Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Know Your Financial Statements: Finance Area KIIT School of Management
Загружено:
Raja Ram0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
21 просмотров32 страницыswain
Оригинальное название
Prof. r. n. Swain_readbs
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документswain
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
21 просмотров32 страницыKnow Your Financial Statements: Finance Area KIIT School of Management
Загружено:
Raja Ramswain
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 32
Finance Area
KIIT School of Management
KNOW YOUR
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
ACCOUNTING
IS A MEASURING DEVICE
Accounting plays a very significant role in
recording the transactions & events of business
in financial terms. It is otherwise known as the
language of business. Every limited company in
India whether Private or Public is statutorily
required to maintain accounting records.
One of the important objectives of accounting is
to :
(i) Measure the profit or loss of the business
(ii) Ascertain the financial position of the
business
CONTENTS
Information usually available in the Annual Report ( AR)
as per the requirements of the Companies Act1956 are:
1. Directors report to shareholders.
2. Auditors report on the accounts.
3. Balance sheet of the company.
4. Profit and Loss account.
5. Accounting policies and notes to accounts.
Annual report also contains additional information of
interest to all of us.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATIONS
In addition to the statutory requirements reputed
companies usually publish additional information
such as:
Chairmans Speech,
Comparative statistics for different years,
Board committee activities
HRD programs ,
Environmental protection and safety
measures,
Research and Development activities
etc.
INFORMATIONS
FOR VARIOUS INTEREST GROUPS
Shareholders / Owners - rate or return
Creditors, Bankers - solvency & liquidity
position
Employees - earning capacity
Researchers, economists & financial analysts -
research to know solutions to various business
problems
Government - to take decision relating to Duties,
Taxes etc. & effective utilisation of capacity.
Management - Profitability & efficiency.
READING
BETWEEN THE LINES
AR contains many materials to gossip.
An intelligent businessman can read between the lines
to form the basis for his judgement.
Knowledge about the forms and purpose can help to
study the balance sheet intelligently.
We need to know some technical terms and
understand some general principles of
accountancy to form some first tentative
conclusions.
DIRECTORS REPORT- CONTENTS
1. State of Companys affairs.
2. Amount carried forward for resources.
3. Amt.. Recommended for dividend.
4. Material changes & commitments after
closing
date.
5. Conservation of energy, technology
absorption, foreign exchange earning &
outgo.
6. Measures taken for environmental protection.
7. Changes in Companys business subsidiary
and on the industry.
AUDITORS REPORT-
CONTENTS
Whether B/s & P/L reflects true & fair view.
Obtained all information & explanations.
Whether proper books of accounts
maintained.
B/s and P/L in agreement with books of
accounts.
Deviation to accounting policy ,if any.
Conduct of physical verification.
Revaluation of Assets.
Adequacy of internal audit.
Maintenance of Asset Register.
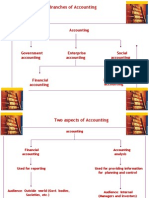
CLASSIFICATION
OF ACCOUNTS
In order to prepare the accounts, one has to
clearly classify the transactions between the
following four classes :
(1) Assets
(2) Liabilities
(3) Income
(4) Expenditure
FIXED ASSETS
* Land
* Buildings
* Plant and Machinery
* Furniture and Fixtures
* Vehicles
* Electrical Installations
* Utilities like heavy mobile equipments, construction
equipment , communication system etc.
These fixed assets are recorded in books at their
cost price which includes the cost of purchase,
taxes, freight, erection and commissioning
charges etc.
This is known as gross block.
Depreciation: a charge towards wear and tear is
reduced from the gross block.
The resultant figure is known as net block.
CURRENT ASSETS
Current Assets of a company are used for
day-to-day operations that is for working capital
needs.
They include:
* Inventories- raw material, WIP, finished
*Accounts Receivable - Sundry Debtor and
other receivables
* Cash and Bank Balances
*Other Current Assets- prepaid expenses,
deposits etc.
* Loans and Advances - employees & outsiders
LIABILITIES-LONG TERM
The liabilities side of a balance sheet
represents the various sources from which a
company obtain the funds which are needed
for its services.
The main sources are :
* Share Capital- true risk capital- Dividend
and liquidation
* Reserves & Surplus-profit ploughed back
Reserve may arise due to Share Premium,
Capital subsidy or Revaluation
* Loan Fund - Secured or unsecured.
