Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Phardose Report - Capsules
Загружено:
Biyaya San Pedro0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
56 просмотров22 страницыCapsule-filling machines are affixed with a cleaning vacuum that removes any extraneous material from the capsules as they exit the equipment. Soft gelatin capsules are Used to encapsulate and hermetically seal liquids, suspensions, pasty materials, dry powders and even performed tablets.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документCapsule-filling machines are affixed with a cleaning vacuum that removes any extraneous material from the capsules as they exit the equipment. Soft gelatin capsules are Used to encapsulate and hermetically seal liquids, suspensions, pasty materials, dry powders and even performed tablets.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
56 просмотров22 страницыPhardose Report - Capsules
Загружено:
Biyaya San PedroCapsule-filling machines are affixed with a cleaning vacuum that removes any extraneous material from the capsules as they exit the equipment. Soft gelatin capsules are Used to encapsulate and hermetically seal liquids, suspensions, pasty materials, dry powders and even performed tablets.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 22
Small amounts of powder may adhere to
the outside of capsules after filling. The
powder maybe bitter or otherwise
unpalatable and should be removed
before packaging or dispensing.
Small Scale may be cleaned
individually or in small numbers by
rubbing them with a clean gauze or
cloth.
Large Scale capsule-filling machines
are affixed with a cleaning vacuum that
removes any extraneous material from
the capsules as they exit the equipment.
Accela-Cota
Apparatus
- equipment
use in cleaning
and polishing of
filled hard
capsules.
Made of gelatin, glycerin or a polyhydric
alcohol such as sorbitol
Contain more moisture than hard
capsules
May have a preservative, such as
methylparaben and/or propylparaben,
to retard microbial growth
May be oblong, oval, or round.
Single colored or two toned
May be imprinted with identifying
markings
As with hard gelatin capsules, they
maybe prepared with opaquants to
reduce transparency and render
characteristic features to the capsule
shell
Used to encapsulate and hermetically
seal liquids, suspensions, pasty materials,
dry powders and even performed
tablets
Pharmaceutically elegant
Easily swallowed
Plate Process using set of molds to form
the capsules.
- A warm sheet of plain or colored gelatin is
placed on the bottom plate of the mold
- Medication liquid is evenly poured
- Second sheet of gelatin is carefully placed
on top and the top plate is put into place
- Pressure is then applied to the mold to form,
fill and seal the capsules
Rotary Die Process or Reciprocating Die
Process capsules are filled and sealed in a
continuous operation
Rotary Die Process most soft gelatin
capsules are prepared by this process
- Liquid gelatin flowing from an overhead
tank into continuous ribbons
- Metered fill material is injected between
the ribbons
- The dies form pockets of the gelatin ribbons
- These pockets of fill containing gelatin are
sealed by pressure and heat and then
severed from ribbons
Reciprocating Die Process similar to
rotary die process but it differs in actual
encapsulating process
- The gelatin ribbons are fed between a set
of vertical dies that continually open and
close to form rows of pockets in the
gelatin ribbons
- Pockets filled with medication
- Sealed, shaped and cut out of the film
- The capsules are cut from the ribbons
Water-immiscible volatile and non-volatile
liquids (vegetable and aromatic oils,
aromatic and aliphatic hydro carbons,
etc.)
Water-miscible non volatile liquids
(polyethylene glycols, and nonionic surface
active agents, such as polysorbate 80
Water miscible and relatively non volatile
compounds (propylene glycol and
isopropyl alcohol)
Liquids that can easily migrate through
shell are not suitable for soft gelatin
capsule (water above 5% and low-
molecular-weight-water-soluble and
volatile organic compounds
Solids may be encapsulated into soft
gelatin capsules as solutions in a liquid
solvents, suspensions, dry powder,
granules, pellets or small tablets
ADDED SUBSTANCES
-Substances added to official preparations
including capsules may be use only if they
1. Are harmless in the quantities used
2. Do not exceed the minimum amounts
required to provide their intended effect
3. Do not impair the products bioavailability,
therapeutic efficacy, or safety
4. Do not interfere with requisite compendial
assays and tests
CONTAINERS FOR DISPENSING CAPSULES
- Depending on the item, the container may
be required to be tight, well-closed, light-
resistant, and/or all of these
DISINTEGRATION TEST FOR CAPSULES
- Capsules are placed in the basket rack
assembly which is immersed 30 times per
minute into thermostatically controlled fluid
at 37C
- To satisfy the test, the capsules disintegrate
completely into a soft mass having no
palpably firm core and only some
fragments of the gelatin shell
DISSOLUTION TEST FOR CAPSULES
- The empty capsule shells dissolved in the
dissolution medium before proceeding
with the sampling and chemical analysis
WEIGHT VARIATION
- The uniformity of dosage units may be
demonstrated by determining weight
variation and/or content uniformity
HARD CAPSULES
- Individually weighed ad contents
removed. Net weight of the contents is
calculated by subtraction
SOFT CAPSULES
- gross weight is determined individually.
