Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Kuliahgeokimia5 110722232627 Phpapp01
Загружено:
Ifan Aziz0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
9 просмотров58 страницgeokimia
Оригинальное название
kuliahgeokimia5-110722232627-phpapp01
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документgeokimia
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
9 просмотров58 страницKuliahgeokimia5 110722232627 Phpapp01
Загружено:
Ifan Azizgeokimia
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPTX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 58
On Monday, August 6, 1945, at 8:15 AM, the nuclear bomb
"Little Boy" was dropped on Hiroshima by an American B-29
bomber, the Enola Gay,
directly killing an estimated 80,000
people. By the end of the year, injury and radiation brought
total casualties to 90,000140,000
]
. Approximately 69% of
the city's buildings were completely destroyed, and about 7%
severely damaged.
On August 9, 1945, Nagasaki was the target of the world's second
atomic bomb attack (and second detonation of a plutonium bomb; the
first was tested in central New Mexico, USA) at 11:02 a.m., when the
north of the city was destroyed and an estimated 40,000 people were
killed by the bomb codenamed "Fat Man." According to statistics
found within Nagasaki Peace Park, the death toll from the atomic
bombing totaled 73,884, as well as another 74,909 injured, and
another several hundred thousand diseased and dying due to fallout
and other illness caused by radiation.
[7]
"Little Boy" was the codename of the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945
by the Boeing B-29 Superfortress Enola Gay, piloted by Colonel Paul Tibbets of the 393d
Bombardment Squadron, Heavy, of the United States Army Air Forces.
[2]
It was the first atomic
bomb to be used as a weapon.
"Fat Man" is the codename for the atomic bomb that was detonated over Nagasaki, Japan, by
the United States on August 9, 1945, at 11:02 AM (JSP). It was the second of the only two
nuclear weapons to be used in warfare to date"Fat Man" was detonated at an altitude of about
1,800 feet (550 m) over the Japanese city of Nagasaki and was dropped from a B-29 bomber
Bockscar, piloted by Major Charles Sweeney of the 393d Bombardment Squadron, Heavy.
Distribution Of Nuclear Reactors
DEPARTEMENT GEOSCIENCE
Isotope geochemistry is an aspect of geology
based upon study of the relative and absolute
concentrations of the elements and their
isotopes in the Earth.
1. The nucleus which contains:
2. Orbiting electrons.
protons
neutrons
The Atom
The atom consists of two parts:
.
The Atom
All matter is made up of elements (e.g.
carbon, hydrogen, etc.).
Atom of different elements contain different
numbers of protons.
The mass of an atom is almost entirely due to
the number of protons and neutrons
X
A
Z
A = number of protons + number of neutrons
Z = number of protons
A Z = number of neutrons
Number of neutrons = Mass Number Atomic Number
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms that contain the same number of
protons but a different number of neutrons. The
number of protons (the atomic number) is the same
for each isotope
U
235
92
U
238
92
There are many types of uranium:
Isotopes of any particular element contain the same
number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons.
A 235
Z 92
Number of protons 92
Number of Neutrons 143
A 238
Z 92
Number of protons 92
Number of neutrons 146
Most of the isotopes which occur naturally are
stable.
A few naturally occurring isotopes and all of
the man-made isotopes are unstable.
Unstable isotopes can become stable by
releasing different types of particles.
This process is called radioactive decay and
the elements which undergo this process are
called radioisotopes/radionuclides.
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay results in the emission of
either:
an alpha particle (a)
a beta particle (b)
or a gamma ray(g).
.
Alpha Decay
An alpha particle is an emission of particle
identical to that of a helium nucleus
It contains two protons and two neutrons.
X
A
Z
Y
A - 4
Z - 2
+
He
4
2
unstable atom
more stable atom
alpha particle
Alpha Decay
Ra
226
88
Rn
222
86
He
4
2
Alpha Decay
X
A
Z
Y
A - 4
Z - 2
+
He
4
2
Ra
226
88
Rn
222
86
+
He
4
2
Alpha Decay
Rn
222
86
He
4
2
+
Po
218
84
He
4
2
Rn
222
86
+
Y
A
Z
He
4
2
Alpha Decay
He
4
2
U
234
92
+
Th
230
90
He
4
2
X
A
Z
+
Th
230
90
He
4
2
Alpha Decay
Th
230
90
+
Y
A
Z
He
4
2
He
4
2
+
Ra
226
88
He
4
2
Th
230
90
Alpha Decay
X
A
Z
+
Pb
214
82
He
4
2
He
4
2
+
Pb
214
82
He
4
2
Po
218
84
Alpha Decay
Beta Decay
A beta particle is a fast moving electron which is
emitted from the nucleus of an atom undergoing
radioactive decay.