CURRENT LIABILITIES
Current liabilities are other sources of fund which arise
out of business transactions & mainly consists of :
Accounts payable for goods & services- Sundry
Creditors, EMD & Security Deposits received and
interest accrued but not due.
Provision for expenses, taxes etc.
Provision for income tax and sales tax, proposed
dividend etc.
BALANCE SHEET
Two sides of the balance sheet always tally.
It can be vertical or horizontal.
Schedule-VI of the Companies Act 1956 has
stipulated the form of reporting.
Whatever may be the form, it tallies because of
double entry principle of accounting.
It is the finishing stage for the accountant but the
beginning stage for the analyst.
BALNCE SHEET
A. Liabilities 2004-05 2003-04 2002-03 2001-02 2000-01 1999-00
a)Paid up Capital 490.22 490.22 490.22 490.22 490.22 490.22
b) Reserve & surplus 151.08 142.87 133.84 118.04 152.51 216.30
c) Borrowings 101.39 126.26 188.24 238.69 261.82 318.71
d) Current Liab & Prov 93.90 86.51 246.72 383.09 213.35 131.30
e) Deferred Tax Liability 1.47
TOTAL 838.06 845.86 1059.02 1230.04 1117.90 1156.53
B. Assets
a) Gross Block 1114.00 1112.55 1112.66 1109.74 1107.37 1105.68
b) Less - Depreciation 700.32 642.33 585.64 502.42 419.65
334.86
c) Net Fixed Assets 413.68 470.22 527.02 607.32 687.72 770.82
d) Capital W-I-P 22.96 17.65 23.23 24.54 24.65 24.65
e)Current Assets
I)Inventories 36.09 37.85 50.97 51.39 48.70 49.52
II)Sundry Debtors 136.94 128.74 233.72 197.73 174.10 152.12
III)Cash & Bank Balances 206.15 172.98 133.94 255.19 97.59 89.41
IV)Other Current Assets 10.82 8.91 0.15 0.18 0.79 0.25
V) Loans & Advances 9.44 8.31 46.67 31.76 21.74 6.48
VI)Investments 0 0 42.00 60.00 60.00 60.10
Sub-Total 399.43 356.80 465.44 536.25 402.92 357.88
f)Misc.Expenditure 1.99 1.19 1.33 1.93 2.60 3.19
TOTAL 838.06 845.86 1059.02 1230.04 1117.90 1156.53
C. Capital Employed 845.02 901.95 1022.04
D. Net Worth 606.33 640.13 703.33
INCOME
Sale is the main business income for
manufacturing company.
Other income includes:
*Interest on investments
*Dividend on investment.
*Delayed payment surcharge arising out
of
administrative decision.
* Sale of scrap
* House rent
* Equipment hire charges received
*Commission received.
EXPENSES
Raw material is the main expenditure for any
manufacturing activity.
Production expenses.
Employees Remuneration and benefit
Administrative expenses
Selling & distribution Expenses.
Interest & financing charges
Depreciation
Misc. expenses written off.
Difference between the income & expenditure is
profit. Dividend, Income Tax & reserve are charged
after profit is derived. Net available is surplus.
ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS
Business Entry Concept - Business Unit is distinct and
completely separate
Going Concern Concept - Valuation of assets on
productivity basis..
Money Measurement Concept - All transactions interpreted
in terms of money.
Cost Concept - Valued at historical cost
Dual Aspect Concept
1.Yielding or receiving benefit
2.Giving that benefit
Accounting Period Concept - Choice dates.
Matching Concept -
Realisation Concept - Earned on the date when it is
realised.
CONVENTIONS
Convention of Disclosure - Be honest and full
disclosure of all significant nformations
Convention of Materiality -Depends on the amount
involved .
Convention of consistency - Rule, practice &
convention should be continuously observed and
applied
Convention of Conservatism - Accounts play safe
in determining profit.
ACCOUNTING METHODS
1) Cash Basis of Accounting.
2) Accrual Basis of Accounting.
3) Hybrid System of Accounting
Under Cash Basis of Accounting all incomes
are considered to be earned only when they are
actually received in cash. Similarly expenses are
deemed to be incurred only when they are
actually paid in cash. This method is usually
followed by individuals like Doctors, Lawyers,
Auditors, Engineers and small businessmen.
