Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 6: Nutrition: 6.9 Macronutrients & Micronutrients in Plants
Загружено:
Santhiya Madhavan0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров36 страницMACROnutrients : needed in LARGER quantities Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, Potassium (Kalium), Calcium, Magnesium and Sulphur. Micronutrients needed in SMALLER quantities Boron, Molybdenum, Zinc, Manganese, Copper and Ferum.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
61 9macromicronutrientsinplants 120530224106 Phpapp01
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документMACROnutrients : needed in LARGER quantities Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, Potassium (Kalium), Calcium, Magnesium and Sulphur. Micronutrients needed in SMALLER quantities Boron, Molybdenum, Zinc, Manganese, Copper and Ferum.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров36 страницChapter 6: Nutrition: 6.9 Macronutrients & Micronutrients in Plants
Загружено:
Santhiya MadhavanMACROnutrients : needed in LARGER quantities Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorous, Potassium (Kalium), Calcium, Magnesium and Sulphur. Micronutrients needed in SMALLER quantities Boron, Molybdenum, Zinc, Manganese, Copper and Ferum.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 36
CHAPTER 6 : NUTRITION
6.9 Macronutrients &
Micronutrients in Plants
List elements required by
plants,
Classify elements required
by plants based on the
amount needed,
Relate the effects of
macronutrient deficiency in
plants.
Explain the function of each
macronutrient in plants,
State the function of
micronutrients & effects of
micronutrient deficiency in
plants.
MACROnutrients : needed in
LARGER quantities
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen,
Phosphorous, Potassium (Kalium),
Calcium, Magnesium & Sulphur.
MICROnutrients : needed in
SMALLER quantities.
Boron, Molybdenum, Zinc,
Manganese, Copper & Ferum
Table 1
Wilhelm Knop (scientist) successfully prepared a solution which can provide a
plant with all the nutrients it needs
The solution is known as Knops Solution.
Calcium nitrate, Ca(NO
3
)
2
0.8g
Potassium nitrate, KNO
3
0.2g
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, KH
2
PO
4
0.2g
Magnesium sulphate, MgSO
4
0.2g
Ferum (III) phosphate, FePO
4
Trace
Distilled water 1 litre
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Describe the development that leads to
the discovery of photosynthesis,
State the substances required for
photosynthesis,
State the substances produced from
photosynthesis,
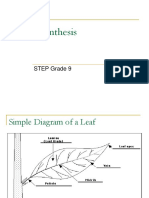
Draw & label the cross section of leaf
State the function of each part of the
leaf with respect to photosynthesis,
Explain leaf adaptation to optimise
photosynthesis,
Explain how plants from different
habitats are adapted to carry out
photosynthesis.
The Discovery of Photosynthesis
1692 Dutch scientist, Van Helmont carried out
an investigation to study the nutrition of plants.
He filled a big pot with exactly 91kg of dry soil
planted a plant (2.4kg) the surface covered
with a metal sheet with small holes to allow
water to enter Van watered the plants for 5
years consistently plant (increased to 75kg),
soil (decreased by 0.057kg)
Van Helmont concluded that the increase in
weight of the plant came from the water & not
the soil.
The Discovery of Photosynthesis
1772 Joseph Priestly carried out an
experiment using mouse, candle & plants.
The plant had changed the air in the container.
1770s Jan Ingenhouse discovered that a plant
could only change the air container if there was
light. He also discovered that only the green
parts of the plant were able to do so. (light &
chlorophyll both play a part in photosynthesis0
1780s Jean Senebier showed that the plants
gave out oxygen when they were provided with
CO
2
The biochemical process through
which light energy is absorbed
by chlorophyll, and is used to
fuel the synthesis of sugar
molecules
The process where organic
compounds are synthesised from
water & carbon dioxide in the
presence of sunlight &
chlorophyll.
Adaptations of Leaf for Optimal
Photosynthesis
The internal structure of a leaf, the shape of a
leaf & the arrangement of leaves on a plants are
all adapted for obtaining optimum light & CO
2
Table 2
The shape of a leaf is also adapted for
photosynthesis. Most leaves are broad & thin.
Large surface area enables the leaf to absorb
maximum light & CO
2
The thinness light & CO
2
need not travel too
far to reach every mesophyll cell
Adaptations of Leaf for
Optimal Photosynthesis
The arrangement of leaves is also
adapted to optimize photosynthesis.