Beta decay occurs when a neutron changes into a
proton and an electron.
Beta Decay
As a result of beta decay, the nucleus has one
less neutron, but one extra proton.
The atomic number, Z, increases by 1 and the
mass number, A, stays the same.
Po
218
84
b
0
-1
At
218
85
Beta Decay
X
A
Z
Y
A
Z + 1
+
b
0
-1
Po
218
84
Rn
218
85
+
b
0
-1
Th
234
90
Y
A
Z
+
b
0
-1
Beta Decay
Th
234
90
Pa
234
91
+
b
0
-1
X
A
Z
Pb
210
82
+
b
0
-1
Beta Decay
Tl
210
81
Pb
210
82
+
b
0
-1
Bi
210
83
Y
A
Z
+
b
0
-1
Bi
210
83
Po
210
84
+
b
0
-1
Beta Decay
X
A
Z
Bi
214
83
+
b
0
-1
Pb
214
82
Bi
214
83
+
b
0
-1
Beta Decay
Gamma Decay
Gamma rays are not charged particles like a and b
particles.
Gamma rays are electromagnetic radiation with
high frequency.
When atoms decay by emitting a or b particles to
form a new atom, the nuclei of the new atom
formed may still have too much energy to be
completely stable.
This excess energy is emitted as gamma rays
(gamma ray photons have energies of ~ 1 x 10
-12
J).
Exponential Decay
Decay of
226
Ra
Half-Life
There are a large range of half-lives seen in
nature
Half-lives are unaffected by the nucleis
surroundings and only depend on what goes
on inside the nucleus
238
U has a half-life of 4.5 billion years
Half-Life
To summarize, one-half of the sample will
decay in one half-fife
One-half of that one-half will decay in the next
half life
One-half of that one-fourth will decay in the
next half life
Half-Life
Transmutations
The changing of one element to another is
called transmutation
This occurs whenever there is an alpha decay
or a beta decay
Remember, that for a gamma decay, the
nucleus just changes internal energy levels,
but doesnt change the identity of nucleons
Transmutations
Artificial Transmutation
First example was Rutherford bombarding
nitrogen with alpha particles
4
He +
14
N ->
17
O +
1
H
He viewed the reaction with a cloud chamber
The particles left a vapor trail in the mist
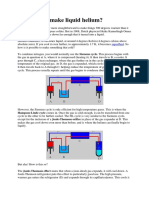
Cloud Chamber
When you pull the piston down suddenly,
you reduce the air pressure in the
chamber. This means vapor is now
super-saturated. A charged particle acts
as a nucleation seed to condense the
liquid from the vapor. This is the same
principle as cloud-seeding to make it
rain.
Isotopic Dating
Cosmic rays (mostly high energy protons)
strike upper atmosphere and cause
transmutations that result in many protons
and neutrons being sprayed out
Protons tend to grab electrons from other
atoms and become simple hydrogen
Neutrons keep going and smash into other
atoms
Isotopic Dating
When a neutron strikes nitrogen
1
n +
14
N ->
14
C +
1
H
In the atmosphere,
14
C is about 1 part in 10
11
Reacts with plants just like
12
C
14
C decays via beta emission
14
C ->
14
N + beta half life of 5730 years
Carbon Dating
When a plant dies, it stops the intake of
carbon
Since the
14
C decays, after 5730 years, half of
it will be gone
We can just weigh a piece of dead wood,
calculate how much
14
C it originally had and
measure to how much it has now to get the
age
Uranium Dating
We know the half -life of
238
U and
235
U
They have series that end in
206
Pb and
207
Pb
Compare how much U vs. special lead and
calculate the age of the rock!!
