Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
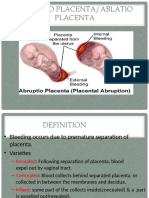
Placenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji Hospital
Загружено:
TRECEKILLERИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Placenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji Hospital
Загружено:
TRECEKILLERАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Placenta Previa
Liu Wei
Department of Ob & Gy
Ren Ji hospital
General considerations
Definition
In placenta previa, the placenta is implanted in
the lower uterine segment and located over the
internal os. It constitutes an obstruction of
descent of the presenting part.
Main cause of obstetrical hemorrhage
Incidence
0.24%-1.57% (our country).
Etiology
Uncertain
High risk factors
1. maternal age: >35 years
2. multiparity: 85% - 90%
3. prior cesarean delivery: 5 times
4. smoking
Etiology
Causes
1. Endometrial abnormality
1) Scared or poorly vascularized endometrium
in the corpus.
2) Curettage, Delivery, CS and infection of
endometrium
2. Placental abnormality
Large placenta (multiple pregnancy),
succenturiate lobe ()
3. Delayed development of trophoblast
Classification
Total placenta previa
The internal cervical os is covered completely by
placenta
Partial placenta previa
The internal os is partially covered by placenta
Marginal placenta previa
The edge of the placenta is at the margin of the
intenal os.
classification
Manifestation
Painless hemorrhage
1. The most characteristic symptom
2. Time: late pregnancy (after the 28
th
week)
and delivery
3. Characteristics: sudden, painless and profuse
4. Cause of bleeding
Mechanical separation of the placenta from its
implantation site, either during the formation
of the lower uterine segment, during
effacement and dilatation of the cervix in
labor. Placentitis. Rupture of the venous in
the decidua basalis
Manifestation
Anemia or shock
repeated bleeding anemia
heavy bleeding shock
Abnormal fetal position
a high presenting part
breech presentation (often)
Diagnosis
History
1. Painless hemorrhage
2. At late pregnancy or delivery
3. History of curettage or CS
Diagnosis
Signs
1. Abdominal findings
1) Uterus is soft, relaxed and nontender.
2) Contraction may be palpated.
3) A high presenting part cant be pressed into
the pelvic inlet. Breech presentation
4) Fetal heart tones maybe disappear (shock or
abruption)
Diagnosis
Speculum examination ()
Rule out local causes of bleeding, such as
cervical erosion or polyp or cancer.
Limited vaginal examination (seldom used)
Palpation of the vaginal fornices to learn if
there is an intervening bogginess between the
fornix and presenting part.
Rectal examination is useless and dangerous
Diagnosis
Ultrasonography
1. The most useful diagnostic method: 95%
2. Not make the diagnosis at the mid pregnancy.
(34 weeks)
MRI
Check the placenta and membrane after
delivery
Differential Diagnosis
Placental abruption
vagina bleeding with pain, tenderness of uterus.
Vascular previa
Abnormality of cervix
cervical erosion or polyp or cancer
Effects
obstetrical hemorrhage
Placenta accreta
Anemia and infection
Premature labor or fetal death or fetal
distress
Treatments
Expectant therapy
1. Rest: keep the bed
2. Controlling the contraction: MgSO
4
3. Treatment of anemia
4. Preventing infection
Treatments
Termination of pregnancy
1. CS
1) total placenta previa (36
th
week), Partial
placenta previa (37
th
week) and heavy
bleeding with shock
2) Preventing postpartum hemorrhage: pitocin
and PG
3) Hysterectomy: Placenta accreta or
uncontroled bleeding
Treatments
2. Vaginal delivery
Marginal placenta previa
Vaginal bleeding is limited
END
Вам также может понравиться
- Placenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta: Presenter Eessaa ShresthaДокумент72 страницыPlacenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta: Presenter Eessaa ShresthaEsa SthaОценок пока нет
- PNM Report Subashini EditedДокумент3 страницыPNM Report Subashini EditedPooneethawathi SantranОценок пока нет
- Midwifery and Obstetrical Nursing CourseДокумент24 страницыMidwifery and Obstetrical Nursing CourseSudipta Kumar BeraОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalДокумент18 страницPlacenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalJehan Fauzi RОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalДокумент18 страницPlacenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalheldaseptivanyОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalДокумент18 страницPlacenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalAlex AguirreОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalДокумент18 страницPlacenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitaluhmusmahОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalДокумент18 страницPlacenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalGabriel Guillen AsencioОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalДокумент18 страницPlacenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji Hospitalmade044Оценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalДокумент18 страницPlacenta Previa: Liu Wei Department of Ob & Gy Ren Ji HospitalDisti Hartikasari RuslanОценок пока нет
- PLACENTA PREVIA: CAUSES AND MANAGEMENTДокумент16 страницPLACENTA PREVIA: CAUSES AND MANAGEMENTElisabet AugustinaОценок пока нет
- Introduce Myself: Chinese Name: English Name: Dong Dirong Profession: Obstetrics and Work In: Zhongnan HospitalДокумент80 страницIntroduce Myself: Chinese Name: English Name: Dong Dirong Profession: Obstetrics and Work In: Zhongnan Hospitalapi-19641337Оценок пока нет
- Placenta PreviaДокумент18 страницPlacenta PreviaMohnnad Hmood AlgaraybhОценок пока нет
- Antepartum HaemorrhageДокумент74 страницыAntepartum HaemorrhageApex College of Nursing100% (1)
- Aph Family MedicineДокумент79 страницAph Family MedicineMohammad Nahel SorourОценок пока нет
- Antepartum Hemorrhage (APH): Causes, Diagnosis, and Management of Placental Abruption and Placenta PreviaДокумент81 страницаAntepartum Hemorrhage (APH): Causes, Diagnosis, and Management of Placental Abruption and Placenta PreviaOmar mohamedОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa and Placental AbruptionДокумент49 страницPlacenta Previa and Placental AbruptionFathimathОценок пока нет
- Early Pregnancy Bleeding Causes and ManagementДокумент20 страницEarly Pregnancy Bleeding Causes and ManagementMuhammad NadeemОценок пока нет
- APH DR DaudДокумент56 страницAPH DR DaudMohd Daud Che YusofОценок пока нет
- Antepartum HemorrhageДокумент105 страницAntepartum HemorrhageBablablo LolaleОценок пока нет
- ANTEPARTUM HAEMORRHAGEДокумент34 страницыANTEPARTUM HAEMORRHAGESHOWMAN DEEPAKОценок пока нет
- CA MaternalДокумент156 страницCA MaternalLovely Hope LugatimanОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of Mothers With Gestational Conditions:: 1. Abortion 2. Ectopic PregnancyДокумент59 страницNursing Care of Mothers With Gestational Conditions:: 1. Abortion 2. Ectopic PregnancyGwyneth FisherОценок пока нет
- Seminar G2 (Early Trimester Pregnancy Vaginal Bleeding)Документ47 страницSeminar G2 (Early Trimester Pregnancy Vaginal Bleeding)Chalie MequanentОценок пока нет
- Antepartum Hemorrhage Previa &abruptio PlacentaДокумент25 страницAntepartum Hemorrhage Previa &abruptio PlacentaHannah HalimОценок пока нет
