Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Introduction To Networking: ENG224 Information Technology - Part Ii
Загружено:
Muhammad Kamran Akram0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
28 просмотров28 страниц12
Оригинальное название
Best Networking
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ12
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
28 просмотров28 страницIntroduction To Networking: ENG224 Information Technology - Part Ii
Загружено:
Muhammad Kamran Akram12
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 28
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
1
5. Introduction to Networking
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
2
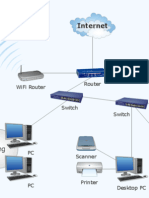
What is a Network?
A network consists of 2 or more computers
connected together, and they can communicate and
share resources (e.g. information)
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
3
Why Networking?
Sharing information i.e. data communication
Do you prefer these?
Or this?
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
4
Sharing hardware or software
Centralize administration and support
E.g. print document
E.g. Internet-based, so everyone can access the same
administrative or support application from their PCs
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
5
How many kinds of Networks?
Depending on ones perspective, we can classify
networks in different ways
Based on transmission media: Wired (UTP, coaxial
cables, fiber-optic cables) and Wireless
Based on network size: LAN and WAN (and MAN)
Based on management method: Peer-to-peer and
Client/Server
Based on topology (connectivity): Bus, Star, Ring
:
:
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
6
Two main categories:
Guided wires, cables
Unguided wireless transmission, e.g. radio,
microwave, infrared, sound, sonar
We will concentrate on guided media here:
Twisted-Pair cables:
Unshielded Twisted-Pair (UTP) cables
Shielded Twisted-Pair (STP) cables
Coaxial cables
Fiber-optic cables
Transmission Media
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
7
If the pair of wires are not twisted, electromagnetic
noises from, e.g., motors, will affect the closer wire more
than the further one, thereby causing errors
Twisted-Pair Cables
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
8
Unshielded Twisted-Pair (UTP)
Typically wrapped inside a plastic cover (for mechanical
protection)
A sample UTP cable with 5 unshielded twisted pairs of wires
Metal Insulator
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
9
Shielded Twisted-Pair (STP)
STP cables are similar to UTP cables, except there
is a metal foil or braided-metal-mesh cover that
encases each pair of insulated wires
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
10
Categories of UTP Cables
EIA classifies UTP cables according to the quality:
Category 1 the lowest quality, only good for voice,
mainly found in very old buildings, not recommended now
Category 2 good for voice and low data rates (up to
4Mbps for low-speed token ring networks)
Category 3 at least 3 twists per foot, for up to 10 Mbps
(common in phone networks in residential buildings)
Category 4 up to 16 Mbps (mainly for token rings)
Category 5 (or 5e) up to 100 Mbps (common for
networks targeted for high-speed data communications)
Category 6 more twists than Cat 5, up to 1 Gbps
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
11
Coaxial Cables
In general, coaxial cables, or coax, carry signals of
higher freq (100KHz500MHz) than UTP cables
Outer metallic wrapping serves both as a shield
against noise and as the second conductor that
completes the circuit
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
12
Fiber-Optic Cables
Light travels at 310
8
ms
-1
in free space and is the
fastest possible speed in the Universe
Light slows down in denser media, e.g. glass
Refraction occurs at interface, with light bending away
from the normal when it enters a less dense medium
Beyond the critical angle total internal reflection
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
13
An optical fiber consists of a core (denser material)
and a cladding (less dense material)
Simplest one is a multimode step-index optical fiber
Multimode = multiple paths, whereas step-index =
refractive index follows a step-function profile (i.e.
an abrupt change of refractive index between the
core and the cladding)
Light bounces back and forth along the core
Common light sources: LEDs and lasers
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
14
Advantages and Disadvantages
Noise resistance external light is blocked by outer
jacket
Less signal attenuation a signal can run for miles
without regeneration (currently, the lowest measured
loss is about ~4% or 0.16dB per km)
Higher bandwidth currently, limits on data rates come
from the signal generation/reception technology, not the
fiber itself
Cost Optical fibers are expensive
Installation/maintenance any crack in the core will
degrade the signal, and all connections must be perfectly
aligned
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
15
LAN and WAN
Local Area Network (LAN)
Small network, short distance
A room, a floor, a building
Limited by no. of computers and distance covered
Usually one kind of technology throughout the LAN
Serve a department within an organization
Examples:
Network inside the Student Computer Room
Network inside CF502
Network inside your home
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
16
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A network that uses long-range telecommunication links
to connect 2 or more LANs/computers housed in different
places far apart.
