Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MOS Transistor
Загружено:
ManikandanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MOS Transistor
Загружено:
ManikandanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EE314
IBM/Motorola Power PC620
IBM Power PC 601
Motorola MC68020
Field Effect
Transistors
Chapter 12: Field
Effect Transistors
1.Construction of MOS
2.NMOS and PMOS
3.Types of MOS
4.MOSFET Basic Operation
5.Characteristics
The MOS Transistor
Polysilicon
Aluminum
JFET Junction Field Effect Transistor
MOSFET - Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
n-channel MOSFET (nMOS) & p-channel MOSFET (pMOS)
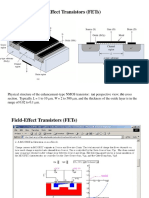
The MOS Transistor
n+ n+
p-substrate
Field-Oxide
(SiO
2
)
p+ stopper
Polysilicon
Gate Oxide
Drain
Source
Gate
Bulk Contact
CROSS-SECTION of NMOS Transistor
Switch Model of NMOS Transistor
Gate
Source
(of carriers)
Drain
(of
carriers)
| V
GS
|
| V
GS
| < | V
T
|
| V
GS
| > | V
T
|
Open (off) (Gate = 0)
Closed (on) (Gate = 1)
R
on
Switch Model of PMOS Transistor
Gate
Source
(of carriers)
Drain
(of carriers)
| V
GS
|
| V
GS
| > | V
DD
| V
T
| | | V
GS
| < | V
DD
|V
T
| |
Open (off) (Gate = 1)
Closed (on) (Gate = 0)
R
on
MOS transistors Symbols
D
S
G
D
S
G
G
S
D D
S
G
NMOS
Enhancement NMOS
PMOS
Depletion
Enhancement
B
NMOS with
Bulk Contact
Channel
JFET and MOSFET Transistorsor
L = 0.5-10 m
W = 0.5-500 m
SiO
2
Thickness = 0.02-0.1 m
Device characteristics depend on L,W, Thickness, doping levels
Symbol
MOSFET Transistor Fabrication Steps
Building A MOSFET Transistor Using Silicon
http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/electromag/java/transistor/index.html
It is done. Now, how does it
work?
n-channel MOSFET Basic Operation
Operation in the Cutoff region
Schematic
pn junction:
reverse bias
i
D
=0
for v
GS
<V
t0
When v
GS
=0 then i
D
=0 until v
GS
>V
t0
(V
t0
threshold voltage)
n-channel MOSFET Basic Operation
Operation in the Triode Region
For v
DS
<v
GS
-V
t0
and v
GS
>V
t0
the NMOS is operating in the triode region
Resistor like characteristic
(R between S & D,
Used as voltage controlled R)
For small v
DS
, i
D
is proportional
to the excess voltage v
GS
-V
t0
n-channel MOSFET Basic Operation
Operation in the Triode Region
( ) | |
2
0
2
DS DS t GS D
v v V v K i =
2
KP
L
W
K
|
.
|
\
|
=
Device parameter KP for
NMOSFET is 50 A/V
2
n-channel MOSFET Basic Operation
Operation in the Saturation Region (v
DS
is increased)
Tapering
of the
channel
- increments
of i
D
are
smaller
when
v
DS
is
larger
When v
GD
=V
t0
then the channel
thickness is 0 and
( )
2
0 t GS D
V v K i =
n-channel MOSFET Basic Operation
Example 12.1
An nMOS has W=160 m, L=2 m, KP= 50 A/V
2
and V
to
=2 V.
Plot the drain current characteristic vs drain to source voltage
for v
GS
=3 V.
2
KP
L
W
K
|
.
|
\
|
=
( ) | |
2
0
2
DS DS t GS D
v v V v K i =
( )
2
0 t GS D
V v K i =
n-channel MOSFET Basic Operation
Characteristic
2
DS D
Kv i =
Example 12.1
Channel length
modulation
i
d
depends on v
DS
in
saturation region
(approx: i
D
=const in
saturation region)
p-channel MOSFET Basic Operation
It is constructed by interchanging the n and p regions of n-
channel MOSFET.
