Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Transformers
Загружено:
Reygil Lingling Capuno0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
24 просмотров18 страницtypes of transformers
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документtypes of transformers
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
24 просмотров18 страницTransformers
Загружено:
Reygil Lingling Capunotypes of transformers
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PPT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 18
transforms electric potential or current into
higher & lower intensity through process of
electromagnetic induction.
operate only with a changing electric current
(AC).
The ratio of the
number of coil turns in
the primary winding to
the number of coil
turns in the secondary
winding is equal to the
ratio of the primary
voltage to the
secondary voltage
Transformer can increase
or decrease voltage.
Depends on ratio of the
number of turns in the two
coils
N
S
> N
P
: step-up
transformer, increases
secondary voltage
N
S
< N
P
: step-down
transformer, decreases
secondary voltage
Autotransformers (VRT)
Consists of a single coil of wire wrapped around an iron
core
Operates on principle of self-induction rather than
mutual induction
Smaller increases or decreases in secondary voltage
than normal transformers
Does not electrically isolate primary from secondary
circuit
Air-Core
insulated primary
and secondary coils are
in close proximity to
each other, no iron core
and very innefficient
- Simplest type of transformer core.
Open-Ended Core
A simple design has a core within each coil.
- this core is more
efficient than the air core
because the iron core in
each coil intensifies the
magnetic flux in both
primary and secondary coils
when they become
magnetized as current flows
through each set of coils.
Closed-Ended Core
- this type of core is
moderately efficient due
to closing the core and
layering design which
reduces power loss from
less leakage flux which
provides a continuous
path for magnetic flux
and an increase in field
strength.
Shell Type Core
- highly insulated coils,
laminated core consisting of
piles of alternating sheets of
silicon and steel on top of
each other, each have 2
rectangular holds that
minimizes the distance
between coils and maximizes
the coupling effectiveness of
the induction.
Copper Losses
-aka I^2 loss. caused by inherent resistance to
current flow found in all conductors.
-power lost due to resistance is proportional to
square of current.
- using low resistance, large diameter copper
wire can reduce loss.
Eddy Current
- result of currents opposing
cause that produces them in
accordance w/ Lenz's law.
produced in any conducting
material subjected to
changing magnetic field.
Useless currents produce
heat in core. laminating core
reduces eddy current into
thin layers.
Lenzs Law
- An induced electromotive force (emf) always gives rise to a
current whose magnetic field opposes the original change in
magnetic flux.
- Heinrich Lenz
Hysteresis Losses
- aka Lagging loss. transformer operates on and
puts out AC. happens because energy is expended
as continually changing AC current magnetizes,
demagnetizes and re-magnetizing core material.
- Continuous reorientation of magnetic dipoles
requires energy and produces heat in core, wasting
electrical power. This waste is reduced by utilizing
a laminated silicon iron core.
- (originally known as a condenser) is a passive
two-terminal electrical component used to store
energy electrostatically in an electric field. The
forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all
contain at least two electrical conductors (plates)
separated by a dielectric (i.e., insulator).