Towns, states, countries
Examples:
Network of our Campus
Internet
WAN
Student
Computer
Centre
Your home
USA
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
17
Example WAN technologies:
ISDN Integrated Service Digital Network
Basic rate: 192 Kbps Primary rate: 1.544Mbps
T-Carriers basically digital phone lines
T1: 1.544Mbps T3: 28T1
Frame relay
Each link offers 1.544Mbps or even higher
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Support B-ISDN: 155Mbps or 622Mbps or higher
SONET Synchronous Optical Network
Basic rate OC1: 51.84Mbps
Support OC12 and up to OC192 (9953.28Mbps) or
even higher in the future
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
18
Example of WAN: Broadband Cable Network
Cable TV services have been extensively developed in most
modern cities
Cable TV companies try to make use of their coaxial cable
installed (that are supposed to carry TV signals) to deliver
broadband data services
Many cable network wiring has been replaced with hybrid
fiber-coax (HFC) i.e. use of fiber-optic cable to connect to
the subscribers buildings, and then the original coaxial
cable to connect to each household
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
19
The connection is shared by a
number of subscribers, hence
may raise performance and
security problems
Cable company Coaxial
Cable
TV
PC
Cable
Drop
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
20
Cable is an asymmetrical technology
Downstream: max 36 Mbps
Upstream: max 10 Mbps
May be reduced to 3 10 Mbps downstream and 2
Mbps upstream, depending on no. of subscribers
Need a special cable modem
Ethernet
link to PC
Coaxial link
from cable TV
socket
Teryon Cable Modem
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
21
Peer-to-Peer Networks
Peer-to-peer network is also called workgroup
No hierarchy among computers all are equal
No administrator responsible for the network
Peer-to-peer
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
22
Advantages of peer-to-peer networks:
Low cost
Simple to configure
User has full accessibility of the computer
Disadvantages of peer-to-peer networks:
May have duplication in resources
Difficult to uphold security policy
Difficult to handle uneven loading
Where peer-to-peer network is appropriate:
10 or less users
No specialized services required
Security is not an issue
Only limited growth in the foreseeable future
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
23
Clients and Servers
Network Clients (Workstation)
Computers that request network resources or services
Network Servers
Computers that manage and provide network resources
and services to clients
Usually have more processing power, memory and
hard disk space than clients
Run Network Operating System that can manage not
only data, but also users, groups, security, and
applications on the network
Servers often have a more stringent requirement on its
performance and reliability
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
24
Advantages of client/server networks
Facilitate resource sharing centrally administrate and
control
Facilitate system backup and improve fault tolerance
Enhance security only administrator can have access
to Server
Support more users difficult to achieve with peer-to-
peer networks
Disadvantages of client/server networks
High cost for Servers
Need expert to configure the network
Introduce a single point of failure to the system
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
25
Topology 3 basic types
How so many computers are connected together?
Bus Topology Ring Topology
Star Topology
Switch
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
26
Bus Topology
Simple and low-cost
A single cable called a trunk (backbone, segment)
Only one computer can send messages at a time
Passive topology - computer only listen for, not
regenerate data
Star Topology
Each computer has a cable connected to a single point
More cabling, hence higher cost
All signals transmission through the hub; if down, entire
network down
Depending on the intelligence of hub, two or more
computers may send message at the same time
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
27
How to construct a network
with Bus / Star Topology?