Symbol
Characteristic
How does p-channel
MOSFET operate?
-voltage polarities
-i
D
current
-schematic
Вам также может понравиться
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesОт EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (7)
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsОт EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsОценок пока нет
- MOSFET Seminar: An Introduction to the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorДокумент23 страницыMOSFET Seminar: An Introduction to the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorRahulKushwahaОценок пока нет
- Lecture8 MOS TransistorДокумент21 страницаLecture8 MOS TransistorKartika MunirОценок пока нет
- Analog Layout Design: Kanazawa University Microelectronics Research Lab. Akio KitagawaДокумент48 страницAnalog Layout Design: Kanazawa University Microelectronics Research Lab. Akio Kitagawaaminkhan83Оценок пока нет
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignОт EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - CMOS Logic, Fabrication and LayoutДокумент34 страницыUnit 2 - CMOS Logic, Fabrication and LayoutphillipОценок пока нет
- Concepts in VLSI DesignДокумент59 страницConcepts in VLSI DesignA.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMANОценок пока нет
- CmosДокумент207 страницCmossuneeldvОценок пока нет
- Solns 9Документ66 страницSolns 9ramprakash_rampelliОценок пока нет
- Mosfet PowerPoint PresentationДокумент71 страницаMosfet PowerPoint PresentationMohammad Rameez100% (7)
- Mosfet Vs BJT: Mos Field-Effect Transistors (Mosfets)Документ31 страницаMosfet Vs BJT: Mos Field-Effect Transistors (Mosfets)chinchouОценок пока нет
- EI2403 - VLSI Design 2 Marks With AnswersДокумент23 страницыEI2403 - VLSI Design 2 Marks With AnswersAnand GvphОценок пока нет
- CMOS VLSI DESIGN NOTES Made by Barun Dhiman From Various Books Like Kamran Neil E WasteДокумент226 страницCMOS VLSI DESIGN NOTES Made by Barun Dhiman From Various Books Like Kamran Neil E WasteBarun DhimanОценок пока нет
- Lecture8 MOS TransistorДокумент21 страницаLecture8 MOS Transistorpalak parmarОценок пока нет
- Lecture - MOS & MOSFET-1Документ21 страницаLecture - MOS & MOSFET-1Kartika MunirОценок пока нет
- VLSI DESIGN: MOS TRANSISTORДокумент162 страницыVLSI DESIGN: MOS TRANSISTORBasheer V.PОценок пока нет
- VijuДокумент14 страницVijuilesh yadav66Оценок пока нет
- MOSFET DC analysisДокумент29 страницMOSFET DC analysisSaurav ChourasiaОценок пока нет
- Mos ModelsДокумент39 страницMos Modelsch0071Оценок пока нет
- Lect 4,5,6,7 MOSFET Construction, Working Principle SND ChsrscteridticsДокумент26 страницLect 4,5,6,7 MOSFET Construction, Working Principle SND Chsrscteridticsshashikala kotiОценок пока нет
- MOSFET SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORДокумент38 страницMOSFET SEMICONDUCTOR FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORVimal KunwarОценок пока нет
- Mosfet (1)Документ16 страницMosfet (1)challhatt1234Оценок пока нет
- Lab-2: V-I Characteristics of NMOS and PMOSДокумент18 страницLab-2: V-I Characteristics of NMOS and PMOSDarsh GuptaОценок пока нет
- Mosfet CharacteristicsДокумент12 страницMosfet CharacteristicsNavaneethaan NathamoorthyОценок пока нет