CONT..
Under Accrual or Mercantile Basis of Accounting
Incomes are recorded or credited to the period in
which they are earned in respective of the fact
when it is recorded. Similar is the case with
expenses. This method is universally followed
and is generally acceptable.
Вам также может понравиться
- Financial Accounting & AnalysisДокумент6 страницFinancial Accounting & AnalysisAmandeep SinghОценок пока нет
- Investments Profitability, Time Value & Risk Analysis: Guidelines for Individuals and CorporationsОт EverandInvestments Profitability, Time Value & Risk Analysis: Guidelines for Individuals and CorporationsОценок пока нет
- Soutions To Practice Problems For Modules 1 & 2Документ17 страницSoutions To Practice Problems For Modules 1 & 2b1234naОценок пока нет
- J.K. Lasser's Small Business Taxes 2021: Your Complete Guide to a Better Bottom LineОт EverandJ.K. Lasser's Small Business Taxes 2021: Your Complete Guide to a Better Bottom LineОценок пока нет
- Finance For Non FinanceДокумент56 страницFinance For Non Financeamitiiit31100% (3)
- Company ProfileДокумент72 страницыCompany ProfilePriti MenezesОценок пока нет
- CH 1 - End of Chapter Exercises SolutionsДокумент37 страницCH 1 - End of Chapter Exercises SolutionssaraОценок пока нет
- Finance For NonfinanceДокумент35 страницFinance For Nonfinancelasyboy20Оценок пока нет
- Task:1 Theoretically, A Financial Model Is A Set of Assumptions About Future Business ConditionsДокумент7 страницTask:1 Theoretically, A Financial Model Is A Set of Assumptions About Future Business ConditionsDILIP KUMARОценок пока нет
- Ch2 Financial Statement SДокумент101 страницаCh2 Financial Statement SK60 NGUYỄN THỊ HƯƠNG QUỲNHОценок пока нет
- Problemas de Opciones Reales Con SoluciónДокумент192 страницыProblemas de Opciones Reales Con SoluciónCarlos Jesús Ponce AranedaОценок пока нет
- Financial Reporting & Analysis Session Provides InsightsДокумент41 страницаFinancial Reporting & Analysis Session Provides InsightspremoshinОценок пока нет
- ACCOUNTS CASE STUDYДокумент7 страницACCOUNTS CASE STUDYshivam tripathiОценок пока нет
- Dev Financial Analysis-2Документ8 страницDev Financial Analysis-2Adam BelmekkiОценок пока нет
- DFS December 2009 AnswersДокумент12 страницDFS December 2009 AnswersPhilemon N.MalingaОценок пока нет
- Short and Long-Term: On Balance Sheet DebtДокумент8 страницShort and Long-Term: On Balance Sheet DebtNitin KumarОценок пока нет
- Mrs. Bella LlegoДокумент182 страницыMrs. Bella Llegototo titiОценок пока нет
- Fin 22 Chapter 12Документ37 страницFin 22 Chapter 12Jao FloresОценок пока нет
- F1 May 2011 AnswersДокумент11 страницF1 May 2011 AnswersmavkaziОценок пока нет
- (5414) Specialized Design Services Sales Class: $500,000 - $999,999Документ15 страниц(5414) Specialized Design Services Sales Class: $500,000 - $999,999Christyne841Оценок пока нет
- SEx 9Документ24 страницыSEx 9Amir Madani100% (1)
- Accounts & Adv Account BookДокумент308 страницAccounts & Adv Account Bookvishnuverma100% (1)
- Asics CorporationДокумент6 страницAsics Corporationasadguy2000Оценок пока нет
- FMGT 1321 Midterm 1 Review Questions: InstructionsДокумент7 страницFMGT 1321 Midterm 1 Review Questions: InstructionsAnnabelle Wu0% (1)
- 4.1-Hortizontal/Trends Analysis: Chapter No # 4Документ32 страницы4.1-Hortizontal/Trends Analysis: Chapter No # 4Sadi ShahzadiОценок пока нет
- Ias 7 Cash FlowДокумент15 страницIas 7 Cash FlowManda simzОценок пока нет
- Process Financial Transactions and Extract Interim Reports - 025735Документ37 страницProcess Financial Transactions and Extract Interim Reports - 025735l2557206Оценок пока нет
- Industry OverviewДокумент7 страницIndustry OverviewBathula JayadeekshaОценок пока нет
- Account BookДокумент311 страницAccount BookRam patharvat100% (1)