Most plants spread out their leaves in
such a way that there is minimal
overlapping known as leaf mosaic
every leaf can receive sunlight.
ADAPTATION OF PLANTS FROM DIFFERENT HABITATS FOR
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Two main aspects :
The distribution of stomata
The distribution of chloroplasts
Examples :
Hibiscus : land
Water lily : water surface
Hydrilla : in the water
Cactus : desert
To identify the parts of chloroplast
related to photosynthesis,
To explain the light reaction & dark
reaction of photosynthesis,
To compare & contrast light reaction
& dark reaction in photosynthesis,
To relate light reaction with dark
reaction in photosynthesis,
To write an equation to represent
the process of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
occurs in in the
chloroplasts of
mesophyll cells &
guard cells of the
leaf.
Consist of two part :
stroma & grana
Each granum
contain chlorophyll
that absorb energy
of sunlight
The process of photosynthesis is divided
into two :
Light reaction
Dark reaction
Light reaction : occurs in the granum (contain
chlorophyll) photolysis of water
Dark reaction : occurs in the stroma (gel-like
matrix contain enzymes) CO
2
is reduced to
carbohydrate in a process called fixation of CO
2
(reduction of CO
2
)
LIGHT REACTION
Occurs in granum
Chlorophyll captures light excites the
electrons of chlorophyll to higher level
Light energy is used to split the water molecules
hydroxyl ions + hydrogen ions (photolysis of
water)
4H
2
O 4H
+
+ 4(OH)
-
The hydrogen ions combine with the electrons
released by chlorophyll to from hydrogen atoms
4(H)+ + 4 electrons 4(H)
sunlight
chlorophyll
LIGHT REACTION
The hydrogen atom are used in dark reaction to
reduce CO
2
.
Each hydroxyl ion loses an electron to the
chlorophyll hydroxyl groups combine
together to form H
2
O & O
2
4(OH)
-
- 4 electrons 4(OH)
4(OH) 2H
2
O + O
2
Oxygen is released into the atmosphere & later
used for cellular respiration
Energy released from the excited electrons is
used to form ATP
DARK REACTION
Occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast
Hydrogen atoms from light reaction are
used in dark reaction to reduce carbon
dioxide to basic units of glucose (CH
2
O)
Involves a series of complex chemical
reactions which require enzymes
CO
2
+ 4(H) (CH
2
O) + H
2
O
Six units of (CH2O) combine together to
form a molecule of glucose
DARK REACTION
6(CH
2
O) C
6
H
12
O
6
Glucose is converted into starch, cellulose,
sucrose & lipids. When combined with
nitrogen protein
Overall process :
12H
2
O + 6CO
2
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
+ 6H
2
O
Water + carbon dioxide glucose + oxygen + water
sunlight
chlorophyll
sunlight
chlorophyll
COMPARISON OF LIGHT REACTION
& DARK REACTION
LIGHT REACTION DARK REACTION
SIMILARITIES
Both occur in the chloroplast
Both involve chemical reactions
Both are reactions related to photosynthesis
Both occur during the day
DIFFERENCES
Occurs in granum Occurs in stroma
Requires sunlight Does not require sunlight
Involves photolysis of water Involves reduction of carbon dioxide
Produces water & oxygen Produces glucose
Substance required in reaction is
water
Substance required in reaction is
carbon dioxide
Identify the factors affecting the rate
of photosynthesis,
Identify the factor that limits the rate
of photosynthesis at different light
intensities,
Explain the effects of temperature &
concentration of CO2 on the rate of
photosynthesis,
Explain the difference in the rate of
photosynthesis in plants throughout the
day based on the changes in light
intensity & temperature,
Identify some ways to meet the need of
increasing the productivity of crops
based on factors affecting the rate of
photosynthesis.
CONCENTRATION OF CO
2
Conc. of CO2 in the
atmosphere varies between
0.03% to 0.04%
Light intensity & temperature
are kept constant the rate
of photosynthesis increases
until a saturation point is reach
After this point, any further
increase in the conc. of CO2
has no effect on the rate of
photosynthesis
Limited by other factors (light
intensity), not enough to
increase the rate of
photosynthesis
Effect of concentration of CO2 on the
rate of photosynthesis
0
2
4
6
8
10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
concentration of CO2
r
a
t
e
o
f
p
h
o
t
o
s
y
n
t
h
e
s
i
s
LIGHT INTENSITY
Temperature &
concentration of CO2 are
kept constant, the rate of
photosynthesis can be
increased by increasing the
light intensity up to the light
saturation point.
