Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Programmable DSP Lecture2
Загружено:
Paresh SawantОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Programmable DSP Lecture2
Загружено:
Paresh SawantАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
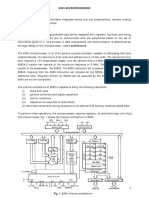
PROGRAMMABLE DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
1 P.D. Sawaant
Contents:
Architecture of TMS320C67xx
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Accumulators
Barrel Shifter
Multiplier/Adder Unit
2
Architecture of TMS320C67xx digital signal
processors
P.D. Sawaant
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The C67x CPU is common to all C67xE devices.
The C67x CPU contains:
40-bit arithmetic logic unit (ALU).
Two 40-bit Accumulators.(A and B)
Barrel shifter.
17 X 17-bit multiplier.
40-bit adder.
A Compare, select, and store unit (CSSU).
A exponent Encoder (EXP)
Data address generation unit.(DAGEN)
Program address generation unit.(PAGEN)
3
Architecture of TMS320C67xx digital signal
processors
P.D. Sawaant
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The C67x DSP performs 2s-complement arithmetic with a 40-bit
arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and two 40-bit accumulators (accumulators
A and B). The ALU can also perform Boolean operations. The ALU uses
these inputs:
16-bit immediate value.
16-bit word from data memory.
16-bit value in the temporary register, T.
Two 16-bit words from data memory.
32-bit word from data memory.
40-bit word from either accumulator.
The ALU can also function as two 16-bit ALUs and perform two 16-
bit operations simultaneously.
4
Functional Diagram of CPU of TMS320C67xx digital signal
processors
P.D. Sawaant
5
Functional Diagram of CPU of TMS320C67xx digital signal
processors
P.D. Sawaant
Accumulators:
Accumulators A and B store the output from the ALU or the
multiplier/adder block. They can also provide a second input to the ALU;
accumulator A can be an input to the multiplier/adder. Each accumulator
is divided into three parts:
Guard bits (bits 3932)
High-order word (bits 3116)
Low-order word (bits 150)
Instructions are provided for storing the guard bits, for storing the
high- and the low order accumulator words in data memory, and for
transferring 32-bit accumulator words in or out of data memory.
Also, either of the accumulators can be used as temporary storage for
the other.
6
Functional Diagram of Barrel Shifter
P.D. Sawaant
7
Functional Diagram of CPU of TMS320C67xx digital signal
processors
P.D. Sawaant
Barrel Shifter :
Provides the capability to scale the data during an operand read or
write.
The C67x DSP barrel shifter can produce a left shift of 0 to 31 bits and
a right shift of 0 to 16 bits on the input data.
The shift requirements are defined in the shift count field of the
instruction, the shift count field (ASM) of status register ST1, or in
temporary register T (when it is designated as a shift count register).
The barrel shifter and the exponent encoder normalize the values in an
accumulator in a single cycle.
The LSBs of the output are filled with 0s, and the MSBs can be either
zero filled or sign extended, depending on the state of the sign-extension
mode bit (SXM) in ST1.
An additional shift capability enables the processor to perform
numerical scaling, bit extraction, extended arithmetic, and overflow
prevention operations.
8
Functional Diagram of Multiplier/Adder unit of TMS320C67xx
processors
P.D. Sawaant
Multiplier/Adder Unit:
9 P.D. Sawaant
Multiplier/Adder Unit
The multiplier/adder unit performs 17 X 17-bit 2s-complement
multiplications with a 40- bit addition in a single instruction cycle.
The multiplier/adder block consists of several elements:
A multiplier
An adder
Signed/unsigned input control logic
Fractional control logic,
A zero detector
A rounder (2s complement),
Overflow/saturation logic, and
A 16-bit temporary storage register (T).
The multiplier has two inputs: one input is selected from T, a data-
memory operand, or accumulator A; the other is selected from program
memory, data memory, accumulator A, or an immediate value.
10 P.D. Sawaant
Multiplier/Adder Unit
The fast, on-chip multiplier allows the C67x DSP to perform
operations efficiently such as convolution, correlation, and filtering.
In addition, the multiplier and ALU together execute
multiply/accumulate (MAC) computations and ALU operations in
parallel in a single instruction cycle.
