Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
PiThe Filipino has a strong respect for the dignity of the human person and considers the other as an equal. He is sensitive to people’s feelings, very trusting to a point of naivete. He is capable of genuinely relating to others, empathizing during times of stress, of need (pakikiramay, bayanihan). On the one hand, this makes a good point d’ appui for a theology of liberation, a source of moral consciousness, a Filipino concept of justice based on human dignity. On the other hand, this very quality makes the Filipino tend to interpret personally any praise or criticism regarding business or work relationships. He has difficulty viewing things objectively. Contrary to this other-orientedness is the kanya-kanya syndrome, the so-called crab mentality of pulling down, through gossips and intrigues, persons seen to have by-passed one in rank, wealth, and honor. Family orientation towards, not only the nuclear members, but also the members of the clan (and even kumpadres) gives the Fil
Загружено:
Mante Cros NalzaroАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PiThe Filipino has a strong respect for the dignity of the human person and considers the other as an equal. He is sensitive to people’s feelings, very trusting to a point of naivete. He is capable of genuinely relating to others, empathizing during times of stress, of need (pakikiramay, bayanihan). On the one hand, this makes a good point d’ appui for a theology of liberation, a source of moral consciousness, a Filipino concept of justice based on human dignity. On the other hand, this very quality makes the Filipino tend to interpret personally any praise or criticism regarding business or work relationships. He has difficulty viewing things objectively. Contrary to this other-orientedness is the kanya-kanya syndrome, the so-called crab mentality of pulling down, through gossips and intrigues, persons seen to have by-passed one in rank, wealth, and honor. Family orientation towards, not only the nuclear members, but also the members of the clan (and even kumpadres) gives the Fil
Загружено:
Mante Cros NalzaroАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pioneers and
History
of
RADIOACTIVITY
Reporters:
Nalzaro
Larong
Santiago
Diaz
Fazon
Paloma
1895
In November, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen
discovered X-rays.
1896
At the Museum of Natural History, Henri
Becquerel discovered that the element
uranium emits penetrating radiation (natural
radioactivity).
1897
J.J. Thomson characterized the electron by
measuring its speed and charge-to-mass
ratio, and showed that all atoms contain
electrons.
1898
Pierre and Marie Curie discovered polonium
and radium at the School of Industrial
Physics and Chemistry (EPCI) in Paris. To
determine the atomic mass of radium, the
Curies processed several tonnes of a natural
uranium ore, pitchblende (1 tonne of which
yields 1 to 2 mg of radium chloride). Marie
Curie coined the term radioactivity.
1899
Several scientists demonstrated that
uranium emits two types of radiation. In
January, Ernest Rutherford called them
respectively a and radiation . On 6
November, Pierre and Marie Curie published
a paper in which they reported a singular
property of radium: induced radioactivity.
1900
In April, Paul Villard identified ? radiation.
1901-1904
Jean Perrin (and independently Hantaro
Nagaoka) imagined a representation of
atoms as miniature solar systems.
1901-1903
Ernest Rutherford and Frederic Soddy
demonstrated the period (according to
the law of radioactive decay) that
characterizes each radioactive element.
They showed that radioactivity is the
transmutation of one element into another.
1906
Ernest Rutherford identified a radiation as a
helium particle.
1910
In collaboration with Andr Debierne, Marie
Curie isolated metallic radium and
determined its atomic mass.
1911
Frdric Soddy established the existence of
isotopes. Ernest Rutherford demonstrated
the presence of a nucleus at the center of
the atom.
1913
Niels Bohr worked out a model of the atom
in which electrons orbit the nucleus.
1919
Ernest Rutherford performed the first artificial
nuclear transmutation, by transforming
nitrogen into oxygen through particle
bombardment.
1928
Hans Geiger and Karl Mller developed a
new Geiger-Mller counter (improvement
of the Geiger counter of 1908).
1930
Ernest Lawrence built the first cyclotron at
Berkeley.
1932
James Chadwick demonstrated the
existence of the neutron.
1934
Frdric and Irne Joliot-Curie discovered
artificial radioactivity. They created for the
first time a radioactive element (by
bombarding an aluminium sheet with
particles emitted by polonium), which they
baptized radiophosphorus.
1938
Otto Hahn(the father of nuclear chemistry)
and Fritz Strassmann reported the fission of
uranium.
1939
Frdric Joliot, Hans Halban, Lew Kowarski
and Francis Perrin demonstrated the
possibility of the chain reaction and
therefore of its energy applications (they
showed that fission is accompanied by
great release of energy and by the emission
of neutrons which can break open other
uranium nuclei, and so on).