- Statements of Cash FlowsДокумент23 страницыStatements of Cash FlowslesterОценок пока нет
- Figure 1 Structure of Finance DepartmentДокумент5 страницFigure 1 Structure of Finance DepartmentHiteshОценок пока нет
- Financial Statements and Accounting Transactions: Solutions Manual For Chapter 2 9Документ70 страницFinancial Statements and Accounting Transactions: Solutions Manual For Chapter 2 9Tấn Lộc LouisОценок пока нет
- Management AccountingДокумент101 страницаManagement AccountingKartikОценок пока нет
- Suggested Answers Intermediate Examination - Spring 2012: Realization AccountДокумент7 страницSuggested Answers Intermediate Examination - Spring 2012: Realization AccountAhmed Raza MirОценок пока нет
- Ratio Analysis of L&T InfotechДокумент36 страницRatio Analysis of L&T Infotechrajwindernijjar1100% (1)
- ACCT550 Homework Week 1Документ6 страницACCT550 Homework Week 1Natasha DeclanОценок пока нет
- Fa ProjectДокумент16 страницFa Projecttapas_kbОценок пока нет
- Advanced Accounting Week 1-2Документ5 страницAdvanced Accounting Week 1-2rahmaОценок пока нет
- RM April 2021 MTP SДокумент7 страницRM April 2021 MTP SdsdsОценок пока нет
- Corporate Finance (CF) Notes: What Is Accounting?Документ11 страницCorporate Finance (CF) Notes: What Is Accounting?Saumyadeep BardhanОценок пока нет
- T Thhee Ffrraam Meew Woorrkk Ooff AaccccoouunnttiinnggДокумент9 страницT Thhee Ffrraam Meew Woorrkk Ooff AaccccoouunnttiinnggLuvlene mullos saltonОценок пока нет
- 11th Accounts by CA, Cma Santosh Kumar SirДокумент206 страниц11th Accounts by CA, Cma Santosh Kumar SirMillat Afridi100% (1)
- Cash Flow StatementДокумент19 страницCash Flow Statementasherjoe67% (3)
- Fundamentels of Accounting Lect 1Документ9 страницFundamentels of Accounting Lect 1Jahanzaib ButtОценок пока нет
- Manage Finance - 1Документ7 страницManage Finance - 1Aileen KhorОценок пока нет
- Lecture Common Size and Comparative AnalysisДокумент28 страницLecture Common Size and Comparative AnalysissumitsgagreelОценок пока нет
- Accounting 1-4Документ37 страницAccounting 1-4Abed M. SallamОценок пока нет
- Finance For Non-FinanceДокумент35 страницFinance For Non-FinanceDr Sarbesh Mishra100% (5)
- Corporations Act 2001Документ8 страницCorporations Act 2001vicky singhОценок пока нет
- Mercury Athletic Footwear: Ashutosh DashДокумент49 страницMercury Athletic Footwear: Ashutosh DashSaurabh ChhabraОценок пока нет
- Cash Flow From Assets - Solution PDFДокумент3 страницыCash Flow From Assets - Solution PDFSeptian Sugestyo PutroОценок пока нет
- Real Estate Financial Analysis Workbook: Revised June 21, 2010Документ31 страницаReal Estate Financial Analysis Workbook: Revised June 21, 2010Truong Pham33% (3)
- Financial Statement AnalysisДокумент19 страницFinancial Statement AnalysisMohammad Ajmal AnsariОценок пока нет
- Measuring Financial PerformanceДокумент41 страницаMeasuring Financial PerformanceRafael KusumaОценок пока нет
- Answers March2012 f1Документ10 страницAnswers March2012 f1kiransookОценок пока нет
- December 2010 TC6AДокумент7 страницDecember 2010 TC6AAhmed Raza MirОценок пока нет
- Financial Analysis & ValuationДокумент49 страницFinancial Analysis & ValuationSudhir Kumar AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Answer KeupysДокумент5 страницAnswer KeupysRaja RamОценок пока нет
- HVDC Transmission: History and Advantages Over ACДокумент21 страницаHVDC Transmission: History and Advantages Over ACErsaliaDNОценок пока нет
- Ant Colony Optimization OverviewДокумент31 страницаAnt Colony Optimization OverviewMohammed LubbadОценок пока нет
- 03-Back Propagation NetworkДокумент33 страницы03-Back Propagation NetworkKirtesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Ee2032 ND 2012Документ2 страницыEe2032 ND 2012Raja RamОценок пока нет