Star Topology
Bus Topology
BNC T-Connector
Coaxial
cable
Network Card
ENG224
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Part II
5. Introduction to Networking
28
Ring Topology
Every computer serves as
a repeater to boost signals
Typical way to send data:
Token passing
only the computer who
gets the token can send
data
Disadvantages
Difficult to add computers
More expensive
If one computer fails, whole network fails
T
T
T
data
T
data
T
data
T
data
T
data
T
data
T
Ack
T
Ack
T
Ack
T
Ack
T
Вам также может понравиться
- Intro To NetworkingДокумент29 страницIntro To NetworkingQueniel QuezmarОценок пока нет
- 5 Intro To NetworkingДокумент28 страниц5 Intro To Networkingbelkin123456Оценок пока нет
- 5 Intro To NetworkingДокумент35 страниц5 Intro To NetworkingsumairОценок пока нет
- Networking Notes.4275287.PowerpointДокумент17 страницNetworking Notes.4275287.PowerpointKarthi KeyanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To NetworkingДокумент12 страницIntroduction To NetworkingMichael RicardeОценок пока нет
- Intro to Networking: Media, Topologies & MoreДокумент30 страницIntro to Networking: Media, Topologies & MoreRozitarmizi MohammadОценок пока нет
- Configuring Computer Systems and Networks Module 3Документ27 страницConfiguring Computer Systems and Networks Module 3Jennyvi NapodОценок пока нет
- NDДокумент43 страницыNDpeter haileОценок пока нет
- Guide To Networking Essentials Fifth EditionДокумент60 страницGuide To Networking Essentials Fifth EditionKhamis SeifОценок пока нет
- Data Communication & Networking: Shreykumar G. Bhavsar Network Engineer Teamlease Private LimitedДокумент157 страницData Communication & Networking: Shreykumar G. Bhavsar Network Engineer Teamlease Private LimitedDONIKA MARKANDEОценок пока нет
- Introduction To NetworksДокумент11 страницIntroduction To NetworksIqra KhanОценок пока нет
- 8+network DevicesДокумент43 страницы8+network DevicesGauravОценок пока нет
- Topic 6a Computer Networks PDFДокумент66 страницTopic 6a Computer Networks PDFTheo NdedaОценок пока нет
- BT3-IT Networking: Hussein KashmarДокумент33 страницыBT3-IT Networking: Hussein Kashmarhussein amhazОценок пока нет
- 8 Network - DevicesДокумент66 страниц8 Network - DevicesacasОценок пока нет
- Optical EthernetДокумент13 страницOptical Ethernetjsingh19100% (1)
- Advanced Networking For 3 Year Information Technology Regular StudentsДокумент64 страницыAdvanced Networking For 3 Year Information Technology Regular StudentsMafuz KemalОценок пока нет
- Scope and Coverage: Topic 5 - Network Media & Connectors Computer NetworksДокумент17 страницScope and Coverage: Topic 5 - Network Media & Connectors Computer NetworksSarge ChisangaОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK - FinalДокумент26 страницINTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK - Finalcharmanejoy.barrientosОценок пока нет
- LAN Architecture & Protocols: Business Data Communications, 5eДокумент29 страницLAN Architecture & Protocols: Business Data Communications, 5eDyeing DyeingОценок пока нет
- Introduction to computer networksДокумент26 страницIntroduction to computer networksRui CostaОценок пока нет
- Week 10 Networking Connecting Computing DevicesДокумент41 страницаWeek 10 Networking Connecting Computing DevicesAffif FarhanОценок пока нет
- Case StudyДокумент15 страницCase StudyTejas DatkhileОценок пока нет
- Topic 1.1 Basic Concepts of Computer NetworkДокумент39 страницTopic 1.1 Basic Concepts of Computer NetworkمحمدجوزيايОценок пока нет
- A Brief History of Computer NetworksДокумент55 страницA Brief History of Computer Networks116TanzeelОценок пока нет
- Data Communications, Data Networks, and The InternetДокумент30 страницData Communications, Data Networks, and The InternetMuhammad Bin ShehzadОценок пока нет