Вам также может понравиться
- Thermodynamics - J. P. HolmanДокумент68 страницThermodynamics - J. P. Holmansivakkumar14Оценок пока нет
- Master List of Investigatory ProjectsДокумент23 страницыMaster List of Investigatory ProjectsMante Cros NalzaroОценок пока нет
- Audio Reality Bruce Rozenblit PDFДокумент124 страницыAudio Reality Bruce Rozenblit PDFmehdi_mohebi2009100% (7)
- Atoms From The Eyes of Philosophers and ScientistsДокумент11 страницAtoms From The Eyes of Philosophers and ScientistsMarArizala100% (3)
- Timeline of Atomic NatureДокумент19 страницTimeline of Atomic NatureLesly Justin FuntechaОценок пока нет
- Purlin & GirtДокумент96 страницPurlin & GirtudayvadapalliОценок пока нет
- English - Cater, Joseph - The Awesome Life Force - OrgoneДокумент453 страницыEnglish - Cater, Joseph - The Awesome Life Force - Orgoneheritzin100% (9)
- Atom Bomb Lecture NotesДокумент47 страницAtom Bomb Lecture NotesMonroe OrtizanoОценок пока нет
- Atom Bomb Lecture NotesДокумент46 страницAtom Bomb Lecture Notessn_crowley9661Оценок пока нет
- Atomic ScientistsДокумент142 страницыAtomic ScientistsAdel SukerОценок пока нет
- Conservation of MomentumДокумент17 страницConservation of MomentumWilma Y. VillasanОценок пока нет
- A Project On Radioactive ElementsДокумент23 страницыA Project On Radioactive ElementsMK Jas75% (4)
- Only BelieveДокумент76 страницOnly Believeknightrupert50% (2)
- Impacts of HVDC Lines On The Economics of HVDC ProjectsДокумент149 страницImpacts of HVDC Lines On The Economics of HVDC ProjectsArturo Isidro Conde Pérez0% (1)
- RadioactivityДокумент4 страницыRadioactivityWilly Martinez RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Periodic Table HistoryДокумент5 страницPeriodic Table HistoryMarybeth BobadillaОценок пока нет
- Periodic Table HistoryДокумент4 страницыPeriodic Table Historytawananyashatheodore495Оценок пока нет
- Radioactivity: Historical Figures Access Excellence Classic CollectionДокумент4 страницыRadioactivity: Historical Figures Access Excellence Classic CollectionKIRAERISОценок пока нет
- Marie Curie, A Radioactive TaleДокумент1 страницаMarie Curie, A Radioactive Talearunkk1010Оценок пока нет
- Document NFДокумент3 страницыDocument NFRazvan888Оценок пока нет
- Chemical ChangesДокумент3 страницыChemical ChangesFrankОценок пока нет
- Discovery of Sub Atomic ParticlesДокумент4 страницыDiscovery of Sub Atomic ParticlesManasvi SharmaОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of ChemistryДокумент27 страницA Brief History of ChemistryRaymond BeligoloОценок пока нет
- Ernest RutherfordДокумент3 страницыErnest RutherfordfelicevidanesОценок пока нет
- History of Nuclear PhysicsДокумент2 страницыHistory of Nuclear PhysicsHesbon MomanyiОценок пока нет
- Time Intervals Specifi C Times Events Description: Hammurab IДокумент10 страницTime Intervals Specifi C Times Events Description: Hammurab IKc MolinaОценок пока нет
- Radioactivity Overview ArticleДокумент4 страницыRadioactivity Overview Articleapi-267255264Оценок пока нет
- History of RadioactivityДокумент116 страницHistory of RadioactivityВладимир КурпаянидиОценок пока нет
- Periodic Table HistoryДокумент1 страницаPeriodic Table HistoryjavervalinoОценок пока нет
- History of Nuclear EneregyДокумент1 страницаHistory of Nuclear EneregykantsappaОценок пока нет
- ETT Seminar - Isotopes in MedicineДокумент71 страницаETT Seminar - Isotopes in MedicineisocenterОценок пока нет
- History of RadioactivityДокумент2 страницыHistory of RadioactivityAndre SumampouwОценок пока нет
- Ramil DrugsДокумент3 страницыRamil DrugsAileen Labastida BarcenasОценок пока нет
- ScientistsДокумент6 страницScientistsNadine BuñolОценок пока нет
- Atomic Theory TimelineДокумент3 страницыAtomic Theory TimelineYhan Brotamonte BoneoОценок пока нет
- History of Particle PhysicsДокумент13 страницHistory of Particle PhysicsjunaidtayarОценок пока нет