- 03-Back Propagation NetworkДокумент33 страницы03-Back Propagation NetworkKirtesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Tidal Power: Its Meaning, Causes of Tides and Their Energy Potential, Enhancement ofДокумент1 страницаTidal Power: Its Meaning, Causes of Tides and Their Energy Potential, Enhancement ofRaja RamОценок пока нет
- HVDC UNIT I - OptДокумент38 страницHVDC UNIT I - OptRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Grid-Connected PV System Sizing and Economics (39Документ9 страницGrid-Connected PV System Sizing and Economics (39Marius AbduramanОценок пока нет
- UPДокумент1 страницаUPVelmurugan SivaramanОценок пока нет
- 04 - Associative - Memory - CSE TUBEДокумент41 страница04 - Associative - Memory - CSE TUBERaja RamОценок пока нет
- 05 Adaptive Resonance Theory ART - CSE TUBEДокумент59 страниц05 Adaptive Resonance Theory ART - CSE TUBERaja RamОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Neural Networks Soft Computing Course Lectures 7-14 NotesДокумент39 страницFundamentals of Neural Networks Soft Computing Course Lectures 7-14 NotesRaja RamОценок пока нет
- 03 - Back - Propagation - Network - CSE TUBEДокумент33 страницы03 - Back - Propagation - Network - CSE TUBERaja RamОценок пока нет
- 01 Introduction To Soft Computing - CSE TUBEДокумент59 страниц01 Introduction To Soft Computing - CSE TUBERaja RamОценок пока нет
- 1mtech Ee PCDДокумент89 страниц1mtech Ee PCDRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Ocp For Oil Handling-ModiДокумент3 страницыOcp For Oil Handling-ModiRaja RamОценок пока нет
- PedДокумент32 страницыPedPartha SarathyОценок пока нет
- P PartsДокумент19 страницP PartsRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Exide Industries Ltd. Welcomes You: Presentation On Inverter BatteriesДокумент33 страницыExide Industries Ltd. Welcomes You: Presentation On Inverter BatteriesRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Electrical Supply SchemeДокумент14 страницElectrical Supply SchemeRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Welcome: © 2003, Exide Industries Limited. All Rights ReeservedДокумент30 страницWelcome: © 2003, Exide Industries Limited. All Rights ReeservedRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Air CompressorsДокумент68 страницAir CompressorsRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Industrial Batteries - Product ProfileДокумент10 страницIndustrial Batteries - Product ProfileRaja RamОценок пока нет
- 2Документ90 страниц2Raja RamОценок пока нет
- Oracle Advanced Security: Administrator's GuideДокумент282 страницыOracle Advanced Security: Administrator's GuideRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Dealer PresentationДокумент39 страницDealer PresentationRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Everything You Need to Know About Electric MotorsДокумент37 страницEverything You Need to Know About Electric MotorsRaja RamОценок пока нет
- Shree Mega Power FinalДокумент114 страницShree Mega Power FinalRaja RamachandranОценок пока нет
- Electric Machinery and Transformers - I. L. KosowДокумент413 страницElectric Machinery and Transformers - I. L. KosowRaja Ram50% (2)
- Pass Issuance Receipt: Now You Can Also Buy This Pass On Paytm AppДокумент1 страницаPass Issuance Receipt: Now You Can Also Buy This Pass On Paytm AppAnoop SharmaОценок пока нет
- 10 Appendix RS Means Assemblies Cost EstimationДокумент12 страниц10 Appendix RS Means Assemblies Cost Estimationshahbazi.amir15Оценок пока нет
- Converting An XML File With Many Hierarchy Levels To ABAP FormatДокумент8 страницConverting An XML File With Many Hierarchy Levels To ABAP FormatGisele Cristina Betencourt de OliveiraОценок пока нет