The exponent encoder unit supports the EXP instructions, which stores
in the T register the number of leading redundant bits of the accumulator
content. This information is useful while shifting the accumulator content
for the purpose of scaling.
Вам также может понравиться
- Etl Testing Real Time Interview QuestionsДокумент20 страницEtl Testing Real Time Interview QuestionsSai Vasu75% (16)
- MultiPOS - Point of Sale (POS) For WooCommerce by Devdiggers - CodeCanyonДокумент4 страницыMultiPOS - Point of Sale (POS) For WooCommerce by Devdiggers - CodeCanyonOBIOMA FRANCWHITEОценок пока нет
- Introduction To mc68hc11Документ35 страницIntroduction To mc68hc11SHRIYAM MALVIYAОценок пока нет
- 8085 MicroprocessorДокумент23 страницы8085 Microprocessorauromaaroot196% (55)
- Thesis (Time Synchronization in Wireless Telecommunication) NewДокумент50 страницThesis (Time Synchronization in Wireless Telecommunication) NewParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Hyperconverged Infrastructure For Dummies 2019 Edition PDFДокумент65 страницHyperconverged Infrastructure For Dummies 2019 Edition PDFAlex Irmel Oviedo Solis100% (1)
- Homework 1Документ3 страницыHomework 1Aditya MishraОценок пока нет
- Sv-Pro: High-Performance Network Security ApplianceДокумент2 страницыSv-Pro: High-Performance Network Security ApplianceEhsan RohaniОценок пока нет
- Features of Tms320C54X Dsps IncludeДокумент20 страницFeatures of Tms320C54X Dsps IncludechethanОценок пока нет
- C6713 DSP Lab Mannual 2Документ40 страницC6713 DSP Lab Mannual 2dangvuduongОценок пока нет
- Rohini 90925466680Документ6 страницRohini 90925466680SubraОценок пока нет
- DSPAДокумент29 страницDSPADrakshayaniMurgodОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Programmable Digital Signal ProcessorsДокумент66 страницUnit 3 Programmable Digital Signal ProcessorsBonsai TreeОценок пока нет
- Architecture of TMS320C54XДокумент14 страницArchitecture of TMS320C54XVigneshОценок пока нет
- Adsp ManualДокумент28 страницAdsp ManualShweta KhobragadeОценок пока нет
- Signal Processing Lab: Department of Electronics and Communications EngineeringДокумент53 страницыSignal Processing Lab: Department of Electronics and Communications EngineeringRavi Teja TsapparapuОценок пока нет
- Architecture: TMS320C54xДокумент14 страницArchitecture: TMS320C54xKarpagamОценок пока нет
- Data Arithmetic Logic Unit: Figure 3-1 Is A Block Diagram of The Data ALUДокумент24 страницыData Arithmetic Logic Unit: Figure 3-1 Is A Block Diagram of The Data ALUVipul ThummarОценок пока нет
- UNIT-V-TMS320C54x-DSP ProcessorДокумент47 страницUNIT-V-TMS320C54x-DSP ProcessorVasant DivekarОценок пока нет
- Presentation 1Документ23 страницыPresentation 1khushalee.chavadaОценок пока нет
- TMS320LF2407Документ90 страницTMS320LF2407Polumuri RamanaОценок пока нет
- Digital Signal Processing Lab MannualДокумент37 страницDigital Signal Processing Lab Mannualsreenathreddy100% (4)
- 8085 MaterialДокумент12 страниц8085 MaterialsameerОценок пока нет
- Unit I The 8086 MicroprocessorДокумент21 страницаUnit I The 8086 Microprocessor16211a0470100% (1)
- Basics of Micro ProcessorДокумент27 страницBasics of Micro ProcessorBibin LeeОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor 8085Документ25 страницMicroprocessor 8085hetal_limbaniОценок пока нет
- CPU Design Documentation SampleДокумент27 страницCPU Design Documentation SampleJoseph Kerby J. NavaОценок пока нет
- Avr ArchitectureДокумент29 страницAvr ArchitectureOdoch HerbertОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor - SGДокумент15 страницMicroprocessor - SGSugata Ghosh0% (1)
- Architecture of TMS320C54XX Digital Signal ProcessorsДокумент20 страницArchitecture of TMS320C54XX Digital Signal ProcessorsLydia Elezabeth Alappat100% (7)
- SDM Module IДокумент28 страницSDM Module IKiran KrishnanОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor Lab Manual EE0310Документ44 страницыMicroprocessor Lab Manual EE0310sathishkumar.vОценок пока нет
- 8051 Uc CompleteДокумент129 страниц8051 Uc CompletemalhiavtarsinghОценок пока нет
- MICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualДокумент53 страницыMICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualAjay PatilОценок пока нет
- Blockdiagramof 8085Документ40 страницBlockdiagramof 8085Akhil NameirakpamОценок пока нет
- Unit Ii 8085 Micro Processor 8085 Architecture:: ME 6702 Mechatronics Mechanical Engineering 2019-20Документ26 страницUnit Ii 8085 Micro Processor 8085 Architecture:: ME 6702 Mechatronics Mechanical Engineering 2019-20GopinathОценок пока нет
- 8-Bit Microcontroller With 2K Bytes Flash Attiny26 Attiny26LДокумент182 страницы8-Bit Microcontroller With 2K Bytes Flash Attiny26 Attiny26LMario Aarón JiménezОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Microprocessor and Microcomputer ArchitectureДокумент6 страницIntroduction To Microprocessor and Microcomputer Architecturesri vatsaОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor 8085 ArchitectureДокумент8 страницMicroprocessor 8085 ArchitectureHarjot KaurОценок пока нет
- MCT Unit 2Документ26 страницMCT Unit 2Aravind RajОценок пока нет
- 1-Architecture of 8085Документ34 страницы1-Architecture of 8085Pinki KumariОценок пока нет
- Unit I PDFДокумент25 страницUnit I PDFSomnath2014Оценок пока нет
- AtMega32 Data SheetДокумент313 страницAtMega32 Data SheetSumeet TiwanaОценок пока нет
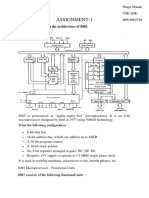
- MPMC Assignment-1Документ7 страницMPMC Assignment-113Panya CSE2Оценок пока нет
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960От EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960Оценок пока нет
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationОт EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationОценок пока нет
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.От EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.Оценок пока нет
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3От EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3Оценок пока нет
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCОт EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Radio Shack TRS-80 Expansion Interface: Operator's Manual: Catalog Numbers: 26-1140, 26-1141, 26-1142От EverandRadio Shack TRS-80 Expansion Interface: Operator's Manual: Catalog Numbers: 26-1140, 26-1141, 26-1142Оценок пока нет
- Arduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsОт EverandArduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsОценок пока нет
- PLD Architectures and TestingДокумент37 страницPLD Architectures and TestingParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Introduction To VerilogДокумент77 страницIntroduction To VerilogParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 Stack and QueuesДокумент79 страницUnit 4 Stack and QueuesParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Crystal OscillatorДокумент7 страницCrystal OscillatorParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- BJT-Transistor AnalysisДокумент100 страницBJT-Transistor AnalysisParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Programmable DSP Lecture1Документ19 страницProgrammable DSP Lecture1Paresh Sawant50% (2)
- Analog Circuits II Lab ManualДокумент47 страницAnalog Circuits II Lab ManualParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Wave Shaping CircuitsДокумент15 страницWave Shaping CircuitsParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Contents:: Instruction and Programming of TMS320C67XX. Interrupts of TMS320C67XX ProcessorДокумент15 страницContents:: Instruction and Programming of TMS320C67XX. Interrupts of TMS320C67XX ProcessorParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Programmable DSP Lecture3Документ17 страницProgrammable DSP Lecture3Paresh SawantОценок пока нет
- Clippers and ClampersДокумент13 страницClippers and ClampersParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- VHDL Data Types and OperatorsДокумент61 страницаVHDL Data Types and OperatorsParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Introduction To DSP ProcessorsДокумент15 страницIntroduction To DSP ProcessorsParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Basics of Rectifiers and FiltersДокумент32 страницыBasics of Rectifiers and FiltersParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Basics of Rectifiers and FiltersДокумент32 страницыBasics of Rectifiers and FiltersParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Types of DSP ArchitecturesДокумент45 страницTypes of DSP ArchitecturesParesh Sawant100% (3)