Carbon dating only good for about 50,000
years
Uranium rock dating good for millions of years
Nuclear Fission
1
n +
235
U ->
91
Kr +
142
Ba + 3
1
n
Chain Reaction
Chain Reaction
The key to keeping the reaction going is that
at least one of the neutrons given off, must
cause another fission
Controlled reaction in a nuclear reactor
If two or three cause fissions, you can get a
bomb!
Idea of critical mass
Critical Mass
Atom Bomb
Nuclear Reactor
Mass-Energy Relationship
So, where does the mass go?
It is the binding energy that is holding the
nucleus together
Interesting to look at the mass per nucleon as
we change the atomic number (change which
element we look at)
Fusion Reactions
BERITA CHERNOBYL
Pada 26 April 1986, penduduk Kiev dikejutkan oleh sebuah ledakan besar. Ledakan ini memuntahkan potongan inti
reaktor sampai 1500 meter ke langit dan menebarkan awan beracun ke 70 persen daratan eropa. Radioaktivitas
total ledakan Chernobyl, menurut WHO, ditaksir 200 kali radiasi bom atom Hiroshima dan Nagasaki.
Kelompok pecinta lingkungan Greenpeace bahkan menaksir, 160 ribu kilometer persegi tanah terkontaminasi
bahan radioaktif. Sementara Mantan Sekretaris Jenderal PBB Boutros Boutros Ghali mengatakan, "Kecelakaan
Chernobyl tidak dapat dianggap sebagai masalah beberapa abad saja, tapi juga masalah kekinian karena banyak
program sosial, ekonomi, dan lingkungan yang harus didefinisikan kembali."
Yang pasti, fakta menunjukkan lima juta orang di sekitar Chernobyl terkena radiasi. Sekitar 650 ribu diantaranya
adalah para buruh yang bertugas membersihkan muntahan ledakan Chernobyl. Dan sekitar 200 ribu dari 650
buruh tersebut, merupakan kelompok kunci beresiko tinggi terpapar radiasi. Mereka berada dalam zona
penyingkiran, atau sekitar 30 kilometer dari pusat ledakan Chernobyl.
Sepuluh tahun kemudian tercatat, 60 ribu buruh pembersih yang kebanyakan berusia 30 tahunan, meninggal
dunia. Sementara 30 persen laki-laki pekerja pembersih yang masih hidup menderita impotensi. Yang menjadi
masalah, sebagian besar buruh ini ditolak dalam kehidupan sosialnya. Penyebabnya, mereka dicurigai akan
menularkan radiasi dari reaktor PLTN kepada orang-orang di sekitarnya. Hal inilah yang memicu mereka meninggal
akibat kecanduan alkohol, mati dalam kemiskinan, serta bunuh diri.
Dokter spesialis penyakit -yang berkaitan dengan tragedi Chernobyl- Natalya Preobrashenskaya mengatakan,
selain pekerja pembersih muntahan radioaktif, jutaan anak-anak yang tetap hidup pasca ledakan merupakan
kelompok berisiko tinggi terpapar radiasi. Preobrashenskaya bahkan menyatakan, jutaan anak-anak yang lahir di
masa mendatang juga akan terkena cemaran radiasi Chernobyl, sesuai prilaku radioaktif yang dipakai sebagai
bahan bakar PLTN, jutaan tahun!
Penyakit akibat Radiasi
Apa saja penyakit yang timbul setelah tragedi Chernobyl? Boutros Boutros Ghali menyebutkan, lebih dari 300 anak-anak terdiagnosis kanker
gondok, kesuburan pria wanita menurun drastis, dan angka kematian naik.
Secara lebih terperinci, 60 persen anak-anak Ukraina atau sejuta orang lebih menderita kanker gondok, sepuluh persen lainnya yang masih duduk di
bangku SD mengalami rusak mental, serta sebagian besar anak-anak Ukraina menderita penyakit tulang. Preobrashenskaya mengatakan, kekebalan
tubuh anak-anak Ukraina pun menurun drastis sehingga disebut pula AIDS-Chernobyl.