- Abruptio Placenta For StudentsДокумент26 страницAbruptio Placenta For Studentssonam MaclayОценок пока нет
- Antepartum HemorrhageДокумент48 страницAntepartum HemorrhageJoshua EvansОценок пока нет
- Pa and PPДокумент23 страницыPa and PPapi-19916399Оценок пока нет
- Miscarriage (Abortion) : (Adhesions Inside The Uterine Cavity)Документ10 страницMiscarriage (Abortion) : (Adhesions Inside The Uterine Cavity)Rashed Shatnawi100% (1)
- 5f.antepartum HemorrhageДокумент31 страница5f.antepartum HemorrhageWadhha AlsenaidiОценок пока нет
- Early Pregnancy Complications: Ectopic Pregnancy Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Ji Aggasid, JanniecelДокумент60 страницEarly Pregnancy Complications: Ectopic Pregnancy Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Ji Aggasid, JanniecelmedicoОценок пока нет
- Managing High Risk Pregnancy ComplicationsДокумент94 страницыManaging High Risk Pregnancy ComplicationsErica Veluz LuyunОценок пока нет
- Midwifery 102 Module 2aДокумент18 страницMidwifery 102 Module 2aWynjoy NebresОценок пока нет
- Placental Abruption: Causes, Risks, and TreatmentДокумент30 страницPlacental Abruption: Causes, Risks, and TreatmentNafisat AdepojuОценок пока нет
- First Trimester BleedingДокумент48 страницFirst Trimester BleedingEliana ArshidОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa: Supervised By: Dr. Pim Gonta, SP - OGДокумент24 страницыPlacenta Previa: Supervised By: Dr. Pim Gonta, SP - OGPrincella MonicaОценок пока нет
- Disorders During PregnancyДокумент12 страницDisorders During PregnancyazlanОценок пока нет
- ANTEPARTUM HAEMORRHAGEДокумент20 страницANTEPARTUM HAEMORRHAGEabhay jainОценок пока нет
- Antepartum HemorrhageДокумент43 страницыAntepartum HemorrhageashwiniОценок пока нет
- Diagnosis of Abruptio Placentae: Placenta PreviaДокумент42 страницыDiagnosis of Abruptio Placentae: Placenta PreviaRirin Dwi LestariОценок пока нет
- Maternal MidtermДокумент253 страницыMaternal MidtermTrishaОценок пока нет
- 1 Chapter 21 Pregnancy Complication BLEEDING DURING PREGNANCYДокумент76 страниц1 Chapter 21 Pregnancy Complication BLEEDING DURING PREGNANCYCAÑADA, JOHANNELYN M.Оценок пока нет
- Bleeding in Early PregnancyДокумент40 страницBleeding in Early PregnancyOmar mohamedОценок пока нет
- High Risk PregnancyДокумент108 страницHigh Risk PregnancyVincent Maralit MaterialОценок пока нет
- Miscarriage and Its Types: Farhad Ali 15 - 177 3 Year MBBSДокумент21 страницаMiscarriage and Its Types: Farhad Ali 15 - 177 3 Year MBBSmarviОценок пока нет
- Shubrat Singh: EctopicДокумент25 страницShubrat Singh: Ectopicshubham royalОценок пока нет
- Bleeding Causes and ManagementДокумент90 страницBleeding Causes and ManagementAbdullah GadОценок пока нет
- Life-Threatening Uterine Inversion Complication of ChildbirthДокумент5 страницLife-Threatening Uterine Inversion Complication of ChildbirthJemin KimОценок пока нет
- Ectopic PregnancyДокумент44 страницыEctopic Pregnancygea pandhita sОценок пока нет
- Precipitate Labor To Uterine Inversion 1.28.22Документ42 страницыPrecipitate Labor To Uterine Inversion 1.28.22coco brillqnteОценок пока нет
- High Risk Mother ComplicationsДокумент22 страницыHigh Risk Mother ComplicationsAlyssa DeleonОценок пока нет
- Antepartum Haemorrhage - FinalДокумент44 страницыAntepartum Haemorrhage - FinalMLV AbayОценок пока нет
- Placenta PreviaДокумент43 страницыPlacenta PreviaAngela Joy AmparadoОценок пока нет
- Abortionme 200907085856Документ77 страницAbortionme 200907085856tengizbaindurishviliОценок пока нет
- Acute AbdomenДокумент71 страницаAcute AbdomenariОценок пока нет
- Ectopic Pregnancy (Autosaved)Документ56 страницEctopic Pregnancy (Autosaved)susmita shresthaОценок пока нет