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Cat 308 C SR Diagrama ElectricoДокумент15 страницCat 308 C SR Diagrama Electricohector hernan100% (12)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Price List 2023Документ110 страницPrice List 2023Lenny ErastoОценок пока нет
- Handbook User Guide Peugeot 207Документ250 страницHandbook User Guide Peugeot 207Milos100% (1)
- Presentation Slides Understanding NECДокумент48 страницPresentation Slides Understanding NECMarcosGodoyPereyraОценок пока нет
- Siemens Switchgear Medium Voltage MV 33kV T Plug Cable Connectors PDFДокумент172 страницыSiemens Switchgear Medium Voltage MV 33kV T Plug Cable Connectors PDFhaОценок пока нет
- EMI RFI Suppression Capacitors Film IEC 60384-14 International StandardДокумент1 страницаEMI RFI Suppression Capacitors Film IEC 60384-14 International StandardmubafawОценок пока нет
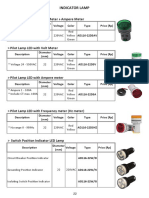
- Lamp IndicatorДокумент2 страницыLamp IndicatorNurdin FahimОценок пока нет
- Full Wave Rectifier Circuit Lab ManualДокумент3 страницыFull Wave Rectifier Circuit Lab ManualMohammadОценок пока нет
- Shallco Series 1610 Part No.: 16A10A1-B-1: GeneralДокумент1 страницаShallco Series 1610 Part No.: 16A10A1-B-1: GeneralRodОценок пока нет
- SSP 390 7 Speed Double Clutch Gearbox 0AMДокумент76 страницSSP 390 7 Speed Double Clutch Gearbox 0AMEdgar Oswaldo Hinojosa Mayoral100% (1)
- Distribution Transformer Calculations: Developed By: Mahmoud SalamaДокумент1 страницаDistribution Transformer Calculations: Developed By: Mahmoud SalamaMothilalОценок пока нет
- Iec 60204 32 2008Документ15 страницIec 60204 32 2008Ricardo AlconОценок пока нет
- M20 Datasheet 01-5959-01r0 ENДокумент8 страницM20 Datasheet 01-5959-01r0 ENTudorache IulianОценок пока нет
- Catalogo Jokab Safety - RTДокумент18 страницCatalogo Jokab Safety - RTDavid ZacariasОценок пока нет
- Ac Phase Control of TriacДокумент4 страницыAc Phase Control of Triacjassisc0% (1)
- RCP Sample DrawingДокумент1 страницаRCP Sample DrawingChristelle Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Swingtel Line Card 2016 PDFДокумент2 страницыSwingtel Line Card 2016 PDFAnonymous n30qTRQPoIОценок пока нет
- Installation: Melody Technical ManualДокумент22 страницыInstallation: Melody Technical ManualNassima BELILОценок пока нет
- Electrical BoxesДокумент34 страницыElectrical BoxesOphir MaverickОценок пока нет
- Presentation On DC GeneratorДокумент36 страницPresentation On DC GeneratorShubham prajeshОценок пока нет
- Problem: NMOS Inverter (Solution) : VLSI-Design of Integrated Circuits, WS 2002/03Документ6 страницProblem: NMOS Inverter (Solution) : VLSI-Design of Integrated Circuits, WS 2002/03SOUMYABROTO BANERJEEОценок пока нет
- Beacon 200 ManualДокумент56 страницBeacon 200 ManualCrystal CobosОценок пока нет
- HTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFДокумент29 страницHTTPSWWW - Sathyabama.ac - Insitesdefaultfilescourse Material2020 10UNIT II 4 PDFVigneshwaran J vОценок пока нет
- EMERGENCY LIGHTING General Test Procedure: 1. Inspect The Battery Unit For Any Signs of Physical DamageДокумент2 страницыEMERGENCY LIGHTING General Test Procedure: 1. Inspect The Battery Unit For Any Signs of Physical DamageSaleem JavedОценок пока нет
- 1855 Rules For The Management and Cleaning of US Rifle Model 1855Документ41 страница1855 Rules For The Management and Cleaning of US Rifle Model 1855Hugh KnightОценок пока нет
- Basics of Power ElectronicsДокумент34 страницыBasics of Power ElectronicsSharween KaurОценок пока нет
- ABB IndustrialTransformer PDFДокумент10 страницABB IndustrialTransformer PDFFreddy EscorzaОценок пока нет
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker CatalogueДокумент11 страницVacuum Circuit Breaker Cataloguedabs_orangejuice0% (1)
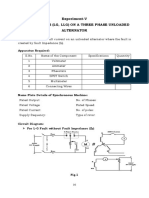
- 5.fault Analysis (LG, LLG) On A Three Phase Unloaded AlternatorДокумент4 страницы5.fault Analysis (LG, LLG) On A Three Phase Unloaded Alternatorarjuna430650% (2)
- Fieldstar Led Floodlight: Division Digital SolutionsДокумент9 страницFieldstar Led Floodlight: Division Digital SolutionsAkash PanigrahiОценок пока нет