Penelitian Preobrashenskaya senada dengan penelitian WHO. Badan Kesehatan Dunia itu menyatakan, setelah peristiwa Chernobyl terjadi
peningkatan kasus kanker gondok anak, 100 kali dibanding prakecelakaan Chernobyl. Kenyataan lainnya, penduduk Kiev banyak yang terkena
kanker paru-paru dan jantung. Dan banyak dokter memperkirakan, dalam waktu mendatang, epidemi berbagai penyakit menular akan meningkat
di sekitar lokasi kejadian, dan di kalangan mereka yang terpapar radiasi nuklir.
Tragisnya, terapi kimia normal tidak efektif (mempan-red) pada penderita kanker akibat radiasi Chernobyl. Menurut Dr Andrei Butenko dari rumah
sakit nomor satu di Kiev, dipastikan kanker gondok ganas yang menimpa anak-anak Ukraina akibat kontaminasi isotop iodium-131, isotop iodium
yang radioaktif. Imbasnya, dengan terapi kimia di atas normal, kepala para pasien membotak dan wajah mereka bengkak-bengkak.
Horor yang kurang lebih sama dialami anak-anak Yunani. Anak-anak di negara tersebut berisiko terkena kanker dua hingga tiga kali akibat
Chernobyl. Bahkan, anak-anak Yunani yang terpapar radioaktif ketika masih dalam kandungan ibunya berisiko menderita leukimia 2,6 kali lipat
dibanding anak-anak lainnya. Hal ini karena adanya mutasi gen yang diberi nama 11q23.
Mutasi Gen
Mutasi gen merupakan imbas lain dari kejamnya radiasi Chernobyl. Mutasi gen 11q23 ini merupakan salah satu contoh nyata yang berhubungan
dengan leukimia pada bayi. "Temuan ini merupakan bukti langsung pertama, bahwa radiasi ternyata menimbulkan mutasi pada anak manusia," ulas
Sir Alec Jeffreys, ahli genetika dari Universitas Leicester.
Sir Alec melakukan penelitian pada 79 keluarga yang tinggal di Mogilev, Belarus, kawasan yang terkena radiasi tinggi, kurang lebih 300 kilometer
dari Chernobyl. Ia meneliti anak-anak di keluarga tersebut yang lahir antara Februari-September 1994. Sebagai perbandingan, ia juga meneliti 105
anak-anak yang tidak terkena radiasi dari Inggris.
Hasilnya, anak-anak Mogilev terbukti mengalami mutasi gen dua kali lebih tinggi dibandingkan anak-anak di Inggris. Mutasi tersebut jelas
diturunkan oleh orang tua mereka, dan secara permanen terkode pada gen anak-anak mereka. Artinya, mutasi tersebut juga akan diturunkan pada
generasi-generasi selanjutnya.
Menurut Sir Alec, mutasi pada keluarga di Mogilev berhubungan dengan tingkatan kontaminasi permukaan oleh caesium 137, sebuah isotop
radioaktif. Bahkan ahli genetika dari Akademi Sains Rusia Yuri Dubrova menyatakan, kelompoknya melihat lokasi genetik tertentu yang dikenal
dengan nama minisatellites yang mengalami laju mutasi 1000 kali lipat lebih tinggi dibandingkan gen lainnya.
Sementara itu, Robert Baker dari Universitas Teknologi Texas meneliti dua kelompok tikus, yaitu kelompok yang tinggal satu kilometer dari reaktor,
dan yang hidup 32 kilometer dari reaktor. Yang diteliti adalah mitokondria DNA (bagian sel yang diturunkan induk betina) pada anak tikus-tikus.
Hasilnya, walau tikus yang hidup dekat reaktor terlihat sehat dan subur, tapi mereka mengalami laju mutasi ratusan kali lebih tinggi dari kondisi
normal. "Artinya, lingkungan yang tercemar akibat ledakan Chernobyl memberikan dampak nyata perubahan gen pada mahluk hidup sekitarnya,"
ulas Robert Baker.
Nada miris terdengar dari mulut peneliti Universitas Texas Austin David Hillis. "Kita sekarang tahu, dampak mutasi akibat kecelakaan nuklir mungkin
lebih besar daripada yang diharapkan," komentar Hillis.
