Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Concentration
Загружено:
Heather WrightАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Concentration
Загружено:
Heather WrightАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chemistry
SOME BASIC CONCEPT OF CHEMISTRY
SESSION -IV
Session Opener
Session Objecties
Session Objectives
!" Equivalent mass
#" Normality
$" Molarity
%" Molality
&" Strength of solution
'" Percentage concentration
Equivalent Mass
Equivalent mass
Base
Salt
Acid
Equivalent Mass of Acid
Equivalent mass of acid =
Molecular mass of acid
Number of replacable !Basicity"
+
E#ample$
Equivalent mass of %l and
&
SO
'
%l %l
+
+
& ' '
SO & SO
+
+
( )*+*
Equivalent mass of %l ),+*
(
+
= =
& '
& ( )& ' (,
Equivalent mass of SO '-
&
+ +
= =
Equivalent Mass of Base
Equivalent mass of base =
Molecular mass
Number of replacable O !Acidity"
E#ample$
Equivalent mass of NaO and %a!O"
&
NaO Na O
+
+
&
%a!O" %a &O
++
+
&) (, (
Equivalent mass of NaO '.
(
+ +
= =
&
'. & (, & (
Equivalent mass of %a!O" )/
&
+ +
= =
Equivalent mass of salt
Equivalent mass of salt =
Molecular mass
0otal number of positive or
negative charge
E#ample$
Equivalent mass of Na%l and Mg%l
&
Na%l Na %l
+
+
&) )*+*
Equivalent mass of Na%l *1+*
(
+
= =
&
&'. & )*+*
Equivalent mass of Mg%l '/+*
&
+
= =
&
Mg%l Mg &%l
++
+
%oncentration of solutions
(!) Norm*+ity
Number of equivalents of solute
present in one litre of solution+
Equivalent of solute
N
2olume of solution in litre
=
Mass of solute (...
N
Equivalent mass of solute volume !in ml"
Equivalents
Also N
2!in litre"
=
Equivalents = N # 2 !in litre"
Milli equivalents = N # 2 !in ml"
,-estion
3llustrative e#ample
4ind the normality of
&
SO
'
having
'-g of
&
SO
'
present in *.. ml of
solution+
So+-tion.
Mass of solute (...
N
Equivalent mass volume !in ml"
'- (...
N
-1
*..
&
= &N
Most important point about
equivalents
Equivalent and milliequivalents of
reactants reacts in equal number to
give same number of equivalents or
milliequivalents of products separately+
E#ample$
& ' & ' &
& Equivalents
& Equivalents & Equivalents
& moles ( mole ( mole & mole
&NaO SO Na SO & O + +
,-estion
3llustrative 5roblem
&. ml of .+( N Ba%l
&
is mi#ed 6ith ). ml
of .+& N Al
&
!SO
'
"
)
+ o6 many gram of
BaSO
'
are formed7
& & ' ) ) '
Ba%l Al !SO " Al%l BaSO + +
So+-tion.
&.
.+(
(...
By equivalent method8 no need of balancing the
equation+ Because equivalents of reactants and
products are same+
& & ' ) ) '
Ba%l Al !SO " Al%l BaSO + +
Equivalents of Ba%l
&
=
).
.+&
(...
= & # (.
9)
= , # (.
9)
Equivalents of Al
&
!SO
'
"
)
=
Solution contd:
Since equivalents of Al
&
!SO
'
"
)
is in e#cess8 hence
equivalents of BaSO
'
= equivalents of Ba%l
&
= equivalents of Al%l
)
= & # (.
9)
ence8 mass of BaSO
'
= Equivalents # equivalent mass
)
&))
& (. +&))g
&
= =
I/ 0e 0i++ 1isc-ss this
2rob+em thro-3h mo+e
conce2t4 then 0e h*e
to b*+*nce1 the
e5-*tion"
Molarity
Number of moles of solute present in
one litre of solution+
Moles of solute
M
2olume !in litre"
=
Moles of solute (...
M
Molecular mass volume !in ml"
Moles = Molarity # volume !in litre"
Milli moles = Molarity # volume !in ml"
,-estion
3llustrative e#ample
%alculate the molarity of a solution of
NaO in 6hich .+'.g NaO dissolved
in *.. ml solution+
.+'.
M (...
'. *..
=
So+-tion.
= .+.& M
;elation bet6een normality and
molarity
Mass of solute (...