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Mbiine Ronald Nakiyemba OliviaДокумент30 страницEctopic Pregnancy: Mbiine Ronald Nakiyemba OliviaDIANEОценок пока нет
- 8 Placenta and HemorrhageДокумент60 страниц8 Placenta and HemorrhagelianmbasogОценок пока нет
- Cmca2 (Prelim) 2Документ16 страницCmca2 (Prelim) 2NOEL YRIGONОценок пока нет
- NCM 109-Module 1 Lesson 1Документ30 страницNCM 109-Module 1 Lesson 1MARY ROSE DOLOGUINОценок пока нет
- Topics Today: Normal Puerperium Diseases of Puerperium Ectopic Pregnancy AbortionДокумент52 страницыTopics Today: Normal Puerperium Diseases of Puerperium Ectopic Pregnancy AbortionBitto_Singh_5952Оценок пока нет
- IUFDДокумент30 страницIUFDhiba alqamОценок пока нет
- Ob NormalДокумент18 страницOb NormalEspinoza AdrianОценок пока нет
- Komplikasi Kehamilan dan Diagnosa EktopikДокумент24 страницыKomplikasi Kehamilan dan Diagnosa EktopikAldha S PutriiОценок пока нет
- Globalization and BreastfeedingДокумент52 страницыGlobalization and BreastfeedingMichele RochaОценок пока нет
- Antenatalcare CPG SlideДокумент62 страницыAntenatalcare CPG SlideAdam ChungОценок пока нет
- Effectiveness of reflex zone stimulation on lactation post-C-sectionДокумент30 страницEffectiveness of reflex zone stimulation on lactation post-C-sectionAGERI PUSHPALATHAОценок пока нет
- Kehamilan Persalinan NifasДокумент29 страницKehamilan Persalinan NifaschoiimmaОценок пока нет
- Obs MCQДокумент13 страницObs MCQaaycee100% (3)
- Antenatal AssessmentДокумент40 страницAntenatal Assessmentmanjuvm91% (11)
- Large For Gestational Age (LGA)Документ4 страницыLarge For Gestational Age (LGA)Aira AlaroОценок пока нет
- Placenta PreviaДокумент11 страницPlacenta PreviaKashmala ZiaОценок пока нет
- PPH Briefer (Amtsl)Документ2 страницыPPH Briefer (Amtsl)Lina AbuarqoubОценок пока нет
- Optimal Obstetric Management For Women With Diabetes - The Benefits and Costs of Fetal SurveillanceДокумент9 страницOptimal Obstetric Management For Women With Diabetes - The Benefits and Costs of Fetal SurveillanceWillians ReyesОценок пока нет
- Case in Point-Shagmet, A 30-Year-Old Accountant Whose Family Emigrated To The UnitedДокумент2 страницыCase in Point-Shagmet, A 30-Year-Old Accountant Whose Family Emigrated To The Unitedjosh familarОценок пока нет
- Ujian Patol B 21/10/2022: A. 2500 ML B. 3200 ML C. 4500 ML D. 5000 MLДокумент4 страницыUjian Patol B 21/10/2022: A. 2500 ML B. 3200 ML C. 4500 ML D. 5000 MLBernas Arion NapitupuluОценок пока нет
- Ayantu MekonnenДокумент30 страницAyantu Mekonnenmbgeletu1221Оценок пока нет
- Cme (Tdhi)Документ64 страницыCme (Tdhi)OB-Gyne TDHIОценок пока нет
- 2 Rebusan Daun Katuk-DikonversiДокумент6 страниц2 Rebusan Daun Katuk-DikonversiNenci HaryadiОценок пока нет
- Responsables Ee - Ss Refcon Red Ambo 2018Документ10 страницResponsables Ee - Ss Refcon Red Ambo 2018Wildor Samir Cubas LlalleОценок пока нет
- Jurnal GemelliДокумент7 страницJurnal GemelliIka SeptianiОценок пока нет
- Multiple PregnancyДокумент39 страницMultiple PregnancyNoahОценок пока нет
- ABORTIONДокумент6 страницABORTIONMarice Abigail MarquezОценок пока нет
- Obstetrics MnemonicsДокумент17 страницObstetrics MnemonicsNariska CooperОценок пока нет
- Placental SeparationДокумент4 страницыPlacental SeparationAjit M Prasad Prasad100% (1)
- Amnioinfusion DR PadmeshДокумент13 страницAmnioinfusion DR PadmeshOptimistic Person100% (1)
- RoleplayДокумент2 страницыRoleplayAulia Rifqa PratiwiОценок пока нет
- Assignment For OB AssessmentДокумент4 страницыAssignment For OB AssessmentErika Anne Mercado CadawanОценок пока нет
- RNC Content and Study GuideДокумент11 страницRNC Content and Study GuideNicole CanadaОценок пока нет