After this point, any further
increase in light intensity
has no effect on the rate of
photosynthesis (limiting
factor : CO2 conc.)
Can be increased by
increasing the CO2 conc.
Effect of light intensity on the rate of
photosynthesis at different levels of
CO2 concentration
0
2
4
6
8
10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
light intensity
r
a
t
e
o
f
p
h
o
t
o
s
y
n
t
h
e
s
i
s
karbon dioksida t inggi
karbon dioksida rendah
TEMPERATURE
Dark reaction involves
enzymes
The rate of photosynthesis
increases as the temperature
increase enzymes more
active
Optimum temp. is between
30
o
C to 35
o
C
>40oC, the rate of reaction
decrease enzymes
denatured photosynthesis
stops
If the light intensity is too low,
any increase in temperature
will not increase the rate of
photosynthesis
Effect of temperature on the rate of
photosynthesis at different light intensity
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
temperature
r
a
t
e
o
f
p
h
o
t
o
s
y
n
t
h
e
s
i
s
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE RATE OF
PHOTOSYNTHESIS THROUGHOUT THE
DAY WITH THE CHANGES IN LIGHT
INTENSITY & TEMPERATURE
Closely related & change throughout the
day
Light intensity high, the temperature is
also high.
Tropical country, LI & T are at their
maximum at noon time. The rate of
photosynthesis is also maximum.
If temperature increases above 40
o
C, the rate of
photosynthesis decreases.
In temperate country (4 seasons), LI & T change
throughout the year.
Winter : LI & T are very low. Photosynthesis
hardly occurs
Autumn : the rate of photosynthesis is at its
lowest plants shed their leaves & light
intensity as well as the temperature are very low
Summer : LI & T are at their optimum level for
photosynthesis, the rate of photosynthesis is at
its max.
Summer is the best time for agricultural
To overcome the problem, the plants need
to be planted in greenhouse.
In a greenhouse, the conc. of carbon
dioxide, temperature & light intensity are at
optimum levels for photosynthesis.
The rate of photosynthesis is at its
maximum throughout the year, ensure the
crop production throughout the year.
6.13 Practising a Caring Attitude
Towards Plants
Must be thankful to plants & practise a caring
attitude towards them
Why?
Plants produce food as a source of energy for
us, maintaining the oxygen & carbon dioxide
content in atmosphere
Without plants, there will be more CO2 & less
O2 in the atmosphere cause global warming
Not destroy forests @ chop down plants
indiscriminately. Should grow more plants
around us.
6.14 Technology in Food
Production
To improve the quality & quantity of food
production in Malaysia through :
Direct seeding from rice
Hydroponics & aeroponics
Breeding
Tissue culture
Genetic engineering
Soil management
Biological control
Fresh food can last only for a short time,
easily spoilt.
Need to be processed in order to last
longer
Technology for food processing :
Changing raw food materials to other forms
Adding certain chemical
The necessity for food processing are :
Destroying m/organisms
Extending the lifespan of food
Avoiding food wastage
Diversifying the uses of food, like milk & dairy
products
Ensuring sufficient food supply because
processed food can last longer & they can be
easily sent to places with insufficient food
supply
FOOD PROCESSING
METHODS
Cooking (to kill the bad bacteria)
Using salt, sugar & vinegar (osmosis)
Fermentation process (yeast is used glucose
ethanol + CO2)
Drying (dehydration)
Pasteurisation (heated to certain temp and
rapid cooling)
Canning (sterilised at high temp, above 120oC,
the container is vacuum to kill bacteria,
prevent bacteria from growing)
Refrigeration (slow down the action of
microorganism, temp low to -15oC)
Вам также может понравиться
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- PHOTOSYNTHESISДокумент24 страницыPHOTOSYNTHESISSaurabh kumarОценок пока нет
- Plant Nutrition IgcseДокумент54 страницыPlant Nutrition IgcseZizol Othman100% (1)
- Energy Transformations That Sustain LifeДокумент17 страницEnergy Transformations That Sustain LifeTrinity BenjaminОценок пока нет
- Ecology PPT ch06 PDFДокумент78 страницEcology PPT ch06 PDFAbood alfshekatОценок пока нет
- 6.9 PhotosynthesisДокумент50 страниц6.9 PhotosynthesisNurul NasaruddinОценок пока нет
- Nutrition in PlantsДокумент33 страницыNutrition in PlantsBenedicta SarfoОценок пока нет