- NetwokingДокумент117 страницNetwokingjahanvi trivediОценок пока нет
- Chapter Two NetworkingДокумент52 страницыChapter Two NetworkingDaniel AshagrieОценок пока нет
- LAN WAN Networking GuideДокумент43 страницыLAN WAN Networking GuidesonaltopiwalaОценок пока нет
- Cabling - Lec 1Документ21 страницаCabling - Lec 1Mohammad MahfouzОценок пока нет
- Ccna1 m5 Cabling Lans WansДокумент16 страницCcna1 m5 Cabling Lans WanshanumambnsОценок пока нет
- Selecting Technologies and DevicesДокумент31 страницаSelecting Technologies and DevicesSathish KumarОценок пока нет
- Telecomminucation and Networking: Management Information SystemsДокумент71 страницаTelecomminucation and Networking: Management Information SystemsAVICK BISWASОценок пока нет
- Network Devices: ENG224 Information Technology - Part IДокумент43 страницыNetwork Devices: ENG224 Information Technology - Part IsiddiquentcОценок пока нет
- Topology of NetworkДокумент22 страницыTopology of NetworkMariem KhlifiОценок пока нет
- Physical LayerДокумент47 страницPhysical LayerlitoОценок пока нет
- DIOS Philippines IT Training: Network FundamentalsДокумент81 страницаDIOS Philippines IT Training: Network Fundamentalshamph113Оценок пока нет
- Training IP NetworkingДокумент280 страницTraining IP NetworkingPriskila Inggrit L.Оценок пока нет
- @chapter 7Документ28 страниц@chapter 7Silabat AshagrieОценок пока нет
- l9 Osi ModelДокумент172 страницыl9 Osi ModelSaitejОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Computer NetworksДокумент35 страницIntroduction To Computer NetworksAnanya SОценок пока нет
- Computer Communication (1) - RemovedДокумент42 страницыComputer Communication (1) - RemovedAdityaОценок пока нет
- 18CSS202J - COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS CourseДокумент235 страниц18CSS202J - COMPUTER COMMUNICATIONS CourseAlankriti KalsiОценок пока нет
- CSE 453 Lecture-1Документ22 страницыCSE 453 Lecture-1turjo987Оценок пока нет
- CN LAB 1902629 Hritik SharmaДокумент94 страницыCN LAB 1902629 Hritik SharmaXavier KingdomОценок пока нет
- Cabling and ConnectorsДокумент11 страницCabling and ConnectorsPushpinder Singh KhalsaОценок пока нет
- CompTIA Network+Документ262 страницыCompTIA Network+Abhijit SarkarОценок пока нет
- Best Fit TopologyДокумент106 страницBest Fit TopologyBikila SeketaОценок пока нет
- Advance Concepts of NetworkingДокумент168 страницAdvance Concepts of NetworkingSaptarishi BhattacharjeeОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ36 страницLecture 2joeh angeloОценок пока нет
- ???? ???-2Документ62 страницы???? ???-2Denaw AgimasОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ129 страницModule 1Aswini SanthanamОценок пока нет
- Datacom Mid PresentationДокумент21 страницаDatacom Mid Presentationclangdelacruz007Оценок пока нет
- Powerpont Nework Traning FinalДокумент45 страницPowerpont Nework Traning FinalGudata GechoОценок пока нет
- Cabling: The Complete Guide to Copper and Fiber-Optic NetworkingОт EverandCabling: The Complete Guide to Copper and Fiber-Optic NetworkingОценок пока нет
- The 5G Revolution: How the Next Generation of Wireless Will Change EverythingОт EverandThe 5G Revolution: How the Next Generation of Wireless Will Change EverythingОценок пока нет