Each capsule is cut open and the
contents are removed by washing with a
suitable solvent
CONTENT UNIFORMITY
- The amount of active ingredient ,
determined by assay, is within the range
of 85% to 115% of the label claim for 9
days of 10 dosage units assayed, with no
unit outside the range of 70% to 125% of
the label claim
CONTENT LABELING REQUIREMENT
- All official capsules must be labeled to
express the quantity of each active
ingredient in each dosage unit
STABILITY TESTING
- Help determine the appropriate
conditions for storage and the products
anticipated shell life
MOISTURE PERMEATION TEST
- To ensure the suitability of single-unit and
unit-dose containers for packaging
capsules
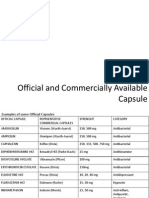
Approximately 200 officially recognized
medications in capsule form are listed in
the USP.
However, many times this number of
capsule products are available from
various manufactures for various drugs
and in various dosage strengths.
Вам также может понравиться
- 8 PolyuriaДокумент5 страниц8 PolyuriaBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- ClinPharLab 1 IntroductionДокумент42 страницыClinPharLab 1 IntroductionBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Anthropometrics for Design: Measurements of the Human BodyДокумент39 страницAnthropometrics for Design: Measurements of the Human BodyBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Rehab Med Upper Extremities Updated NotesДокумент4 страницыRehab Med Upper Extremities Updated NotesBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Template Journal CritiquingДокумент5 страницTemplate Journal CritiquingBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- ABS and GMA CasesДокумент4 страницыABS and GMA CasesBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- CE 321L Plate Template 1Документ2 страницыCE 321L Plate Template 1Biyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- CE 321L Plate Template 1 PDFДокумент2 страницыCE 321L Plate Template 1 PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0378113514000947 MainДокумент7 страниц1 s2.0 S0378113514000947 MainBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- OT 3 Lecture Pedia 2Документ53 страницыOT 3 Lecture Pedia 2Biyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Pracs 5 Video DemoДокумент7 страницAnatomy Pracs 5 Video DemoBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Hospital Intern Meds USTHДокумент42 страницыHospital Intern Meds USTHBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Case Disc Nucleotide MetabolismДокумент4 страницыCase Disc Nucleotide MetabolismBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- 27 Marquez Mark Christian EsДокумент2 страницы27 Marquez Mark Christian EsBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- AITC 1008 DyslipidemiaДокумент42 страницыAITC 1008 DyslipidemiaBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Hospital Intern Meds USTH PDFДокумент20 страницHospital Intern Meds USTH PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Properties and Sources of Natural Betalain PigmentsДокумент12 страницProperties and Sources of Natural Betalain PigmentsBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- OT3 4 Feeding&AssessToolsДокумент5 страницOT3 4 Feeding&AssessToolsBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Stability Study of Betacyanin Extract From Red Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) Peels PDFДокумент7 страницStability Study of Betacyanin Extract From Red Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) Peels PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Safety Assessment of Methanol Extract of Red Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) - Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies PDFДокумент9 страницSafety Assessment of Methanol Extract of Red Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) - Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Characterization and Quanti Cation of Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) Betacyanin Pigments Extracted by Two Procedures PDFДокумент8 страницCharacterization and Quanti Cation of Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) Betacyanin Pigments Extracted by Two Procedures PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Purified Betacyanins From Hylocereus Undatus Peel Ameliorate Obesity and Insulin Resistance in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice PDFДокумент9 страницPurified Betacyanins From Hylocereus Undatus Peel Ameliorate Obesity and Insulin Resistance in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Variability in Nutritional Composition and Phytochemical Properties of Red Pitaya (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) From Malaysia and Australia PDFДокумент9 страницVariability in Nutritional Composition and Phytochemical Properties of Red Pitaya (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) From Malaysia and Australia PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Pigment Identification and Antioxidant Properties of Red Dragon Fruit (Документ5 страницPigment Identification and Antioxidant Properties of Red Dragon Fruit (Fikri ZulfikarОценок пока нет