- Nutrition in PlantsДокумент53 страницыNutrition in PlantsOlamide AyindeОценок пока нет
- 7th Grade Science Chapter 2 PhotosynthesisДокумент38 страниц7th Grade Science Chapter 2 Photosynthesisapi-235404570100% (4)
- PhotosynthesisДокумент6 страницPhotosynthesispwssewwandiОценок пока нет
- Apex Institute of Management Studies and ResarchДокумент35 страницApex Institute of Management Studies and ResarchSHEKHAR PRASADОценок пока нет
- 4 Plant NutritionДокумент43 страницы4 Plant NutritionMunazza SadiaОценок пока нет
- S3 Bio Revision Notes PreMid 1.1 To 1.3 1Документ7 страницS3 Bio Revision Notes PreMid 1.1 To 1.3 1Daniel CannywoodОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5:genetic Control & Protein Synthesis (Week 10 & 11)Документ58 страницChapter 5:genetic Control & Protein Synthesis (Week 10 & 11)RabbitОценок пока нет
- BiomassNotes 2019Документ155 страницBiomassNotes 2019Jonathan WrightОценок пока нет
- PhotosynthesisДокумент39 страницPhotosynthesisAnonymous puLHa9Оценок пока нет
- Bio-Inorganic Allied ChemistryДокумент19 страницBio-Inorganic Allied ChemistrymohanОценок пока нет
- PhotosynthesisДокумент33 страницыPhotosynthesisyusfa khildhaОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesisv 3Документ40 страницPhotosynthesisv 3Sofia CorderoОценок пока нет
- Plant NutritionДокумент37 страницPlant NutritionWen Shan ChuaОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis T5-1Документ9 страницPhotosynthesis T5-1Kyile FernandoОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis: STEP Grade 9Документ14 страницPhotosynthesis: STEP Grade 9Lo ViОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationДокумент48 страницPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respirationharold carbonelОценок пока нет
- FotosintesisДокумент51 страницаFotosintesisDwi HardianiОценок пока нет
- L6 PhotosynthesisДокумент28 страницL6 PhotosynthesisNaomi AceroОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes For O LevelДокумент36 страницBiology Notes For O LevelAhmad Barrun Nidhom92% (158)
- Grade 11 Lessons-1Документ429 страницGrade 11 Lessons-1pumezabalfour8Оценок пока нет
- BOT HW Chapter 8Документ11 страницBOT HW Chapter 8albelqinОценок пока нет
- Plant NutirionДокумент29 страницPlant NutirionRaidioactiveguyОценок пока нет
- PhotosynthesisДокумент35 страницPhotosynthesisChristopher MullenОценок пока нет
- 8 PhotosynthesisДокумент8 страниц8 PhotosynthesisRAVINDRA PRASADОценок пока нет
- Edexcel Biology Unit 4 Model AnswersДокумент47 страницEdexcel Biology Unit 4 Model Answershannah1b1363% (8)
- Photosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsДокумент8 страницPhotosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsBonny Ya SakeusОценок пока нет
- Finals Lesson7 EnergyflowДокумент32 страницыFinals Lesson7 EnergyflowDiana HermosuraОценок пока нет
- Cells Structure and Organisation 1Документ36 страницCells Structure and Organisation 1JessyОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis OverviewДокумент52 страницыPhotosynthesis OverviewClark GabutenОценок пока нет
- Autotrophy: Collecting Energy From The Non-Living EnvironmentДокумент96 страницAutotrophy: Collecting Energy From The Non-Living EnvironmentNathan ArthurОценок пока нет
- PhotosynthesisДокумент45 страницPhotosynthesisUmarОценок пока нет
- BIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisДокумент36 страницBIO1 Lesson-12 PhotosynthesisCath Detoperez100% (1)
- PhotosynthesisДокумент4 страницыPhotosynthesisapi-3729258100% (1)
- Eddie M. Raguindin: Biology TeacherДокумент23 страницыEddie M. Raguindin: Biology TeacherMhimi ViduyaОценок пока нет
- PHOTOSYNTHESISДокумент40 страницPHOTOSYNTHESISBry RafОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5: Aquatic EcosystemsДокумент35 страницChapter 5: Aquatic EcosystemsIsha ShakyaОценок пока нет
- Biogeochemical CyclesДокумент36 страницBiogeochemical CyclesroofheatproofinglahoreОценок пока нет
- Raven, P. H. Et Al. 1992Документ73 страницыRaven, P. H. Et Al. 1992Teflon SlimОценок пока нет
- MF009 5B Photosynthesis James L2Документ18 страницMF009 5B Photosynthesis James L2PikuОценок пока нет
- PP14 Photosynthesis The ProcessДокумент63 страницыPP14 Photosynthesis The Processsaishabhawanipersad81Оценок пока нет