- Libya A Historical AND Cultural Overview: Helen Chapin Metz, Ed. Libya: A Country Study, 1987Документ158 страницLibya A Historical AND Cultural Overview: Helen Chapin Metz, Ed. Libya: A Country Study, 1987Muhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- School of Electrical Engineering: WWW - Tuf.edu - PKДокумент4 страницыSchool of Electrical Engineering: WWW - Tuf.edu - PKMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- VLSI Lab MaualДокумент74 страницыVLSI Lab MaualMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Some of The Major Applications of DIPДокумент17 страницSome of The Major Applications of DIPMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Architecture Results Conclusion: Future DirectionsДокумент1 страницаArchitecture Results Conclusion: Future DirectionsMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- VLSI Systems Design FundamentalsДокумент4 страницыVLSI Systems Design FundamentalsMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Jade Ed Arbil Ugh atДокумент120 страницJade Ed Arbil Ugh atMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Thermal Physics & Blood Pressure Monitoring SourcesДокумент3 страницыThermal Physics & Blood Pressure Monitoring SourcesMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- BS Dissertation Formate TДокумент31 страницаBS Dissertation Formate TMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- MGT602 Entreprenureship - RevisedДокумент110 страницMGT602 Entreprenureship - Revisedalizaday100% (3)
- NurPur FinalДокумент17 страницNurPur FinalMalik Shahid0% (1)
- AHA Scientific StatementДокумент5 страницAHA Scientific StatementMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- 01 Verilog IntroductionДокумент36 страниц01 Verilog IntroductionJeeva BharathiОценок пока нет
- 1 STДокумент11 страниц1 STMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Digital System Design: Course Introduction and VHDL FundamentalsДокумент22 страницыDigital System Design: Course Introduction and VHDL FundamentalsMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Basic Multiplier Circuit in VerilogДокумент9 страницBasic Multiplier Circuit in VerilogMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Week 6 Prpagation DelayДокумент9 страницWeek 6 Prpagation DelayMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- FAQsДокумент33 страницыFAQsMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- VLSI Systems Design FundamentalsДокумент4 страницыVLSI Systems Design FundamentalsMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Service Internship ReportДокумент46 страницService Internship ReportNadeem80% (5)
- Memory: RAM (Random Access Memory)Документ2 страницыMemory: RAM (Random Access Memory)Muhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Manual e 35602213Документ73 страницыManual e 35602213Muhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Classification of ComputersДокумент3 страницыClassification of ComputersMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Technician-I (Electrical) Website ListДокумент2 страницыTechnician-I (Electrical) Website ListMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Types of ComputersДокумент2 страницыTypes of ComputersMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Services Invoice: Pakistan Telecommunicationcompany Limited STN NTNДокумент1 страницаServices Invoice: Pakistan Telecommunicationcompany Limited STN NTNMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Some of The Major Applications of DIPДокумент17 страницSome of The Major Applications of DIPMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Model Sim The Main Purpose of This Lab Is To Understand The The The Verilog Language With A Very Simple Example of Full AdderДокумент3 страницыModel Sim The Main Purpose of This Lab Is To Understand The The The Verilog Language With A Very Simple Example of Full AdderMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Digital Image Processing Lecture 7: Basic Transformations: Presented By: Dr. Umer IJAZДокумент30 страницDigital Image Processing Lecture 7: Basic Transformations: Presented By: Dr. Umer IJAZMuhammad Kamran AkramОценок пока нет