- Take Home Exam Chemistry Essay RevisedДокумент3 страницыTake Home Exam Chemistry Essay RevisedDanita AllenОценок пока нет
- Atomic Theory TimelineДокумент7 страницAtomic Theory Timelinem1e arZОценок пока нет
- Famous ScientistДокумент10 страницFamous Scientistafzal786435Оценок пока нет
- Thinking About MatterДокумент3 страницыThinking About MatterKim TaehyungОценок пока нет
- Nuclear EnergyДокумент8 страницNuclear Energybikramthakur0123Оценок пока нет
- Aaaaaaaaaathe Discovery of The Parts of The AtomДокумент2 страницыAaaaaaaaaathe Discovery of The Parts of The AtomIvan SantosОценок пока нет
- Rutherford, Radioactivity, and The Atomic NucleusДокумент30 страницRutherford, Radioactivity, and The Atomic NucleusanisdangasОценок пока нет
- Nature of MatterДокумент14 страницNature of MatterStudy GuyОценок пока нет
- Radioactivity. Nuclear Reactions.: Prepared by Milla Vladimirova Budeva and Radostina Ivova IvanovaДокумент11 страницRadioactivity. Nuclear Reactions.: Prepared by Milla Vladimirova Budeva and Radostina Ivova IvanovaRadostina IvanovaОценок пока нет
- A Timeline On Atomic StructureДокумент3 страницыA Timeline On Atomic Structuresome oneОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of Element Discovery, Synthesis, and AnalysisОт EverandA Brief History of Element Discovery, Synthesis, and AnalysisОценок пока нет
- Timeline: Advancement of ChemistryДокумент5 страницTimeline: Advancement of ChemistryCHRISTIAN CARL CABAJARОценок пока нет
- The Atomic Model: History of The Atom Khalil SinclairДокумент32 страницыThe Atomic Model: History of The Atom Khalil Sinclairangelgirl101096Оценок пока нет
- History of Chemistry: Name: Vine D. OrtegaДокумент8 страницHistory of Chemistry: Name: Vine D. OrtegaVine OrtegaОценок пока нет
- CommentsДокумент7 страницCommentsManish GulatiОценок пока нет
- Discovery of Radioactivity: Becquerel's PitchblendeДокумент2 страницыDiscovery of Radioactivity: Becquerel's PitchblendeSey S. BarriosОценок пока нет
- History On The Development of Periodic TableДокумент5 страницHistory On The Development of Periodic TablePricilla Jhenry MunozОценок пока нет
- Max Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert EinsteinДокумент4 страницыMax Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert Einsteinkat morenoОценок пока нет
- Ernest Rutherford Is Known For His Pioneering Studies of Radioactivity and The AtomДокумент2 страницыErnest Rutherford Is Known For His Pioneering Studies of Radioactivity and The AtomJASMIN DAMIANОценок пока нет
- CHY 40 Timeline On Discovery of Atom - Gabilan - BSChem1BДокумент2 страницыCHY 40 Timeline On Discovery of Atom - Gabilan - BSChem1BNikkoОценок пока нет
- Science WorksheetДокумент13 страницScience WorksheetRonilo ParagsaОценок пока нет
- Atomic TimelineДокумент3 страницыAtomic TimelineCarlos WatsonОценок пока нет
- Physical Science Week 3Документ10 страницPhysical Science Week 3BbGrace OrilloОценок пока нет
- Module Physical Science Week 3Документ10 страницModule Physical Science Week 3BbGrace OrilloОценок пока нет
- Atomic Model TimelineДокумент5 страницAtomic Model TimelineLayneGelleiMeneses-MillaminaBuenaventeОценок пока нет
- Atomic Nature TimelineДокумент2 страницыAtomic Nature TimelinebokanegОценок пока нет
- Hammurab I: Time Intervals Specifi C Times Events DescriptionДокумент8 страницHammurab I: Time Intervals Specifi C Times Events DescriptionVianne Fides IliganОценок пока нет
- A Nuclear PowerДокумент20 страницA Nuclear Powermukesh8981Оценок пока нет
- Timeline of Atomic StructureДокумент2 страницыTimeline of Atomic StructureHaider AliОценок пока нет
- Beta Rays13Документ1 страницаBeta Rays13Rafay SaifОценок пока нет
- Physics Famous ScientistДокумент14 страницPhysics Famous ScientistUsama mughal Usama mughalОценок пока нет