- SC invalidates Ordinance allowing oil depots in Pandacan due to population densityДокумент2 страницыSC invalidates Ordinance allowing oil depots in Pandacan due to population densityMigs Raymundo100% (1)
- WPB Pitch DeckДокумент20 страницWPB Pitch Deckapi-102659575Оценок пока нет
- CELF Final ProspectusДокумент265 страницCELF Final ProspectusDealBookОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Knowledge and SkillДокумент2 страницыDifference Between Knowledge and SkilljmОценок пока нет
- Superior University: 5Mwp Solar Power Plant ProjectДокумент3 страницыSuperior University: 5Mwp Solar Power Plant ProjectdaniyalОценок пока нет
- Best Homeopathic Doctor in SydneyДокумент8 страницBest Homeopathic Doctor in SydneyRC homeopathyОценок пока нет
- Leapfroggers, People Who Start A Company, Manage Its Growth Until They Get Bored, and Then SellДокумент3 страницыLeapfroggers, People Who Start A Company, Manage Its Growth Until They Get Bored, and Then Sellayesha noorОценок пока нет
- Telangana Budget 2014-2015 Full TextДокумент28 страницTelangana Budget 2014-2015 Full TextRavi Krishna MettaОценок пока нет
- Schedule of Charges General Banking 2022Документ18 страницSchedule of Charges General Banking 2022Shohag MahmudОценок пока нет
- Enhancing reliability of CRA piping welds with PAUTДокумент10 страницEnhancing reliability of CRA piping welds with PAUTMohsin IamОценок пока нет
- Role Played by Digitalization During Pandemic: A Journey of Digital India Via Digital PaymentДокумент11 страницRole Played by Digitalization During Pandemic: A Journey of Digital India Via Digital PaymentIAEME PublicationОценок пока нет
- Exercise No. 7: AIM: To Prepare STATE CHART DIAGRAM For Weather Forecasting System. Requirements: Hardware InterfacesДокумент4 страницыExercise No. 7: AIM: To Prepare STATE CHART DIAGRAM For Weather Forecasting System. Requirements: Hardware InterfacesPriyanshu SinghalОценок пока нет
- CONFLICT ManagementДокумент56 страницCONFLICT ManagementAhmer KhanОценок пока нет
- Kunci Jawaban Creative English 3BДокумент14 страницKunci Jawaban Creative English 3BLedjab Fatima67% (3)
- ETP Research Proposal Group7 NewДокумент12 страницETP Research Proposal Group7 NewlohОценок пока нет
- Afar Partnerships Ms. Ellery D. de Leon: True or FalseДокумент6 страницAfar Partnerships Ms. Ellery D. de Leon: True or FalsePat DrezaОценок пока нет
- Lea 201 Coverage Topics in Midterm ExamДокумент40 страницLea 201 Coverage Topics in Midterm Examshielladelarosa26Оценок пока нет
- Shubh AmДокумент2 страницыShubh AmChhotuОценок пока нет
- Sound Wave Interference and DiffractionДокумент79 страницSound Wave Interference and DiffractionMuhammad QawiemОценок пока нет
- Using The Marketing Mix Reading Comprenhension TaskДокумент17 страницUsing The Marketing Mix Reading Comprenhension TaskMonica GalvisОценок пока нет
- Jodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentДокумент17 страницJodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentWMBF NewsОценок пока нет
- SIWES Report Example For Civil Engineering StudentДокумент46 страницSIWES Report Example For Civil Engineering Studentolayinkar30Оценок пока нет
- Activate Adobe Photoshop CS5 Free Using Serial KeyДокумент3 страницыActivate Adobe Photoshop CS5 Free Using Serial KeyLukmanto68% (28)
- DSP Lab Record Convolution ExperimentsДокумент25 страницDSP Lab Record Convolution ExperimentsVishwanand ThombareОценок пока нет
- Quality Risk ManagementДокумент29 страницQuality Risk ManagementmmmmmОценок пока нет
- Blum2020 Book RationalCybersecurityForBusineДокумент349 страницBlum2020 Book RationalCybersecurityForBusineJulio Garcia GarciaОценок пока нет
- Letter of Recommendation For Nicolas Hallett From Big Ten Network's Casey Peterson.Документ1 страницаLetter of Recommendation For Nicolas Hallett From Big Ten Network's Casey Peterson.Nic HallettОценок пока нет