- Lect13 MosfetДокумент8 страницLect13 MosfetAbhay ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- MOS Rabaey PDFДокумент32 страницыMOS Rabaey PDFalamgirОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 1: Aim: Study of Tanner Tools THEORY: Tanner ToolsДокумент24 страницыExperiment No. 1: Aim: Study of Tanner Tools THEORY: Tanner ToolsVarun GargОценок пока нет
- VLSI Unit 1 - MOSДокумент86 страницVLSI Unit 1 - MOSskh_19870% (1)
- Ec6601 Vlsi DesignДокумент58 страницEc6601 Vlsi DesignRajiv SОценок пока нет
- VLSI Design Lecture NotesДокумент117 страницVLSI Design Lecture NotesRaji SharmiОценок пока нет
- Field Effect TransistorsДокумент40 страницField Effect TransistorsRatanОценок пока нет
- Analog & Digital Electronics: Course No: Ph-218 Lec-26: Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistors (Mosfets)Документ16 страницAnalog & Digital Electronics: Course No: Ph-218 Lec-26: Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistors (Mosfets)Udai SinghОценок пока нет
- FETДокумент91 страницаFETpawan_32Оценок пока нет
- Lec 5Документ36 страницLec 5Amandeep GuptaОценок пока нет
- L #5: Mosfet C A: Sfsu - E 301 - E L AB Haracteristics and PplicationsДокумент14 страницL #5: Mosfet C A: Sfsu - E 301 - E L AB Haracteristics and PplicationsRudra MishraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - Field-Effect Transistors (Fets)Документ129 страницChapter 5 - Field-Effect Transistors (Fets)Srie WidodoОценок пока нет
- FET Transistors LessonДокумент30 страницFET Transistors LessonAlbert OmondiОценок пока нет
- MOSFET Scaling and Its Effects in 40 CharactersДокумент109 страницMOSFET Scaling and Its Effects in 40 CharactersLiferОценок пока нет
- MosfetДокумент15 страницMosfetAnkita BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- MOSFETsДокумент26 страницMOSFETsVidit VishnoiОценок пока нет
- Bakir Chapter5Документ91 страницаBakir Chapter5mehtajay1993Оценок пока нет
- EEE102L: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Devices and ApplicationsДокумент16 страницEEE102L: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Devices and ApplicationsKavi Rohith M 22BEC0147Оценок пока нет
- Mosfet (Iii) - I-V CharacteristicsДокумент11 страницMosfet (Iii) - I-V Characteristics許博凱Оценок пока нет
- Microdevices: Mosfets - Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistors N MosfetДокумент11 страницMicrodevices: Mosfets - Metal Oxide Field Effect Transistors N Mosfetblue7nicoОценок пока нет
- MOSFET Handout ExplainedДокумент25 страницMOSFET Handout ExplainedArun JagaОценок пока нет
- Class10 PDFДокумент34 страницыClass10 PDFspyeagleОценок пока нет
- Electronics Ch5Документ30 страницElectronics Ch5Santi Navarro MoralОценок пока нет
- ElectronicsДокумент22 страницыElectronicsVARSHITH REDDY JОценок пока нет
- Cmos IssuesДокумент180 страницCmos IssuessiddhasenОценок пока нет
- Complete Vlsi NotesДокумент160 страницComplete Vlsi NotesTarun SinghalОценок пока нет
- Stick DiagramДокумент72 страницыStick DiagramBhanu Bond0% (1)
- MOS Field-Effect Transistor MOSFETДокумент34 страницыMOS Field-Effect Transistor MOSFETFrank WanderiОценок пока нет
- Basic MOS Device Physics: Zou Zhige 2007 HUSTДокумент62 страницыBasic MOS Device Physics: Zou Zhige 2007 HUSTSHIVA VERMAОценок пока нет
- Pid00050 2 CmosДокумент8 страницPid00050 2 CmosSaurabh ChakravartyОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Digital ElectronicsДокумент22 страницыIntroduction To Digital ElectronicsLeandroRicardoОценок пока нет
- MOSFET Circuit Design GuideДокумент45 страницMOSFET Circuit Design GuideNam zzzОценок пока нет