N
Molecular mass
volume !in ml"
n factor
N = M # n factor
4or %l8 n = (
&
SO
'
8 n = &
)
5O
'
8 n = )
NaO8 n = (
%a!O"
&
8 n = &
4or monovalent compound !n = ("
Normality and molarity is same+
,-estion
3llustrative 5roblem
%alculate molarity of .+, N Al%l
)
solution+
)
Al%l Al )%l
+++
+
So+-tion.
n = )
.+,
M .+&M
)
= =
Molality
Number of moles of solute present in ( <g
!or (... gram" of solvent+ 3t is represented
by m !small letter"+
Moles of solute
m
Mass of solvent
=
Mass of solute (...
m
Molecular mass Mass of solvent !gram"
,-estion
3llustrative 5roblem
%alculate the molality of ( molar solution
of NaO given density of solution is (+.'
gram=ml+
So+-tion.
( molar solution means ( mole of solute present per
litre of solution+
(
m (... ( molal solution+
(...
= =
0herefore8 mass of ( litre solution = (... # (+.'
= (.'. gram
Mass of solute = ( # '. = '.g
0herefore8 mass of solvent (.'. 9 '. = (...g
Strength of solution
Amount of solute present in one litre
solution+
Mass of solute
Strength
2olume of solution !in litre"
=
Strength Molarity Molecular mass =
Strength Normality Equivalent mass =
,-estion
3llustrative 5roblem
%alculate strength of .+.( N of NaO
solution+
So+-tion.
Strength = Normality # equivalent mass
= .+.( # '.
= .+' gram=litre
%oncentration in terms of percentage
Mass of solute
>by mass (..
2olume of solution
=
?
>
6
=
2olume of solute
>by volume (..
2olume of solution
=
2
>
v
=
,-estion
3llustrative 5roblem
%alculate the concentration of ( molal
solution of NaO in terms of percentage
by mass+
So+-tion.
( molal solution means ( mole !or '.g" NaO present
in (...g of solvent+
0otal mass of solution = (... @ '. = (.'.g
0herefore8 (.'.g solution contains '.g NaO
0herefore8 (..g solution contains
'.
(..
(.'.
=
= )+1'> by mass+
C+*ss e6ercise
%lass e#ercise (
.+((* g of pure sodium metal 6as dissolved
in *.. ml distilled 6ater+
0he molarity of the solution 6ould be
!Na = &)"
!a" .+.(. M !b" .+..((* M
!c" .+.&) M !d" .+.', M
Mass of solute (...
M
Molecular mass of solute 2olume in ml
=
.+((*
(... .+.(M
&) *..
= =
ence8 ans6er is !a"
So+-tion.
%lass e#ercise &
0he number of moles of o#ygen in one
litre of air containing &(> o#ygen by
volume8 in standard conditions8 is
!a" .+(1, mole !b" .+&( mole
!c" &+(. mole !d" .+..-) mole
&(> o#ygen by volume means &( ml o#ygen is
present in (.. ml of solution+
(8... ml of solution 6ill contain &(. ml+
Since at S05 &&8'.. ml of gas = ( mole8
&(.
&(. ml of o#ygen .+..-) mole
&&'..
= =
ence8 ans6er is !d"
So+-tion.
%lass e#ercise )
0he vapour density of a gas is ((+&+
0he volume occupied by ((+& g of the
gas at S05 6ill be
!a" ((+& A !b" &&+' A
!c" ( A !d" ''+1 A
Molecular mass = & B 2apour density
= & B ((+& = &&+'
Since &&+' g contains &&+' A of gas at S058
&&+'
B((+&=((+&A of gas
&&+'
11.2g contains
ence8 ans6er is !a"
So+-tion.
%lass e#ercise '
0he number of 6ater molecules in one
litre of 6ater is
!a" (1 !b" (1 B (...
!c" N
A
!d" **+** N
A
4or 6ater d = ( g=ml
Since8 One litre 6ater = (8... g of 6ater
Number of 6ater molecules
(...
AvogadroC s number
(1
=
= **+** N
A
ence8 ans6er is !d"
So+-tion.
%lass e#ercise *
?hich is not affected by temperature7
!a" Normality
!b" Molarity and molality
!c" Molarity
!d" Molality
Molality involves mass of solute and solvent
6hich are not affected by temperature+
So+-tion.
%lass e#ercise ,
%alculate the molality and mole fraction
of the solute in aqueous solution
containing )+. g of urea
!molecular mass = ,." in &*. g of 6ater+
( )
Mass of solute (...
Molality
Molecular mass of solute mass of solvent in gram
=
)
(... .+&
,. &*.
= =
Mole fraction of urea =
Moles of urea ) = ,.
.+..)*-
) &*.
