Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MP 07
Загружено:
Jake GlobioОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MP 07
Загружено:
Jake GlobioАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
8086 [2]
Ahad
Internal!
External?
8086 vs 8088
U?
8086MIN
MN
33
READY
22
CLK
19
RESET
21
INTR
18
HLDA
30
HOLD
31
NMI
17
TEST
23
AD0
16
AD1
15
AD2
14
AD3
13
AD4
12
AD5
11
AD6
10
AD7
9
AD8
8
AD9
7
AD10
6
AD11
5
AD12
4
AD13
3
AD14
2
AD15
39
A16/S3
38
A17/S4
37
A18/S5
36
A19/S6
35
BHE/S7
34
DEN
26
DT/R
27
M/IO
28
RD
32
WR
29
ALE
25
INTA
24
U?
8088MIN
MN
33
READY
22
CLK
19
RESET
21
INTR
18
HLDA
30
HOLD
31
NMI
17
TEST
23
AD0
16
AD1
15
AD2
14
AD3
13
AD4
12
AD5
11
AD6
10
AD7
9
A8
8
A9
7
A10
6
A11
5
A12
4
A13
3
A14
2
A15
39
A16/S3
38
A17/S4
37
A18/S5
36
A19/S6
35
SSO
34
DEN
26
DT/R
27
IO/M
28
RD
32
WR
29
ALE
25
INTA
24
16_bit Data Bus
20_bit Address
8_bit Data Bus
20_bit Address
8088
8086
Only external bus of 8088 is 8bit
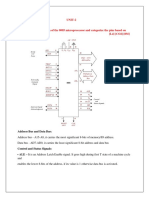
Pin configuration:
8086/8088 Busses
Address Bus
20 address lines so a 2
20
byte address space.
Pins A0-A19 provide the address
For 8086, A0-A15 are multiplexed with D0-D15 to form
AD0-AD15
For 8088, A0-A7 are multiplexed with D0-D7 to form
AD0-AD7
Data Bus
For 8086, 16 bit data bus D0-D15 (multiplexed as AD0-
AD15)
For 8088, 8 bit data bus D0-D7 (multiplexed as AD0-AD7)
Control pins
Control Bus
For memory access, the following pins are used:
RD, WR, M/IO, DT/R, DEN, ALE,
BHE
Other input signals to control 8086 performance:
clk ,reset , ready , hold , test,
intr , nmi ,mn/mx
- The intr and hold are acknowledged
through intra and holda respectively.
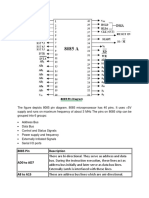
8086 Pin Assignment
8086 Pin Description
Vcc (pin 40) : Power supply input
GND (pin 1 and 20) : Ground pin is the return of the
power supply
AD0AD7, A8...A15 , A19/S6, A18/S5,
A17/S4, A16/S3 : 20-bit Address Bus
When ALE=1 [Address Latch Enable]
AD8-AD15 becomes address bits.
When ALE=0 it becomes data bits.
A19/S6, A18/S5, A17/S4, A16/S3
Address/status bus -
S4 S3 function .
0 0 extra segment
0 1 stack segment
1 0 code or no segment
1 1 data segment
These two status bits could be used to address four
separate 1MByte mem banks by decoding them as
A21 and A20
S5 indicates the condition of the IF flag bit
S6 always a logic 0
MN/MX (33, input) : Indicates Operating
mode min mode or max mode
READY (input, Active High) : Takes P to
wait state
0 P enters into wait states n remains
idle.
1 no effect on the operation of the P
CLK (input) : Provides basic timing for the
processor
CLK must have a duty cycle of 33% (high
for 1/3 of the clocking period & low for
2/3)
DEN (output) : activates external data bus
buffers.
It is LOW when processor wants to
receive data or processor is giving out
data
DT/R (output) : Data Transmit/Receive.
1 data from P to memory
0 data is from memory to P
M/IO (output) : selects mem or I/O.