Vielen Dank
Вам также может понравиться
- Standard for Seismic Data ExchangeДокумент5 страницStandard for Seismic Data ExchangeIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Ann2011 PDFДокумент10 страницAnn2011 PDFIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Titanic 3Документ74 страницыTitanic 3Ifan AzizОценок пока нет
- 14 Pustaka CutДокумент2 страницы14 Pustaka CutIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Pattern 3Документ9 страницPattern 3Ifan AzizОценок пока нет
- Latihan Tpa SNMPTN 2011 KunciДокумент1 страницаLatihan Tpa SNMPTN 2011 KunciRoland LambaОценок пока нет
- Formation Codes and Tops Abbreviations GuideДокумент1 страницаFormation Codes and Tops Abbreviations GuideIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- CV Anjar Taufik Hidayat EnglishДокумент4 страницыCV Anjar Taufik Hidayat EnglishIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Calculation of Instantaneous Frequency and Instantaneous BandwidthДокумент5 страницCalculation of Instantaneous Frequency and Instantaneous BandwidthIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Kurikulum FisikaДокумент10 страницKurikulum FisikaIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Neural NetworksДокумент10 страницNeural NetworksSal ExcelОценок пока нет
- Sinusoids: Tamara Smyth, Tamaras@cs - Sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 16, 2006Документ4 страницыSinusoids: Tamara Smyth, Tamaras@cs - Sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 16, 2006Ifan AzizОценок пока нет
- Writing Letters For Faculty JobsДокумент4 страницыWriting Letters For Faculty Jobsindy_4xОценок пока нет
- Fault Detection Using Coherncy Attibute in Khangiran Gas Field, IranДокумент6 страницFault Detection Using Coherncy Attibute in Khangiran Gas Field, IranIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Essential petrophysical formulaeДокумент12 страницEssential petrophysical formulaeJuan Francisco ViveirosОценок пока нет
- Li Q Sparse Spike Inversion MOD-1Документ4 страницыLi Q Sparse Spike Inversion MOD-1Ifan AzizОценок пока нет
- d023Документ5 страницd023Ifan AzizОценок пока нет
- (Snieder) Trampert Inverse Problems in Geophysics. (BookFi - Org) .PsДокумент27 страниц(Snieder) Trampert Inverse Problems in Geophysics. (BookFi - Org) .PsIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Clarifying The Underlying and Fundamental Meaning of The Approximate Linear Inversion of Seismic DataДокумент13 страницClarifying The Underlying and Fundamental Meaning of The Approximate Linear Inversion of Seismic DataIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- 824 SeisLoader Including Header EditingДокумент22 страницы824 SeisLoader Including Header EditingIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Classification of Seismic Windows Using Artificial Neural NetworksДокумент10 страницClassification of Seismic Windows Using Artificial Neural NetworksIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Daftar Pustaka: Natherlands, Halaman 241-264Документ2 страницыDaftar Pustaka: Natherlands, Halaman 241-264Ifan AzizОценок пока нет
- Daftar Pustaka: Natherlands, Halaman 241-264Документ2 страницыDaftar Pustaka: Natherlands, Halaman 241-264Ifan AzizОценок пока нет
- TP SEG Inversion With Global Convergence Calibration Applications 130922Документ5 страницTP SEG Inversion With Global Convergence Calibration Applications 130922Ifan AzizОценок пока нет
- Least Squares Optimization With L1-Norm RegularizationДокумент12 страницLeast Squares Optimization With L1-Norm RegularizationqsmedsОценок пока нет
- 146S0321 EBliasДокумент4 страницы146S0321 EBliasIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Constrained Optimization in Seismic Reflection Tomography: A Gauss-Newton Augmented Lagrangian ApproachДокумент15 страницConstrained Optimization in Seismic Reflection Tomography: A Gauss-Newton Augmented Lagrangian ApproachIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- Sparse SpikeДокумент4 страницыSparse SpikeIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- A Combined Geomechanics-Seismic Inversion Workflow-LibreДокумент6 страницA Combined Geomechanics-Seismic Inversion Workflow-LibreIfan AzizОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Physical Science Test QuestionsДокумент4 страницыPhysical Science Test QuestionsAllize CatalanОценок пока нет