- Jupiter System DVB s2x h52630 071218Документ4 страницыJupiter System DVB s2x h52630 071218pathtrakОценок пока нет
- HYCU Protégé For Azure: Implementation GuideДокумент19 страницHYCU Protégé For Azure: Implementation GuideRatnodeep RoyОценок пока нет
- Cms SupervisorДокумент116 страницCms SupervisorClyde PereiraОценок пока нет
- Radio Enabling Techniques For IMT-Advanced (4G) and Beyond: WINNER+ ProjectДокумент4 страницыRadio Enabling Techniques For IMT-Advanced (4G) and Beyond: WINNER+ ProjectNaol WorkuОценок пока нет
- Router 6000 Ericsson 6274Документ2 страницыRouter 6000 Ericsson 6274Zoumana KaridioulaОценок пока нет
- Manual de Mikrotik FulllДокумент788 страницManual de Mikrotik FulllLuis Eduardo Chourio Soto100% (1)
- Computer Network & Data Communication Class NotesДокумент24 страницыComputer Network & Data Communication Class NotesRonic DakОценок пока нет
- Fintech K31: April 6, 2021 (Tuesday)Документ49 страницFintech K31: April 6, 2021 (Tuesday)Jan Gavin GoОценок пока нет
- Cyber Security GuidelineДокумент4 страницыCyber Security GuidelineAlejandro B.Оценок пока нет
- 4G Network Charging and Billing SolutionДокумент55 страниц4G Network Charging and Billing SolutionRakesh RanjanОценок пока нет
- Web Chat Application Project ReportДокумент50 страницWeb Chat Application Project ReportRajeev Ranjan Tiwari100% (4)
- D400 Configuration ManualДокумент486 страницD400 Configuration Manualmertoiu8658Оценок пока нет
- TEMS Discovery NEMO - Events Metric Group DescriptionДокумент39 страницTEMS Discovery NEMO - Events Metric Group DescriptionTuấn VũОценок пока нет
- Xes Synergix™ 8825/8830 Hdi Autocad 2000 Print Driver User GuideДокумент27 страницXes Synergix™ 8825/8830 Hdi Autocad 2000 Print Driver User GuideAndrey AvramenkoОценок пока нет
- EPM 2018.3 Install GuideДокумент32 страницыEPM 2018.3 Install GuidepippoОценок пока нет
- Flex Ray Communication SystemДокумент245 страницFlex Ray Communication SystemsusannulОценок пока нет
- Special Instruction: Installation Procedure For The Pro Product Link PL641 and PL631 SystemsДокумент54 страницыSpecial Instruction: Installation Procedure For The Pro Product Link PL641 and PL631 SystemsDanilo Mina MunaycoОценок пока нет
- Hiper LANДокумент15 страницHiper LANarchtfОценок пока нет
- NSX Vsphere - Troubleshooting CommandsДокумент25 страницNSX Vsphere - Troubleshooting Commandstdewanjee100% (1)
- 3G Networks: Chapter SummaryДокумент22 страницы3G Networks: Chapter SummaryYodi HermawanОценок пока нет
- Fluiddrawp6enus PDFДокумент395 страницFluiddrawp6enus PDFWilfredo AchoОценок пока нет
- HwaTel Catalog 2013Документ12 страницHwaTel Catalog 2013Dramane BonkoungouОценок пока нет
- Website: Vce To PDF Converter: Facebook: Twitter:: 300-535.vceplus - Premium.Exam.60QДокумент35 страницWebsite: Vce To PDF Converter: Facebook: Twitter:: 300-535.vceplus - Premium.Exam.60QAla JebnounОценок пока нет
- Is40 Triton System - Im - en - 988 10222 002Документ22 страницыIs40 Triton System - Im - en - 988 10222 002DAFUОценок пока нет
- Adhoc WSN QДокумент6 страницAdhoc WSN QMadhavan SamОценок пока нет
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Current Infomation Technology in Relation To CommunicationДокумент21 страницаAdvantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Current Infomation Technology in Relation To CommunicationKristyl Joyce Colipano OrenseОценок пока нет
- E ComДокумент25 страницE ComĐại Ka Bé XíuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Quiz - CET501f13 Applied Networking IДокумент7 страницChapter 2 Quiz - CET501f13 Applied Networking Iamolas22100% (1)
- Packet SwitchingДокумент21 страницаPacket SwitchingMuhammad Faiz MasroorОценок пока нет
- AMP Timer ConnectorsДокумент132 страницыAMP Timer ConnectorsCBETAОценок пока нет