It indicates that the mP address bus
contains either a memory address or an
I/O port address.
1 P access I/O Device
0 P access memory
RD (output) : When Low, P is performing
a read operation
0 the data bus is receptive to data from the
mem or I/O devices connected to the system.
WR (output) : When Low, P is performing
a write operation
It is outputting data to a mem or I/O
device.
During the time WR=0, the data bus
contains a valid data for mem or I/O.
ALE (output) : Address Latch Enable,
Active High
to latch address
1 P is using AD0..AD7, A19/S6, A18/S5,
A17/S4, A16/S3 as address bus.
This address can be a mem address or an I/O
port number.
RESET (input, Active High) : At least 4 clock cycles causes
the P immediately terminate its present activity.
TEST (input , Active Low) :
it is an input pin that is tested by the
WAIT instruction.
0 the WAIT instr. functions as an NOP.
1 the WAIT instr. waits for TEST to
become a logic 0.
HOLD (input , Active High) :
it requests a DMA [Direct Memory
Access]
1 the mP stops executing software and
places its address, data, and control bus at
the high-impedance state.
0 mP executes SW normally.
HLDA (output , Active High) :
Hold Acknowledge indicates that the mP has entered
the HOLD state.
INTR (input , Active High) :
Interrupt request
It is used to request a hardware interrupt.
1 when IF = 1, mP enters an interrupt
acknowledge cycle (INTA becomes active) after
the current instruction has completed execution.
[IF - Interrupt Flag -Set by user to disable hardware
interrupts temporarily]
INTA (output , Active Low) :
Interrupt Acknowledge
NMI (input , Active High) :
Non-maskable interrupt
similar to INTR except that the NMI
interrupt does not check to see whether
the IF flag is 1.
The AD0-AD15 lines are a 16-bit multiplexed
addressed or data bus.
During the 1
st
clock cycle, AD0-AD15 are the low
order 16-bit address.
The 8086 has a total of 20 address line, the upper
4 lines are multiplexed with the state signal that
is A16/S3, A17/S4, A18/S5, A19/S6.
For memory and i/o operations, AD15-AD0
contain the 16 bit data and S3,S4,S5,S6 become
the status line.
BHE/S7 is used as best high enable during the
1
st
clock cycle of an instruction execution.
BHE can be used in conjunction with AD0 to
select the memory
RD is low when the data is read from memory
or I/O location
TEST is an input pin and is only used by the
wait instruction
8086 enters a wait state after execution of the
wait instruction until a low is seen on the test
pin.
ALE is an address latch enable is an o/p signal
provided by the 8086
- can be used to demultiplexed AD0 to AD15 in
to A10 toA15 and D0 to D15.
M/IO is an 8086 output signal to distinguish a
memory access and i/o access.
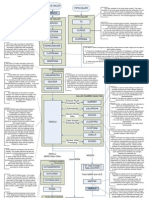
33. MN/MX
The 8086 can operate in two modes:
1. minimum mode and
2. maximum mode
For minimum mode, a unique processor system
with a single 8086
For maximum mode, a multi-processor system
with more than one 8086.
Minimum-Mode and Maximum-
Mode System
Signals common to both minimum and maximum mode
Minimum-Mode and Maximum-
Mode System (cont.)
Unique minimum-mode signals
Minimum-Mode and Maximum-
Mode System (cont.)