- PS 12 Prelim ReviewerДокумент11 страницPS 12 Prelim ReviewerMaribeth Alyssa GoОценок пока нет
- Velan View Spring 2011scrДокумент32 страницыVelan View Spring 2011scrArun BabuОценок пока нет
- Beryllium Window of An X-Ray TubeДокумент2 страницыBeryllium Window of An X-Ray TubeHernán Alejandro Rosero VegaОценок пока нет
- 7697A Headspace Samplers Site Preparation ChecklistДокумент7 страниц7697A Headspace Samplers Site Preparation ChecklistnileshdhamorikarОценок пока нет
- Worksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings - 9Документ6 страницWorksheet - Matter in Our Surroundings - 9Faiz KhanОценок пока нет
- Diffusion Coefficients, Solubilities, and Permeabilities For He, N eДокумент8 страницDiffusion Coefficients, Solubilities, and Permeabilities For He, N eElenaОценок пока нет
- Test Series Neet-2018: Topic: Gaseous State & ThermodynamicsДокумент3 страницыTest Series Neet-2018: Topic: Gaseous State & ThermodynamicsYogesh MishraОценок пока нет
- Thời gian làm bài: 60 phút; không kể thời gian phát đề: weekДокумент22 страницыThời gian làm bài: 60 phút; không kể thời gian phát đề: weekHuong TranОценок пока нет
- OCR Gas Laws Revision Questions & MSДокумент29 страницOCR Gas Laws Revision Questions & MS17guoxiaОценок пока нет
- BBC Knowledge India 2013-12Документ104 страницыBBC Knowledge India 2013-12William Vance100% (3)
- How Do You Make LiquidДокумент2 страницыHow Do You Make LiquidjukortaОценок пока нет
- Regulation of International School-Proposal - Thesis - TemplateДокумент40 страницRegulation of International School-Proposal - Thesis - TemplateYalil UnefaОценок пока нет
- Dijkstra Vereenigde Gerhardt DumathermДокумент5 страницDijkstra Vereenigde Gerhardt Dumathermbondarenkopavel86Оценок пока нет
- Lesson 1: S11/12Ps-Iiib-11Документ8 страницLesson 1: S11/12Ps-Iiib-11Maurice LanceОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Leak Detection enДокумент49 страницFundamentals of Leak Detection enagniva dattaОценок пока нет
- MRI Safety Study GuideДокумент49 страницMRI Safety Study GuideJeremiah A.Оценок пока нет
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Collins Helium Liquefaction Cycle: M.D. AtreyДокумент9 страницThermodynamic Analysis of Collins Helium Liquefaction Cycle: M.D. AtreySid Ahmed BenmeddahОценок пока нет
- Cylinder and Container GuideДокумент12 страницCylinder and Container GuideClaudio SantellanesОценок пока нет
- Discover Interesting Helium FactsДокумент5 страницDiscover Interesting Helium FactsIntan SaviraОценок пока нет
- Lodders, Katharina - ThThe Planetary Scientist's Companion Booke Planetary Scientist's Companion BookДокумент392 страницыLodders, Katharina - ThThe Planetary Scientist's Companion Booke Planetary Scientist's Companion BookGábor Balogh100% (1)
- Cold Facts Buyers Guide (2017) PDFДокумент41 страницаCold Facts Buyers Guide (2017) PDFBinh Thanh LeОценок пока нет
- Recovery of HeliumДокумент15 страницRecovery of Heliumjc_patel1Оценок пока нет
- The Star in YouДокумент6 страницThe Star in YouKiana MagallanesОценок пока нет
- Leak ReportДокумент5 страницLeak ReportZul AtfiОценок пока нет
- IELTS Academic Reading Passage 3Документ5 страницIELTS Academic Reading Passage 3mayura surangaОценок пока нет
- Are We Really Made of StarsДокумент7 страницAre We Really Made of StarsMerlita TuralbaОценок пока нет
- 039Документ66 страниц039jand_20Оценок пока нет
- Thermal Analysis and Investigations On Design Aspects of Aluminum Alloy Based Liquid Helium DewarДокумент7 страницThermal Analysis and Investigations On Design Aspects of Aluminum Alloy Based Liquid Helium DewarVilas AndhaleОценок пока нет
- Chapter 22 The Birth of The Universe: The Cosmic Perspective, 7e (Bennett Et Al.)Документ20 страницChapter 22 The Birth of The Universe: The Cosmic Perspective, 7e (Bennett Et Al.)mark100% (1)