- Signal Attributes 20-02-2014Документ15 страницSignal Attributes 20-02-2014Paresh SawantОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of DSPДокумент15 страницCharacteristics of DSPParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Content Addressable Memories: Cell Design and Peripheral CircuitsДокумент30 страницContent Addressable Memories: Cell Design and Peripheral CircuitsParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- FSM DesignДокумент61 страницаFSM DesignParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- VHDL Design File. Delimiters & Identifiers. User Defined Identifiers. LiteralsДокумент16 страницVHDL Design File. Delimiters & Identifiers. User Defined Identifiers. LiteralsParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- Reliability & Fault Tree AnalysisДокумент25 страницReliability & Fault Tree AnalysisParesh SawantОценок пока нет
- University Question Paper - 2016-2018Документ27 страницUniversity Question Paper - 2016-2018Aditya SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Famis Full User ManualДокумент52 страницыFamis Full User ManualedwindossantosОценок пока нет
- Sriramoju Sanjay. +91-8886028802Документ2 страницыSriramoju Sanjay. +91-8886028802SharathОценок пока нет
- Get Unlimited Downloads With A Membership: Aula 9 - Conectivos - Preposição E ConjunçãoДокумент2 страницыGet Unlimited Downloads With A Membership: Aula 9 - Conectivos - Preposição E ConjunçãoFabExpertОценок пока нет
- Z580C Trouble Shooting Guide: SYS BG-Pad BU-Pro Ctr3-RD Div2-Dep3-RD Sec Taylor Lin 2015/07/23Документ43 страницыZ580C Trouble Shooting Guide: SYS BG-Pad BU-Pro Ctr3-RD Div2-Dep3-RD Sec Taylor Lin 2015/07/23Leo MendesОценок пока нет
- Fusa Catalog Web 2017Документ116 страницFusa Catalog Web 2017tariktunadОценок пока нет
- Python 1Документ111 страницPython 1Euola NoviОценок пока нет
- Computer AccessoriesДокумент8 страницComputer AccessoriesBoon FuiОценок пока нет
- ANTONY SFDC DeveloperДокумент5 страницANTONY SFDC DeveloperHARSHAОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 - Network TopologyДокумент21 страницаLesson 3 - Network TopologyRebel ChinnaОценок пока нет
- GS51Документ230 страницGS51Vidya MuthukrishnanОценок пока нет
- Final Examination: (Notes: Open Book Exam)Документ2 страницыFinal Examination: (Notes: Open Book Exam)Đặng Lê MinhОценок пока нет
- PDP HandbookДокумент205 страницPDP Handbookberkant_atayОценок пока нет
- OpenSAP Ui51 Week4 Unit 1 NARC ExerciseДокумент6 страницOpenSAP Ui51 Week4 Unit 1 NARC Exercisebhavana amarОценок пока нет
- 412 33 Powerpoint Slides 5 Sales Force Automation Chap 5Документ18 страниц412 33 Powerpoint Slides 5 Sales Force Automation Chap 5Juber FarediwalaОценок пока нет
- It's My LaptopДокумент5 страницIt's My LaptopWhosondaFroneОценок пока нет
- Samurai-WTF Course SlidesДокумент216 страницSamurai-WTF Course SlidesJ Sebastian ZupaОценок пока нет
- C++ and Data StructureДокумент231 страницаC++ and Data StructureHabtie TesfahunОценок пока нет
- Ilmi One Linear Capsule For General KnowledgeДокумент196 страницIlmi One Linear Capsule For General KnowledgeQadirОценок пока нет
- Ansi Join SQLДокумент45 страницAnsi Join SQLGul ZaibОценок пока нет
- 05 NewsДокумент1 страница05 Newsapi-277626207Оценок пока нет
- Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Etherchannel: ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыPacket Tracer - Troubleshoot Etherchannel: Objectivesnasywa affhОценок пока нет
- Old Hindi Instrumental Songs Free Download mp3 Zip FileДокумент1 страницаOld Hindi Instrumental Songs Free Download mp3 Zip FileNidhiОценок пока нет
- Network Management SessionalsДокумент10 страницNetwork Management SessionalsShivam ChaturvediОценок пока нет
- Apollo Guidance ComputerДокумент8 страницApollo Guidance ComputerEmanuel DutraОценок пока нет