Unique maximum-mode signals
Вам также может понравиться
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960От EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960Оценок пока нет
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationОт EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationОценок пока нет
- mic_unit1Документ21 страницаmic_unit1xboyxman1000Оценок пока нет
- 8086 Hardware Specification: Segment 5Документ19 страниц8086 Hardware Specification: Segment 5Tigabu YayaОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 8086 System Bus Structures FullunitДокумент36 страницUnit 2 8086 System Bus Structures Fullunitlauro eugin brittoОценок пока нет
- MicroprocessorДокумент29 страницMicroprocessorArnab RayОценок пока нет
- Unit-1 (1) Draw and Explain The Internal Architecture of 8085Документ11 страницUnit-1 (1) Draw and Explain The Internal Architecture of 8085Mann MehtaОценок пока нет
- Berry B Brey Part IДокумент49 страницBerry B Brey Part Ikalpesh_chandakОценок пока нет
- L4 - 8085 ArchitectureДокумент24 страницыL4 - 8085 ArchitectureHabirah Mahmood MutanganaОценок пока нет
- Syllabus: 8085 ArchitectureДокумент25 страницSyllabus: 8085 Architecturetamilvendhan87Оценок пока нет
- 8086 MicroprocessorДокумент4 страницы8086 MicroprocessorTanu GuptaОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor 8088Документ11 страницMicroprocessor 8088bobby khanОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor Slides-2: 8085 MPUДокумент38 страницMicroprocessor Slides-2: 8085 MPURavi TejaОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 FinalДокумент31 страницаUnit 2 Finalswetha bagadi it's good but how it will workОценок пока нет
- Unit I PDFДокумент25 страницUnit I PDFSomnath2014Оценок пока нет
- 8085 Microprocessor Architecture ChapterДокумент35 страниц8085 Microprocessor Architecture ChapterajayroyОценок пока нет
- The 8085 Microprocessor Architecture: Dr. Kuda Nageswara RaoДокумент32 страницыThe 8085 Microprocessor Architecture: Dr. Kuda Nageswara RaoKrishna ChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- Memory Interface and Pin Functions of 8086/8088 MicroprocessorДокумент15 страницMemory Interface and Pin Functions of 8086/8088 Microprocessorpravin2275767Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Microprocessors Pin Function Comparison of 8088 and 8086Документ53 страницыAdvanced Microprocessors Pin Function Comparison of 8088 and 8086Madhav Singh100% (1)
- Chapter 5Документ53 страницыChapter 5RANDOMОценок пока нет
- 8085 Pin Diagram and ArchitectureДокумент8 страниц8085 Pin Diagram and ArchitectureSneha SinghОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingДокумент29 страницUnit 3 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingDere JesusОценок пока нет
- 8086 NotesДокумент43 страницы8086 NotesSuma LathaОценок пока нет
- Microprocessors: BY: Prof. Dileep J Dept. of TCE K.S.I.TДокумент16 страницMicroprocessors: BY: Prof. Dileep J Dept. of TCE K.S.I.TsenthilОценок пока нет
- 8085 Architecture IntroductionДокумент25 страниц8085 Architecture IntroductionMohamed Musthafa100% (1)
- Pin Diagram of 8086Документ21 страницаPin Diagram of 8086Radha SudheeraОценок пока нет
- Microcontrollers and 8-bit ProcessorsДокумент25 страницMicrocontrollers and 8-bit ProcessorsAbraiz Khan KhattakОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ20 страницChapter 9sandeep4672kvkОценок пока нет
- Overview or Features of 8086Документ33 страницыOverview or Features of 8086Supraja SundaresanОценок пока нет