- Characteristics: EXPERIMENT 08: SPICE Simulation of and Implementation For MOSFETДокумент11 страницCharacteristics: EXPERIMENT 08: SPICE Simulation of and Implementation For MOSFETJohnny NadarОценок пока нет
- Unit - 3Документ8 страницUnit - 3AgnathavasiОценок пока нет
- Shanmuga Manuscript 23.11.18Документ14 страницShanmuga Manuscript 23.11.18ManikandanОценок пока нет
- 1Документ27 страниц1ManikandanОценок пока нет
- Unit V Processes and Operating SystemsДокумент37 страницUnit V Processes and Operating SystemsManikandan Annamalai100% (1)
- Vanitha Thesis (Final)Документ126 страницVanitha Thesis (Final)ManikandanОценок пока нет
- Research Article For Soft ComputingДокумент19 страницResearch Article For Soft ComputingManikandanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ8 страницChapter 5ManikandanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ10 страницChapter 4ManikandanОценок пока нет
- ANFIS ClassificationДокумент15 страницANFIS ClassificationManikandanОценок пока нет
- Synopsis SsДокумент22 страницыSynopsis SsManikandanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ25 страницChapter 2ManikandanОценок пока нет
- Chapter-7 Conclusion and Future Work ConclusionДокумент3 страницыChapter-7 Conclusion and Future Work ConclusionManikandanОценок пока нет
- BPJ Copyright FormДокумент2 страницыBPJ Copyright Formrikirdn27Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ12 страницChapter 3ManikandanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ8 страницChapter 6ManikandanОценок пока нет
- 1Документ27 страниц1ManikandanОценок пока нет
- 7Документ4 страницы7ManikandanОценок пока нет
- ECESatelite CommunicationДокумент13 страницECESatelite CommunicationNaresh KumarОценок пока нет
- Arduino Final BrochureДокумент2 страницыArduino Final BrochureManikandanОценок пока нет
- Ec1015 Satellite CommunicationДокумент13 страницEc1015 Satellite Communicationainugiri100% (1)
- EC2045 2 MarksДокумент21 страницаEC2045 2 MarksManikandanОценок пока нет
- Research Journal SukanyaДокумент12 страницResearch Journal SukanyaManikandanОценок пока нет
- EC2045 2 MarksДокумент21 страницаEC2045 2 MarksManikandanОценок пока нет
- Satellite Communications: Look AngleДокумент22 страницыSatellite Communications: Look AngleManikandanОценок пока нет
- Satellite Communications: Look AngleДокумент22 страницыSatellite Communications: Look AngleManikandanОценок пока нет
- C 3Документ44 страницыC 3Shymaa AbdeldayemОценок пока нет
- Sequential Logic in Verilog: Taken From Digital Design and Computer ArchitectureДокумент18 страницSequential Logic in Verilog: Taken From Digital Design and Computer ArchitectureManikandanОценок пока нет
- QZhang FinFETДокумент18 страницQZhang FinFETManikandanОценок пока нет
- Design Rules: Jan M. RabaeyДокумент9 страницDesign Rules: Jan M. RabaeyManikandanОценок пока нет
- Vlsi 10Документ20 страницVlsi 10ManikandanОценок пока нет
- Device Lab Report 9 PDFДокумент5 страницDevice Lab Report 9 PDFScribble RiYaDОценок пока нет
- MOS Inverters: Static Characteristics: Digital Integrated CircuitsДокумент37 страницMOS Inverters: Static Characteristics: Digital Integrated CircuitsPrasad M PrasadОценок пока нет
- ChopShop-PedalPCB V1Документ5 страницChopShop-PedalPCB V1nghtlghtОценок пока нет
- 18CSS201J AdeДокумент148 страниц18CSS201J AdeNilesh bibhutiОценок пока нет