- Betalains From Red Pitaya Peel (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) - Extraction, Spectrophotometric and HPLC-DAD Identification, Bioactivity and Toxicity Screening PDFДокумент7 страницBetalains From Red Pitaya Peel (Hylocereus Polyrhizus) - Extraction, Spectrophotometric and HPLC-DAD Identification, Bioactivity and Toxicity Screening PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Chemical Composition and in Vitro Evaluation of The Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activities of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extracts of Pitaya (Dragon Fruit) Peel PDFДокумент7 страницChemical Composition and in Vitro Evaluation of The Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activities of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extracts of Pitaya (Dragon Fruit) Peel PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Minor Betalains in Fruits of Hylocereus Species PDFДокумент9 страницMinor Betalains in Fruits of Hylocereus Species PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Betacyanins in Red Pitaya FruitДокумент6 страницBetacyanins in Red Pitaya FruitBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- A Review Article On Edible Pigments Properties and Sources As Natural Biocolorants in Foodstuff and Food Industry PDFДокумент8 страницA Review Article On Edible Pigments Properties and Sources As Natural Biocolorants in Foodstuff and Food Industry PDFBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- CapsuleДокумент13 страницCapsuleBiyaya San PedroОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- A Humanistic Approach To Medical PracticeДокумент3 страницыA Humanistic Approach To Medical PracticeFilipos ConstantinОценок пока нет
- Cash Flow Analysis: Restaurant Business PlanДокумент44 страницыCash Flow Analysis: Restaurant Business Plankavirao87Оценок пока нет
- Reflexes Guide: 20+ Human Reflexes ExplainedДокумент37 страницReflexes Guide: 20+ Human Reflexes ExplainedSalman KhanОценок пока нет
- Colours of the RainbowДокумент16 страницColours of the RainbowMd A RAZZAKОценок пока нет
- AMGG-S - 1 - Environmental Safeguard Monitoring - 25.03.2021Документ48 страницAMGG-S - 1 - Environmental Safeguard Monitoring - 25.03.2021Mahidul Islam RatulОценок пока нет
- Form16 (2021-2022)Документ2 страницыForm16 (2021-2022)Anushka PoddarОценок пока нет
- GP Series Portable Generator: Owner's ManualДокумент48 страницGP Series Portable Generator: Owner's ManualWilliam Medina CondorОценок пока нет
- Physical Science Summative Exam. First QuarterДокумент5 страницPhysical Science Summative Exam. First QuarterIsagani WagisОценок пока нет
- Strategies and Tactics for Collecting on Overdue AccountsДокумент9 страницStrategies and Tactics for Collecting on Overdue AccountsAkii WingОценок пока нет
- Knorr FinalДокумент25 страницKnorr Finalimbree100% (3)
- Design AI Platform Using Fuzzy Logic Technique To Diagnose Kidney DiseasesДокумент9 страницDesign AI Platform Using Fuzzy Logic Technique To Diagnose Kidney DiseasesTELKOMNIKAОценок пока нет
- Respiration PHYSIOДокумент23 страницыRespiration PHYSIOTauseef AfridiОценок пока нет
- Sodium Chloride MSDSДокумент5 страницSodium Chloride MSDSIbaharmovic LpuОценок пока нет
- 1154ec108nanoelectronics PDFДокумент3 страницы1154ec108nanoelectronics PDFLordwin CecilОценок пока нет
- Structure Dismantling JSAДокумент2 страницыStructure Dismantling JSAtnssbhaskar69% (13)
- Q 400 SYSTEM BestДокумент9 страницQ 400 SYSTEM BestTeddy EshteОценок пока нет
- 1 6Документ58 страниц1 6Emiliano.Armando Aguilera.Vázquez100% (1)
- Weekly Home Learning Plan: Grade 8 - Quarter 2. Week 7Документ3 страницыWeekly Home Learning Plan: Grade 8 - Quarter 2. Week 7Danmer Jude TorresОценок пока нет
- F 204 (AutoRecovered)Документ27 страницF 204 (AutoRecovered)safiqulislam100% (1)
- Year 8 Drama ScriptДокумент8 страницYear 8 Drama ScriptTISMSecondaryОценок пока нет
- Microeconomics 5th Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual 1Документ23 страницыMicroeconomics 5th Edition Hubbard Solutions Manual 1christina100% (48)
- Lazzaro Spallanzani ExperimentДокумент14 страницLazzaro Spallanzani ExperimentWiwi Pratiwi100% (1)
- Arthropods: A Guide to the Diverse PhylumДокумент10 страницArthropods: A Guide to the Diverse Phylumpkkalai112Оценок пока нет
- Corn Genetics and Chi Square AnalysisДокумент2 страницыCorn Genetics and Chi Square AnalysisBonifacius Budi NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Makalah ThoughtДокумент5 страницMakalah Thoughtifa safiraОценок пока нет
- Intermediate Alloy Steels Properties and SpecificationsДокумент15 страницIntermediate Alloy Steels Properties and Specificationsanon_558118723100% (1)
- Jeremy Tan Resume and CVДокумент3 страницыJeremy Tan Resume and CVapi-359540985Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Abnormal Behavior in Historical ContextДокумент22 страницыChapter 1: Abnormal Behavior in Historical ContextEsraRamos100% (2)
- My PRC Form-Censored Case NumbersДокумент5 страницMy PRC Form-Censored Case NumbersLeah Lou Gerona MontesclarosОценок пока нет
- Self-Adhesive Resin Cements Ph-Neutralization, HydrophilicityДокумент7 страницSelf-Adhesive Resin Cements Ph-Neutralization, HydrophilicityCarolina Rodríguez RamírezОценок пока нет