- Water Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsОт EverandWater Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Decomposition and Isomerization of Organic CompoundsОт EverandDecomposition and Isomerization of Organic CompoundsОценок пока нет
- Transition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesОт EverandTransition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesОценок пока нет
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksОт EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis: A New Approach to the Molecular, Cellular, and Organismal LevelsОт EverandPhotosynthesis: A New Approach to the Molecular, Cellular, and Organismal LevelsSuleyman I. AllakhverdievОценок пока нет
- Chemistrypaper2 130613223816 Phpapp02 PDFДокумент14 страницChemistrypaper2 130613223816 Phpapp02 PDFSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Rate of ReactionДокумент9 страницRate of ReactionChristopher MullenОценок пока нет
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 8Документ52 страницыForm 4 Biology Chapter 8Gaya GayaОценок пока нет
- D687-Unit 4 Life Science PowerpointДокумент17 страницD687-Unit 4 Life Science PowerpointSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Chapter10 110714191611 Phpapp02Документ94 страницыChapter10 110714191611 Phpapp02Cikgu Shaiful KisasОценок пока нет
- By Marinela BuzoДокумент13 страницBy Marinela BuzoSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Rainforest PowerpointДокумент11 страницRainforest PowerpointSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- What Is? Collision Theory?: Factors Affecting?Документ63 страницыWhat Is? Collision Theory?: Factors Affecting?Santhiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- InheritanceДокумент62 страницыInheritanceBalan MuthuОценок пока нет
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorДокумент15 страниц6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 41 2 Menstrualcycle 120603003033 Phpapp01Документ24 страницы41 2 Menstrualcycle 120603003033 Phpapp01Santhiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Module II StudentДокумент16 страницModule II StudentSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants: Cape Biology Unit 1Документ19 страницSexual Reproduction in Plants: Cape Biology Unit 1Santhiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Summary PowerpointДокумент8 страницPhotosynthesis Summary PowerpointSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Parts of A Tree - 87619Документ1 страницаParts of A Tree - 87619svhowardОценок пока нет
- Guess My Name Identifying AnimalsДокумент1 страницаGuess My Name Identifying AnimalsveeramaniОценок пока нет
- Reproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsДокумент25 страницReproduction & Growth: 4.5 - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6: Nutrition: 6.9 Macronutrients & Micronutrients in PlantsДокумент36 страницChapter 6: Nutrition: 6.9 Macronutrients & Micronutrients in PlantsSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Technological Development in Food ProcessingДокумент28 страницTechnological Development in Food Processingridwan100% (14)
- Watercolor Paint Number SnakeДокумент1 страницаWatercolor Paint Number SnakeSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Bananas in PyjamasДокумент4 страницыBananas in PyjamasSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Bananas in Pyjamas RecipeДокумент1 страницаBananas in Pyjamas RecipeSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Blowing Up Balloons With CO2Документ1 страницаBlowing Up Balloons With CO2Santhiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Chapter5waterandsolution 121120021919 Phpapp01Документ58 страницChapter5waterandsolution 121120021919 Phpapp01Ng Lay HoonОценок пока нет
- Ionic and Covalent Bond WorksheetДокумент1 страницаIonic and Covalent Bond WorksheetSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Guess My Name Identifying AnimalsДокумент1 страницаGuess My Name Identifying AnimalsveeramaniОценок пока нет
- AA IGCSE Unit 1 TESДокумент60 страницAA IGCSE Unit 1 TESSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Ions and Ionic BondingДокумент12 страницIons and Ionic BondingSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет
- Ions & Electrons QuizДокумент12 страницIons & Electrons QuizSanthiya MadhavanОценок пока нет