- COE305 Chapter 9Документ55 страницCOE305 Chapter 9Rajesh TiwaryОценок пока нет
- Pin Config1 SNKДокумент6 страницPin Config1 SNKKirthi RkОценок пока нет
- 8085 Features, Signal DescriptionДокумент13 страниц8085 Features, Signal DescriptionRakesh Kumar DОценок пока нет
- System BusДокумент12 страницSystem Busdipyaman patgiriОценок пока нет
- 8086 Pin Diagram and Descriptions in 40 CharactersДокумент9 страниц8086 Pin Diagram and Descriptions in 40 Characters12343567890100% (2)
- Pin Diagram of 8086 MicroprocessorДокумент14 страницPin Diagram of 8086 Microprocessorkranthi6190Оценок пока нет
- Interfacing LectureДокумент136 страницInterfacing LectureTewodrosОценок пока нет
- 8086 Microprocessor Interfacing: Dr.P.Yogesh, Senior Lecturer, DCSE, CEG Campus, Anna University, Chennai-25Документ40 страниц8086 Microprocessor Interfacing: Dr.P.Yogesh, Senior Lecturer, DCSE, CEG Campus, Anna University, Chennai-25Janu100% (2)
- Pinouts of 8086Документ12 страницPinouts of 8086Infinity Star GamingОценок пока нет
- Pin Diagram of 8086Документ21 страницаPin Diagram of 8086adithya123456100% (5)
- Chapter 5 EditedДокумент59 страницChapter 5 EditedTigabu YayaОценок пока нет
- Department of Technical Education Andhra Pradesh: 9CM405.7TO8 1 1Документ19 страницDepartment of Technical Education Andhra Pradesh: 9CM405.7TO8 1 1Y. S.V.Ramana raoОценок пока нет
- St. Joseph College of EngineeringДокумент10 страницSt. Joseph College of EngineeringjaisathiОценок пока нет
- 8086/8088 Hardware Specifications: CEN433 King Saud University Dr. Mohammed Amer ArafahДокумент69 страниц8086/8088 Hardware Specifications: CEN433 King Saud University Dr. Mohammed Amer ArafahHarold Carlos Ureña HerreraОценок пока нет
- Unit III MPMC MaterialДокумент33 страницыUnit III MPMC Materialsree2728Оценок пока нет
- System BusДокумент20 страницSystem BusshyamОценок пока нет
- Overview or Features of 8086: It Is A 16-Bit MicroprocessorДокумент33 страницыOverview or Features of 8086: It Is A 16-Bit MicroprocessorSamuel KuantumОценок пока нет
- Pin DaigramДокумент3 страницыPin Daigramrathavachirag921Оценок пока нет
- Microprocessor 8085 AДокумент134 страницыMicroprocessor 8085 ASaumya MohanОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts in Serial I/O Interfacing I/O DevicesДокумент33 страницыBasic Concepts in Serial I/O Interfacing I/O DevicessubendОценок пока нет
- EE6502 MPMC Two Marks With AnswerДокумент10 страницEE6502 MPMC Two Marks With Answervlsimani9110100% (1)
- 8086 FullДокумент72 страницы8086 FullNandhini Nachiyar100% (4)
- Minimum and Maximum ModesДокумент21 страницаMinimum and Maximum ModesSubash BasnyatОценок пока нет
- Unit III 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingДокумент26 страницUnit III 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingRammanohar Lokiya100% (1)
- 8085 Microprocessor Signal GroupsДокумент27 страниц8085 Microprocessor Signal GroupsSheena Ann StonehillОценок пока нет
- Unit II 8086 SYSTEM Bus Structure: BookДокумент194 страницыUnit II 8086 SYSTEM Bus Structure: BookGomathi PsОценок пока нет
- 8085 ArchitectureДокумент26 страниц8085 ArchitectureLukeОценок пока нет
- 8086/88 Hardware and Bus StructureДокумент27 страниц8086/88 Hardware and Bus StructuredilipsugadevОценок пока нет
- Microprocess ArchitectureДокумент24 страницыMicroprocess ArchitectureNew worldОценок пока нет
- Lesson 8 Instruction Set and ProgrammingДокумент10 страницLesson 8 Instruction Set and ProgrammingJake GlobioОценок пока нет
- Unbalanced 3 PhaseДокумент11 страницUnbalanced 3 PhaseSherwin AgootОценок пока нет