- Famous ScientistsДокумент2 страницыFamous ScientistsNga-nging PusaoОценок пока нет
- 2014.06.12 Dimensional Living Part 12 Coming Back To EarthДокумент8 страниц2014.06.12 Dimensional Living Part 12 Coming Back To EarthMante Cros NalzaroОценок пока нет
- 10-0613 The Kiasdngdom of Heaven - The Third Coming - Pastor Mita EdwardsonДокумент10 страниц10-0613 The Kiasdngdom of Heaven - The Third Coming - Pastor Mita EdwardsonMante Cros Nalzaro50% (2)
- Banned and Restricted Pesticides in The PhilippinesДокумент2 страницыBanned and Restricted Pesticides in The PhilippinesMante Cros NalzaroОценок пока нет
- Thie PhysicsДокумент12 страницThie PhysicsMante Cros NalzaroОценок пока нет
- Citrus Sinesis: Orange Peel Extract As Mosquito RepellantДокумент2 страницыCitrus Sinesis: Orange Peel Extract As Mosquito RepellantMante Cros NalzaroОценок пока нет
- Basic Genetic Concepts & TermsДокумент9 страницBasic Genetic Concepts & TermsMante Cros NalzaroОценок пока нет
- Sampaguita Flower As A DeodorantДокумент2 страницыSampaguita Flower As A DeodorantMante Cros NalzaroОценок пока нет
- The Anatomy of The EyeДокумент3 страницыThe Anatomy of The EyeChezcaDionisioОценок пока нет
- Useful Beam EquationsДокумент8 страницUseful Beam EquationsAXCОценок пока нет
- Full Download Book Physics For Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics PDFДокумент41 страницаFull Download Book Physics For Scientists and Engineers With Modern Physics PDFbonnie.wheeler650100% (14)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityДокумент2 страницыGujarat Technological Universityaxayzala778Оценок пока нет
- Physics Calculations For A MangonelДокумент18 страницPhysics Calculations For A MangonelMiluОценок пока нет
- Seismic Assessment of Hollow Core Concrete Bridge Piers: Research OnlineДокумент11 страницSeismic Assessment of Hollow Core Concrete Bridge Piers: Research Onlineshravan38Оценок пока нет
- Sheet - 3Документ2 страницыSheet - 3Abdel Hamied EbrahemОценок пока нет
- Grade 11 Physics Module4Документ81 страницаGrade 11 Physics Module4JohnRenzoMolinarОценок пока нет
- PPA6 Lecture CH 16Документ49 страницPPA6 Lecture CH 16suhartojagoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Passive DevicesДокумент72 страницыChapter 7 Passive DevicessvijiОценок пока нет
- Grade 7 Chapter 4 WorkbookДокумент19 страницGrade 7 Chapter 4 WorkbookBrennan ColdwellОценок пока нет
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: Massachusetts Institute of Technology RibologyДокумент3 страницыDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: Massachusetts Institute of Technology RibologyHamood Al-bahraniОценок пока нет
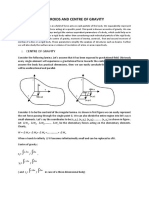
- Centroids and Centre of GravityДокумент31 страницаCentroids and Centre of Gravitysakshm guptaОценок пока нет
- 02whole PDFДокумент256 страниц02whole PDFkhyatichavdaОценок пока нет
- BJT Ebers Moll ModelДокумент5 страницBJT Ebers Moll ModelShiraz HusainОценок пока нет
- 7E Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницы7E Lesson PlanMarie VicОценок пока нет
- Kseb Supply Code 2012 PDFДокумент134 страницыKseb Supply Code 2012 PDFfaizalpsОценок пока нет
- Jun20 QP PDFДокумент32 страницыJun20 QP PDFMay StudiesОценок пока нет
- NIMS PosterДокумент1 страницаNIMS Posterアスリアナ イブラヒムОценок пока нет
- Experiment 5 - ResonanceДокумент6 страницExperiment 5 - ResonanceLeigh Dominique Zaragoza (Ji)Оценок пока нет
- PHD Thesis Andre Calado CoroadoДокумент166 страницPHD Thesis Andre Calado CoroadoAndré Calado CoroadoОценок пока нет
- Thesis Lid DrivenДокумент145 страницThesis Lid DrivenEddieq100% (1)
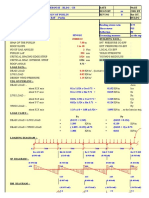
- Design of Footing 1 (ISOLATED FOOTING)Документ32 страницыDesign of Footing 1 (ISOLATED FOOTING)John Paul Hilary EspejoОценок пока нет
- Welding PDFДокумент18 страницWelding PDFsatymu3Оценок пока нет