- q.16) Operation of Positive and Negative ClippersДокумент15 страницq.16) Operation of Positive and Negative Clippersdharshini ravichandranОценок пока нет
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Group Assignment Electronic Principles I (Bnr27103) SEMESTER 1, SESSION 2021/2022Документ16 страницUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Group Assignment Electronic Principles I (Bnr27103) SEMESTER 1, SESSION 2021/2022Izzul HakimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 0Документ37 страницChapter 0Abo Shaker HaboudalОценок пока нет
- IRFP360: 23A, 400V, 0.200 Ohm, N-Channel Power Mosfet FeaturesДокумент7 страницIRFP360: 23A, 400V, 0.200 Ohm, N-Channel Power Mosfet FeaturesFran Javi Vila DiazОценок пока нет
- Intro To FinFetДокумент19 страницIntro To FinFetKota Sai JagadishОценок пока нет
- Molchanov A 2014Документ7 страницMolchanov A 2014mayuri sritharanОценок пока нет
- Vlsi DesignДокумент2 страницыVlsi DesignShribala NagulОценок пока нет
- Lect0 IntroДокумент60 страницLect0 IntroRofyda SaadОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Digital Electronics: Microelectronic Circuit DesignДокумент64 страницыIntroduction To Digital Electronics: Microelectronic Circuit DesignramibotrosОценок пока нет
- Lecture 14Документ23 страницыLecture 14羅鴻100% (1)
- SVF5N60T/F/D/MJ - Datasheet: 5A, 600V N-Channel MosfetДокумент10 страницSVF5N60T/F/D/MJ - Datasheet: 5A, 600V N-Channel MosfetJavier ArcadasОценок пока нет
- (L3) - Semiconductors - 22th DecДокумент52 страницы(L3) - Semiconductors - 22th DecShreshth GuptaОценок пока нет
- Ch6 Transistors Amplifiers02 - 2Документ18 страницCh6 Transistors Amplifiers02 - 2陳啟德Оценок пока нет
- Carbon Nanotube-Based CMOS SRAM: 1 Kbit 6T SRAM Arrays and 10T SRAM CellsДокумент6 страницCarbon Nanotube-Based CMOS SRAM: 1 Kbit 6T SRAM Arrays and 10T SRAM CellsShreevatsa BhatОценок пока нет
- Lesson 007-01 - Working of JFETДокумент15 страницLesson 007-01 - Working of JFETKyle OyongОценок пока нет
- MOSFET-Internal Capacitances PDFДокумент11 страницMOSFET-Internal Capacitances PDFJayanth Sriranga100% (1)
- MG Tint Wai Min Khant (Electrical and Electronic Principle A2)Документ25 страницMG Tint Wai Min Khant (Electrical and Electronic Principle A2)Sniper- KОценок пока нет
- Int J Numerical Modelling - 2020 - Mushtaq - Design and Analysis of INDEP FinFET SRAM Cell at 7 NM TechnologyДокумент14 страницInt J Numerical Modelling - 2020 - Mushtaq - Design and Analysis of INDEP FinFET SRAM Cell at 7 NM Technology예민욱Оценок пока нет
- FinFET-based Product PerformanceДокумент5 страницFinFET-based Product PerformanceHung Lung ChienОценок пока нет
- BJT Input-Output CharacteristicsДокумент8 страницBJT Input-Output CharacteristicsAditya GudlaОценок пока нет
- JFET and MOSFET quiz with answersДокумент15 страницJFET and MOSFET quiz with answersAnonymous eWMnRr70qОценок пока нет
- Transistor C 548 BДокумент4 страницыTransistor C 548 BEdson GomesОценок пока нет
- High-power NPN Darlington transistor for audio and regulationДокумент3 страницыHigh-power NPN Darlington transistor for audio and regulationVictor HemzОценок пока нет
- MOSFET Guide - Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorДокумент2 страницыMOSFET Guide - Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorbofshafiqueОценок пока нет
- Cmos PDFДокумент61 страницаCmos PDFRamakrishna BoyapatiОценок пока нет