0otal moles
,. (1
= =
+
Mole fraction of water = 1 0.00359 = 0.996
So+-tion.
%lass e#ercise /
%alculate the molarity and normality
of a solution containing .+* g of
NaO dissolved in *.. ml+
( )
Mass of solute (...
Molarity
Molecular mass 2olume in ml
=
.+* (...
.+.&* M
'. *..
= =
( )
Mass of solute (...
Normality N
Equivalent mass 2olume in ml
=
.+*
(... .+.&* N
'.
*..
(
= =
Or for monovalent compound liDe NaO normality
and molarity are same+
So+-tion.
%lass e#ercise 1
%alculate the mol fraction of ethanol
and 6ater in a sample of rectified
spirit 6hich contains -*> of ethanol
by mass+
-*> of ethanol by mass means -* g ethanol
present in (.. g of solution+
ence8 mass of 6ater = (.. 9 -* = * g
Moles of C
2
H
5
OH =
95
46
= 2.07 moles
Moles of 6ater!
&
O"=
*
.+&1mol
(1
=
So+-tion.
Solution
Mole fraction of %
&
*
O =
.+&1
.+11
.+&1 &+./
=
+
Mole fraction of 6ater = ( 9 .+11 = .+(&
%lass e#ercise -
A solution contains &*> of 6ater8
&*> of ethanol and *.> of
acetic acid by mass+
%alculate the mole fraction
of each component+
&*# @ &*# @ *.# = (..
# = (
Mass of 6ater = &* g
Mass of ethanol = &* g
Mass of acetic acid = *. g
Moles of water =
&*
(+)11 moles
(1
=
So+-tion.
Solution
Moles of ethanol =
&*
.+*') moles
',
=
Moles of acetic acid =
*.
=.+1)) moles
,.
Mole fraction of ethanol =
(+)11
.+*.&
&+/,'
=
Mole fraction of acetic acid = ( 9 .+*.) 9.+(-,
= .+).(
%lass e#ercise (.
&. ml of (. N %l are diluted 6ith
distilled 6ater to form one litre of the
solution+ ?hat is the normality of the
diluted solution7
1
!
1
=
2
!
2
&
&. (...
(. N
(... (...
=
2
= 0.2
So+-tion.
Th*n7 yo-
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Skilled Worker Overseas FAQs - Manitoba Immigration and Economic OpportunitiesДокумент2 страницыSkilled Worker Overseas FAQs - Manitoba Immigration and Economic OpportunitieswesamОценок пока нет
- Units and MeasurementДокумент41 страницаUnits and MeasurementHeather WrightОценок пока нет
- Thermo ChemistryДокумент60 страницThermo ChemistryHeather WrightОценок пока нет
- Percent Yield and Limiting Reactants - 2Документ24 страницыPercent Yield and Limiting Reactants - 2Heather WrightОценок пока нет
- Solution Conc Raoults ClligativeДокумент66 страницSolution Conc Raoults ClligativeHeather WrightОценок пока нет
- Chemical EquilibriumДокумент77 страницChemical EquilibriumHeather WrightОценок пока нет
- Chemical Kinetics - StudentsДокумент46 страницChemical Kinetics - StudentsHeather WrightОценок пока нет
- Chapter10 NotesДокумент33 страницыChapter10 NotesHeather WrightОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 The Behavior of GasesДокумент59 страницChapter 14 The Behavior of GasesHeather Wright100% (2)
- Chapter 1-2Документ68 страницChapter 1-2Heather WrightОценок пока нет
- Acid Base (A)Документ30 страницAcid Base (A)Heather WrightОценок пока нет
- Adsorption ExperimentДокумент5 страницAdsorption ExperimentNauman KhalidОценок пока нет
- CIGRE Operational Evaluation of RTV Coating Performance Over 17 Years On The Coastal Area at Jubail-SAДокумент9 страницCIGRE Operational Evaluation of RTV Coating Performance Over 17 Years On The Coastal Area at Jubail-SAMalik Shoaib khalidОценок пока нет
- Analysis of MMDR Amendment ActДокумент5 страницAnalysis of MMDR Amendment ActArunabh BhattacharyaОценок пока нет
- April 8/91: All GroupsДокумент33 страницыApril 8/91: All Groupsreza mirzakhaniОценок пока нет
- 4BT3 9-G2 PDFДокумент5 страниц4BT3 9-G2 PDFNv Thái100% (1)
- Translations Telugu To English A ClassifДокумент111 страницTranslations Telugu To English A ClassifGummadi Vijaya KumarОценок пока нет
