока нет
- HP 1910 Switch Series: Product Overview Key FeaturesДокумент13 страницHP 1910 Switch Series: Product Overview Key FeaturesAline Vitoria LuminiОценок пока нет
- Direct Memory AccessДокумент26 страницDirect Memory AccessEswin AngelОценок пока нет
- Implementing Enterprise Storage SolutionsДокумент36 страницImplementing Enterprise Storage SolutionsJUAN CARLOS AMARANTO GONZALEZОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Storage Area Network (SAN) : Flavio Marinone Dipartimento Di Automatica e InformaticaДокумент42 страницыIntroduction To Storage Area Network (SAN) : Flavio Marinone Dipartimento Di Automatica e InformaticasamrakОценок пока нет
- Virtualizing Hadoop in Large Scale InfrastructuresДокумент12 страницVirtualizing Hadoop in Large Scale InfrastructuresSanjeev ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Data ONTAP 8.x 7-Mode Cook Book v1 - 3Документ83 страницыData ONTAP 8.x 7-Mode Cook Book v1 - 3Sanjeev ShuklaОценок пока нет
- NetApp BasicДокумент8 страницNetApp BasicSanjeev ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Eternus StorageДокумент297 страницEternus StorageSanjeev ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Roushini Siddiqua: Contact No.Документ4 страницыRoushini Siddiqua: Contact No.Surabhi KhannaОценок пока нет
- Intro To FmdtoolsДокумент38 страницIntro To FmdtoolsSmurf Account1Оценок пока нет
- Gxv3140 Usermanual EnglishДокумент151 страницаGxv3140 Usermanual Englishindio007Оценок пока нет
- Limits of Variations of Inlet Steam ConditionsДокумент1 страницаLimits of Variations of Inlet Steam ConditionsShashi NaganurОценок пока нет
- Thesis Power System SecurityДокумент8 страницThesis Power System Securitytsfublhld100% (2)
- Breaker Sace EmaxДокумент97 страницBreaker Sace EmaxfujitoОценок пока нет
- Quality Management System (ISO 9001) and Environmental Quality Management System (ISO 14001) : Towards An Integrated ModelДокумент12 страницQuality Management System (ISO 9001) and Environmental Quality Management System (ISO 14001) : Towards An Integrated ModelAtul EknathОценок пока нет
- Budgeting and Financing Substation: SubstationsДокумент2 страницыBudgeting and Financing Substation: SubstationsManuel Henríquez SantanaОценок пока нет
- DMC 550Документ45 страницDMC 550Pandu Sandi PratamaОценок пока нет
- Bank Management System AdvantagesДокумент13 страницBank Management System Advantagesmohit moreОценок пока нет
- Holiday Accident Reduction Program: SSGT 32 Comm/ElectДокумент3 страницыHoliday Accident Reduction Program: SSGT 32 Comm/ElectSteven GarrisОценок пока нет
- Preface 2016 Innovative Bridge Design HandbookДокумент2 страницыPreface 2016 Innovative Bridge Design HandbookGroupe MilleniumОценок пока нет
- YYA-M-RFQ-1116 RFQ For Fire Water Pump Rev.0Документ43 страницыYYA-M-RFQ-1116 RFQ For Fire Water Pump Rev.0Aditya Pranoto100% (2)
- cpp5gs PDFДокумент2 страницыcpp5gs PDFmohammadОценок пока нет
- Ppap Worksheet (GM 1411) : S Master Status: Lab StatusДокумент6 страницPpap Worksheet (GM 1411) : S Master Status: Lab Statuscong daОценок пока нет
- Project ChiptopДокумент39 страницProject ChiptopNikita Patel086Оценок пока нет
- John Deere 7720 Parts CatalogДокумент20 страницJohn Deere 7720 Parts Catalogalejandro100% (38)
- Resume Amit BhagwatДокумент5 страницResume Amit Bhagwatabh93071046100% (3)
- Samsung CS29A5HT8XBWT PDFДокумент53 страницыSamsung CS29A5HT8XBWT PDFHootOwl IDОценок пока нет
- Three-Phase Electric Power - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент12 страницThree-Phase Electric Power - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMohamed RafihОценок пока нет
- TLE Grade 10Документ13 страницTLE Grade 10Althea Bonggal100% (1)
- How to Make a Bootable Windows 7 USB DriveДокумент8 страницHow to Make a Bootable Windows 7 USB DriveBG GopalОценок пока нет
- Rulebook For Technovision'11: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringДокумент5 страницRulebook For Technovision'11: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringKhushbu BuchchaОценок пока нет
- Conventional Software Testing Using White Box Method: KINETIK, Vol. 3, No. 1, February 2018, Pp. 65-72Документ8 страницConventional Software Testing Using White Box Method: KINETIK, Vol. 3, No. 1, February 2018, Pp. 65-72Achmad YuszrilОценок пока нет
- APN-052 Directional Ground-Fault ProtectionДокумент17 страницAPN-052 Directional Ground-Fault ProtectionWalter Andres Estevez VasquezОценок пока нет
- Distributor Installation: Crankshaft Position Sensor RemovalДокумент2 страницыDistributor Installation: Crankshaft Position Sensor RemovalKeyboardMan1960Оценок пока нет
- Revit Architecture NotesДокумент41 страницаRevit Architecture NotesKarishmaОценок пока нет
- 67 Jbiet Civil R14 Syllabus PDFДокумент161 страница67 Jbiet Civil R14 Syllabus PDFGaddam SudheerОценок пока нет
- Uci 401 AssignmentДокумент15 страницUci 401 Assignmentevans kiplimoОценок пока нет
- Chap1 IstqbДокумент42 страницыChap1 IstqbAnil Nag100% (2)