- Lesson 6 Memory ManagementДокумент11 страницLesson 6 Memory ManagementJake GlobioОценок пока нет
- GEAS EngineeringДокумент162 страницыGEAS EngineeringJake GlobioОценок пока нет
- Legit ProgrammingДокумент160 страницLegit Programmingnikko bajarla100% (1)
- Design With Microprocessors: Year III Computer ScienceДокумент25 страницDesign With Microprocessors: Year III Computer ScienceSelmaGogaОценок пока нет
- COBOL V6.2 - Programming GuideДокумент972 страницыCOBOL V6.2 - Programming GuideAnonymous H4k0Q6w100% (1)
- ATG Dynamo Messaging SystemДокумент31 страницаATG Dynamo Messaging SystemPawan100% (2)
- SCM Build and Release PravinДокумент5 страницSCM Build and Release PravinShelly DeanОценок пока нет
- Nokia BSC CommandsДокумент3 страницыNokia BSC CommandsomobenОценок пока нет
- PolymorphismДокумент24 страницыPolymorphismjamesramsdenОценок пока нет
- Readme PV73901 v10.1.4.r11255 PDFДокумент4 страницыReadme PV73901 v10.1.4.r11255 PDFMy Note9Оценок пока нет
- Mt2Dinvmatlab-A Program in Matlab and Fortran For Two-Dimensional Magnetotelluric InversionДокумент14 страницMt2Dinvmatlab-A Program in Matlab and Fortran For Two-Dimensional Magnetotelluric InversionHat CopterОценок пока нет
- Os Notes Unit 1 For BCAДокумент8 страницOs Notes Unit 1 For BCABalaram RathОценок пока нет
- 8.1.2.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Syslog and NTP InstructionsДокумент3 страницы8.1.2.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring Syslog and NTP InstructionsMuhammadОценок пока нет
- Srs Library Management SystemДокумент6 страницSrs Library Management SystemRahulОценок пока нет
- 5 - Assembly Language BasicsДокумент41 страница5 - Assembly Language BasicsAsadОценок пока нет
- Number AnalysisДокумент4 страницыNumber AnalysisaphadaniОценок пока нет
- Database Management System: Multiple Choice Questions & AnswersДокумент7 страницDatabase Management System: Multiple Choice Questions & Answersmallaiah vОценок пока нет
- 17bec1006 Cse2003 Lab RecordДокумент70 страниц17bec1006 Cse2003 Lab RecordZara CooperОценок пока нет
- Network Topology Types ExplainedДокумент5 страницNetwork Topology Types Explainedmd.jewel ranaОценок пока нет
- PortДокумент4 страницыPortDinko DiĐОценок пока нет
- Develop Android Apps Using AndroidДокумент1 страницаDevelop Android Apps Using AndroidHaseeb MogralОценок пока нет
- JUCEДокумент5 страницJUCEGiacomo Costantini100% (1)
- eBAM HomeДокумент3 страницыeBAM HomezvasanthОценок пока нет
- ISA RP 12.6 1996 Wiring Pratices Hazarousous Location InstrumentationДокумент94 страницыISA RP 12.6 1996 Wiring Pratices Hazarousous Location InstrumentationDiego GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Flashboot Xiaomi Mi3wДокумент5 страницFlashboot Xiaomi Mi3wAbdul Hamid0% (1)
- Upgrading NCC 8000 To NCC Windows DN1567-0405Документ2 страницыUpgrading NCC 8000 To NCC Windows DN1567-0405Fiaz BaloochОценок пока нет
- Sequential vs Random Access MethodsДокумент2 страницыSequential vs Random Access MethodsJay PatelОценок пока нет
- Data Domain OSДокумент503 страницыData Domain OSRafael HernándezОценок пока нет
- OS 180-94 Assignment 3Документ3 страницыOS 180-94 Assignment 3Imran HayderОценок пока нет
- Bernd PorrДокумент20 страницBernd PorrMuhammad Nur SururiОценок пока нет
- Atmel Avr Microcontroller Mega and Xmega in Assembly and C 1st Edition Han-Way Huang Test BankДокумент2 страницыAtmel Avr Microcontroller Mega and Xmega in Assembly and C 1st Edition Han-Way Huang Test Banktestbankloo50% (2)
- Msbte - Winter 2007Документ2 страницыMsbte - Winter 2007api-3728136100% (2)