- Aashirwaad Notes For CA IPCC Auditing & Assurance by Neeraj AroraДокумент291 страницаAashirwaad Notes For CA IPCC Auditing & Assurance by Neeraj AroraMohammed NasserОценок пока нет
- LP MAPEH 10 1st Quarter Printing Final.Документ29 страницLP MAPEH 10 1st Quarter Printing Final.tatineeesamonteОценок пока нет
- Wps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawДокумент1 страницаWps For Carbon Steel THK 7.11 GtawAli MoosaviОценок пока нет
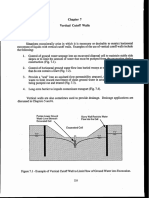
- Vertical Cutoff WallsДокумент18 страницVertical Cutoff WallsMark LaiОценок пока нет
- WeldingДокумент23 страницыWeldingMathan EverОценок пока нет
- TRAVEL POLICY CARLO URRIZA OLIVAR Standard Insurance Co. Inc - Travel Protect - Print CertificateДокумент4 страницыTRAVEL POLICY CARLO URRIZA OLIVAR Standard Insurance Co. Inc - Travel Protect - Print CertificateCarlo OlivarОценок пока нет
- Distance SortДокумент6 страницDistance SortAI Coordinator - CSC JournalsОценок пока нет
- Subject: PSCP (15-10-19) : Syllabus ContentДокумент4 страницыSubject: PSCP (15-10-19) : Syllabus ContentNikunjBhattОценок пока нет
- Influence of Freezing and Pasteurization of The Physical Condition of The Plastik (PE, PP and HDPE) As Selar Fish Packaging (Selaroides Leptolepis) in Sendang Biru, Malang, East Java. IndonesiaДокумент7 страницInfluence of Freezing and Pasteurization of The Physical Condition of The Plastik (PE, PP and HDPE) As Selar Fish Packaging (Selaroides Leptolepis) in Sendang Biru, Malang, East Java. IndonesiaInternational Network For Natural SciencesОценок пока нет
- OracleCarrierManifestingPartnerIntegration PDFДокумент40 страницOracleCarrierManifestingPartnerIntegration PDFvishal_vishnu11Оценок пока нет
- Historical Perspective of OBДокумент67 страницHistorical Perspective of OBabdiweli mohamedОценок пока нет
- Combining Wavelet and Kalman Filters For Financial Time Series PredictionДокумент17 страницCombining Wavelet and Kalman Filters For Financial Time Series PredictionLuis OliveiraОценок пока нет
- Manual TV Hyundai HYLED3239iNTMДокумент40 страницManual TV Hyundai HYLED3239iNTMReinaldo TorresОценок пока нет
- PC Engines APU2 Series System BoardДокумент11 страницPC Engines APU2 Series System Boardpdy2Оценок пока нет
- Course: Introduction To Geomatics (GLS411) Group Practical (2-3 Persons in A Group) Practical #3: Principle and Operation of A LevelДокумент3 страницыCourse: Introduction To Geomatics (GLS411) Group Practical (2-3 Persons in A Group) Practical #3: Principle and Operation of A LevelalyafarzanaОценок пока нет
- (Kazantzakis Nikos) Freedom or DeathДокумент195 страниц(Kazantzakis Nikos) Freedom or DeathTarlan FisherОценок пока нет
- Pds Hempel's Maestro Water Borne Primer 28830 En-GbДокумент2 страницыPds Hempel's Maestro Water Borne Primer 28830 En-GbKalaiyazhagan ElangeeranОценок пока нет
- Iit-Jam Mathematics Test: Modern Algebra Time: 60 Minutes Date: 08-10-2017 M.M.: 45Документ6 страницIit-Jam Mathematics Test: Modern Algebra Time: 60 Minutes Date: 08-10-2017 M.M.: 45Lappy TopОценок пока нет
- State Farm Claims: PO Box 52250 Phoenix AZ 85072-2250Документ2 страницыState Farm Claims: PO Box 52250 Phoenix AZ 85072-2250georgia ann polley-yatesОценок пока нет
- Master Data FileДокумент58 страницMaster Data Fileinfo.glcom5161Оценок пока нет
- Earth and Life Science, Grade 11Документ6 страницEarth and Life Science, Grade 11Gregorio RizaldyОценок пока нет
- Annex A - Scope of WorkДокумент4 страницыAnnex A - Scope of Workمهيب سعيد الشميريОценок пока нет
- The Chassis OC 500 LE: Technical InformationДокумент12 страницThe Chassis OC 500 LE: Technical InformationAbdelhak Ezzahrioui100% (1)